Thin film surface planarization method, array substrate, manufacturing method of array substrate and display device
A technology for surface planarization and array substrates, which is applied in the field of thin film surface planarization and can solve problems such as surface flatness damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
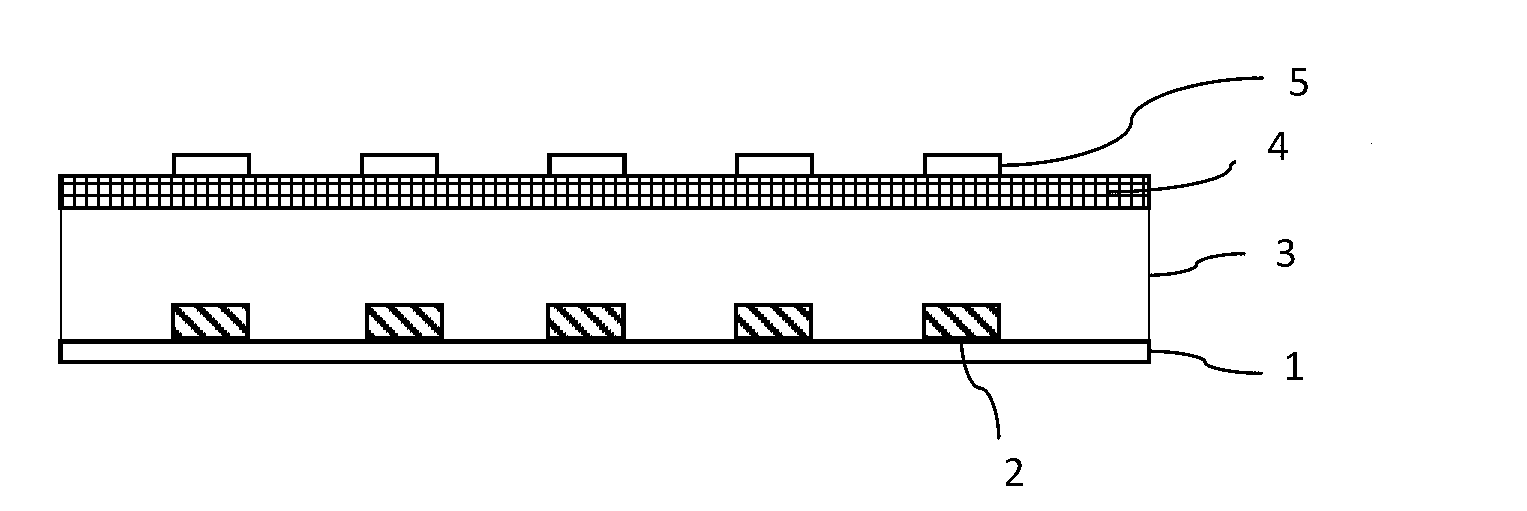
[0038] The invention provides a processing method for flattening the surface of a film after dry etching. After pattern etching is performed on a non-metal layer by dry etching, the surface of a first film layer exposed after dry etching is flattened Processing to restore the flatness of the first film layer whose surface is rough due to dry etching, and the first film layer is located under the non-metal layer.
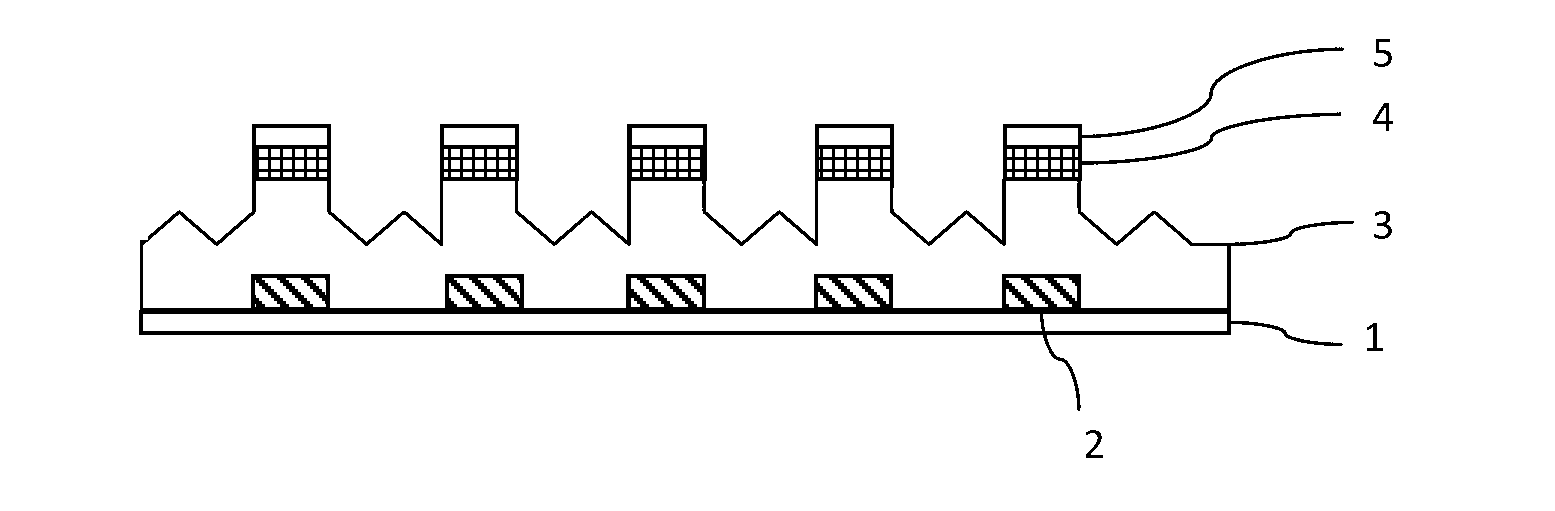
[0039] Dry etching is a pattern transfer method commonly used in the semiconductor field, usually in the form of ion bombardment, bombarding the film layer that is not protected by photoresist (or other protective layer), thereby removing the film layer protected by the photoresist The graphics are retained, but at the same time it will damage the surface flatness of the first film layer under the etched film layer (the damage is particularly serious when the first film layer is made of non-metallic material), making the first film layer rough. Subsequent film formation...
Embodiment 2
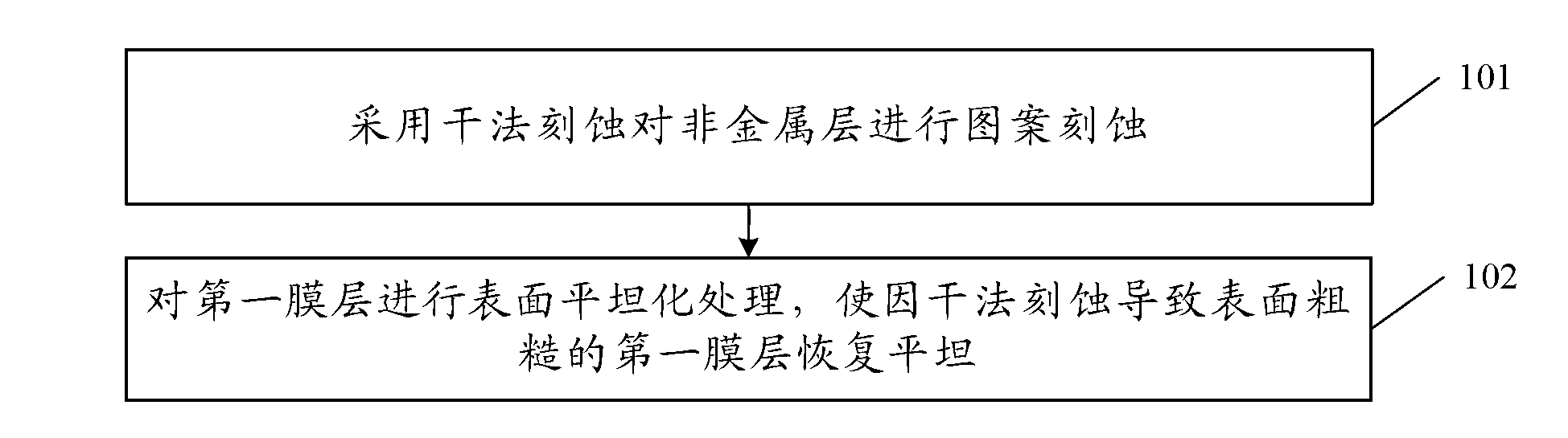
[0051] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an array substrate, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0052] 101. Perform pattern etching on the non-metal layer by dry etching, and after pattern etching on the non-metal layer by dry etching, the method further includes:
[0053] 102. Perform a surface planarization treatment on the first film layer, so that the first film layer whose surface is rough due to dry etching is restored to be flat, and the first film layer is located below the non-metal layer.
[0054] Wherein, the first film layer described in this embodiment is a general term for the film layer located below the etched film layer. For example, optionally, for an array substrate with a bottom gate structure, when the non-metal layer is a semiconductor layer, the The first film layer is a gate insulating layer.
[0055] During the preparation process of the array substrate, it is often necessary to use dry etching to etch the non-metallic layer, but d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com