Method for optimizing coverage of nodes of wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and coverage optimization technology, applied in wireless communication, network topology, network planning, etc., can solve problems such as slow convergence speed, affecting coverage effect, and difficulty in meeting the real-time requirements of dynamic node selection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
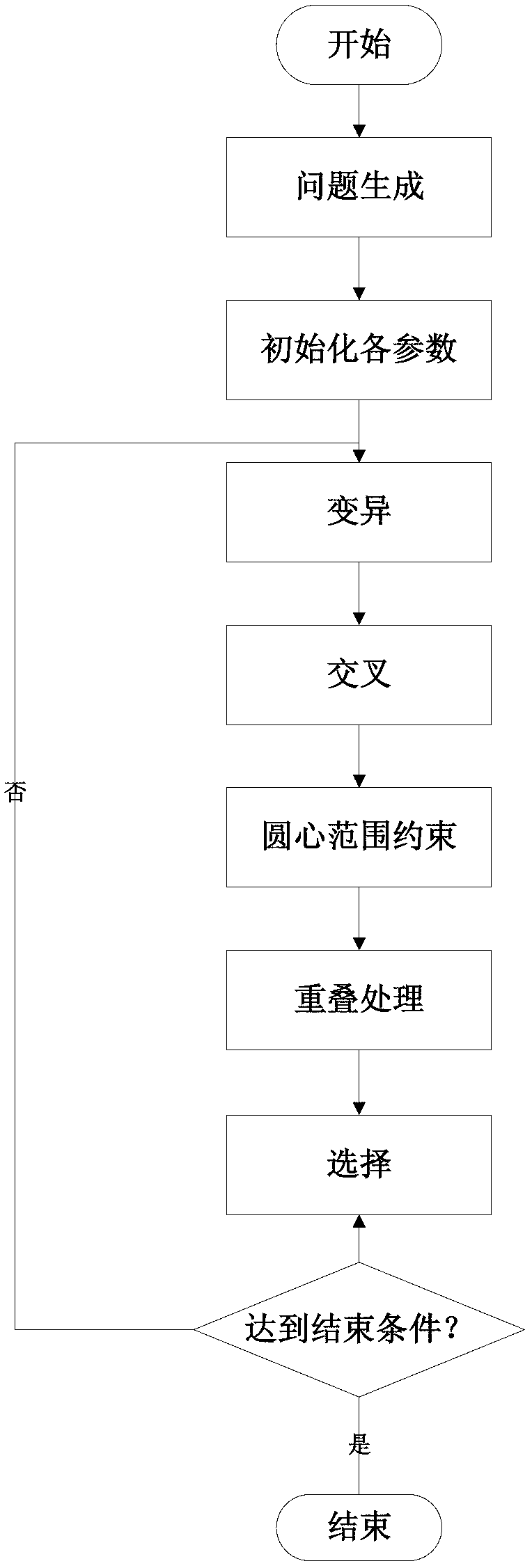
[0034] The method of the invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
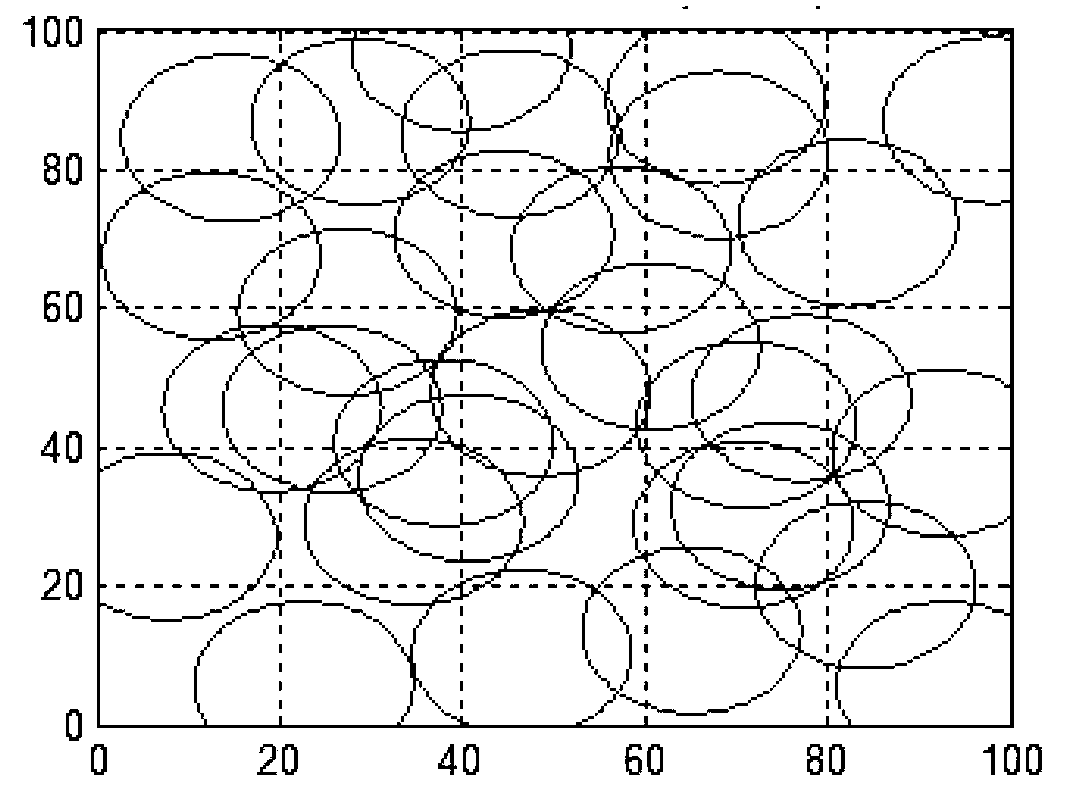
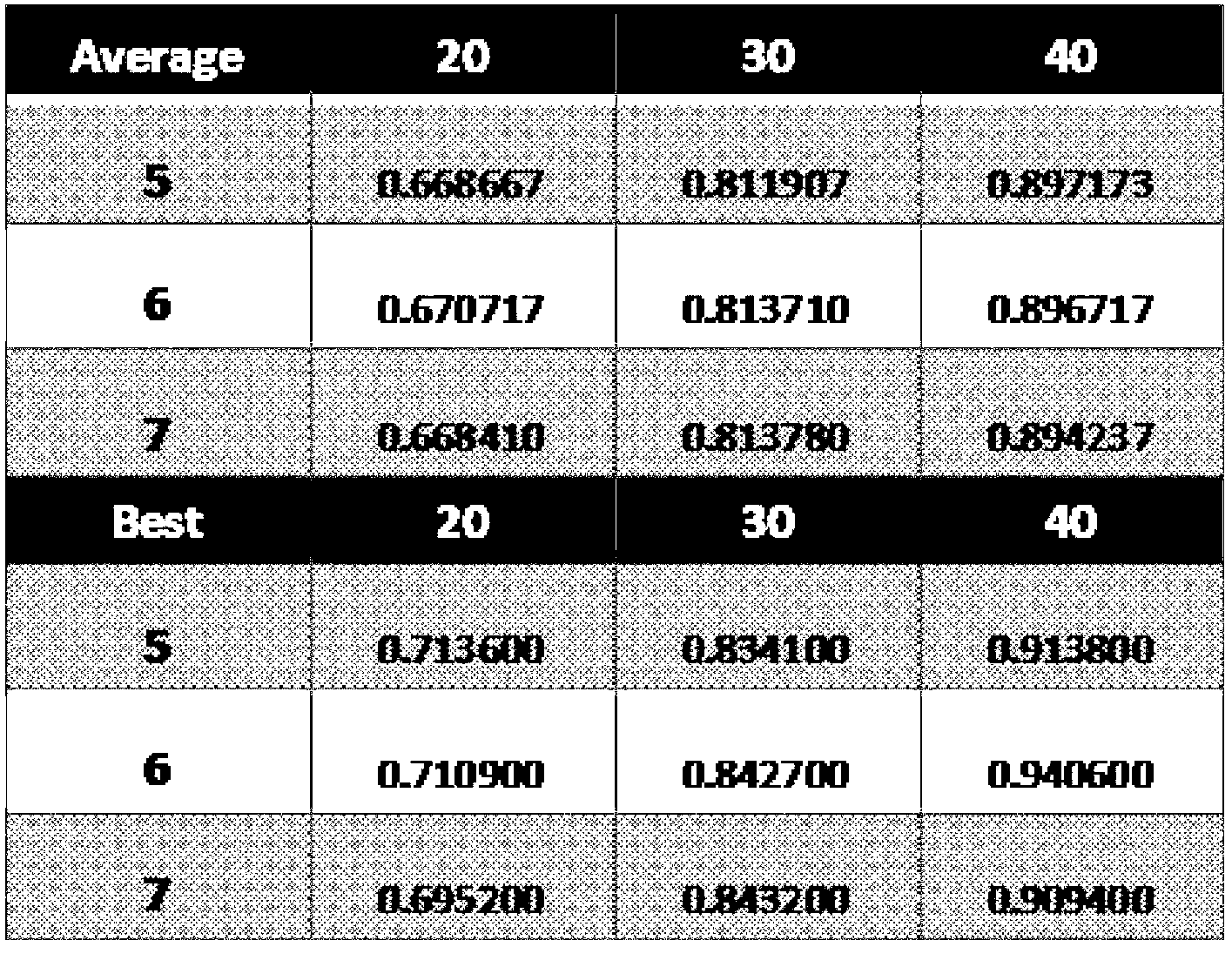
[0035] Differential evolutionary algorithm is an evolutionary algorithm based on real number coding, and its overall structure is similar to other evolutionary algorithms. The evolutionary algorithm model for the distribution of sensing nodes in wireless sensor networks is usually established as follows: Assuming that the monitoring area A is a two-dimensional plane, the monitoring area A is divided into m×n grids, and the set of sensor nodes on the monitoring area expressed as C={c 1 ,c 2 ,...,c N}, where c i ={x i ,y i ,r} is the coverage model of node i, (x i ,y i ) is the coordinate of node i, and r is the perception radius of node i. The present invention selects a binary perception model, and considers that the coverage of a node is a circular area with the node coordinates as the center and a radius of r. For the grid point (x,y) we use the follow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com