Time/wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network
A passive optical network and wave multiplexing technology, applied in the field of passive optical networks, can solve the problem of tight bandwidth allocation, and achieve the effects of low cost, expansion of transmission capacity, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
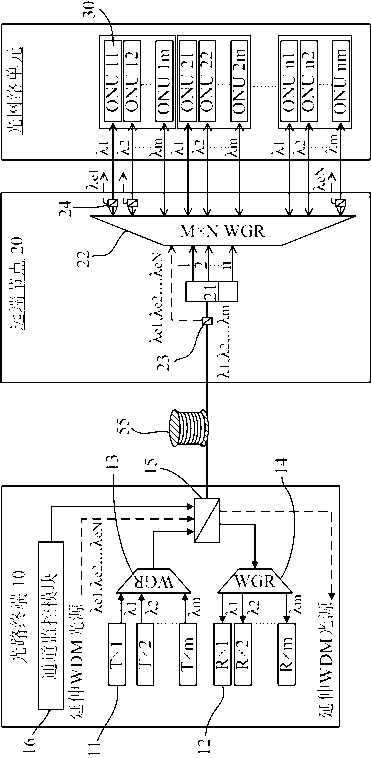
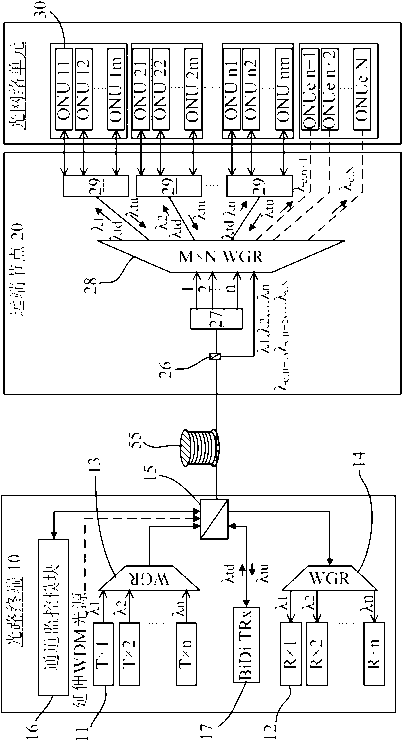
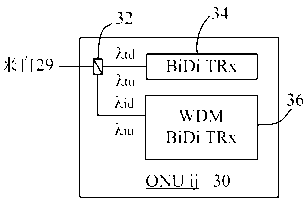
[0023] figure 1 A schematic diagram showing the architecture of a TWDM passive optical network (TW-PON) according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The time-division and wavelength-division multiplexing passive optical network according to the first embodiment of the present invention is a time-division-based wavelength-division passive optical network, or called a wave-division-like passive optical network (WDM-PON like) ,Such as figure 1 As shown, its structure can be divided into an optical terminal 10 (such as located in the central office of a service provider), a remote node 20 and several optical network units 30, and optical signals are transmitted by wiring fibers 55 therebetween.
[0024] Such as figure 1 As shown, a 1×n optical splitter (Optical Splitter) 21 and an M×N MIMO waveguide grating router (WGR) 22 are arranged at the remote node 20 . The optical splitter 21 will receive a group of mixed optical signals {λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...λ m}, and split th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com