Method for manufacturing microchip
A manufacturing method and microchip technology, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, chemical instruments and methods, photoplate making process of patterned surface, etc., can solve the problems of reduced detection accuracy, bad influence of measurement, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing fluorescence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
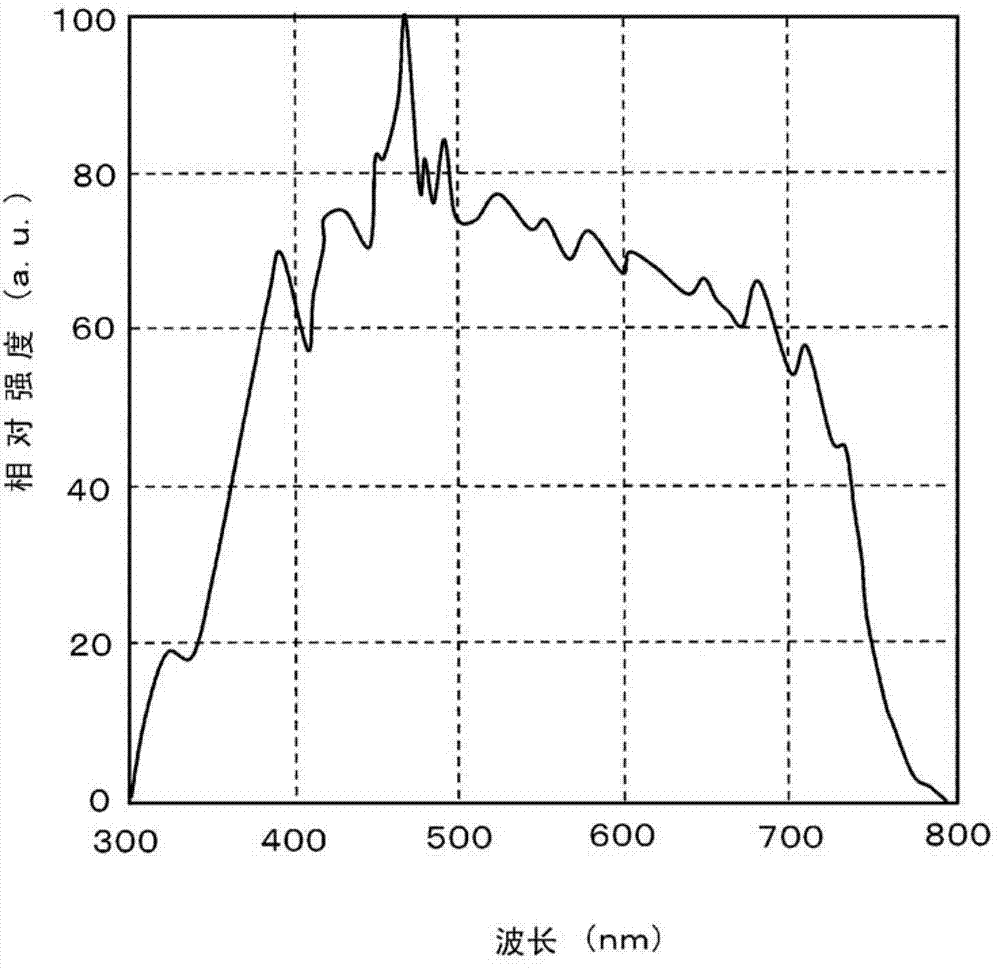
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
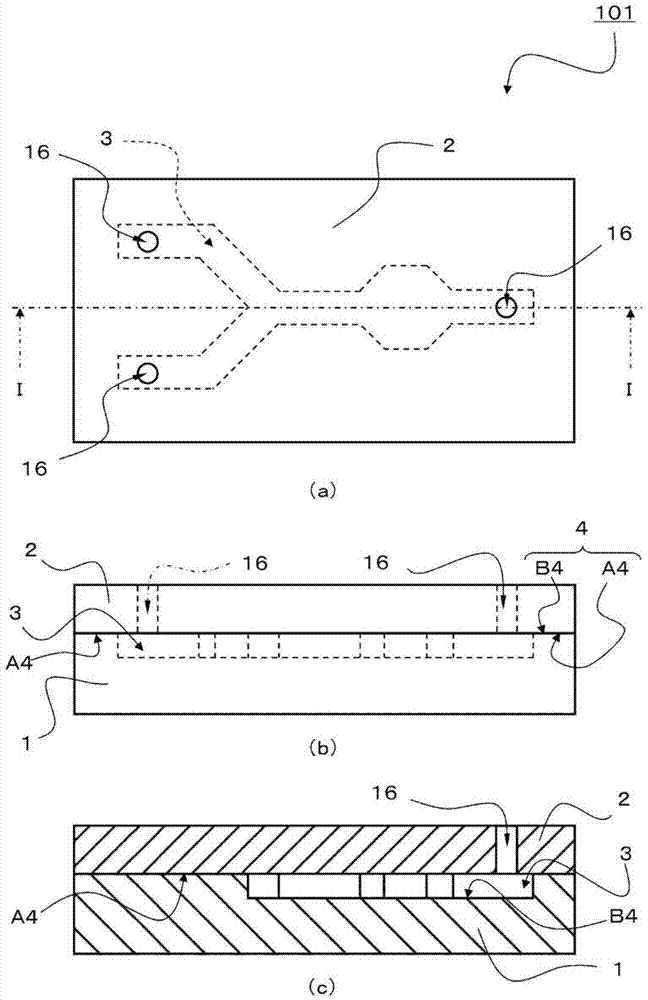
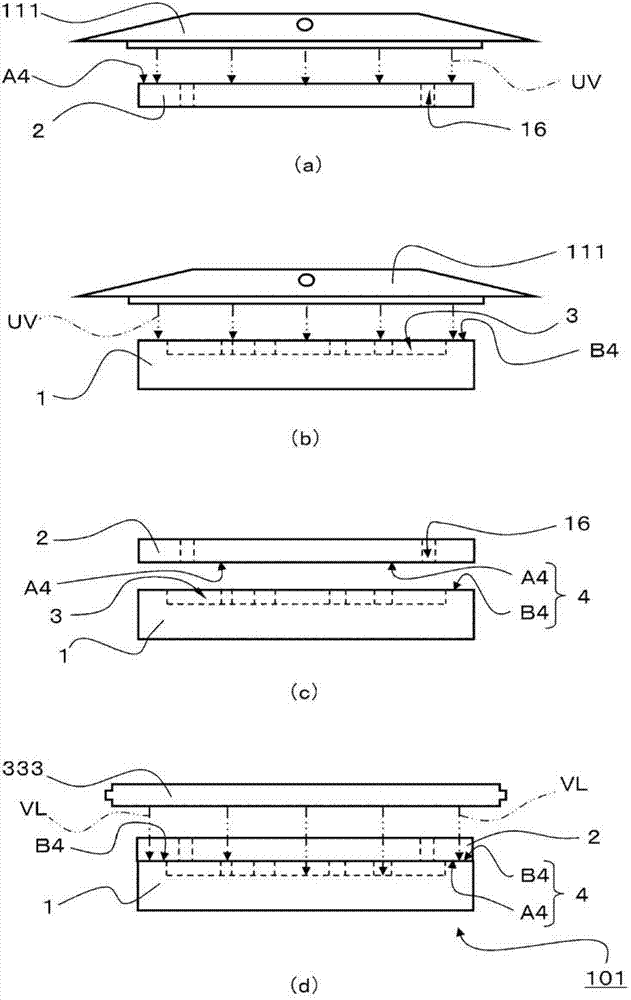
[0035] figure 1 is a diagram illustrating the structure of a microchip 101 manufactured using the manufacturing method of the present invention, figure 1 (a) is a plan view, figure 1 (b) is a side view, figure 1 (c) is figure 1 (a) Cross-sectional view of line I-I. figure 2 It is a figure explaining an example of the manufacturing method of the microchip 101 concerning 1st Embodiment of this invention, figure 2 (a) and figure 2 (b) is a structural diagram showing the ultraviolet light step P11 of irradiating ultraviolet light UV to the light transmissive base material 2 and the resin base material 1, figure 2 (c) is a structural diagram in which the light-transmitting base material 2 before bonding and the resin base material 1 are opposed to each other in the bonding step P12, figure 2 (d) is a structural diagram explaining the visible light process P13 which irradiates the microchip 101 with visible light VL.
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the microch...
Embodiment 1
[0048] Next, the first embodiment of the present invention will be described in more detail through Example 1. The present invention is not limited to the Examples shown below.
[0049] First, as the resin substrate 1 and the light-transmitting substrate 2, a pair of resin substrates (70 mm×20 mm, thickness 2 mm) composed of a cycloolefin polymer (manufactured by Nippon Zeon Co., Ltd., ZEONEX330R, glass transition point 123° C.) were used. The concave portion 3 of the resin base material 1 and the injection hole 16 of the light-transmitting base material 2 are produced by machining the resin base material, respectively.
[0050] Next, the surfaces of the opposing surface B4 of the resin base material 1 and the opposing surface A4 of the light-transmitting base material 2 are irradiated with ultraviolet rays by a Xe excimer lamp (USHIO INC., UER20-172A). Light UV (wavelength 172nm). The irradiation of ultraviolet light UV was carried out in the air, the distance between the l...
no. 2 approach
[0063] Image 6 It is a figure explaining an example of the manufacturing method of the microchip 201 concerning 2nd Embodiment of this invention, Image 6 (a) and Image 6 (b) is a structural diagram showing an ultraviolet light step PU1 for irradiating ultraviolet light UV to a pair of resin substrates, Image 6 (c) and Image 6 (d) is a structural diagram showing a visible light process PV2 in which visible light VL is irradiated to the opposing surfaces 94 of a pair of resin base materials after the ultraviolet light process PU1 is completed, Image 6 (e) is a structural view showing the microchip 201 after the bonding step PA3 is completed. In addition, the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the same member as 1st Embodiment, and description is abbreviate|omitted.
[0064] The manufacturing method of the microchip 201 according to the second embodiment of the present invention is composed of the following steps: an ultraviolet light step PU1, which irradiates u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com