Microwave photonic filter based on stimulated Brillouin scattering dynamic grating, and filtering method thereof
A technology of stimulated Brillouin and dynamic grating, applied in the fields of microwave photonics and optical communication, can solve the problems of non-reconfigurable microwave photonic filter, limited passband bandwidth, inability to continuously tune, etc., to achieve reconfigurable Effects of Features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
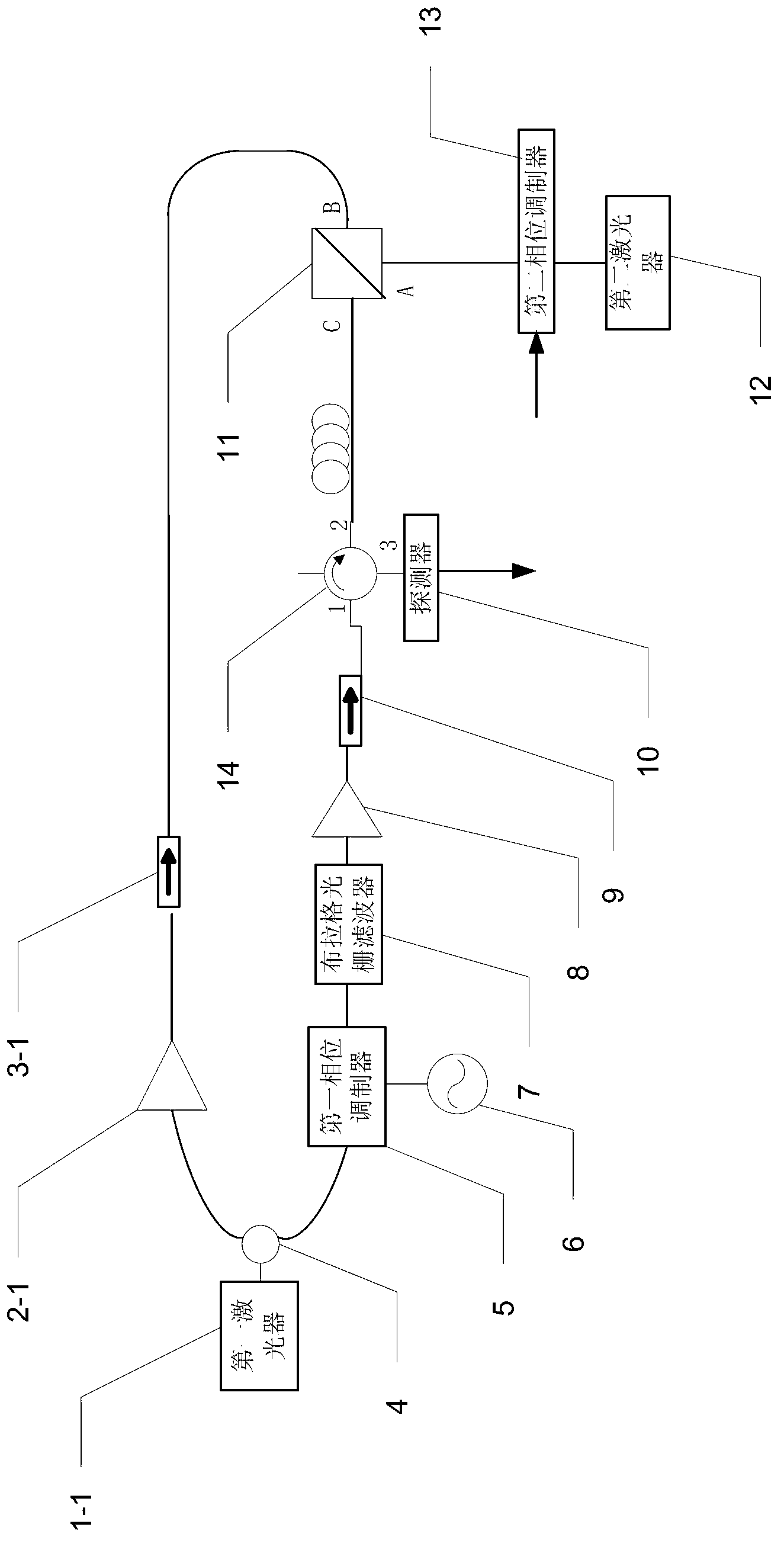
[0023] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Specifically illustrate this embodiment, the microwave photon filter based on stimulated Brillouin scattering dynamic grating described in this embodiment includes a first laser 1-1, a first erbium-doped fiber amplifier 2-1, a first isolator 3- 1. Fiber coupler 4, first phase modulator 5, microwave source 6, Bragg grating filter 7, second erbium-doped fiber amplifier 8, second isolator 9, detector 10, polarizing beam splitter 11, the first Two lasers 12, a second phase modulator 13 and a circulator 14,
[0024] The laser light emitted by the first laser 1-1 is divided into two laser beams through the fiber coupler 4, and the two laser beams are sent to the first erbium-doped fiber amplifier 2-1 and the first phase modulator 5 respectively,
[0025] The first erbium-doped fiber amplifier 2-1 amplifies the power of the received laser light to generate the first pump light, which is incident on the B port of the polari...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the microwave photon filter based on stimulated Brillouin scattering dynamic grating described in Embodiment 1 is that the first laser 1-1 and the second laser 12 are both Distributed feedback semiconductor lasers.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0030] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the microwave photon filter based on the stimulated Brillouin scattering dynamic grating described in Embodiment 1 is that the optical splitting ratio of the fiber coupler 4 is 1:1.
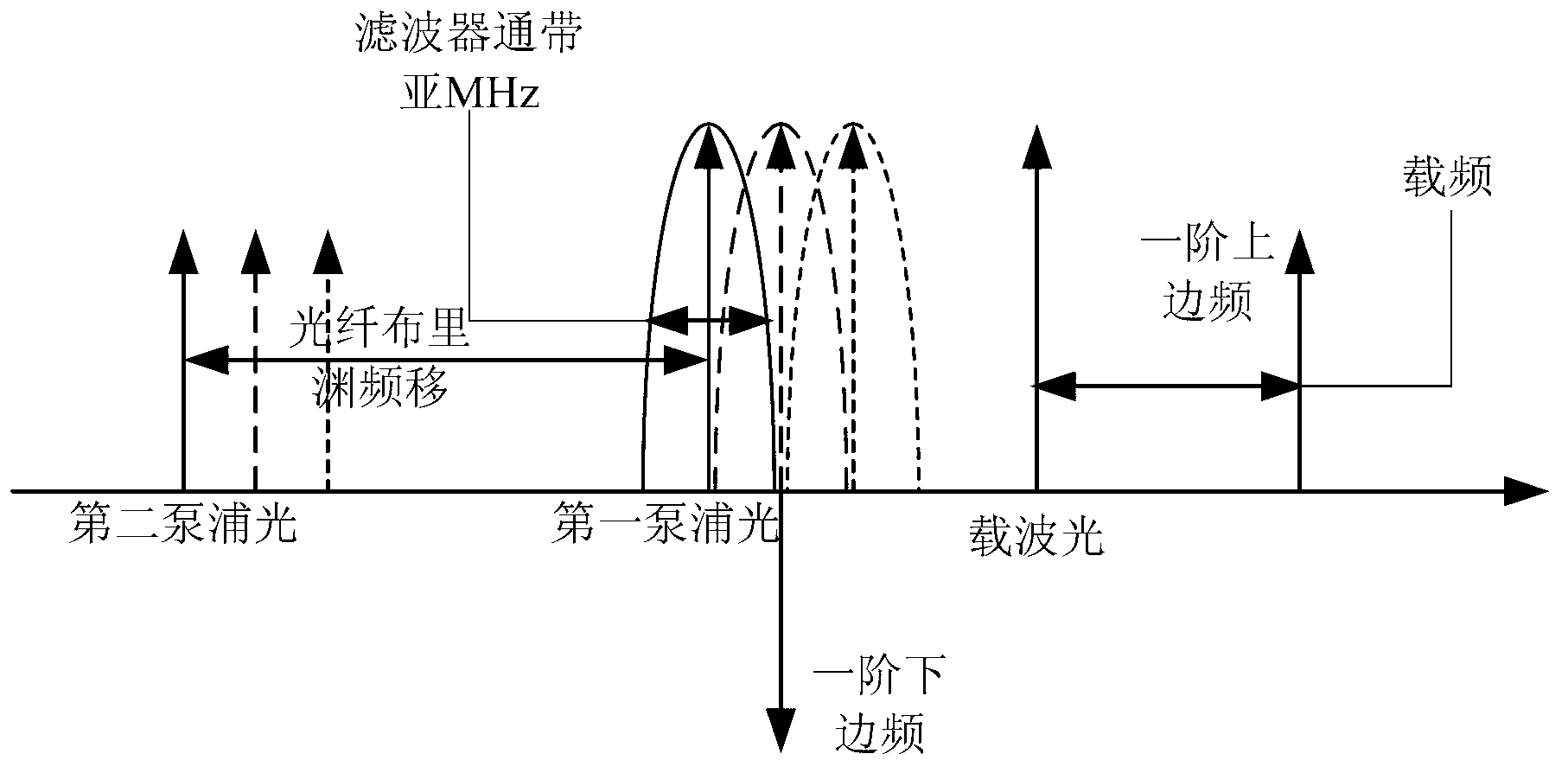
[0031] In this embodiment, the first laser 1-1 is used as a pumping light source, and the frequency is v p , split into two paths through the 50%:50% fiber coupler 4, the upper branch is used as the first pump light, the frequency is v p , providing energy, the lower branch as the second pump light is Stokes light with frequency v p -v B , the two enter the optical fiber to generate stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), forming a dynamic grating (BDG) based on stimulated Brillouin scattering. The second laser 12 outputs light as carrier light in the 155Onm waveband.
[0032] The first pumping light is continuous light, which is amplified through the first erbium-doped fiber amplifier 2-1 (EDFA), and the first isolator 3-1 prevents ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com