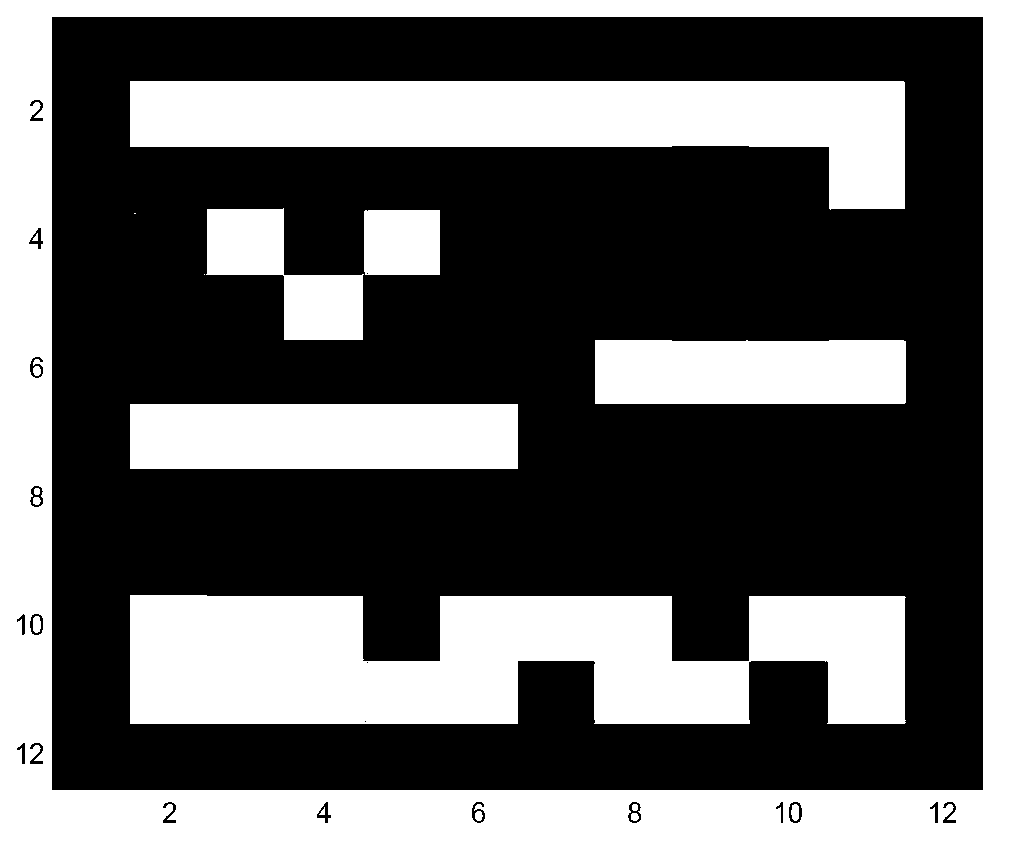Method for estimating abundance of hyperspectral image end member
A hyperspectral image and spectral information divergence technology, which is applied in the field of remote sensing image processing and can solve the problems of long time acquisition of endmember abundance and inability to adapt to use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0152] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The specific steps of the present invention will be described below respectively according to simulated data, experimental data and real hyperspectral image data.
[0153] 1. Establish AEMSC according to the simulated data
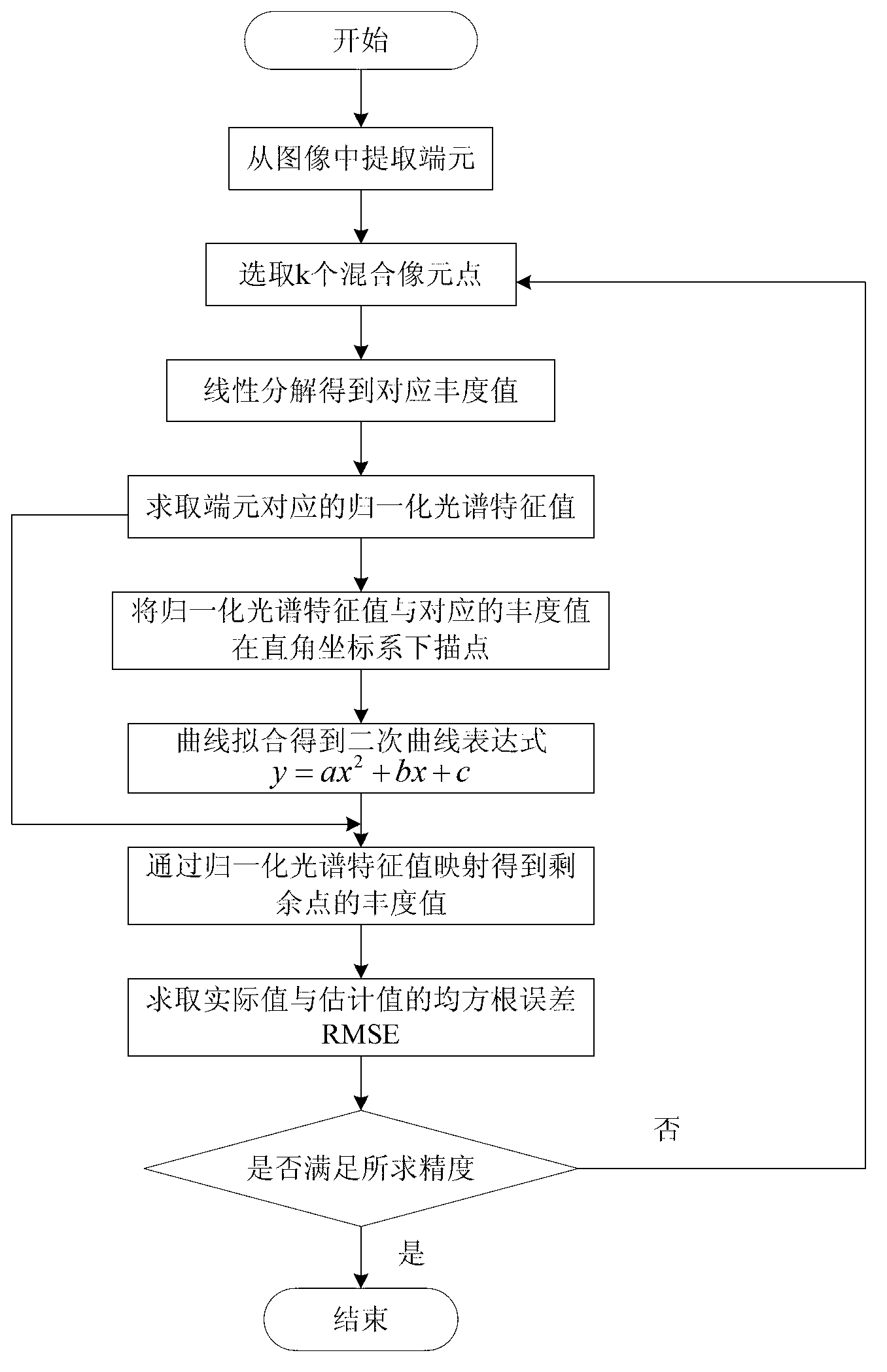
[0154] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for estimating the endmember abundance value in a hyperspectral image, the specific steps are as follows:
[0155] A. According to the correlation coefficient formula (1), randomly simulate several groups of data with small correlation to form simulated end members, among which,
[0156]
[0157] B. According to the random ratio, that is, the random abundance value is mixed into a mixed pixel, so as to obtain a simulated mixed image, such as Figure 2-4 As shown, the size of the image is 12*12 pixels, and the four sides of the image are respectively four end members.
[0158] C. For simulated images,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com