Submersible motor rotor broken bar fault recognition method based on HHT (Hilbert-Huang transform)
A technology for submersible motors and rotor broken bars, which is applied in the direction of motor generator testing, etc., and can solve the problems of motor burnout and broken rotor bars that cannot be detected online
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
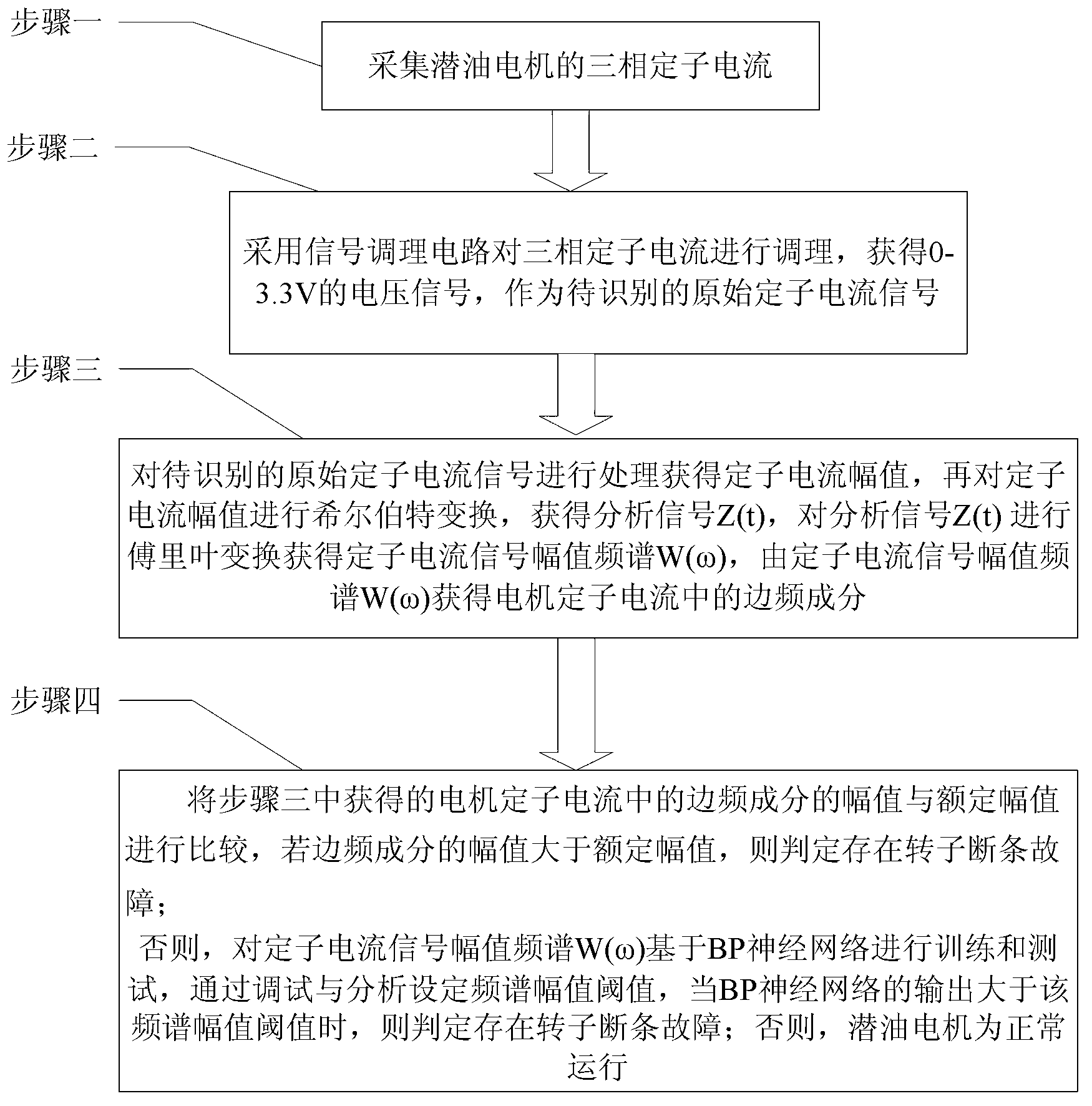
[0051] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Illustrate the present embodiment, the HHT-based submersible motor rotor broken bar fault identification method described in the present embodiment, it comprises the following steps:
[0052] Step 1: collecting the three-phase stator current of the submersible motor;
[0053] Step 2: Use the signal conditioning circuit to condition the three-phase stator current to obtain a voltage signal of 0-3.3V as the original stator current signal to be identified;
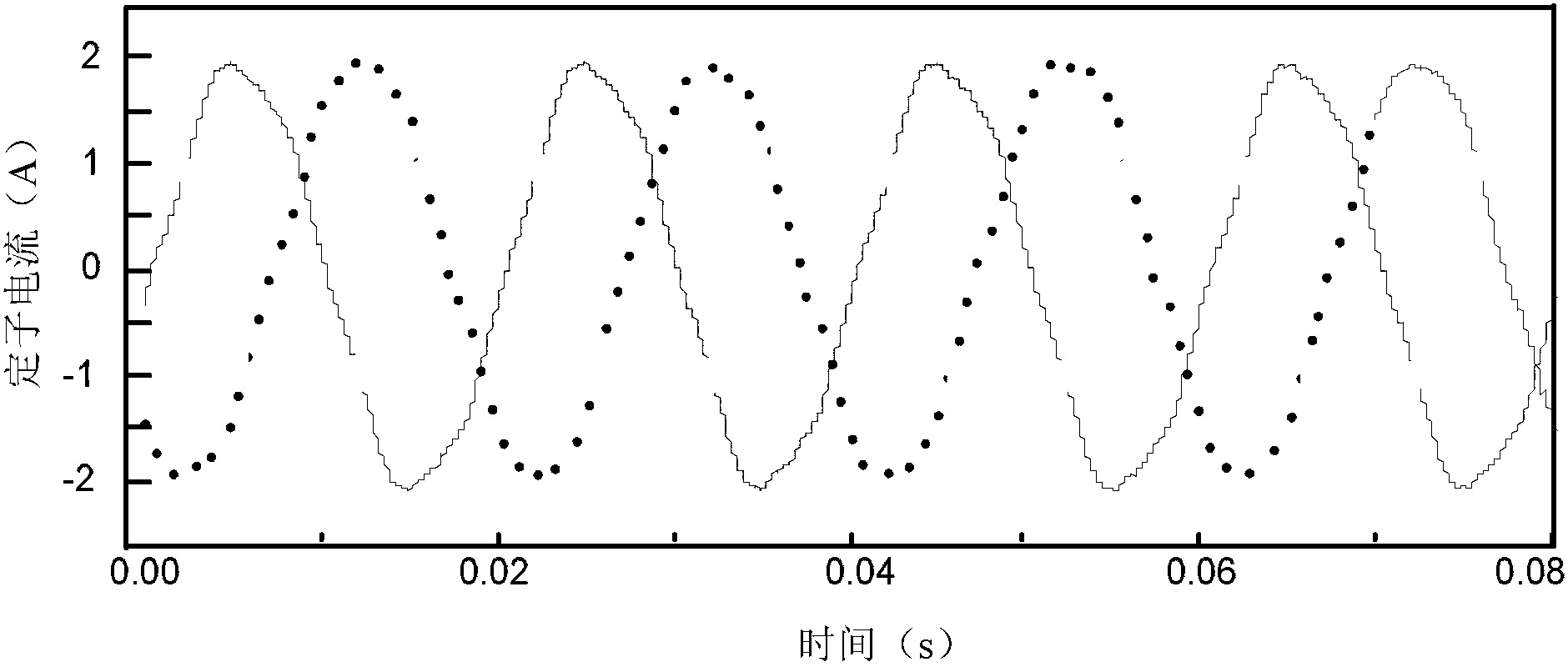
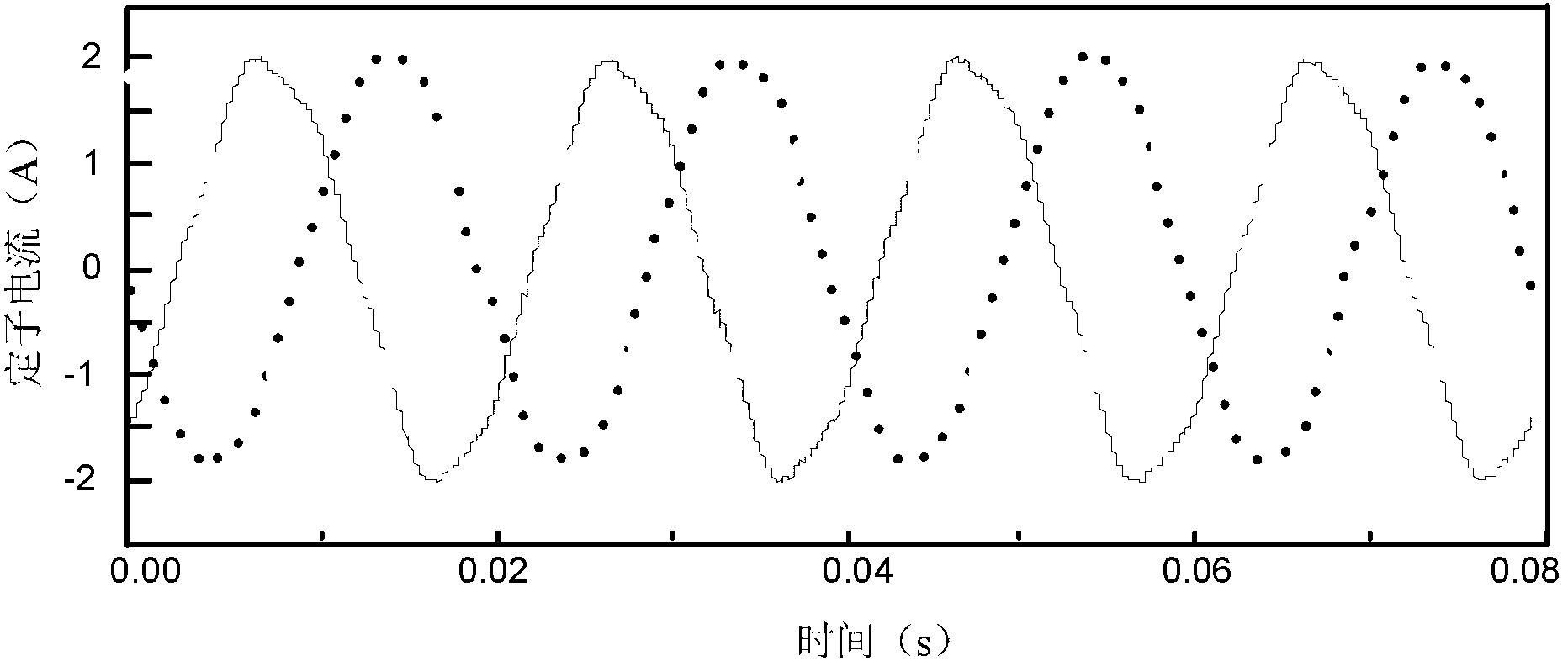
[0054] Step 3: Process the original stator current signal to be identified to obtain the stator current amplitude X(t), and then perform Hilbert transformation on the stator current amplitude X(t) to obtain the analysis signal Z(t), and analyze the signal Z(t) is Fourier transformed to obtain the stator current signal amplitude spectrum W(ω), and the side frequency component in the motor stator current is obtained from the stator current signal ampli...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0061] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode further explains the first implementation mode, the amplitude of the side frequency component in the step four is (1-2s)f in the stator current signal amplitude spectrum W(ω) 0 The amplitude at , where s is the slip rate, f 0 is the fundamental frequency in the stator current signal amplitude spectrum W(ω), f 0 = 50Hz.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0062] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 11 For illustration, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1 or 2. In the step 3, the original stator current signal to be identified is processed to obtain the stator current amplitude X(t), and then the stator current amplitude X(t) Perform Hilbert transform to obtain the analysis signal Z(t), and perform Fourier transform on the analysis signal Z(t) to obtain the stator current signal amplitude spectrum W(ω) The specific process is as follows:
[0063] The original stator current signal to be identified is subjected to empirical mode decomposition until it is screened into the intrinsic mode function, and the intrinsic mode function is used as the stator current amplitude X(t) for Hilbert transformation to obtain the analysis signal Z(t ) The imaginary part Y(t) of the magnitude:
[0064] Y ( t ) = ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com