Inverter control system
A control system and inverter technology, applied in control systems, vector control systems, motor control, etc., can solve problems such as difficult installation of inverters, and achieve the effects of cost and loss reduction, low calculation load and size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
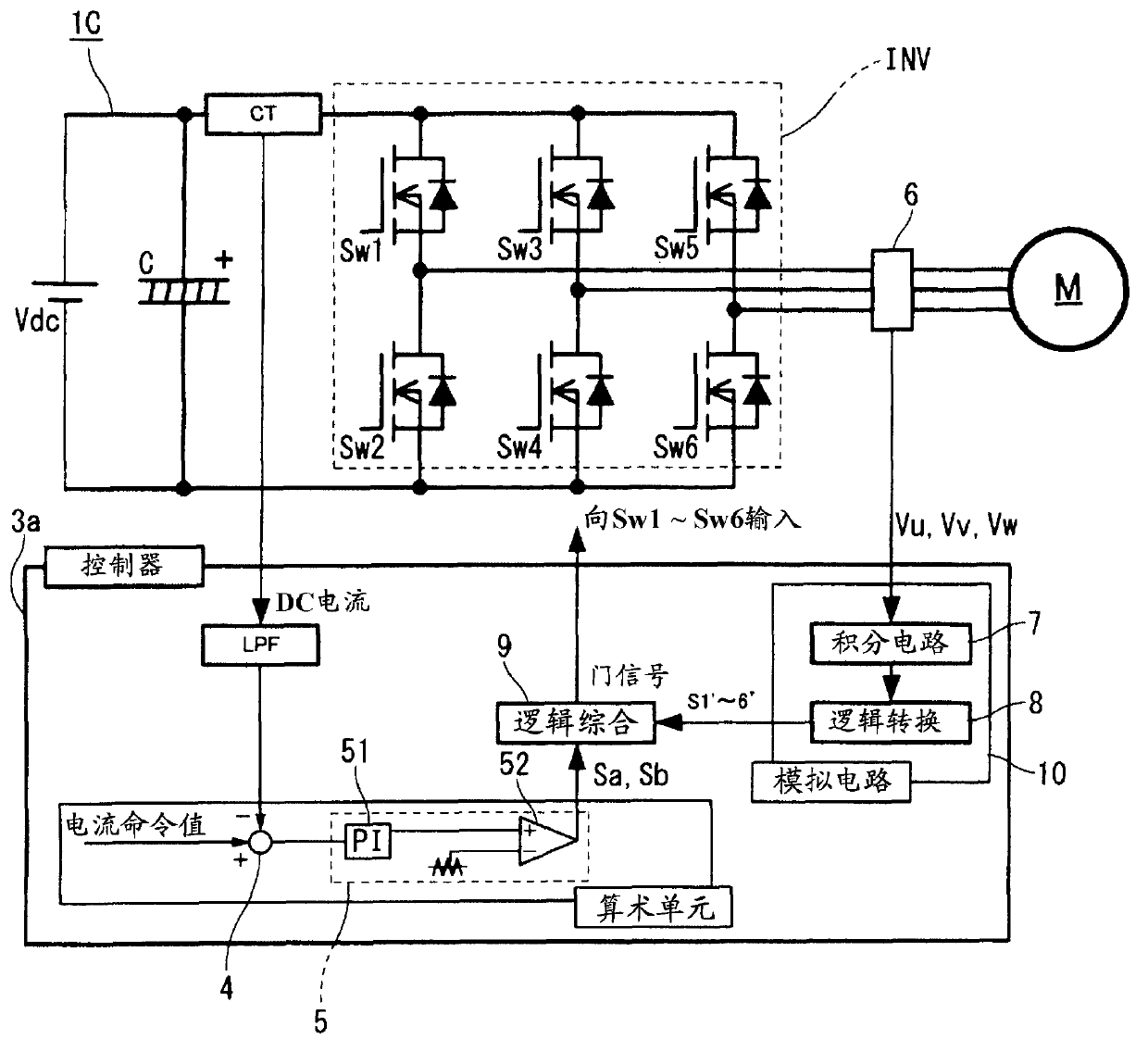
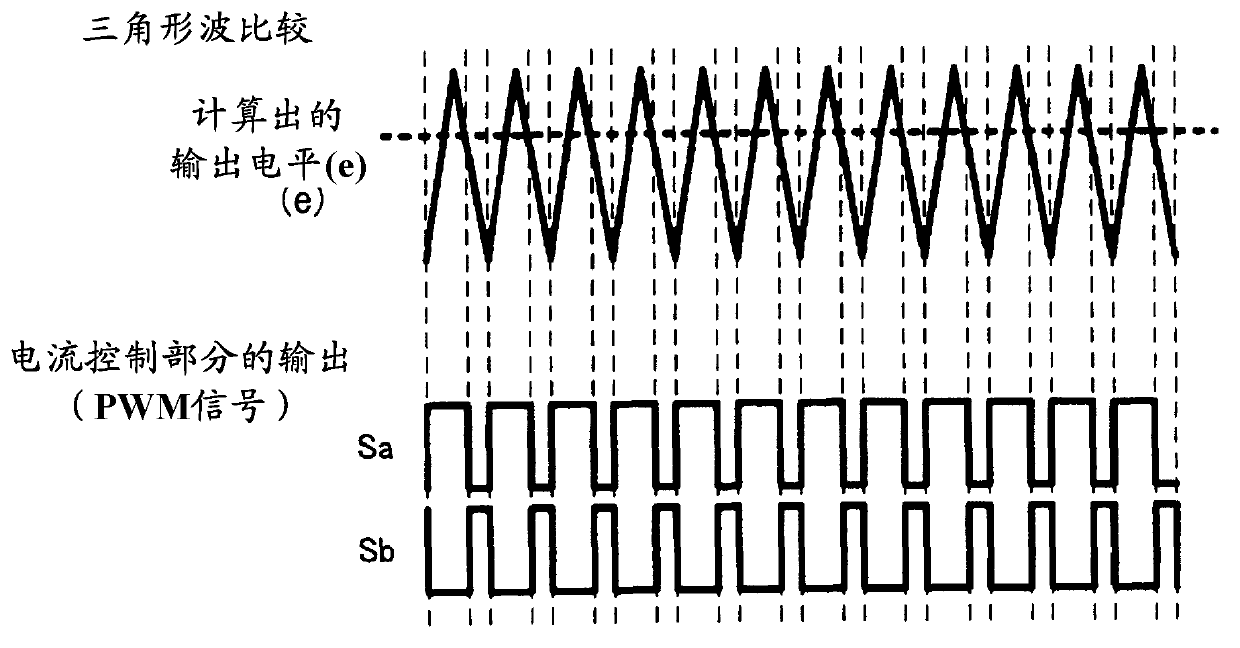
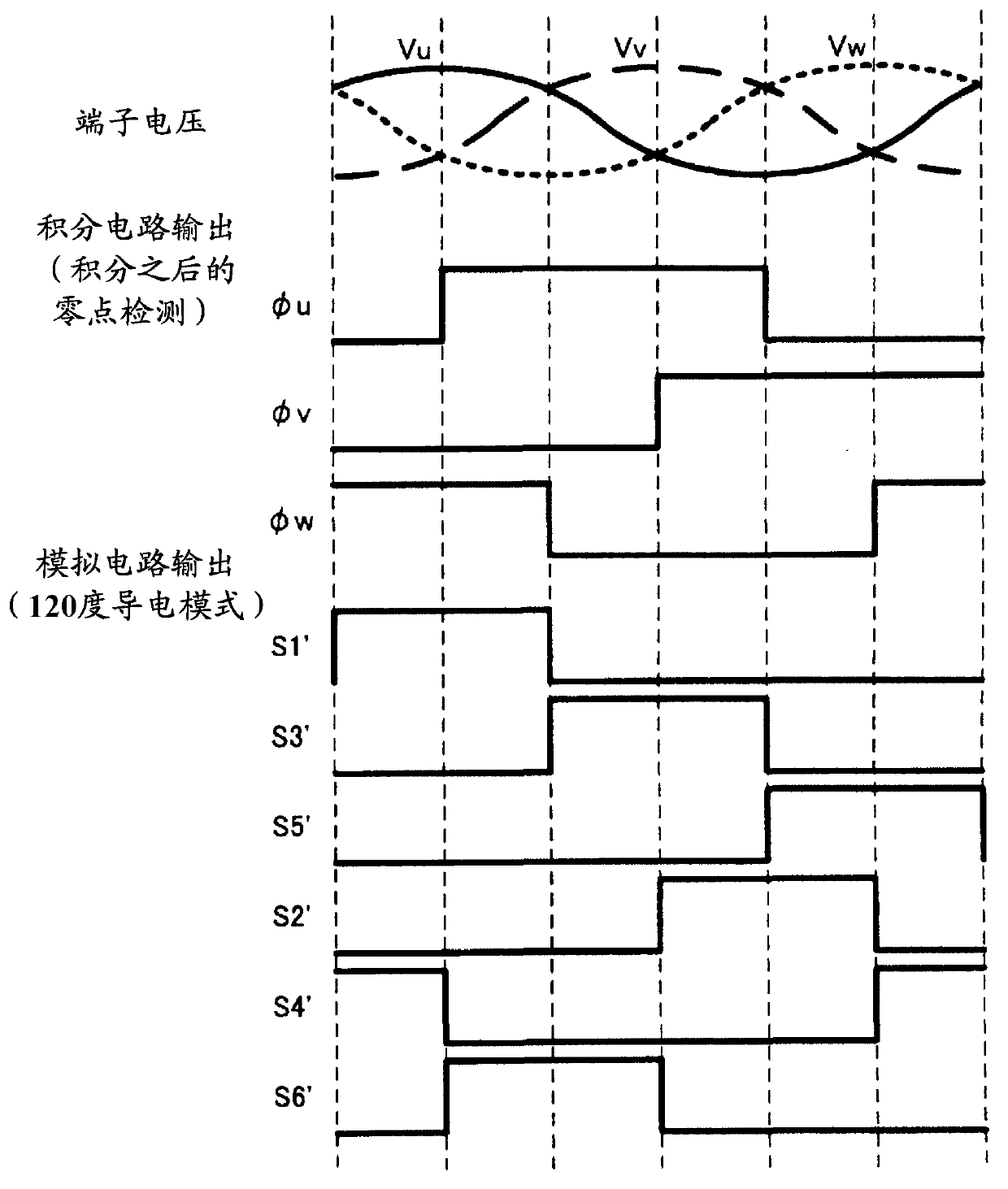
[0033] will now refer to Figures 1 to 4 The inverter control system in the first embodiment according to the present invention will be described. The inverter control system in the first embodiment includes a main circuit 1C and a current control controller 3a.
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the main circuit 1C in the first embodiment is constructed in the same manner as a general voltage source PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) inverter, and includes an inverter INV having a three-phase six-element circuit. In this embodiment, the controlled object (ie, the variable mainly used for control) is the current input to the inverter INV. A direct current (input current of the inverter) between the smoothing capacitor C and the switching elements Sw1 to Sw6 (ie, between the smoothing capacitor C and the inverter INV) is detected or acquired by a current sensor CT or the like. As the current sensor CT, any component that can detect or acquire a current value can be used. For ex...
no. 2 example
[0054] Figure 5 is a block diagram showing the speed control controller of the inverter control system in the second embodiment according to the present invention. Components constructed in the same manner as in the first embodiment are given the same reference numerals as those in the first embodiment, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0055] The structure of the main circuit in the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment. The inverter control system in the second embodiment includes a speed control controller 3b instead of the current control controller 3a of the first embodiment. Furthermore, the input command in the second embodiment is a speed command value.
[0056] In the second embodiment, the 120-degree conduction patterns S1 ′ to S6 ′ output from the sensorless circuit 10 are converted into speed detection values by the speed detector 11 .
[0057] Next, the subtraction section 12 calculates a speed difference (deviation)...
no. 3 example
[0060] Figure 6 is a block diagram showing an electric power control controller of an inverter control system in a third embodiment according to the present invention. Components constructed in the same manner as in the first embodiment are given the same reference numerals as those in the first embodiment, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0061] The structure of the main circuit in the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment. The inverter control system in the third embodiment includes an electric power control controller 3c instead of the current control controller 3a of the first embodiment. Furthermore, the input command in the third embodiment is an electric power command value.
[0062] In the third embodiment, a DC voltage value (the voltage between both ends of the smoothing capacitor C, ie, the input voltage to the inverter) is detected. The electric power detector 14 multiplies this voltage detection value by the DC compone...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com