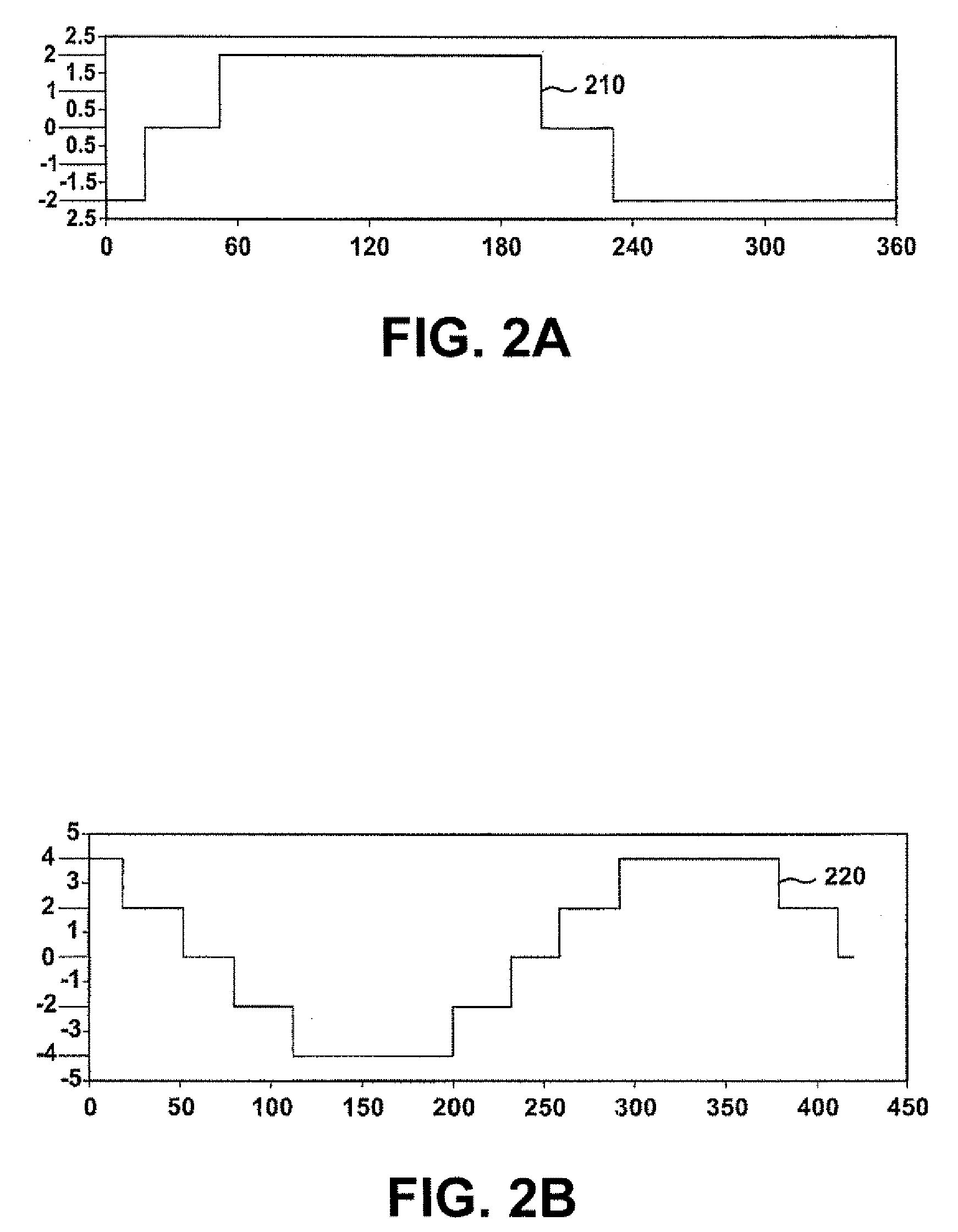
Patents
Literature
147results about "Motor control for high speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
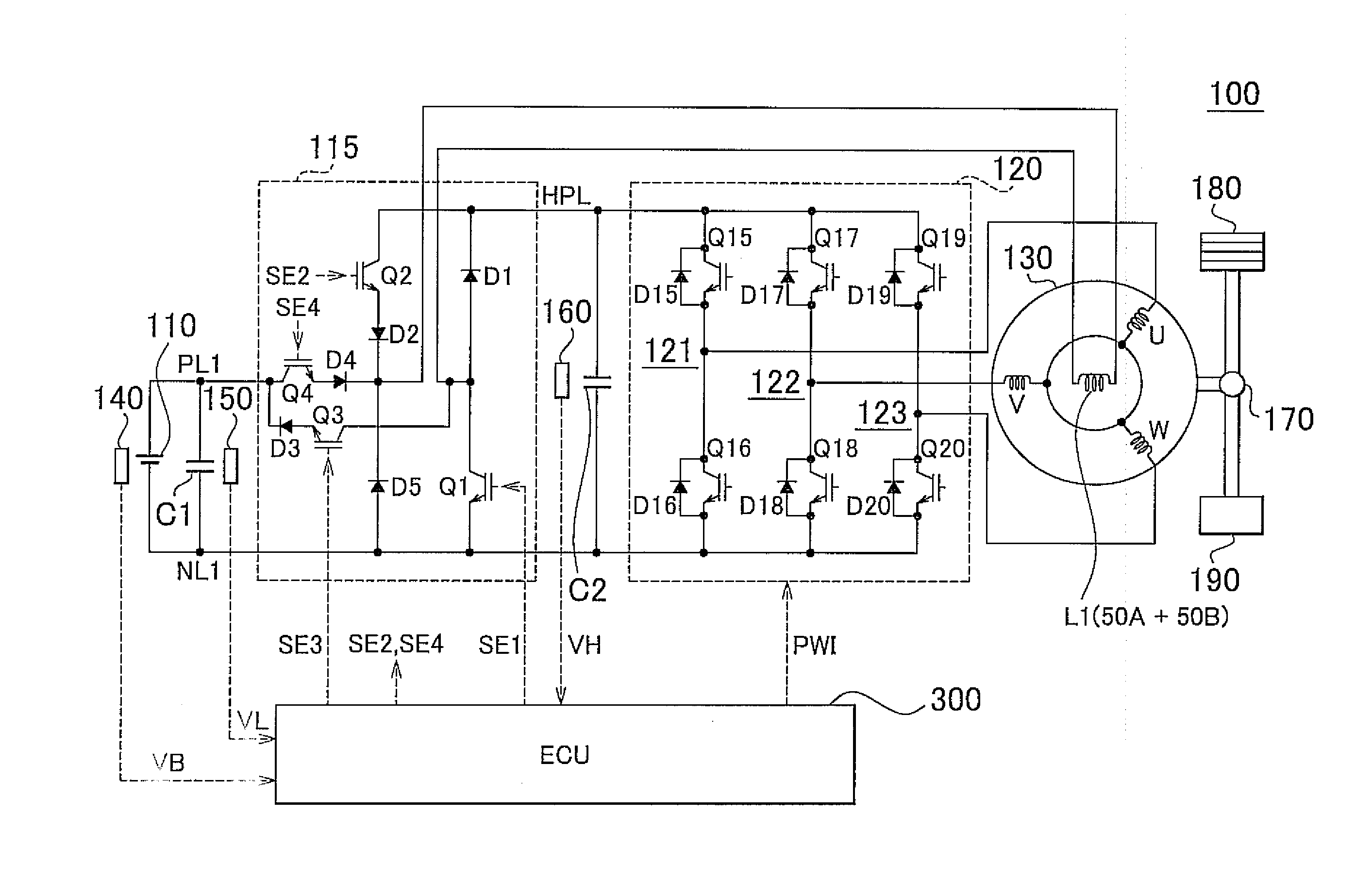
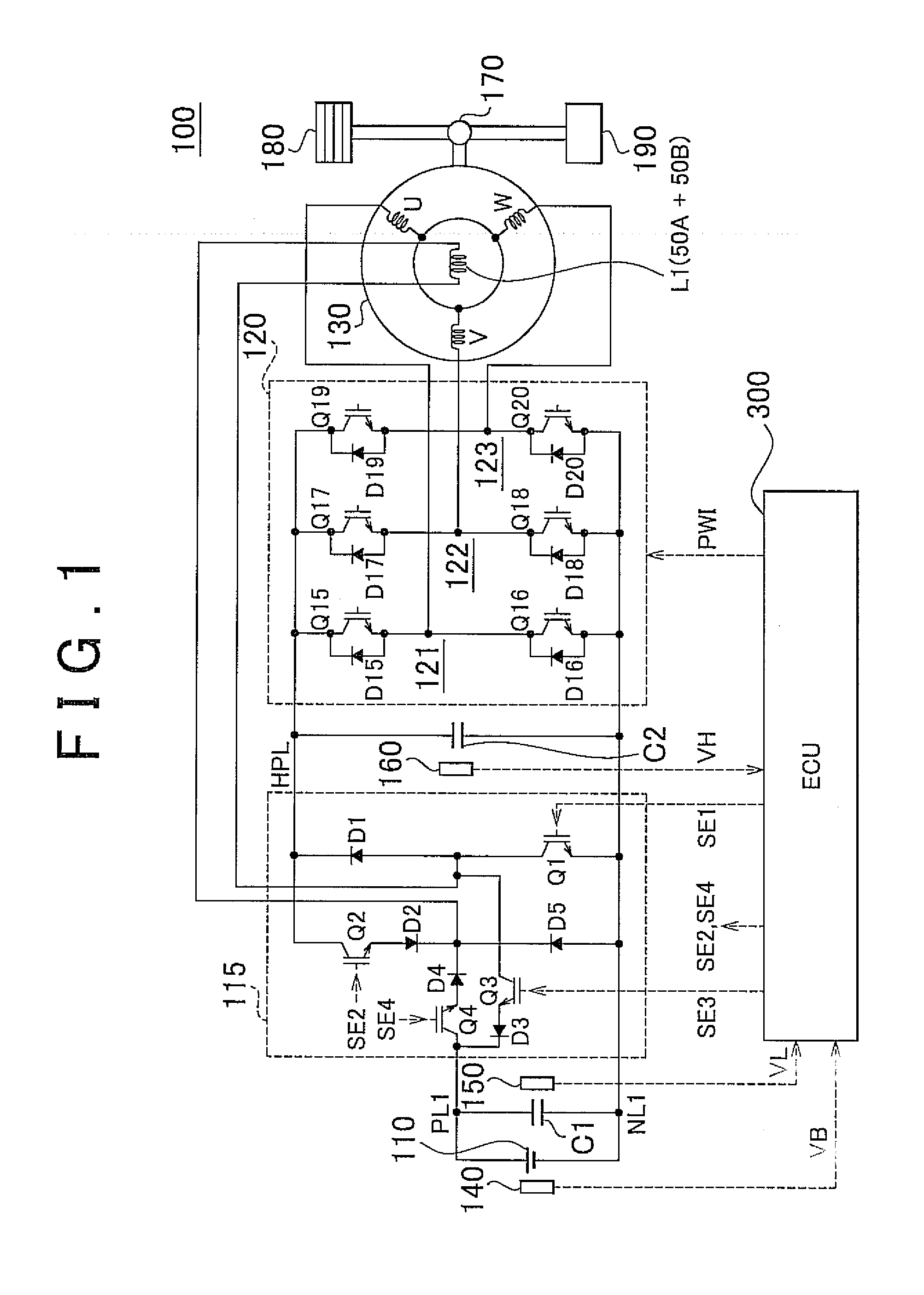
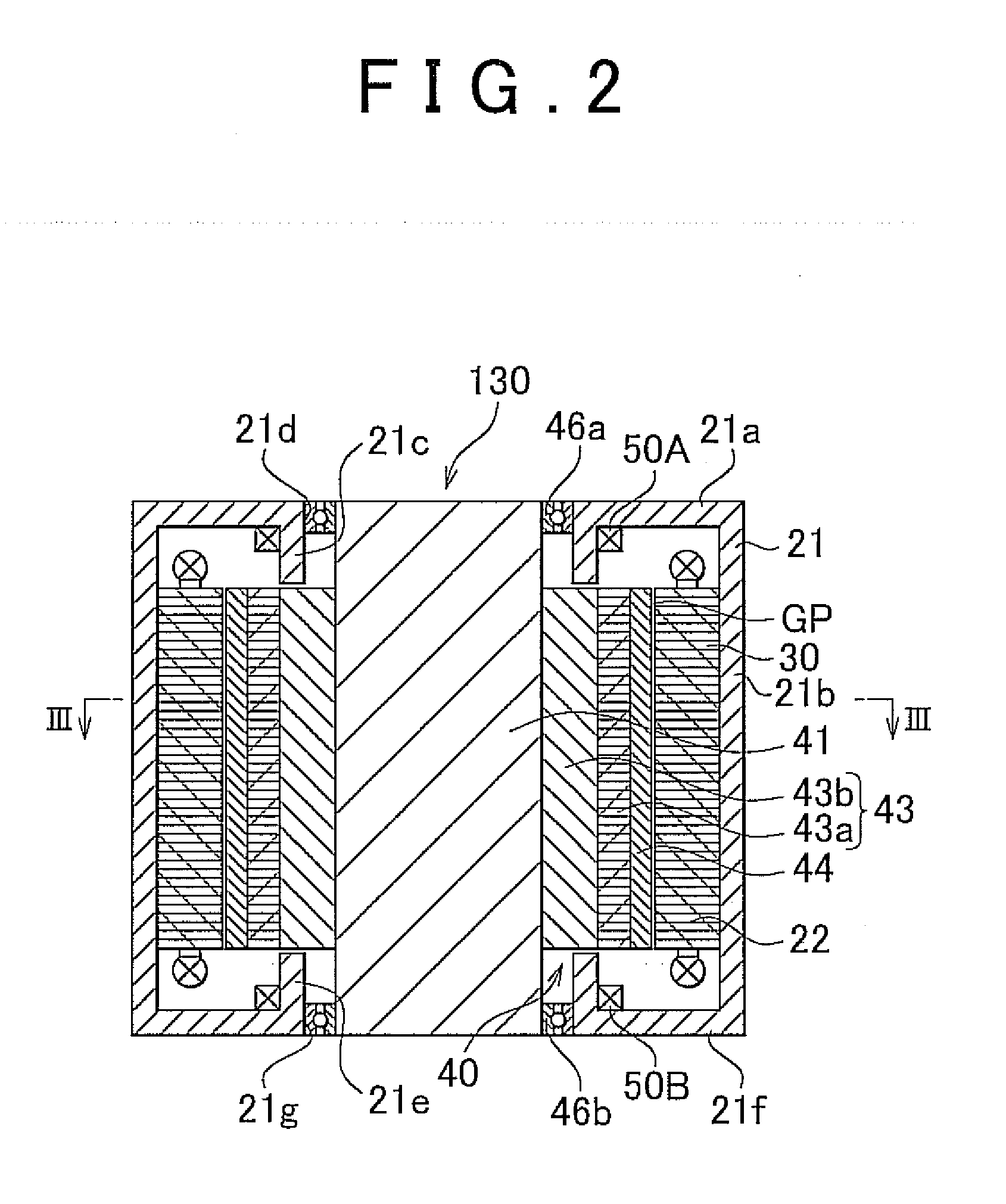
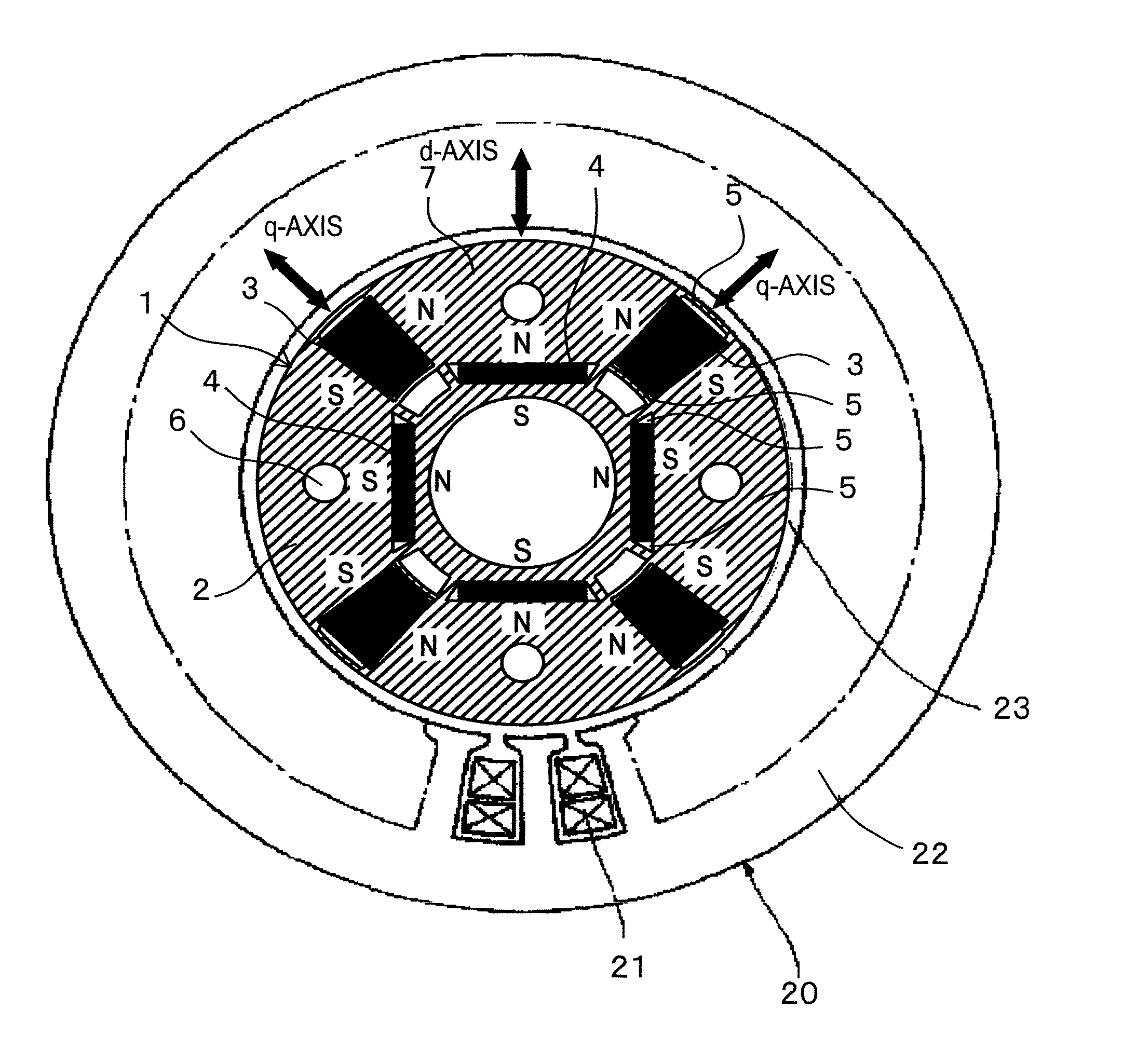
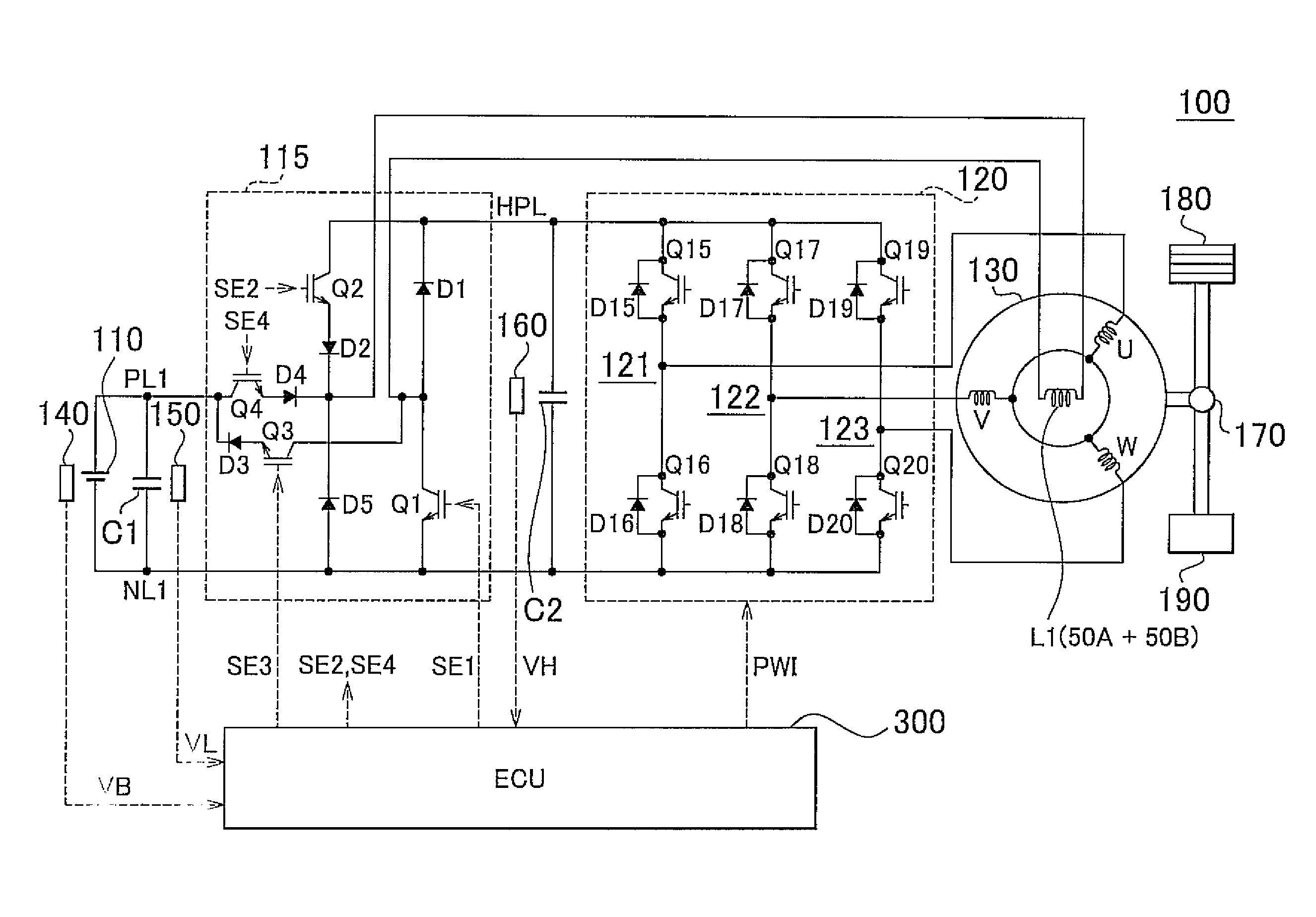
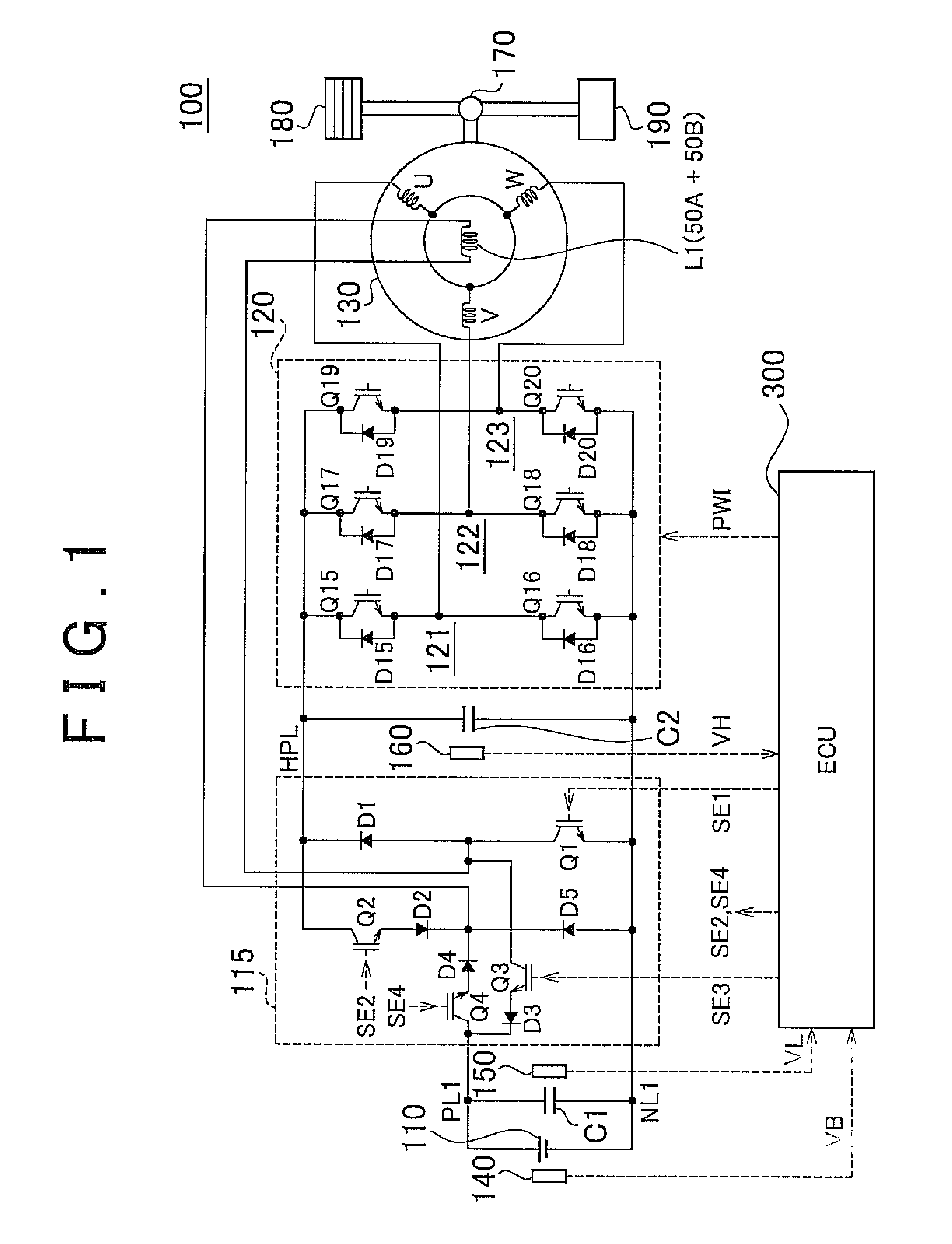
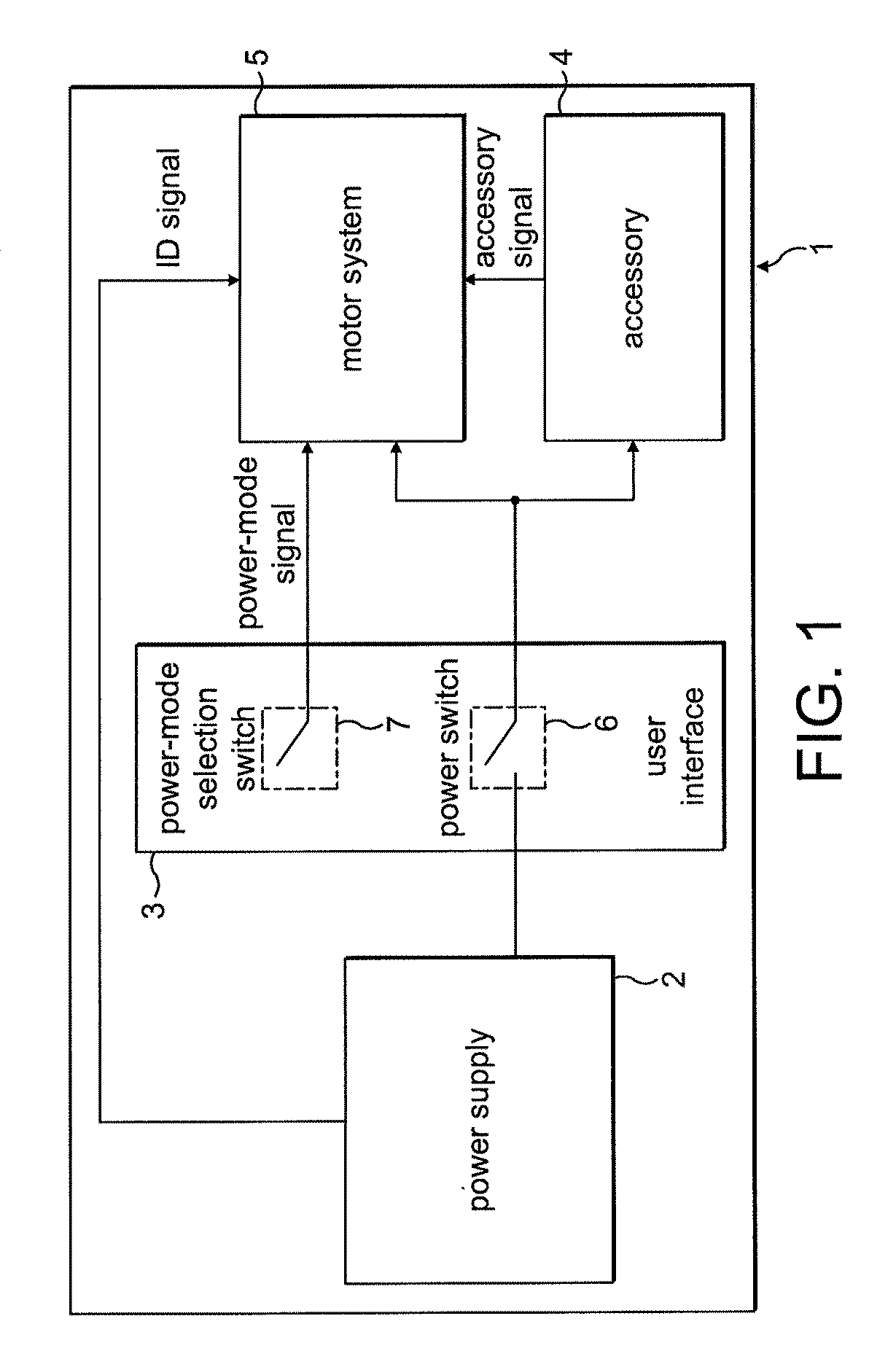
Permanent magnet rotating electrical machine and permanent magnet motor drive system
InactiveUS20100060223A1Vector control systemsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesLow speedMagnetic poles
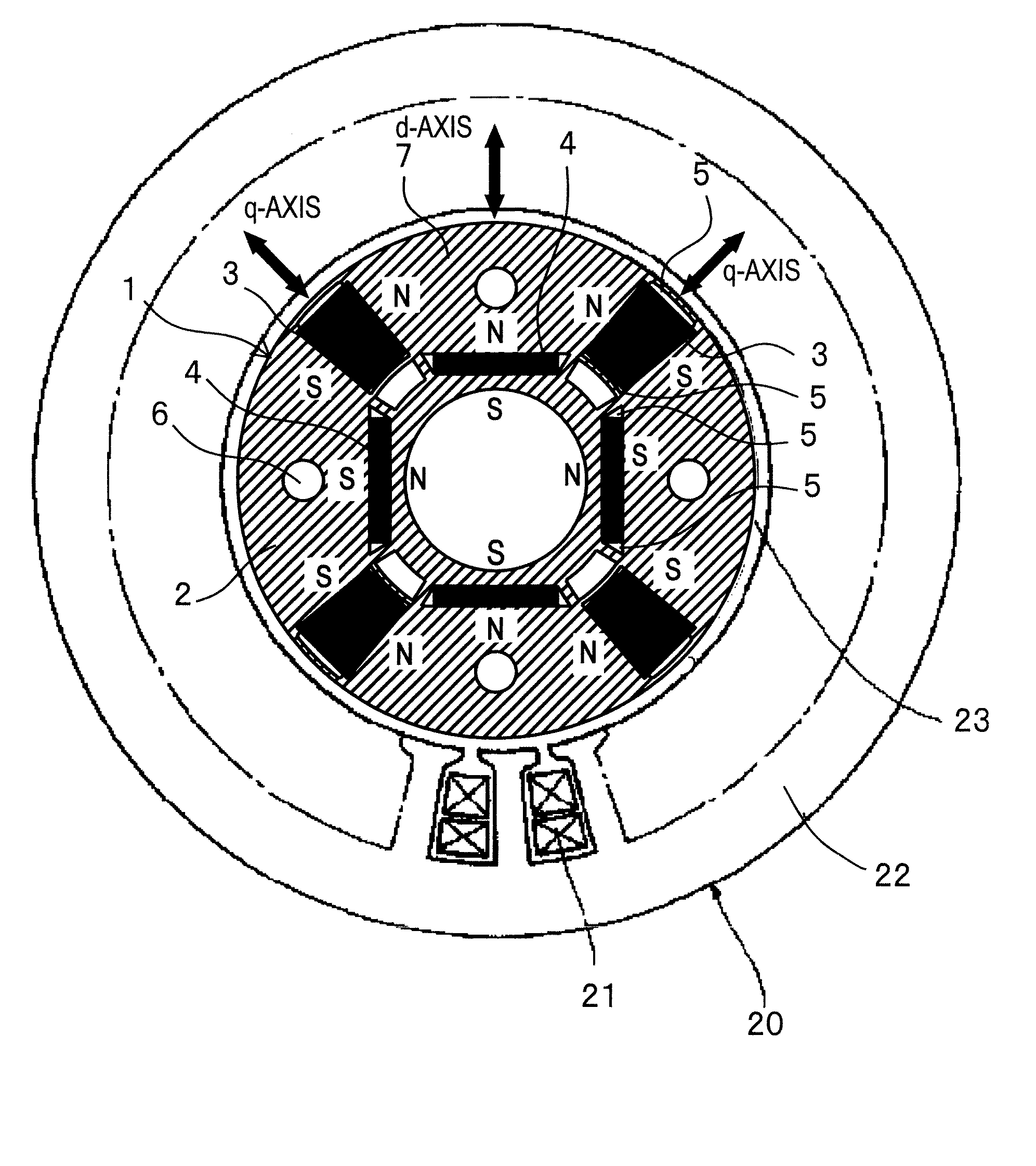
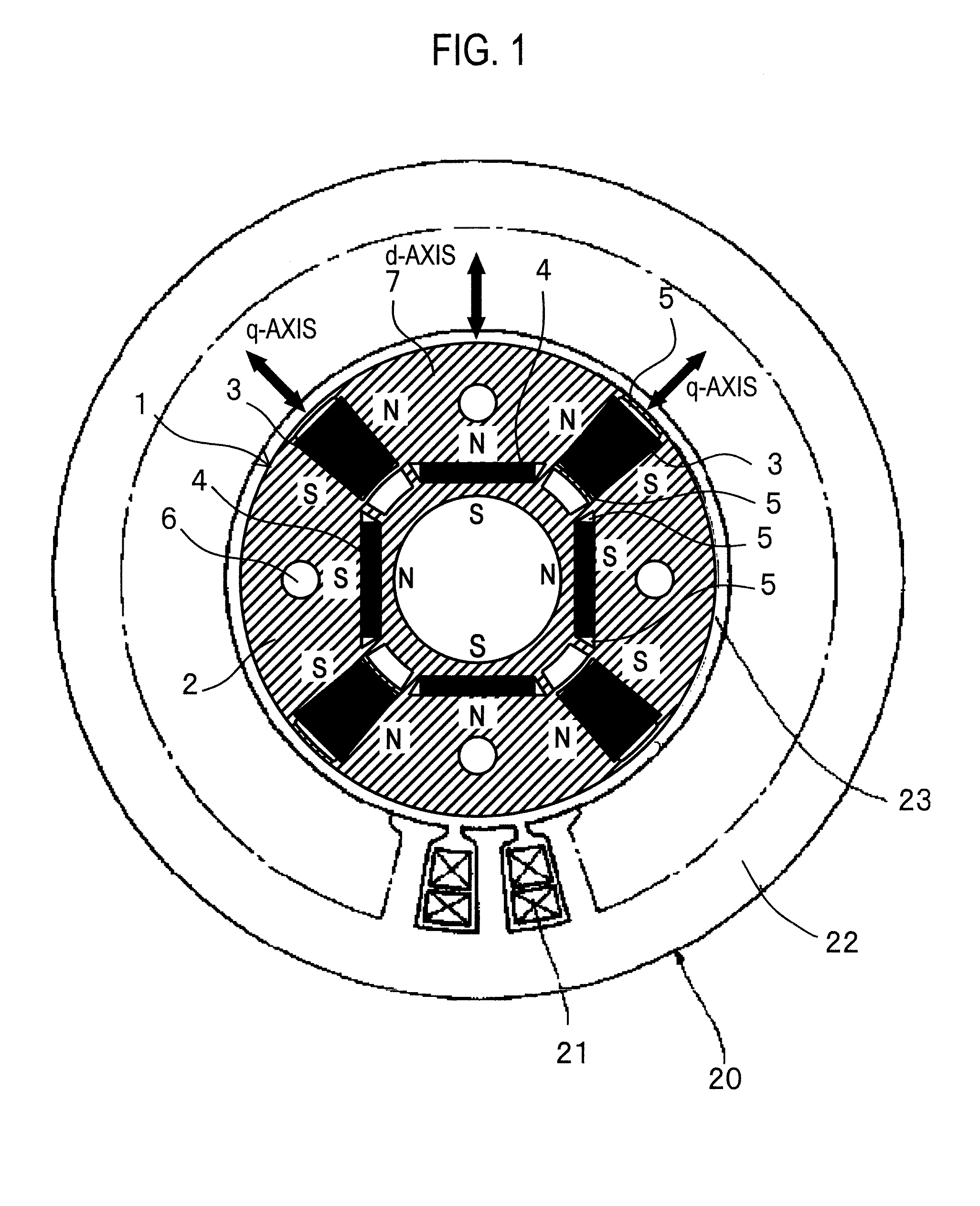
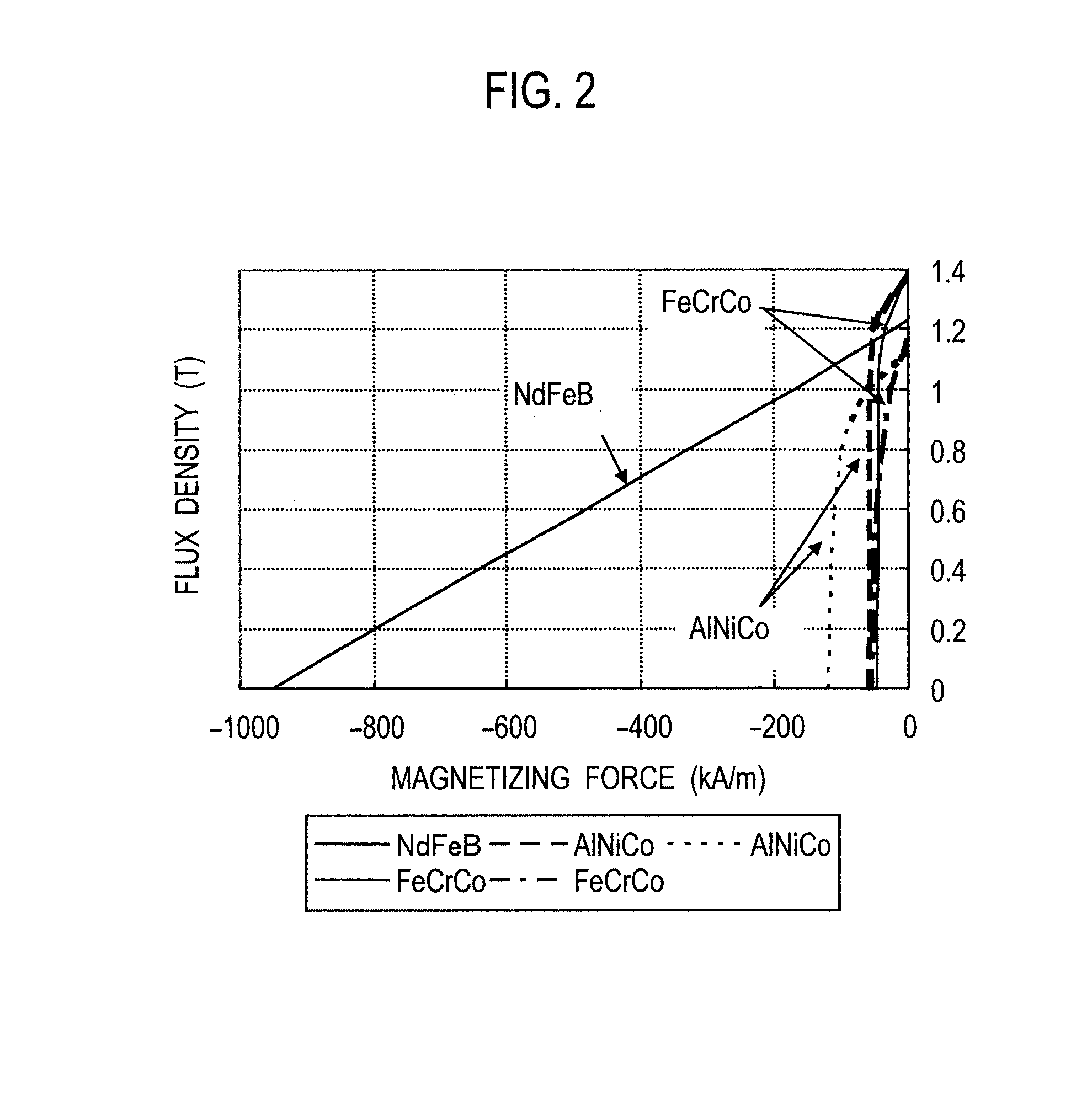
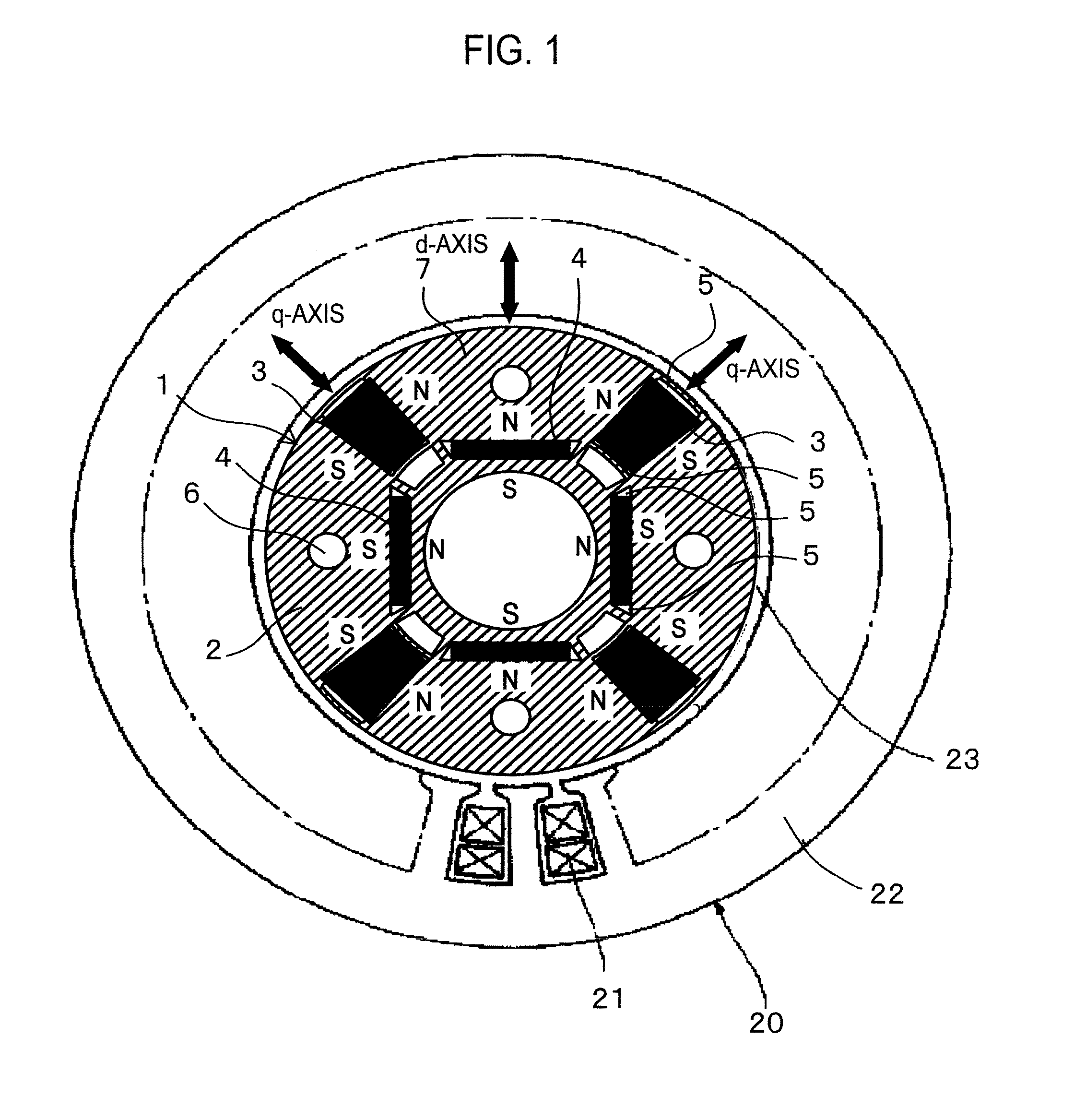
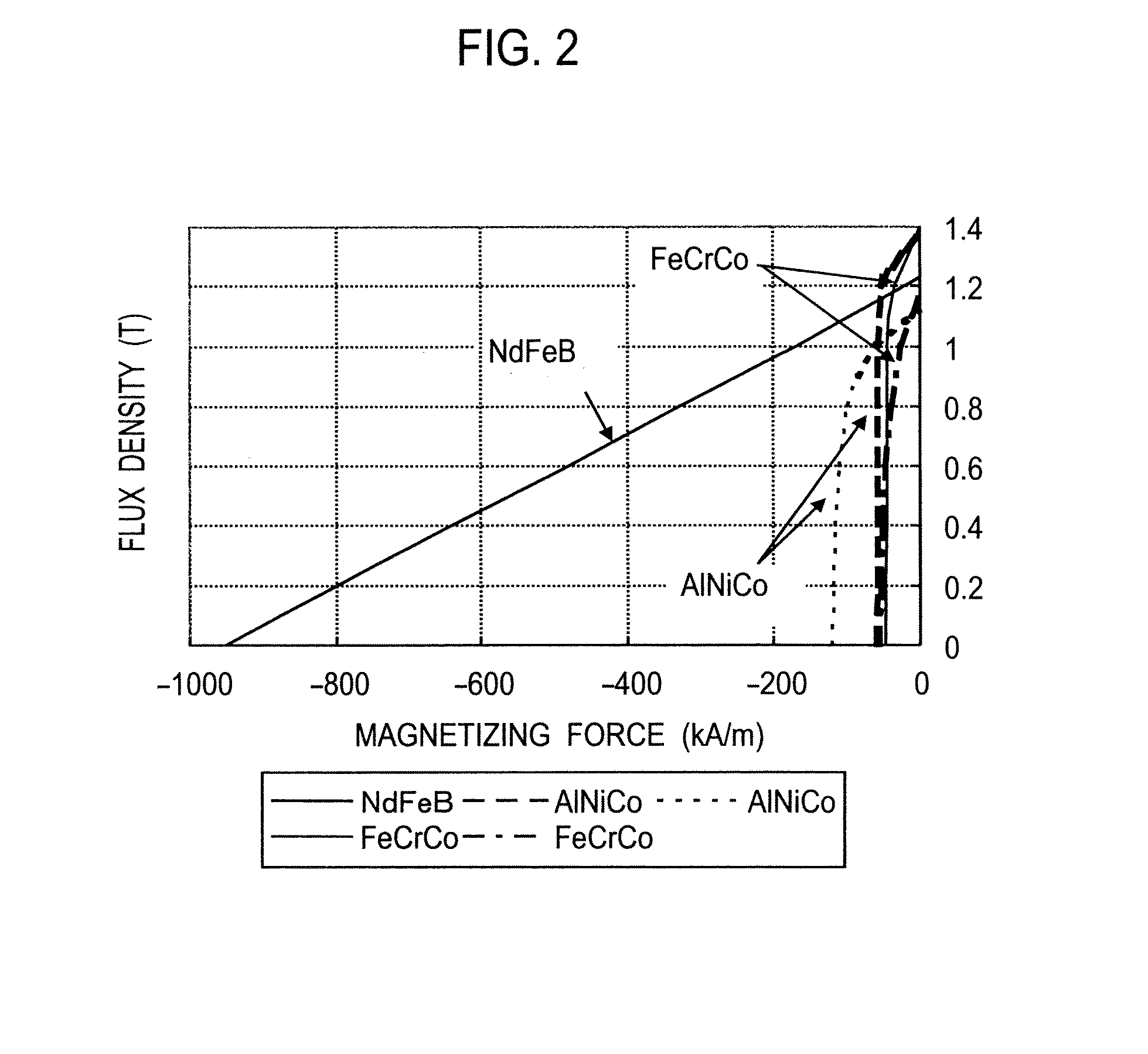
A permanent magnet rotating electrical machine capable of conducting a variable speed operation at high output in a wide range from low speed to high speed and improving efficiency and reliability in a wide operating range. Two kinds of permanent magnets having different shapes or different magnetic characteristics are embedded in a rotor core, to form a magnetic pole. The permanent magnets arranged at the magnetic pole include a permanent magnet whose product of coercive force and thickness along a magnetizing direction is small and the permanent magnet whose product of coercive force and thickness along the magnetizing direction is large. A magnetic field created by passing a current to an armature coil for a short time is used to irreversibly magnetize the permanent magnet whose product of coercive force and thickness along magnetizing direction is small, thereby changing a total linkage flux amount, and a positive d-axis current is passed when torque is large.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
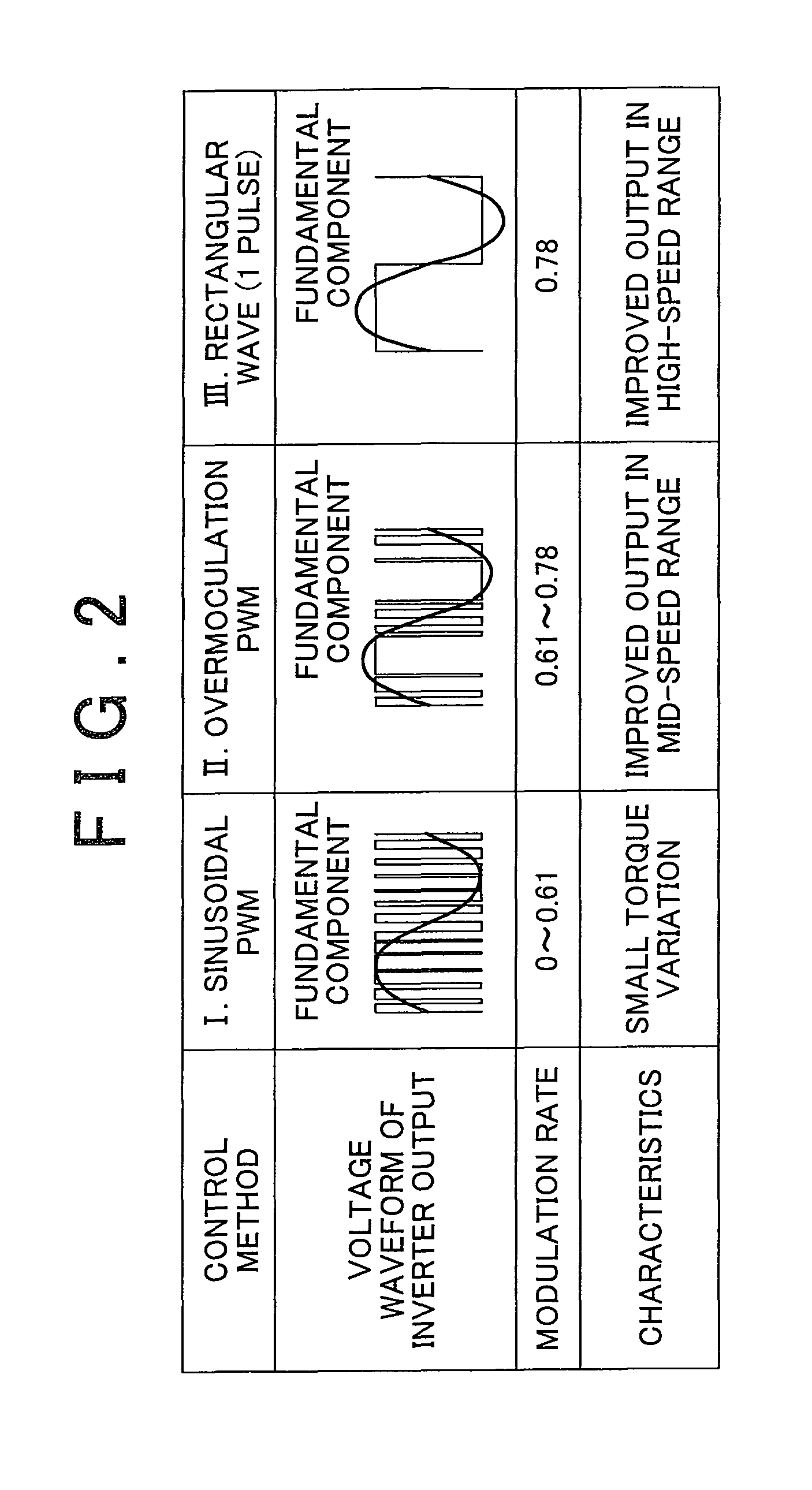
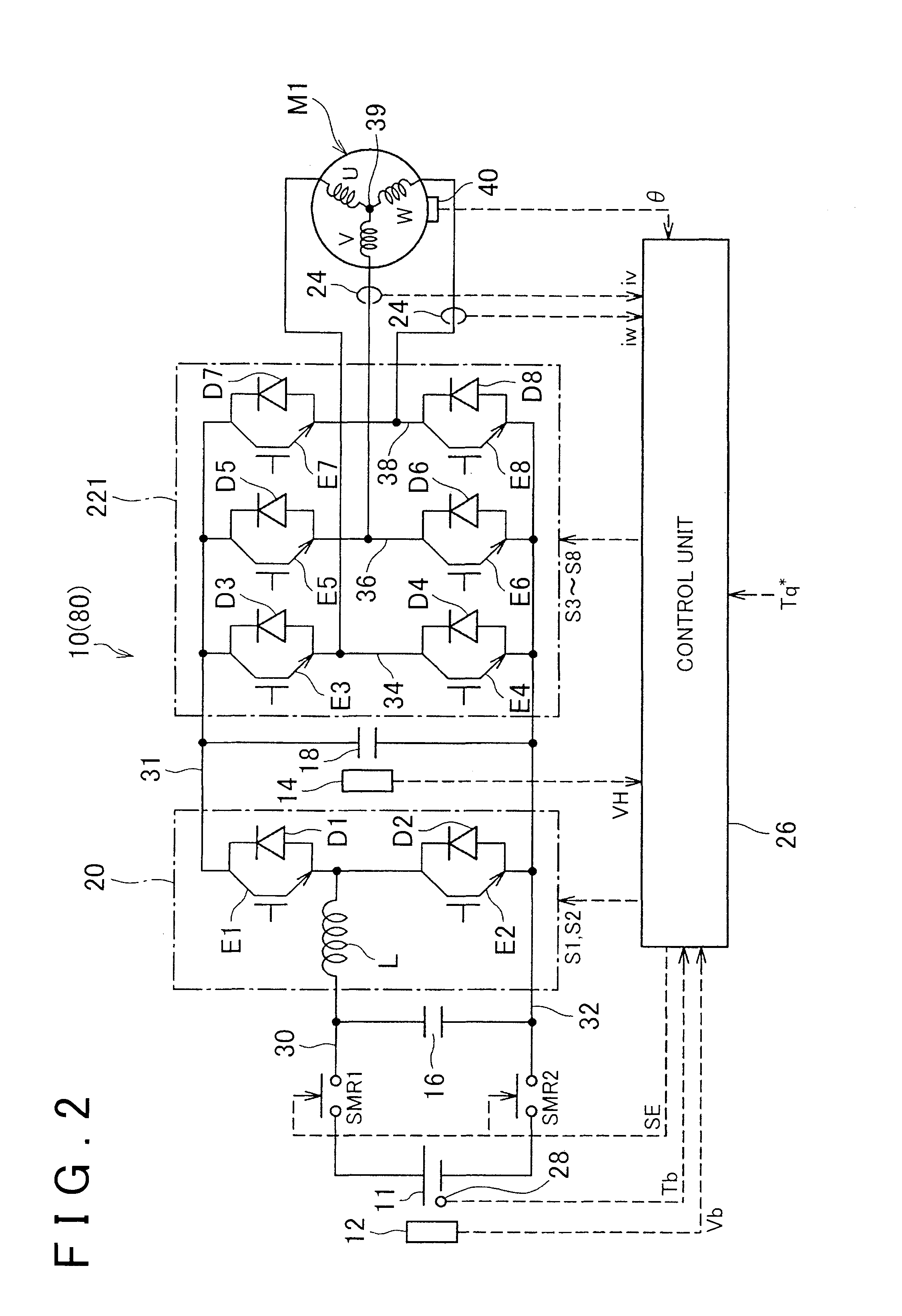
Control system for ac motor
InactiveUS20110248663A1Simple computationSimple calculationVector control systemsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcOperating pointControl system
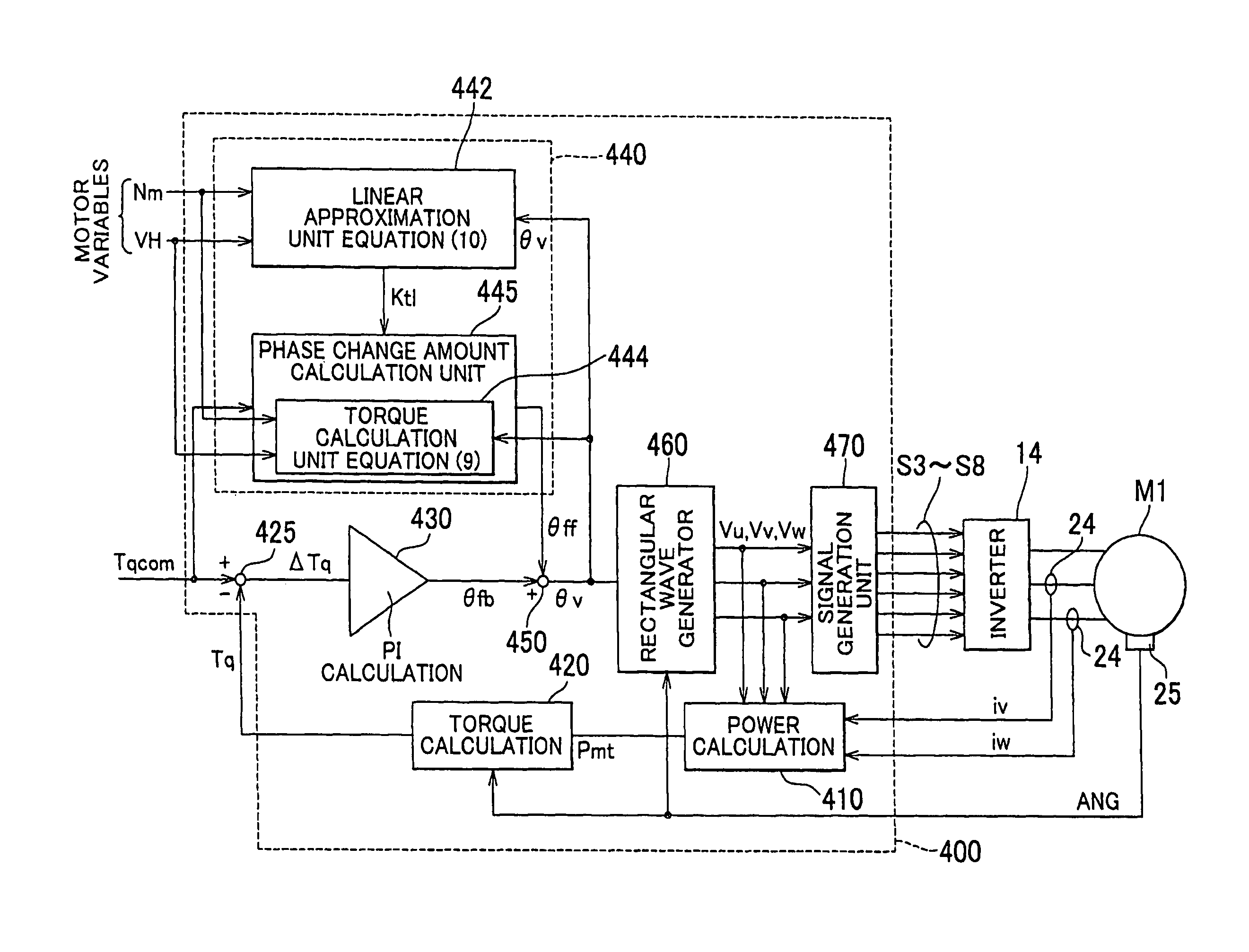
A control system for an AC motor determines a slope Ktl of a tangent TL at an operating point Pa corresponding to the current motor operating state and voltage phase (θ0) on a torque characteristic curve that is plotted according to a torque equation representing an output torque characteristic with respect to the motor operating state and the voltage phase of the rectangular wave voltage. The control system further calculates a voltage phase change amount θff for use in feed-forward control, according to ΔTtl / Ktl obtained by dividing a torque compensation amount ΔTtl for feed-forward control by the slope Ktl.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
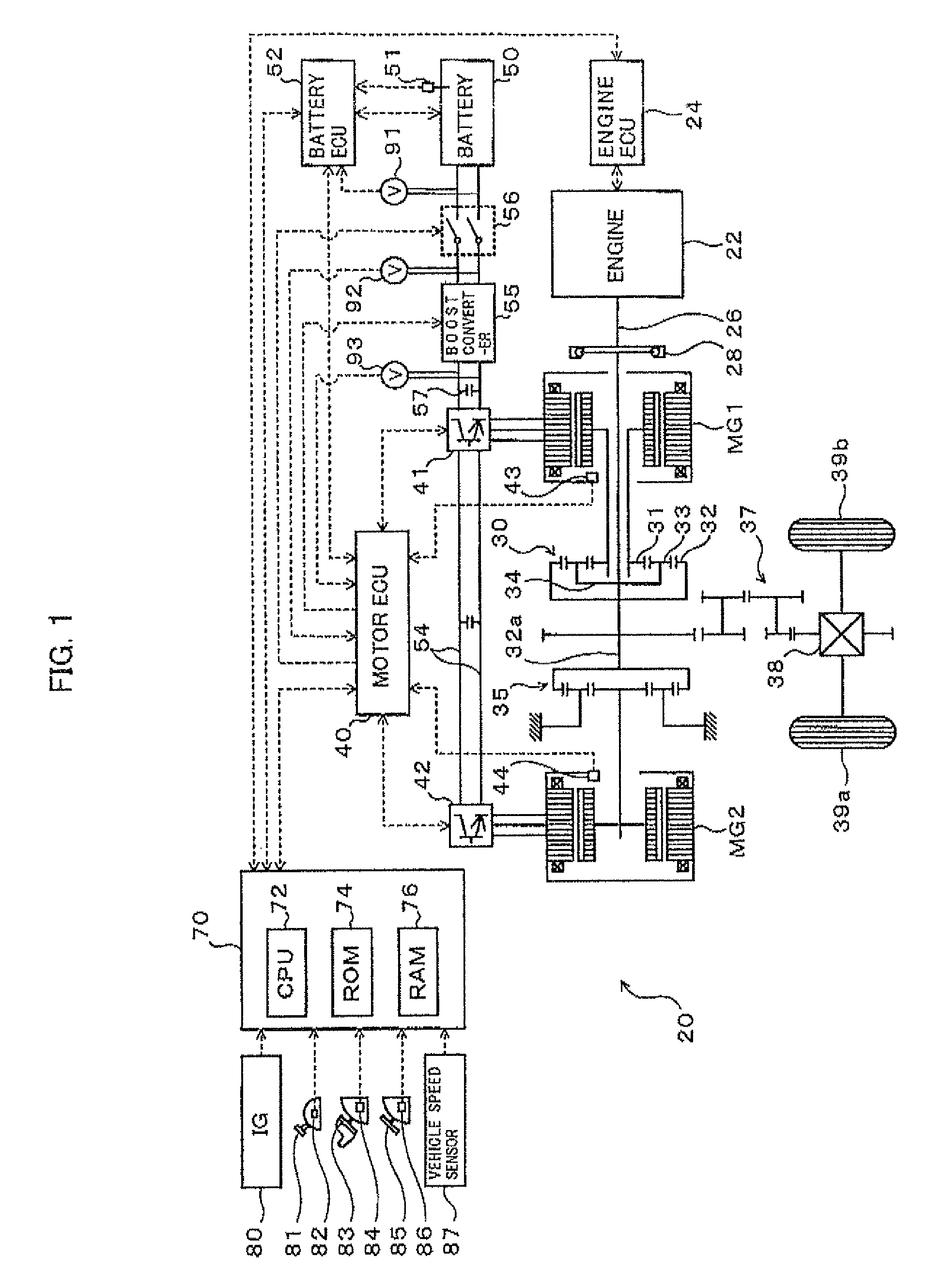
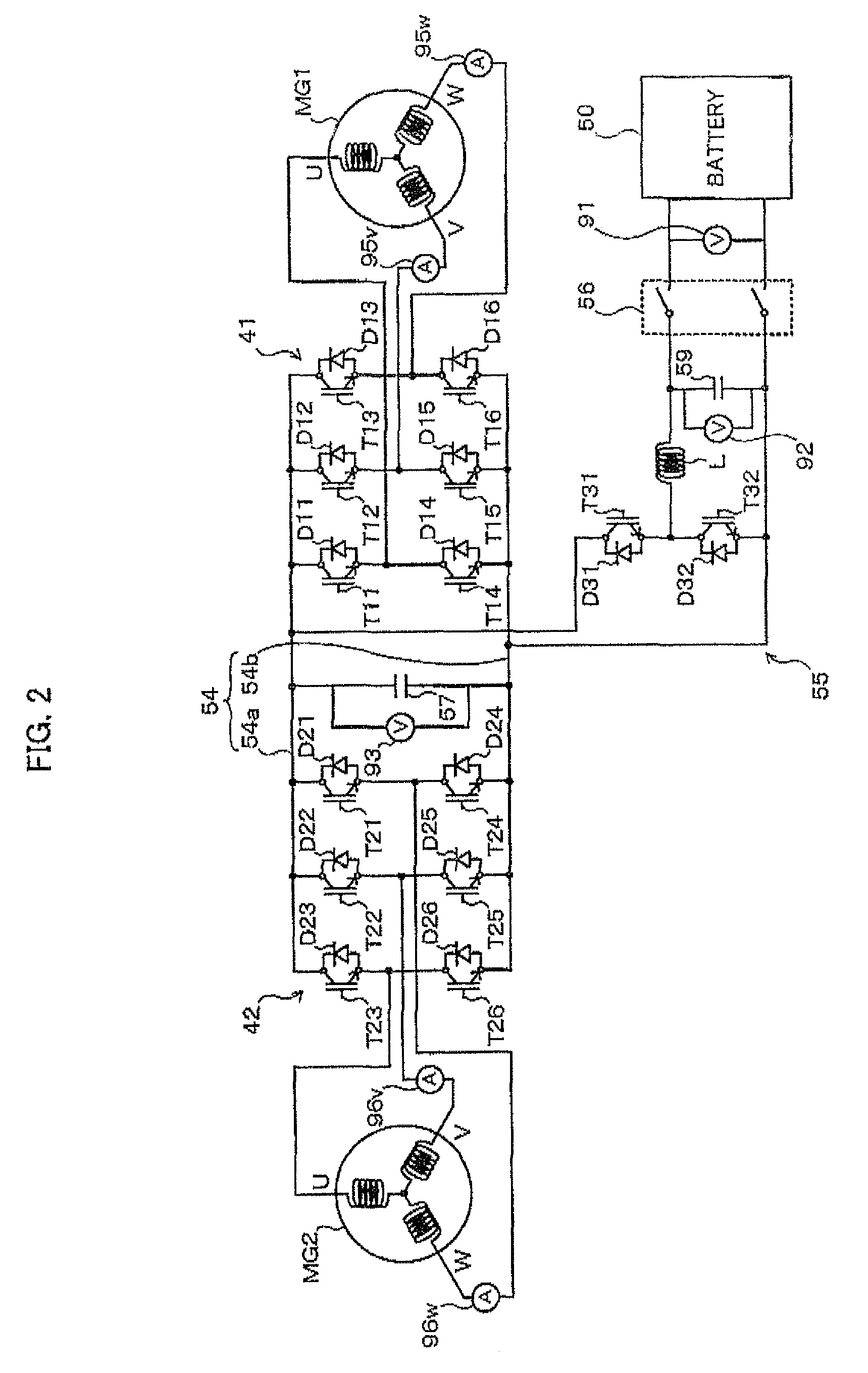
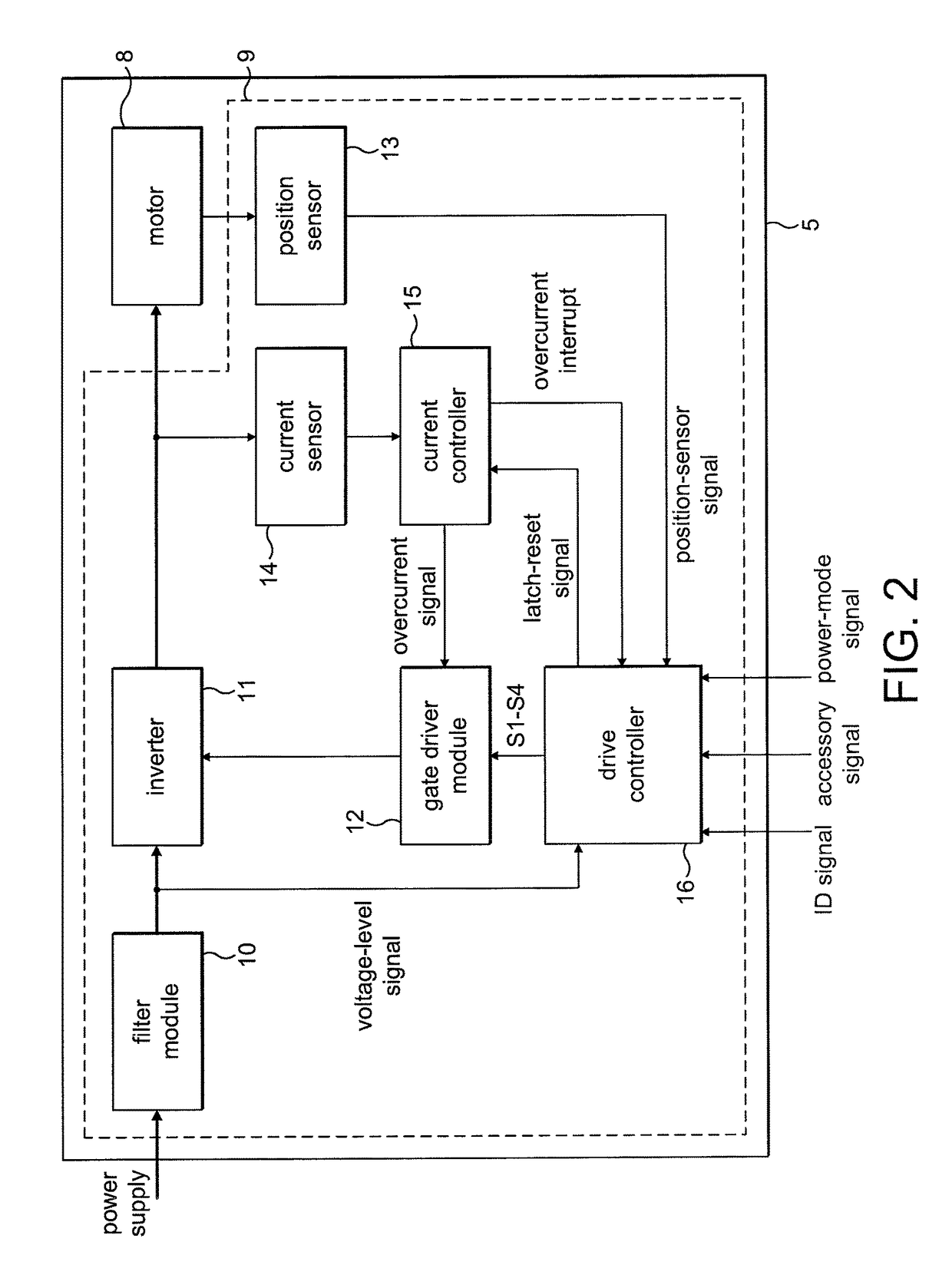
Motor drive control apparatus, vehicle with motor drive control apparatus, and motor drive control method
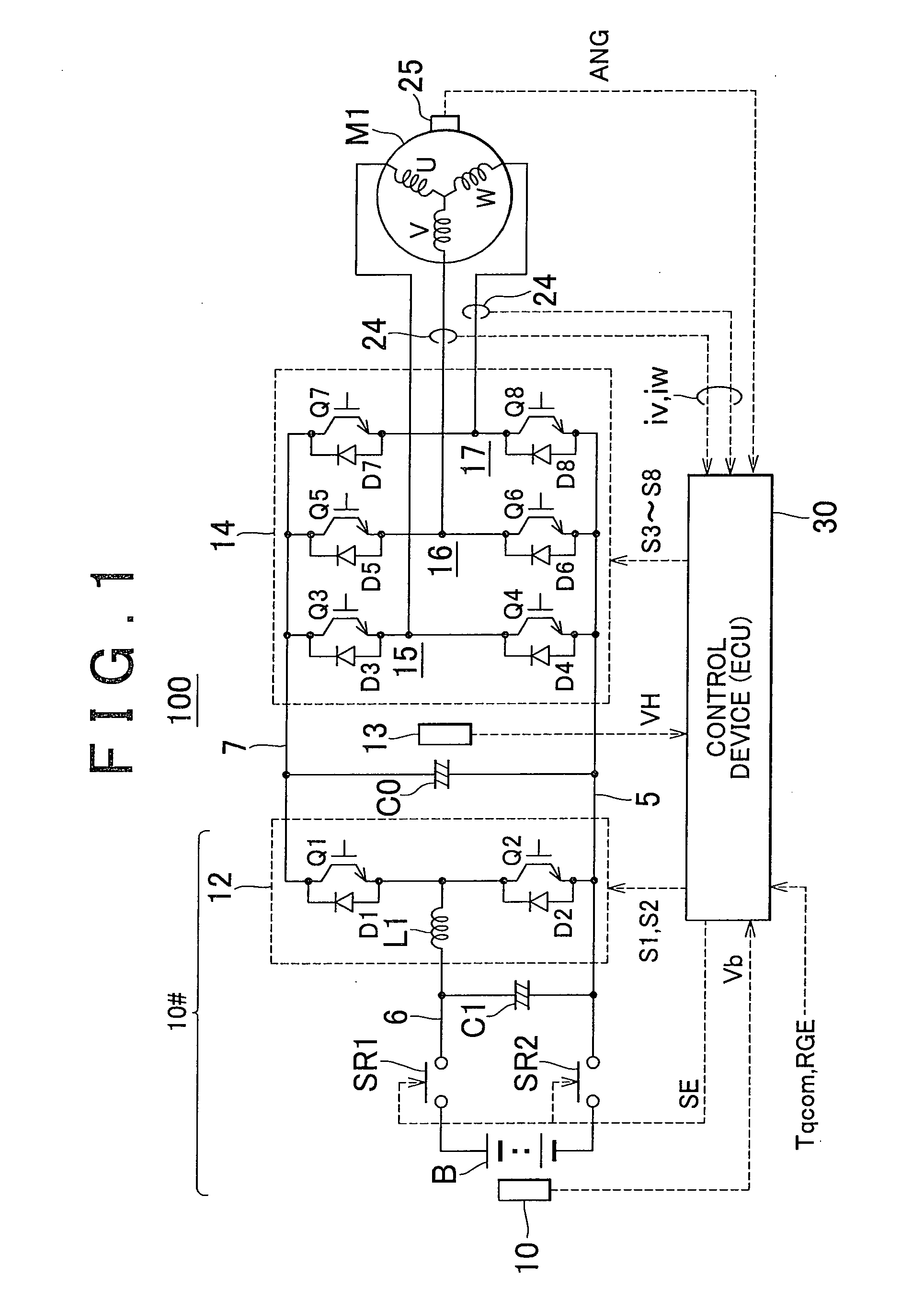
InactiveUS20110006723A1Improve efficiencyHybrid vehiclesSingle-phase induction motor startersOperation pointHybrid vehicle
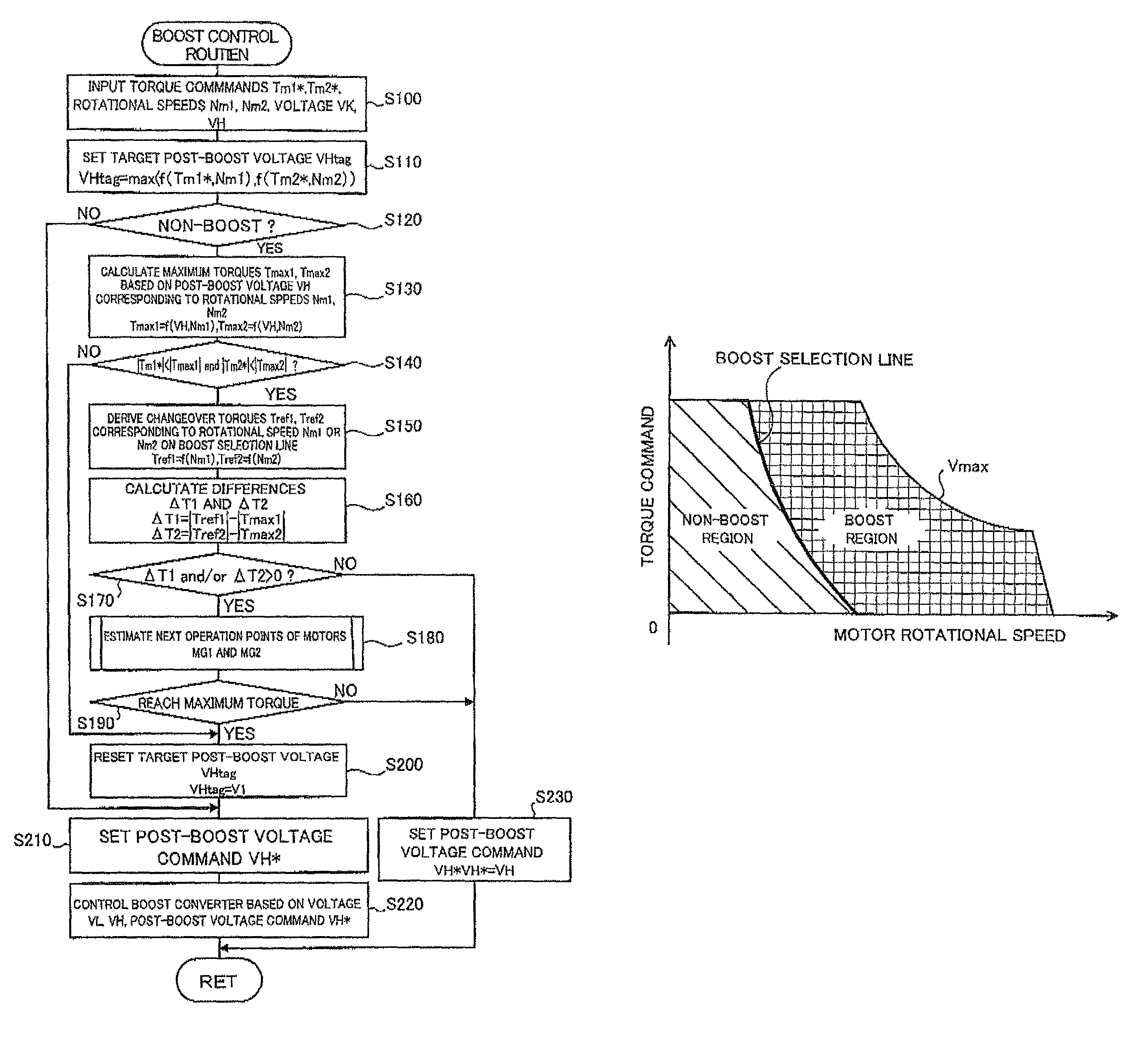
In the hybrid vehicle, a boost converter is controlled to make a post-boost voltage or a voltage on the side of an inverter become a target post-boost voltage corresponding to a target operation point of a motor in accordance with a target post-boost voltage setting map that divides an operation region of the motor into a non-boost region and a boost region when a operation point of the motor is included in the boost region. The target post-boost voltage setting map is prepared so that the non-boost region includes a region in which a loss produced by driving the motor when not boosting the post-boost voltages becomes smaller than the loss produced when boosting the post-boost voltage and the boost region includes a region in which the loss produced when boosting the post-boost voltage becomes smaller than the loss produced when not boosting the post-boost voltage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method of controlling an ac machine and controller for controlling an ac machine
InactiveUS20140203754A1Guaranteed uptimeConducive to stable operationElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersStability parameterPermanent magnet synchronous machine
A method of controlling an AC machine that includes a stator and a rotor. The method includes observing a stability parameter that is indicative of the stability of the AC machine and dependent on a current state of the AC machine; and controlling the AC machine based on the observed stability parameter so as to promote stable operation of the AC machine. The method may include controlling the AC machine to operate as a motor or as a generator. The AC machine may be a permanent magnet synchronous machine. A controller suitable for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
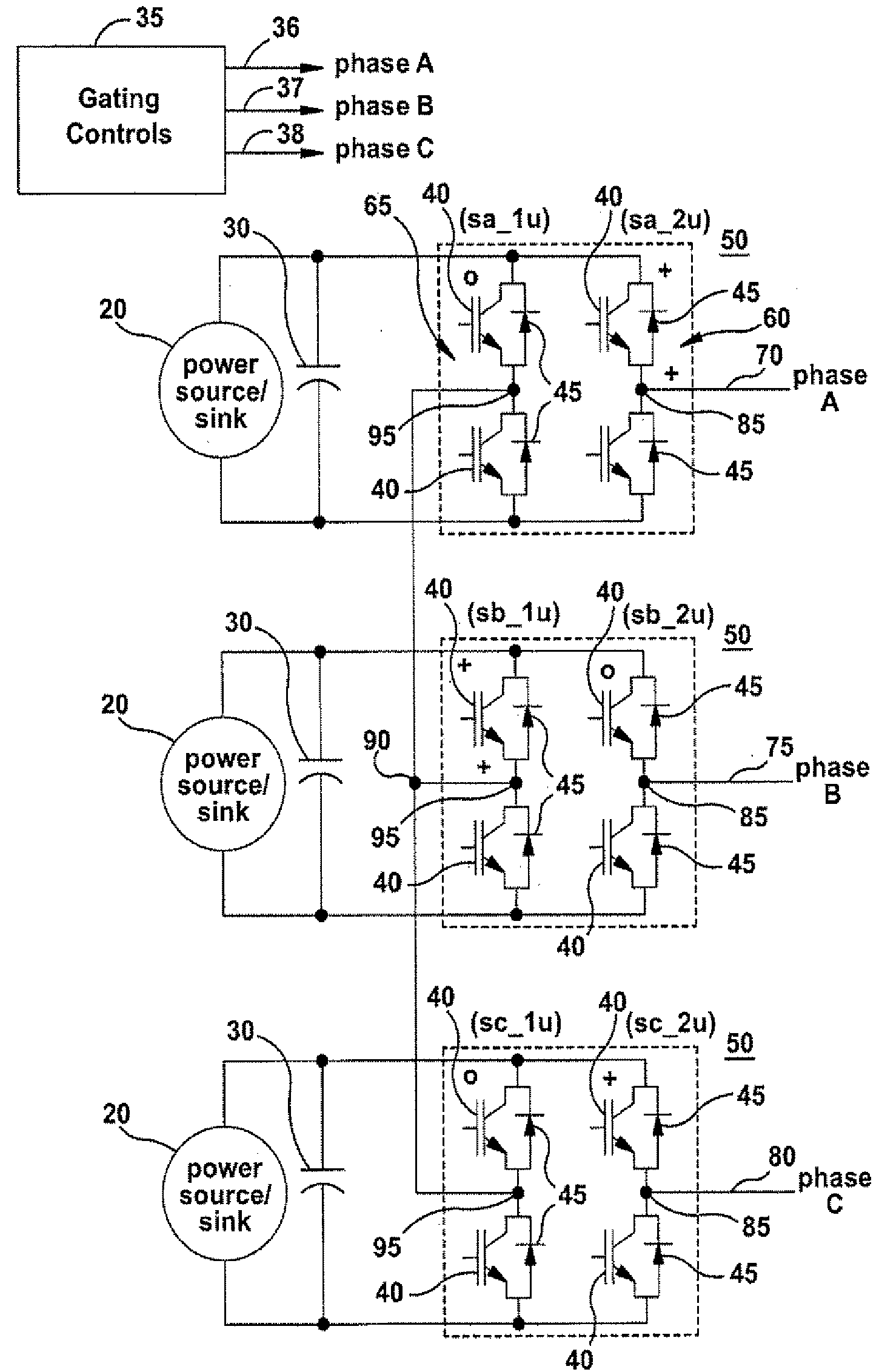
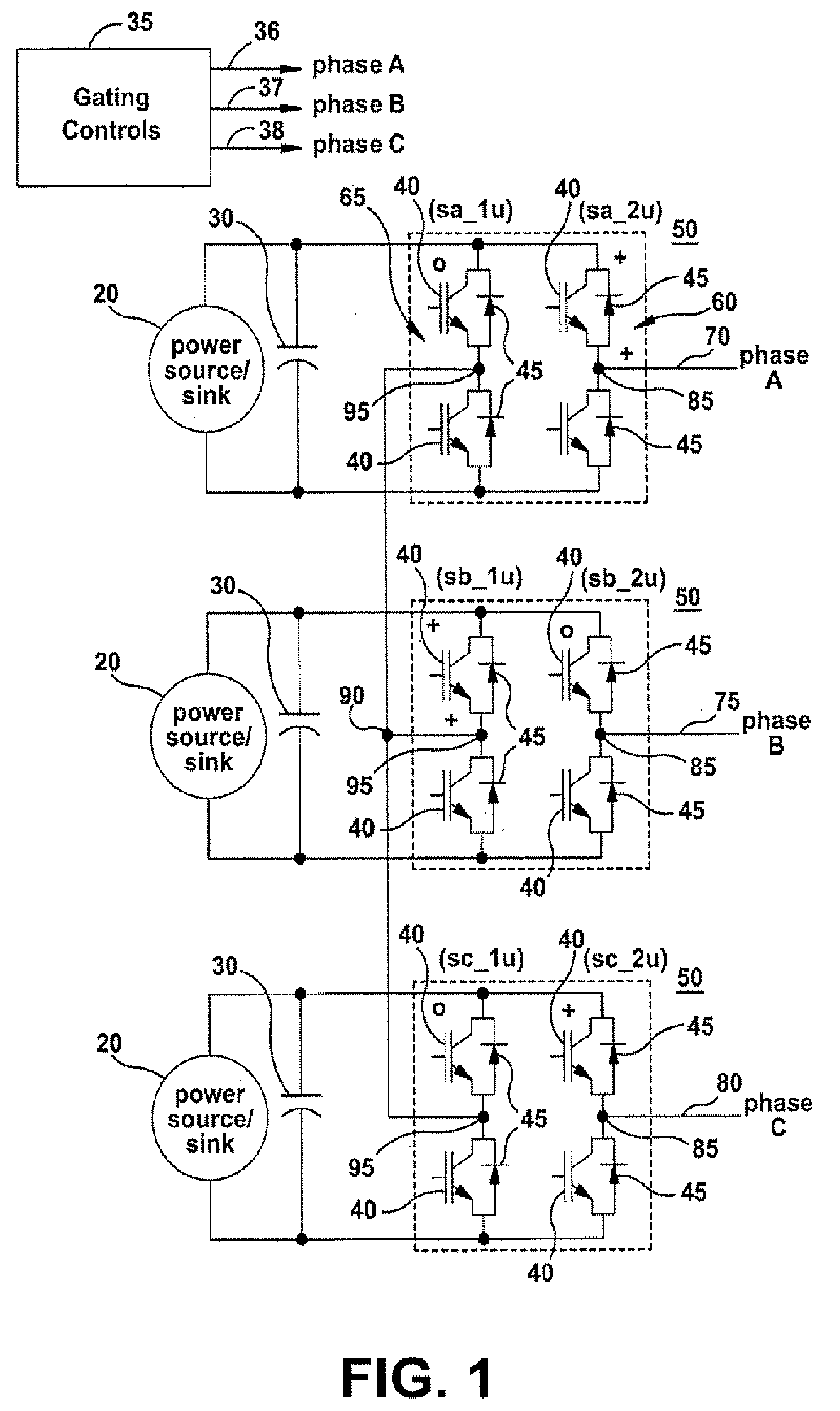
Systems and methods for controlling a converter for powering a load
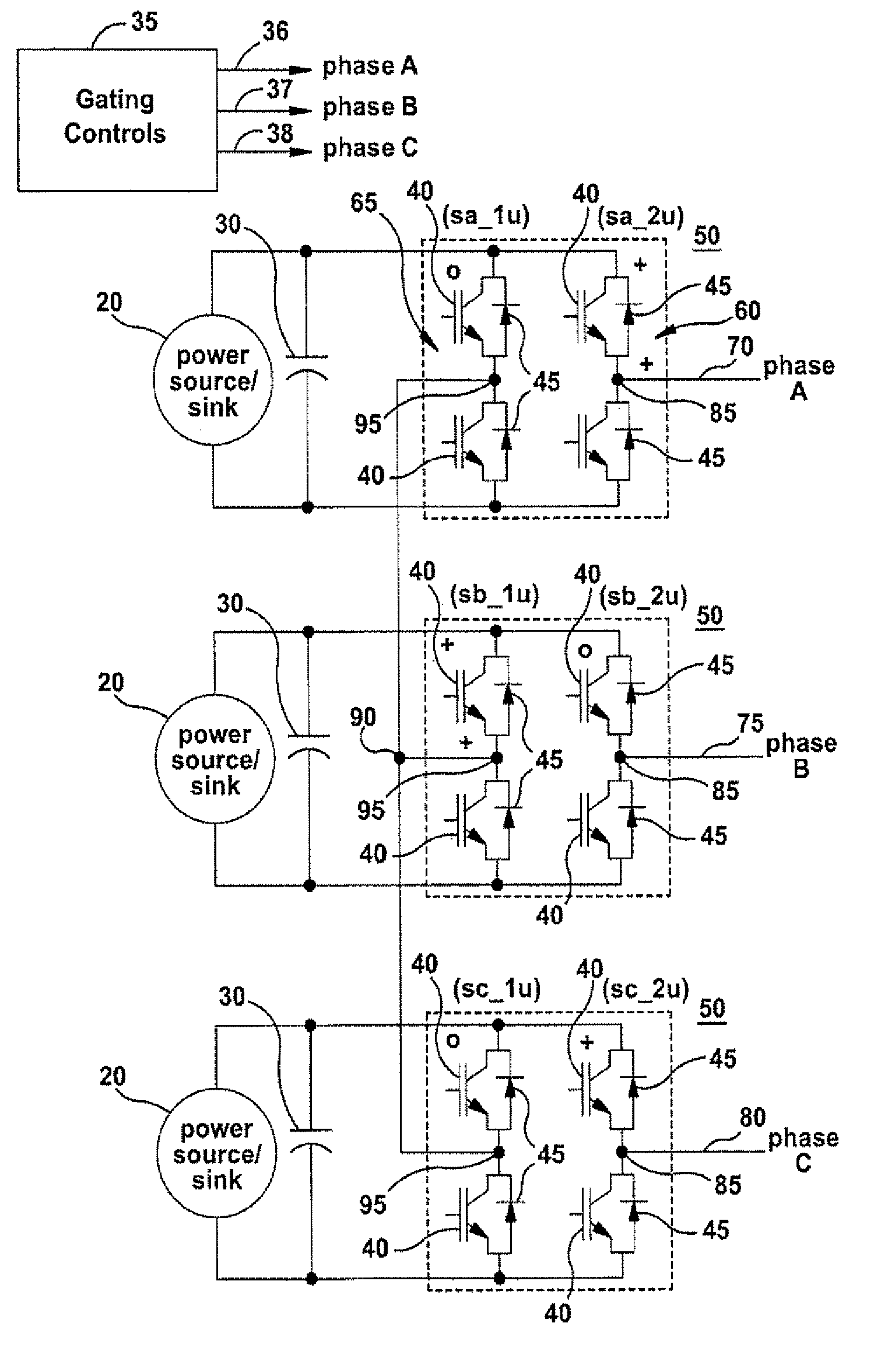
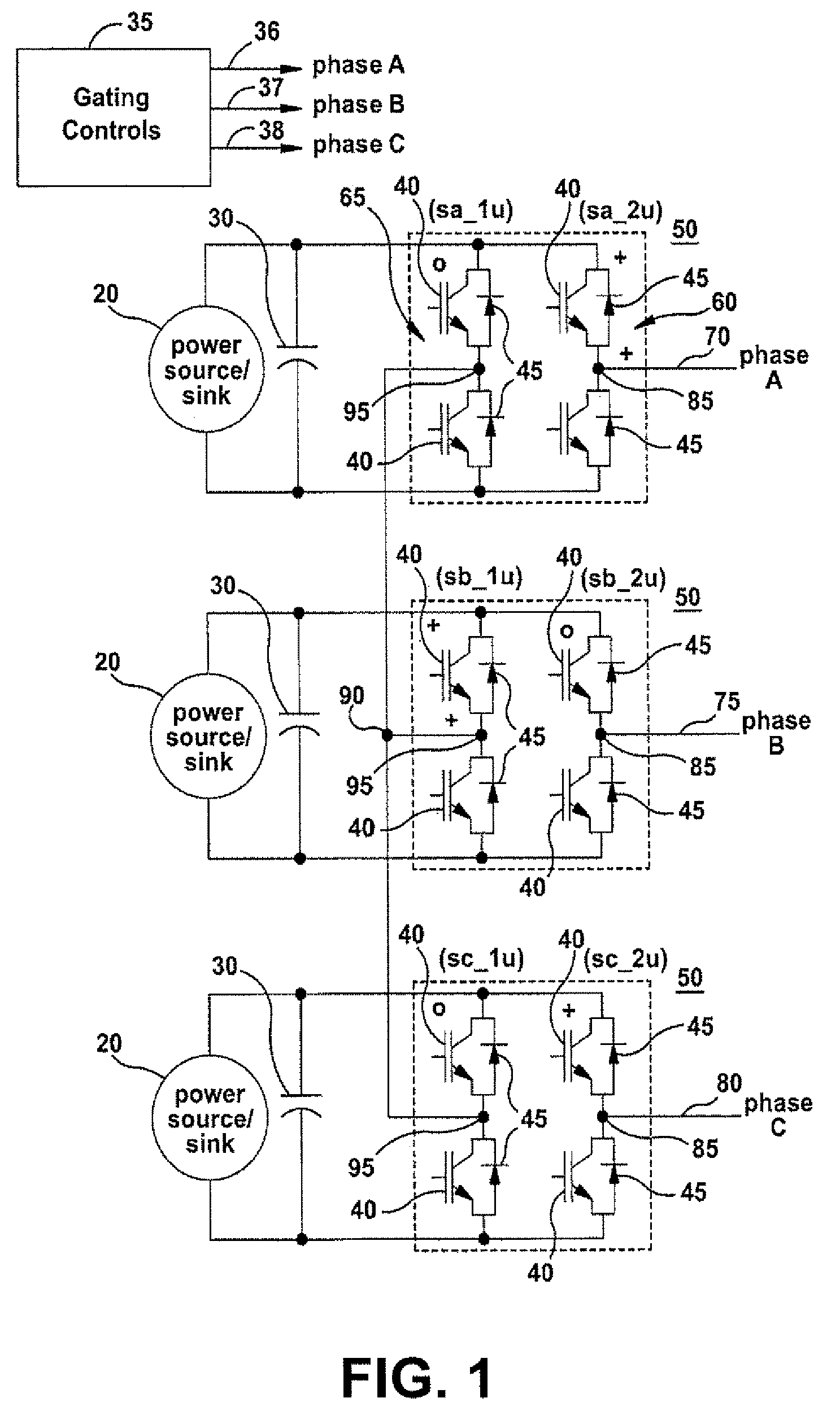
ActiveUS8050063B2Motor control for high speedEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl signalFundamental frequency
Systems and methods for controlling a converter for powering a load are provided. According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for powering a load is provided. A power converter may be provided. At least one gating control signal having a switching pattern may be supplied to the power converter, wherein the switching pattern has a waveform with an effective switching frequency greater than 1 times the fundamental frequency of the switching pattern and less than 2 times the fundamental frequency of the switching pattern. At least one output power signal may be output to the load responsive at least in part to the at least one gating control signal supplied.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
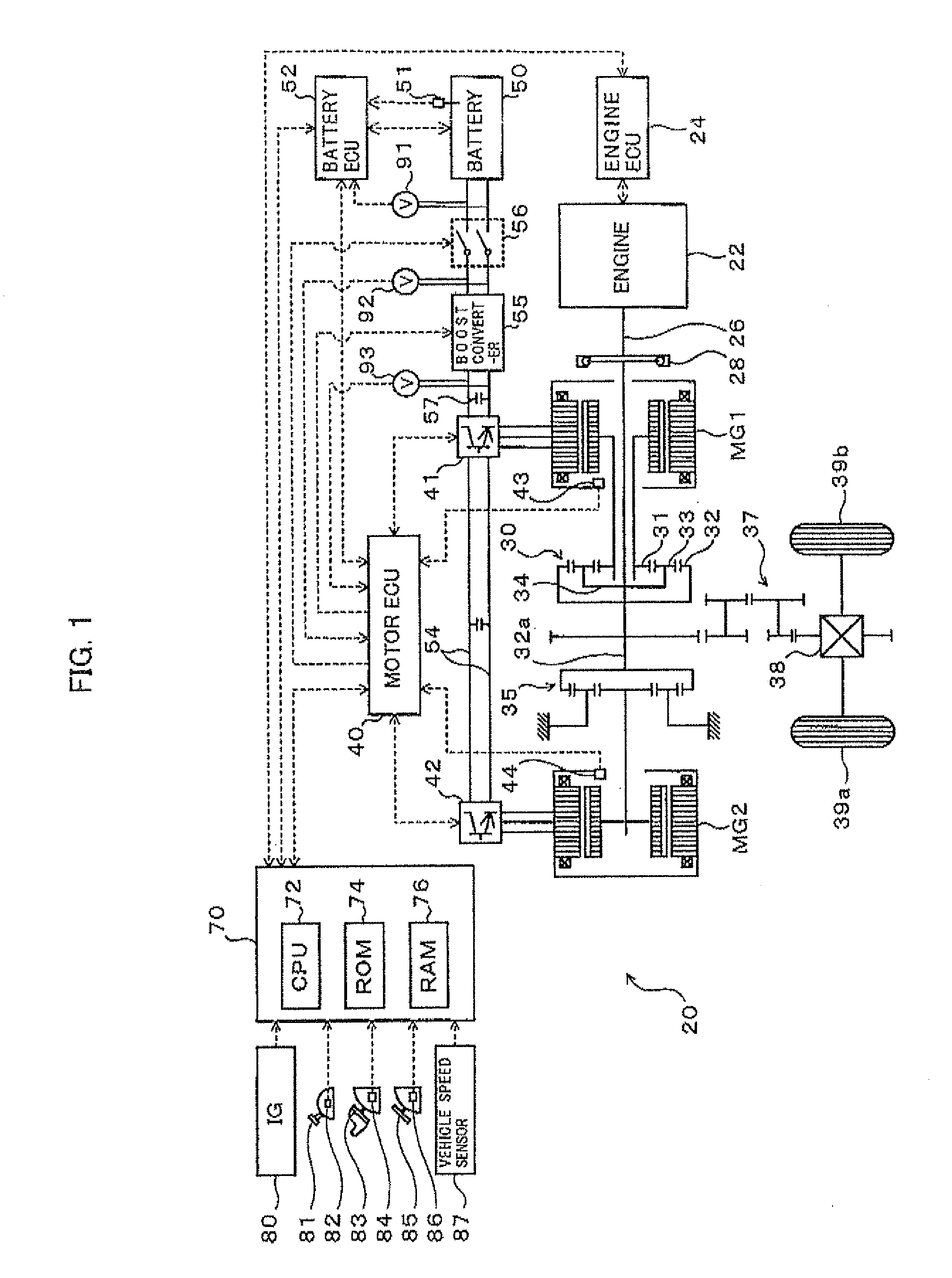
Motor drive control apparatus, vehicle with motor drive control apparatus, and motor drive control method
InactiveUS8324856B2Improve efficiencyHybrid vehiclesSingle-phase induction motor startersMotor driveOperation point
In the hybrid vehicle, a boost converter is controlled to make a post-boost voltage or a voltage on the side of an inverter become a target post-boost voltage corresponding to a target operation point of a motor in accordance with a target post-boost voltage setting map that divides an operation region of the motor into a non-boost region and a boost region when a operation point of the motor is included in the boost region. The target post-boost voltage setting map is prepared so that the non-boost region includes a region in which a loss produced by driving the motor when not boosting the post-boost voltages becomes smaller than the loss produced when boosting the post-boost voltage and the boost region includes a region in which the loss produced when boosting the post-boost voltage becomes smaller than the loss produced when not boosting the post-boost voltage.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
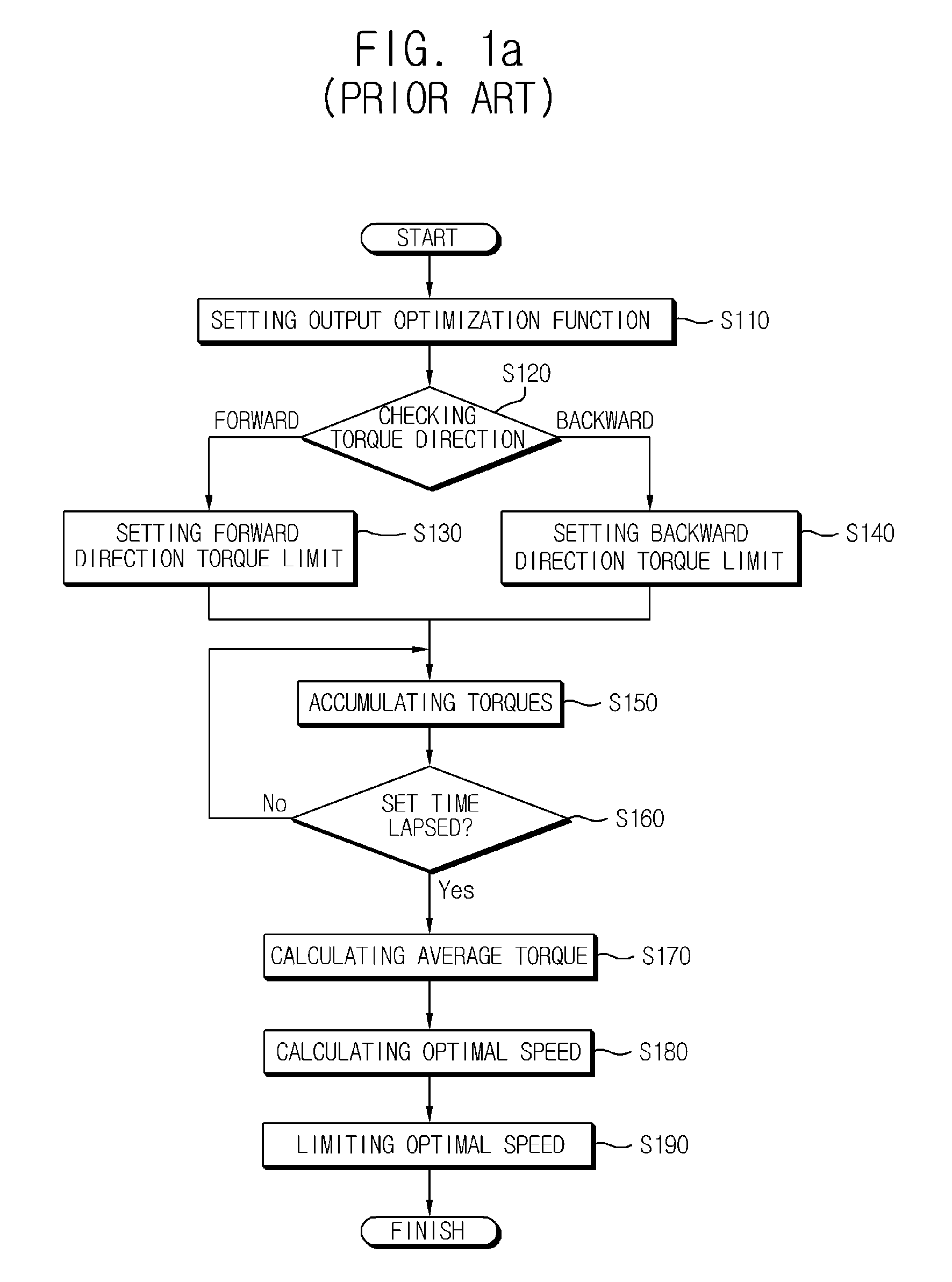
Method for controlling an inverter
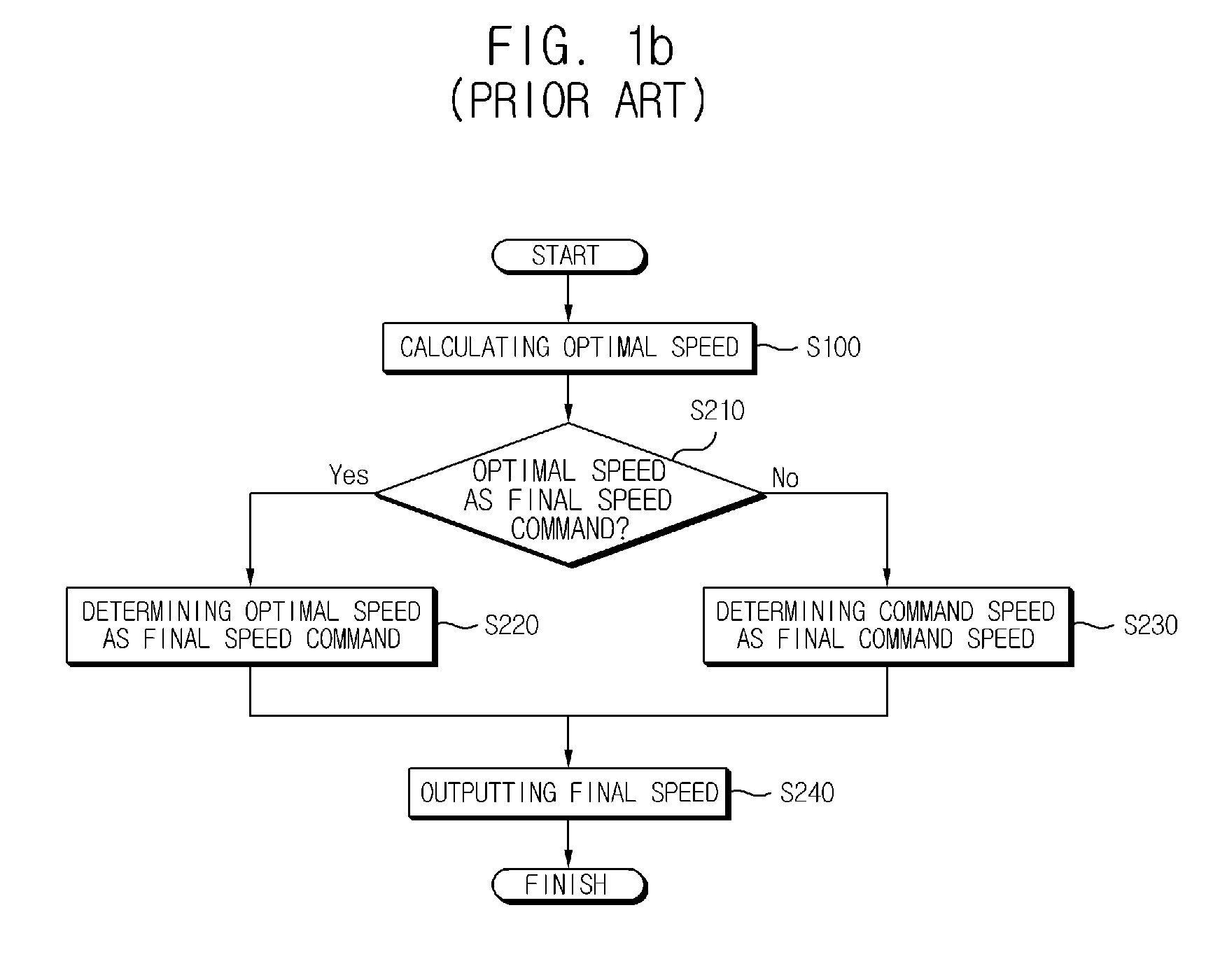
ActiveUS20130207582A1High outputImprove work efficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringControl theory
Provided is a method for controlling an inverter, the method comprising calculating an optimal speed, determining a final speed as the optimal speed when a command speed is higher than a rated speed level of a motor, and determining the final speed as the command speed when the command speed is lower than or equal to the rated speed level, or higher than a predetermined optimal speed level.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
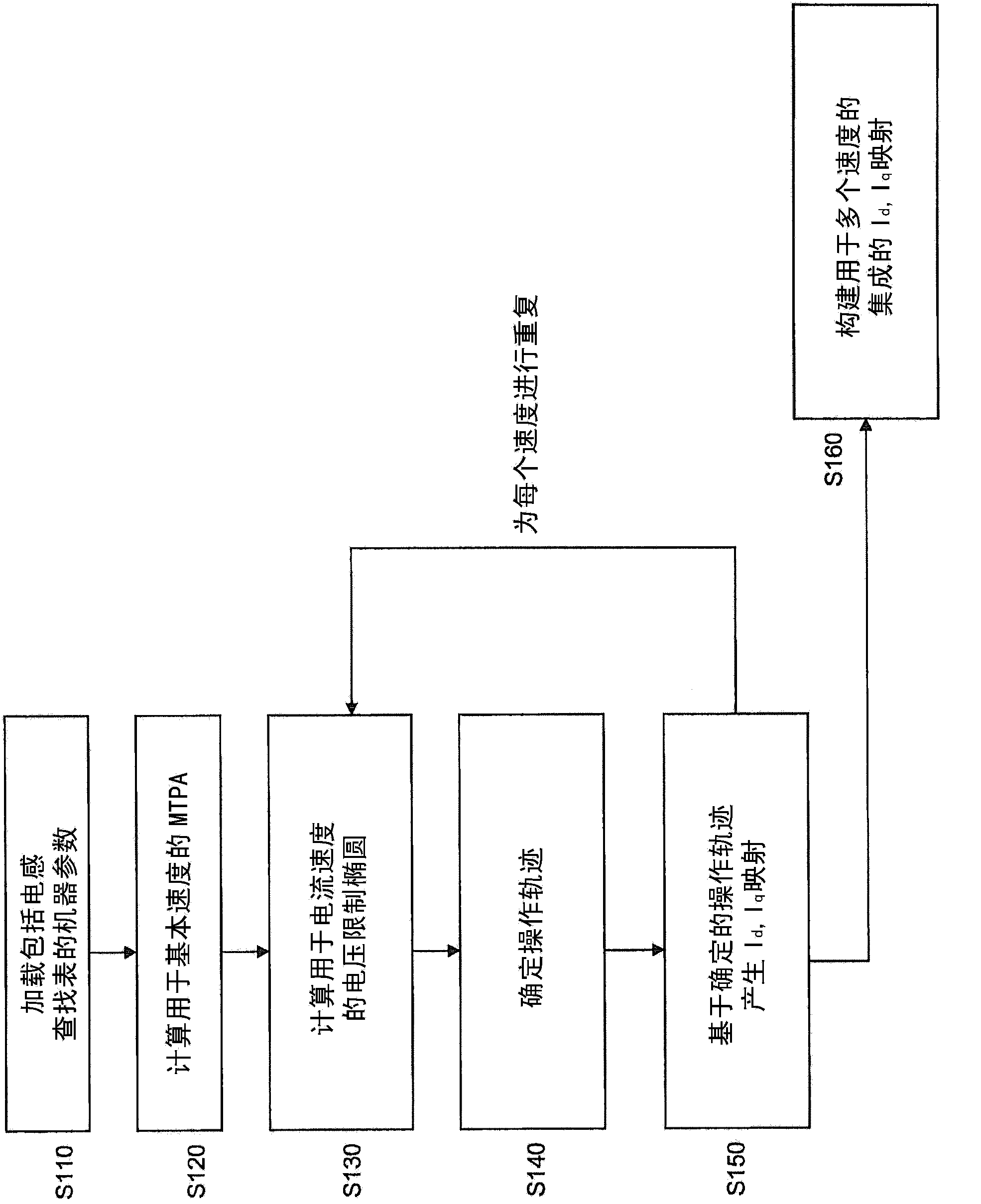
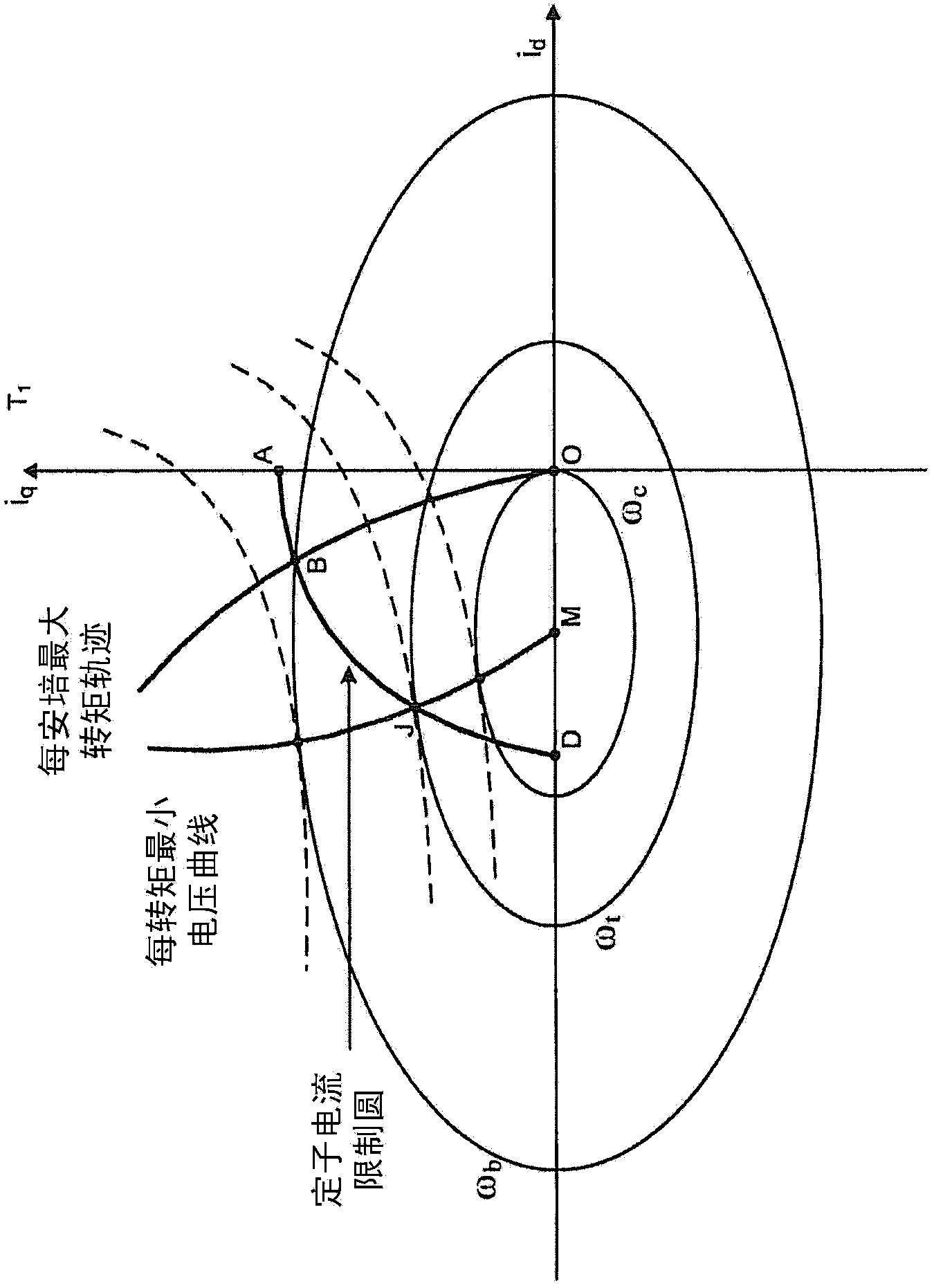
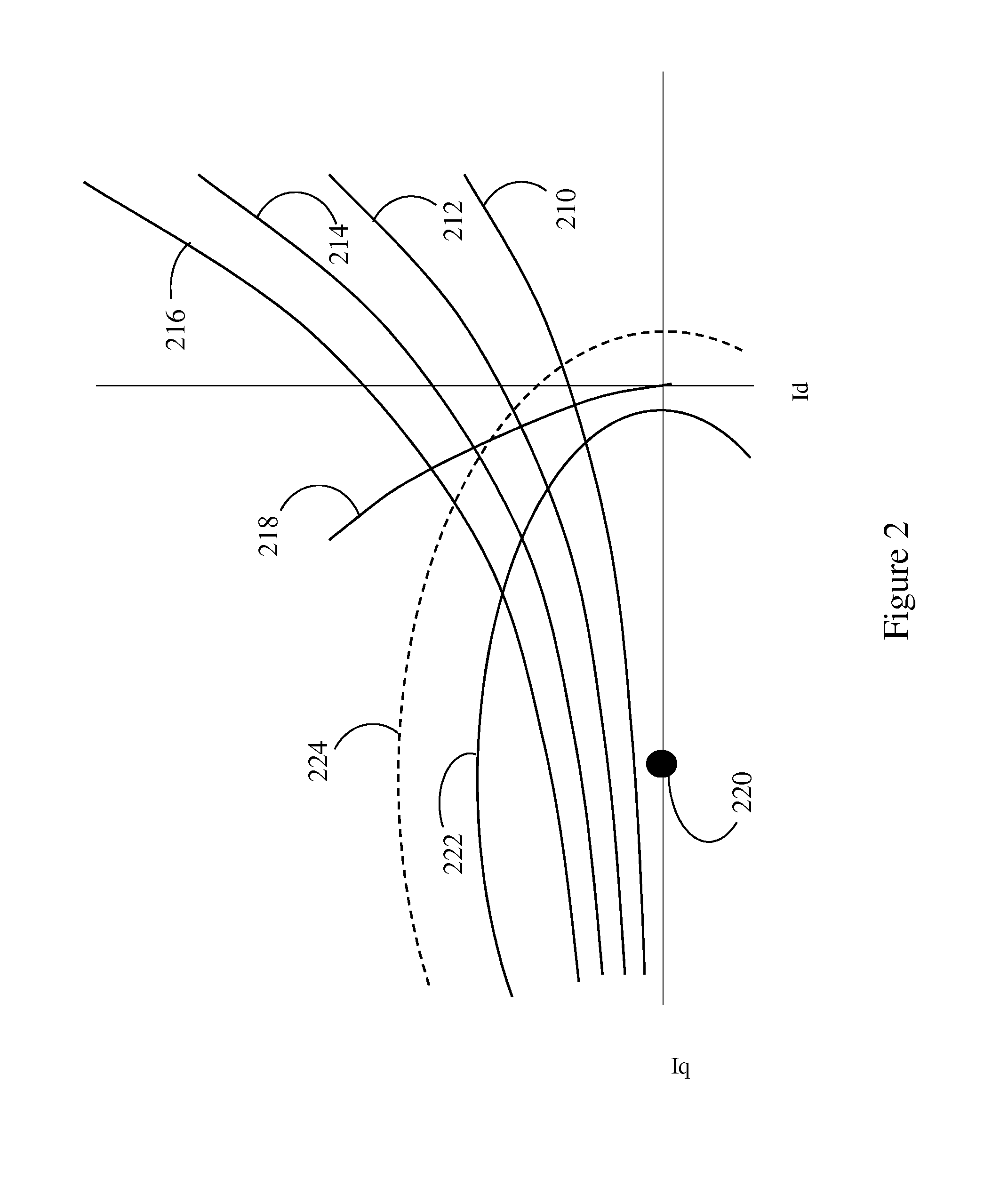
Device and method for generating an initial controller lookup table for an ipm machine
Embodiments of the present invention provide a device and method for generating initial operating points for controlling an interior permanent magnet (IPM) machine. The method includes loading an inductance lookup- table (S110), first calculating a maximum torque per Ampere (MTPA) trajectory for a first threshold speed based on machine parameters of the IPM machine (S120), second calculating a truncated voltage limit ellipse with monotonicaliy increasing torque for a first speed based on the machine parameters (S130), if the first speed is higher than the first threshold speed, determining an operating trajectory at the first speed (S140) based on at least one of the calculated MTPA trajectory and the calculated truncated voltage limit ellipse, and generating an Id,; Iq map that maps an Id value and an lq value to each torque command of a plurality of torque commands for the first speed based on the determined operating trajectory (S150).
Owner:DEERE & CO
Electric motor driving device and vehicle equipped with the same
InactiveUS20110241598A1Increase powerSpeed controllerElectronic commutation motor controlAC - Alternating currentEngineering
An electric motor driving device that drives an electric motor including a field winding, a rotor and a stator, wherein the rotor and the stator each foam a field pole by passing a field current through the field winding, includes: a power supply device; a converter including a reactor that at least partially serves as the field winding shared with the electric motor, and configured to receive a voltage from the power supply device to carry out voltage conversion between first and second power lines and to pass the field current through the field winding during voltage conversion operation; an inverter configured to convert a direct-current power received from the converter to an alternating-current power for driving the electric motor; and a controller controlling the converter so that a current flows through the field winding in the same direction both during power running and regeneration of the electric motor.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Permanent magnet rotating electrical machine and permanent magnet motor drive system
InactiveUS8334667B2Vector control systemsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesLow speedMagnetic poles
A permanent magnet rotating electrical machine capable of conducting a variable speed operation at high output in a wide range from low speed to high speed and improving efficiency and reliability in a wide operating range. Two kinds of permanent magnets having different shapes or different magnetic characteristics are embedded in a rotor core, to form a magnetic pole. The permanent magnets arranged at the magnetic pole include a permanent magnet whose product of coercive force and thickness along a magnetizing direction is small and a permanent magnet whose product of coercive force and thickness along the magnetizing direction is large. A magnetic field created by passing a current to an armature coil for a short time is used to irreversibly magnetize the permanent magnet whose product of coercive force and thickness along magnetizing direction is small, thereby changing a total linkage flux amount, and a positive d-axis current is passed when torque is large.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
PMSM field weakening for appliance motors
ActiveUS8866423B2Synchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlElectric machineRotor flux
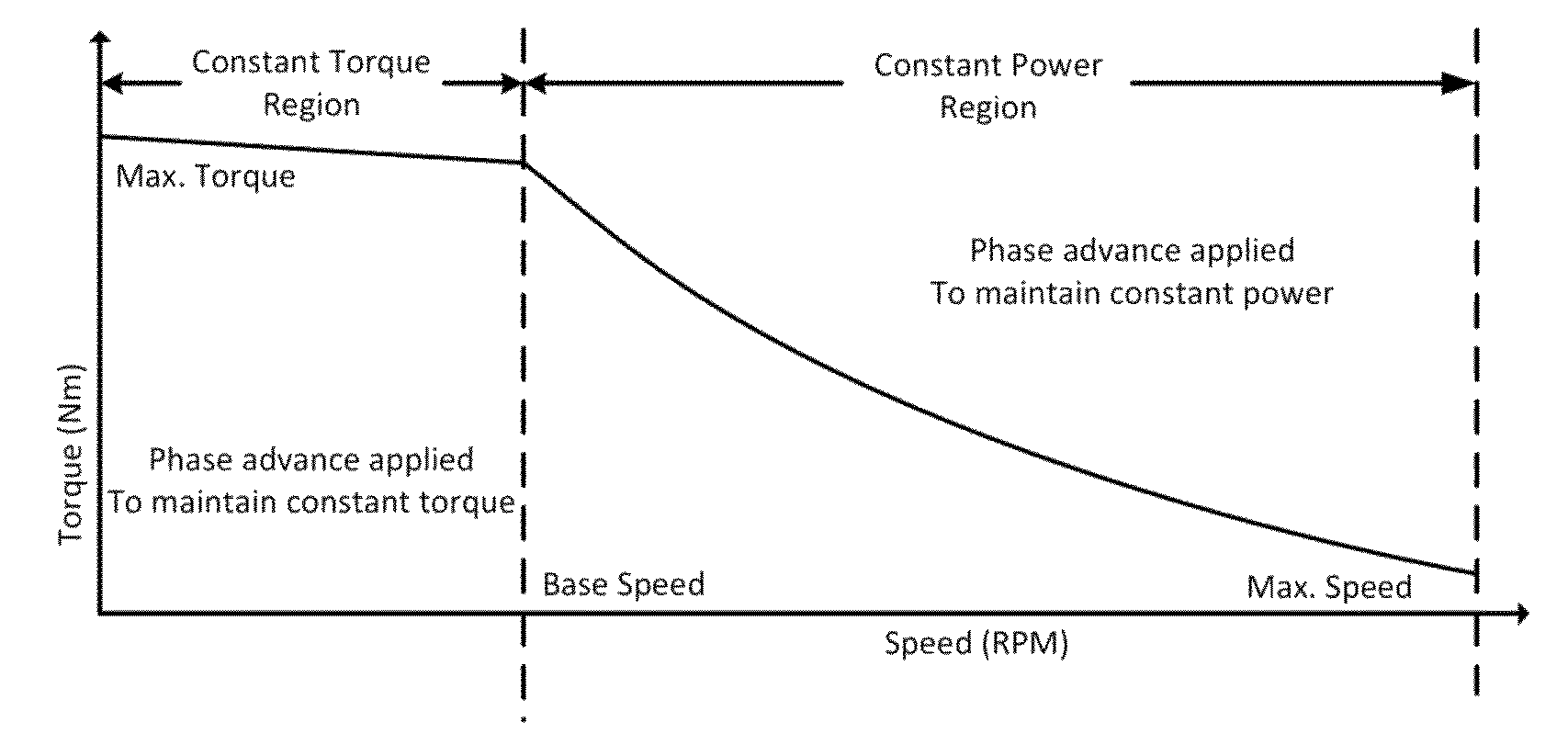
An electric motor in an appliance and a method of controlling the motor to achieve speeds greater than a base speed of the motor is provided. To achieve speeds above the base speed of the motor, field weakening can be implemented by applying a field weakening angle to a phase advance angle between a desired stator flux and a rotor flux. The field weakening angle can be based on the current speed of the motor. The field weakening angle can be a fixed angle and can be determined by comparing the current speed of the motor with a predetermined threshold. In addition, the magnitude of the electrical signal applied to the motor can be adjusted during field weakening based on a desired speed of the motor where the electrical signal can be a voltage.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Control system for AC motor
InactiveUS8558500B2Vector control systemsConversion with intermediate conversion to dcOperating pointControl system
A control system for an AC motor determines a slope Ktl of a tangent TL at an operating point Pa corresponding to the current motor operating state and voltage phase (θ0) on a torque characteristic curve that is plotted according to a torque equation representing an output torque characteristic with respect to the motor operating state and the voltage phase of the rectangular wave voltage. The control system further calculates a voltage phase change amount θff for use in feed-forward control, according to ΔTtl / Ktl obtained by dividing a torque compensation amount ΔTtl for feed-forward control by the slope Ktl.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Motor drive device, and compressor and refrigerator using same
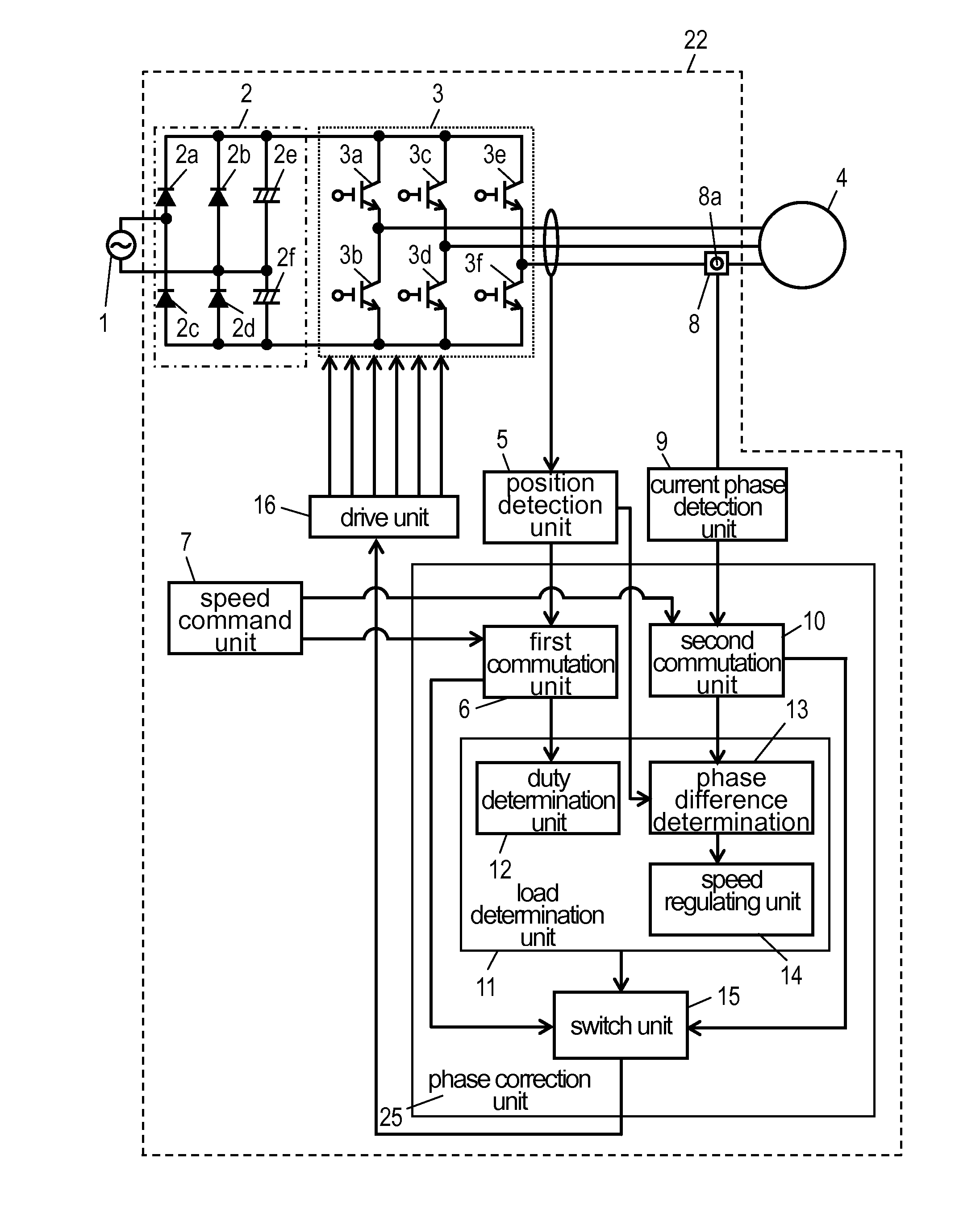
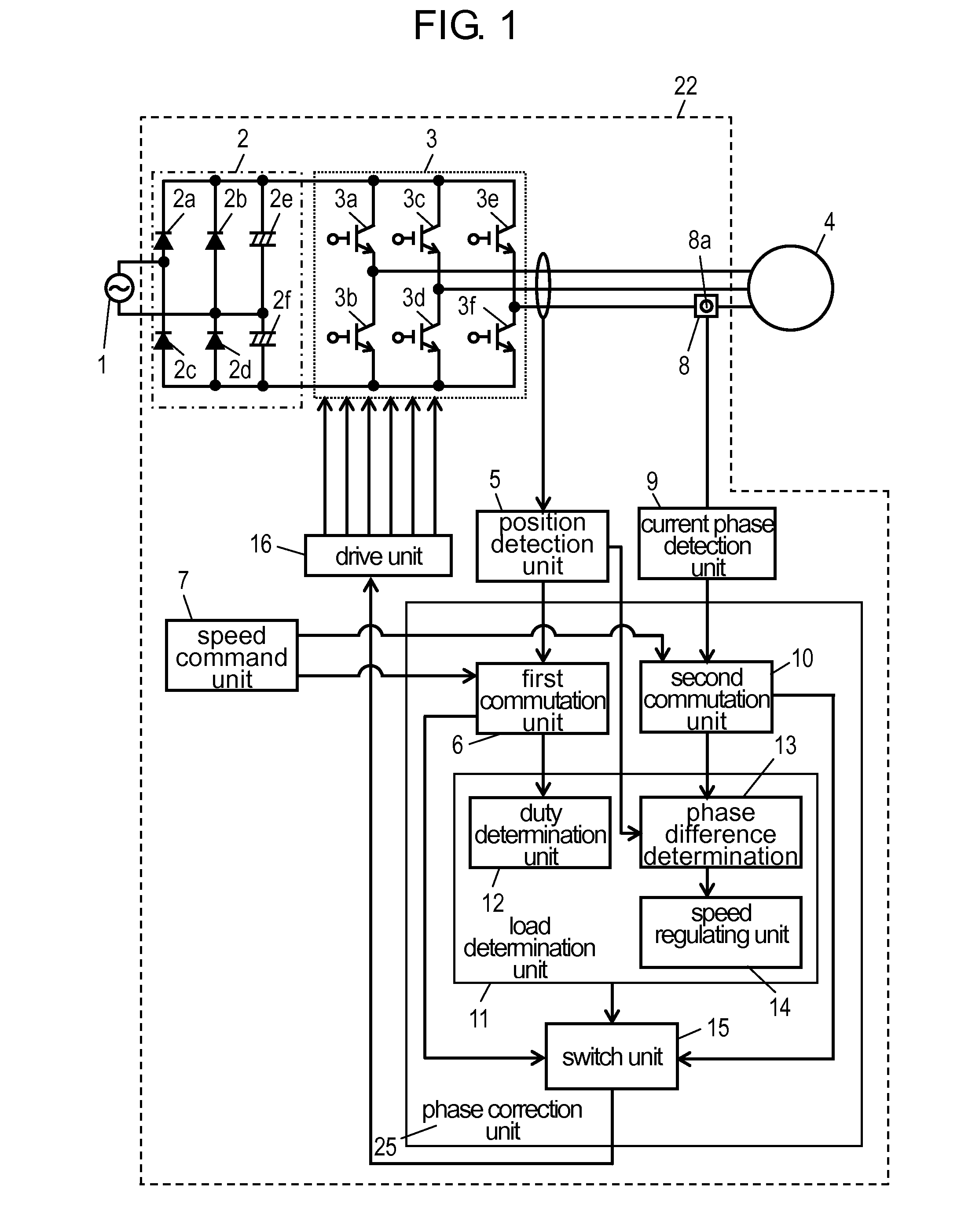
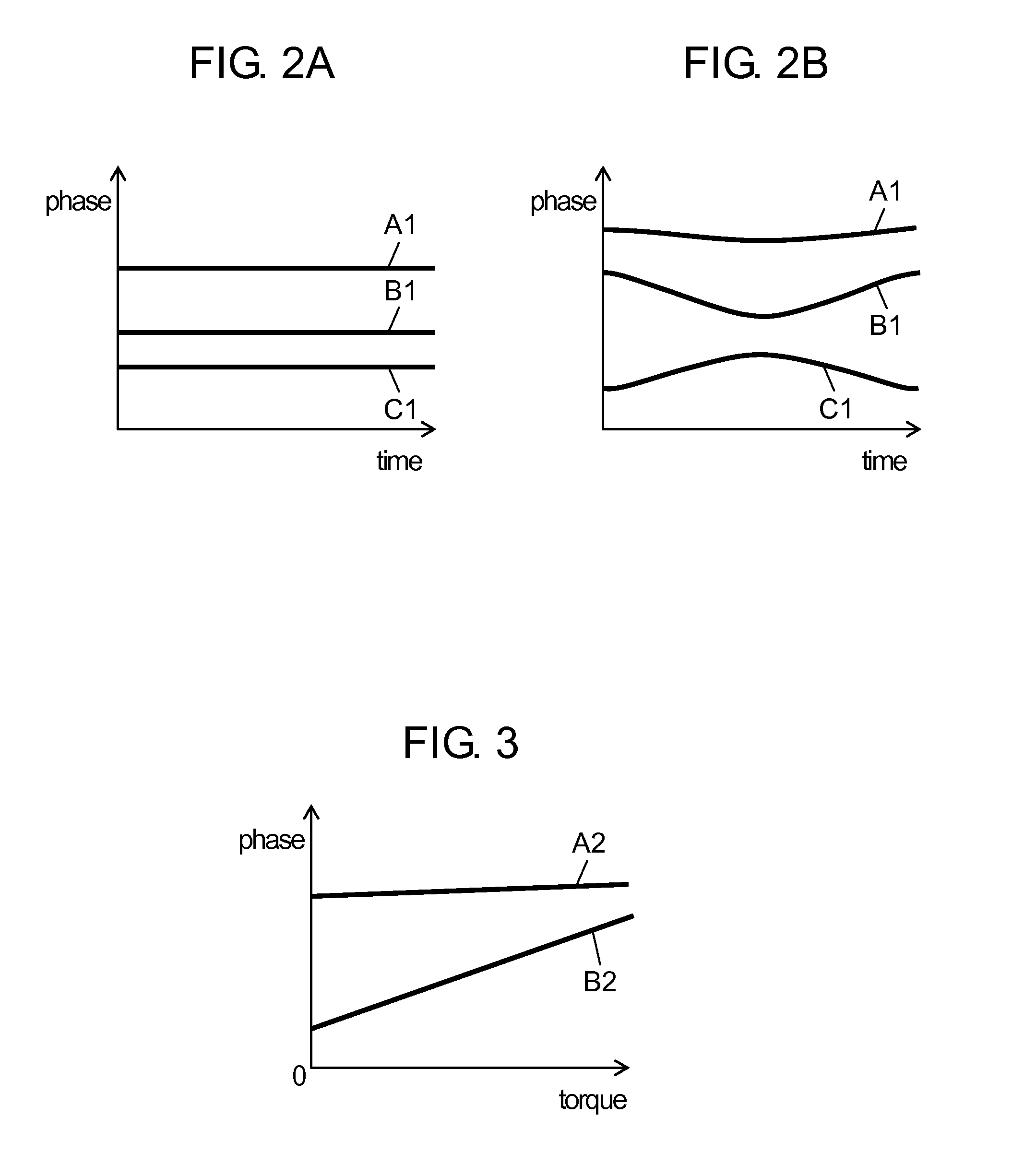
InactiveUS8716964B2Improve reliabilityImprove driving stabilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersPhase correctionMotor drive
Phase correction unit (25) for outputting a commutation signal for switching a winding that allows a current to flow to brushless DC motor (4) and drive unit (16) for outputting a drive signal indicating supplying timing of electric power supplied to brushless DC motor (4) by inverter (3) based on the commutation signal output from phase correction unit (25) are provided so as to maintain a predetermined relation between a phase of a current flowing to a predetermined winding of brushless DC motor (4) and a phase of a voltage. Since brushless DC motor (4) is driven by a signal for holding the predetermined relation between the phase of the current and the phase of the voltage, the stability of drive under high-speed and high-load conditions is enhanced and a drive range is extended.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
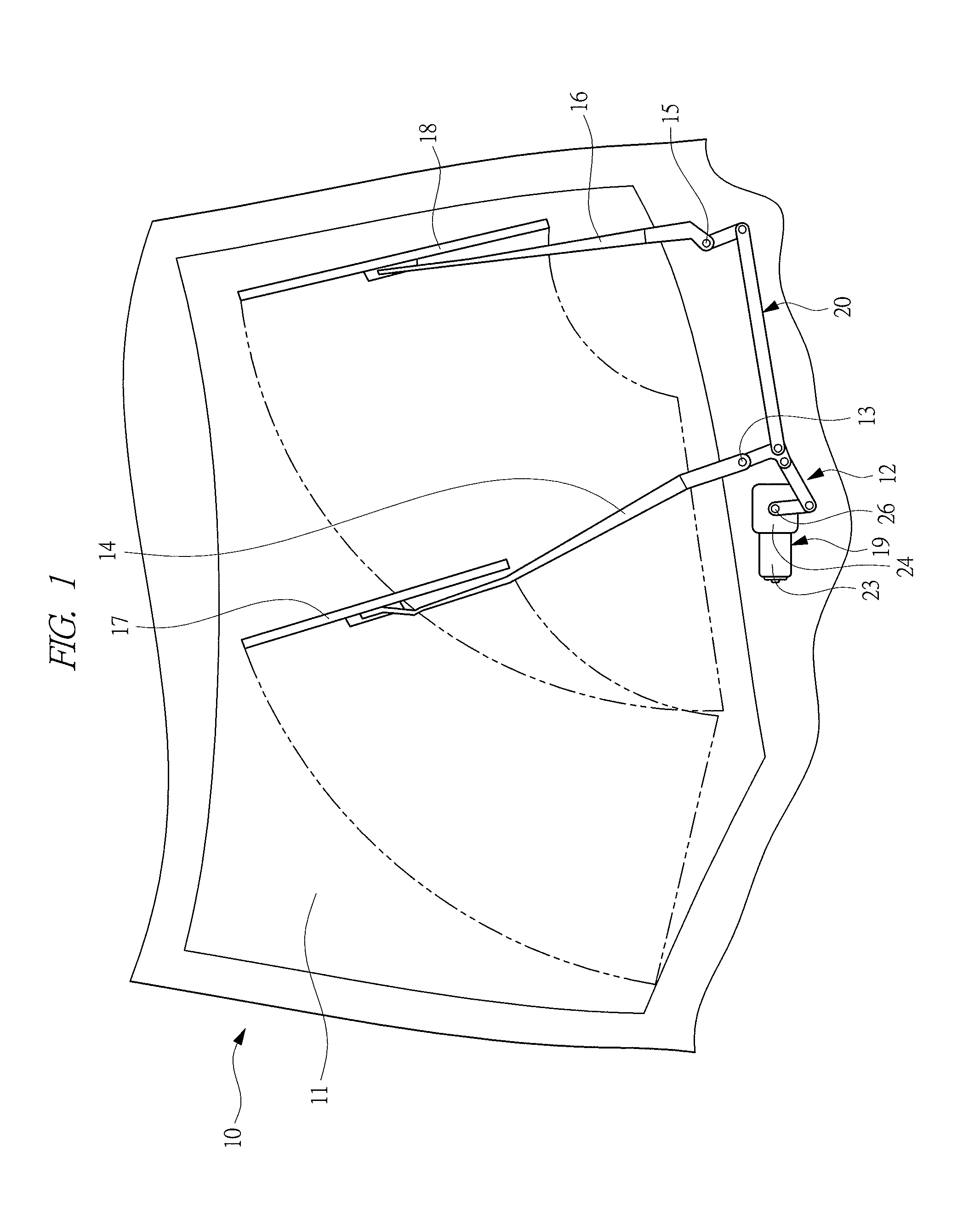
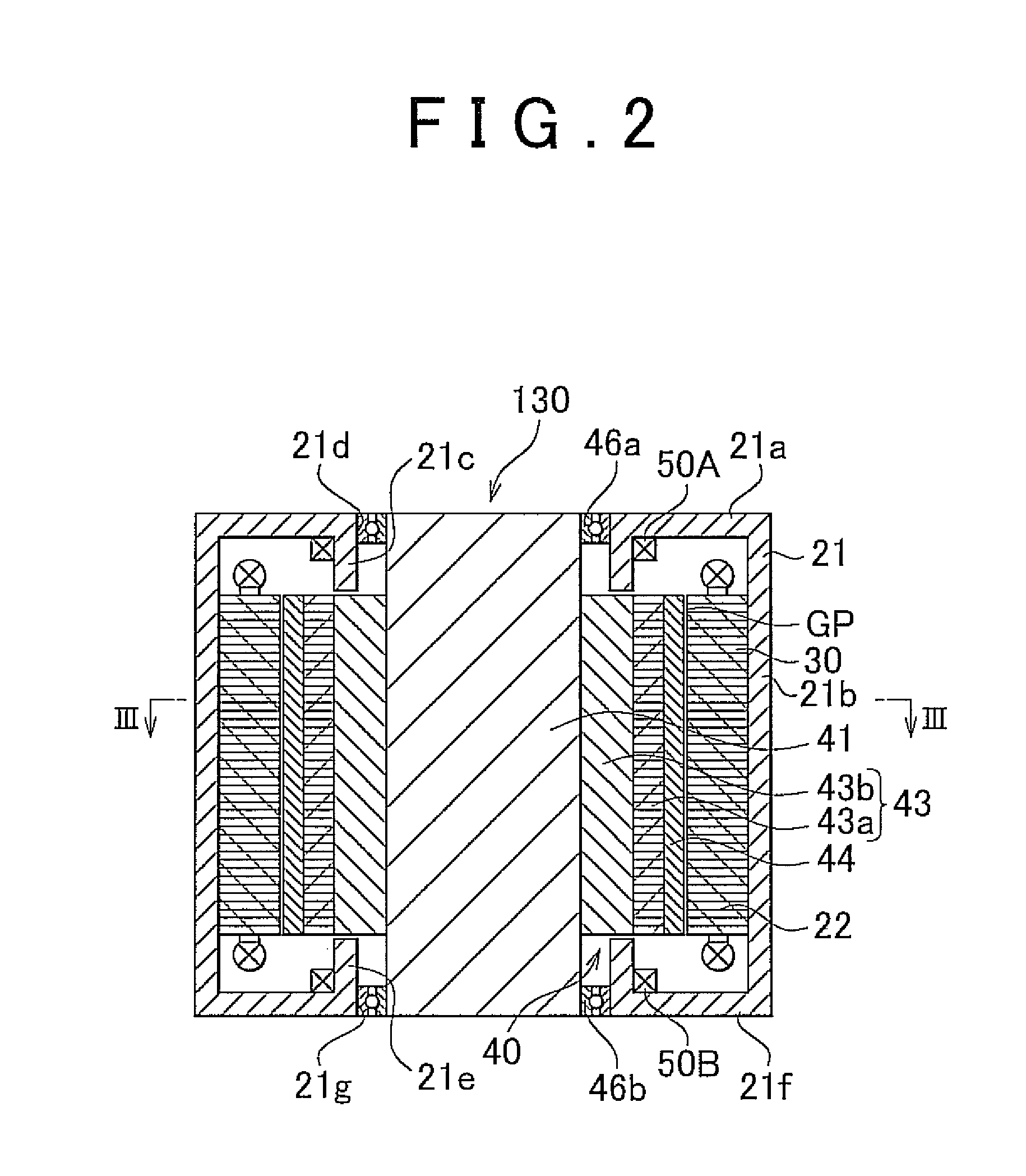
Brushless motor and wiper apparatus
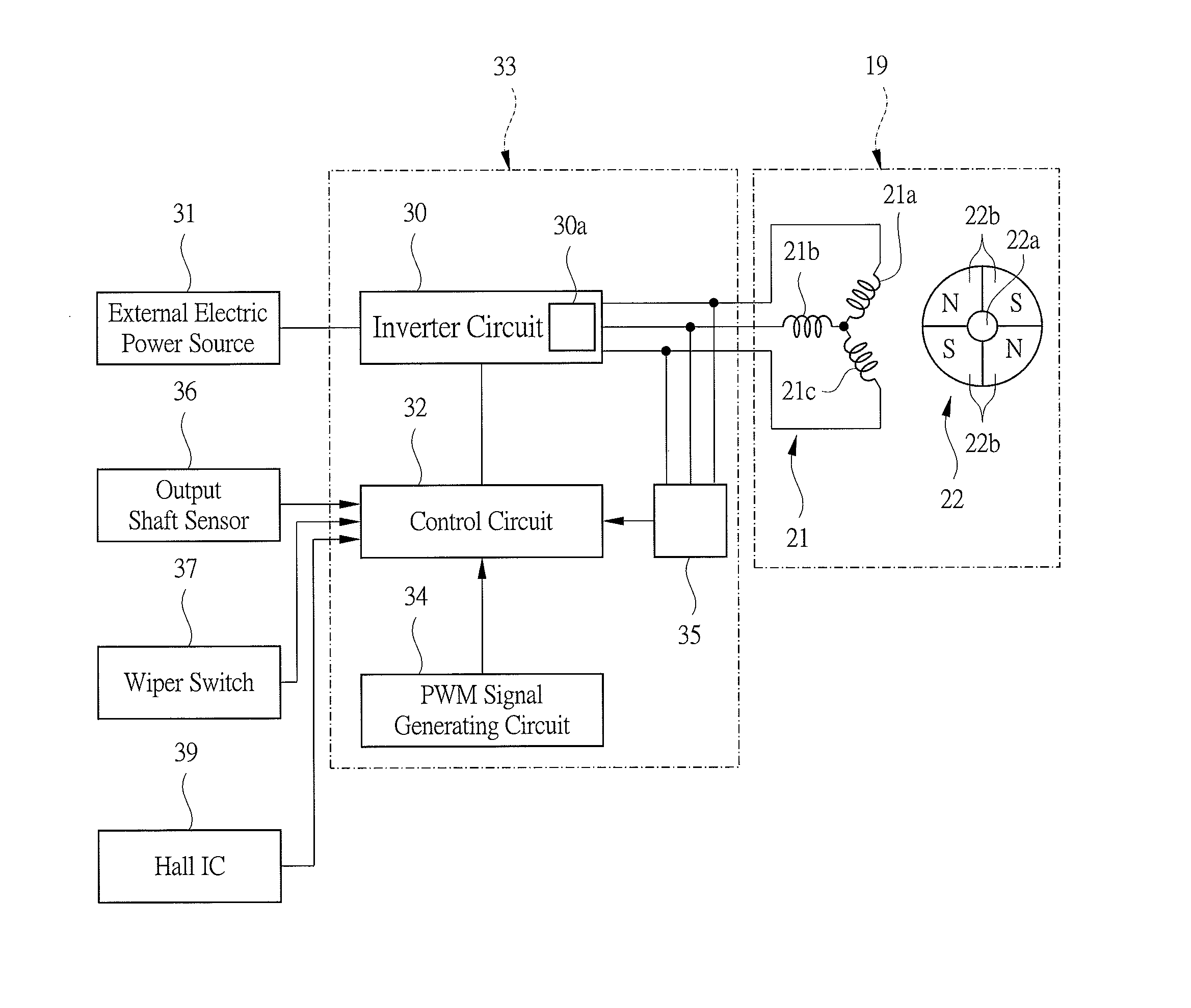
ActiveUS20150082575A1Small sizeLayout improvementSynchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlBrushless motorsSupply current
A brushless motor comprises: a stator 21 having armature coils 21a, 21b, and 21c; a rotor 22 which is rotated by a revolving magnetic field; and a switching element 30a, wherein the brushless motor has a rotation number control unit 33 which switches between low-speed and high-speed mode, wherein in the low-speed mode, the rotation number control unit 33 supplies current to the armature coils 21a, 21b, and 21c at predetermined energization timing and controls a duty ratio to control the rotation number of the rotor 22, and in the high-speed mode, the rotation number control unit 33 supplies current to the armature coils 21a, 21b, and 21c at energization timing advanced from the energization timing for the low-speed mode, thereby performing field weakening control of weakening the revolving magnetic field from that of the low-speed mode to control the rotation number of the rotor 22.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Systems and Methods for Controlling a Converter for Powering a Load
ActiveUS20080304302A1Reduce switching lossesReduce Harmonic DistortionMotor control for high speedAc-ac conversionConvertersControl signal
Systems and methods for controlling a converter for powering a load are provided. According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for powering a load is provided. A power converter may be provided. At least one gating control signal having a switching pattern may be supplied to the power converter, wherein the switching pattern has a waveform with an effective switching frequency greater than 1 times the fundamental frequency of the switching pattern and less than 2 times the fundamental frequency of the switching pattern. At least one output power signal may be output to the load responsive at least in part to the at least one gating control signal supplied.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
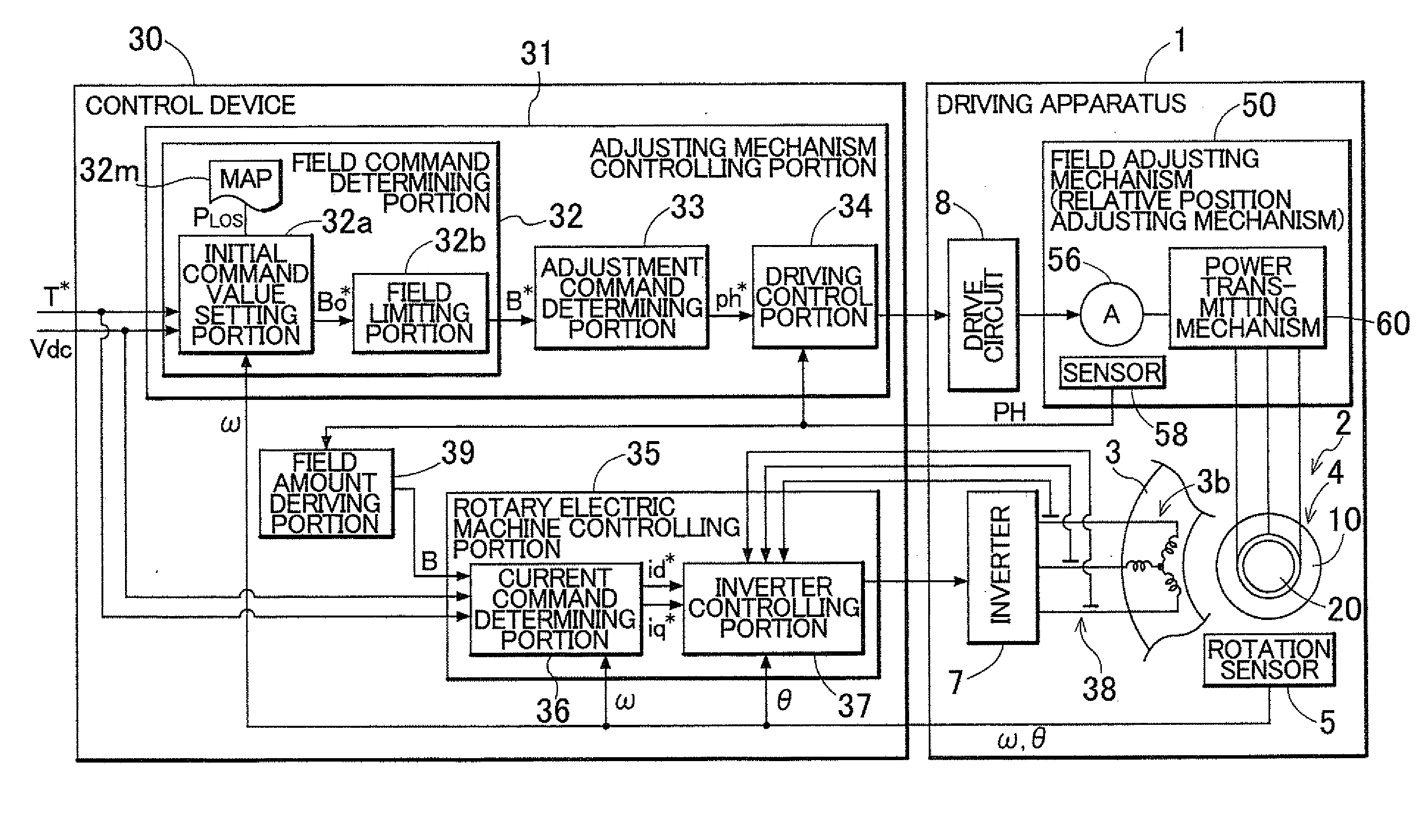
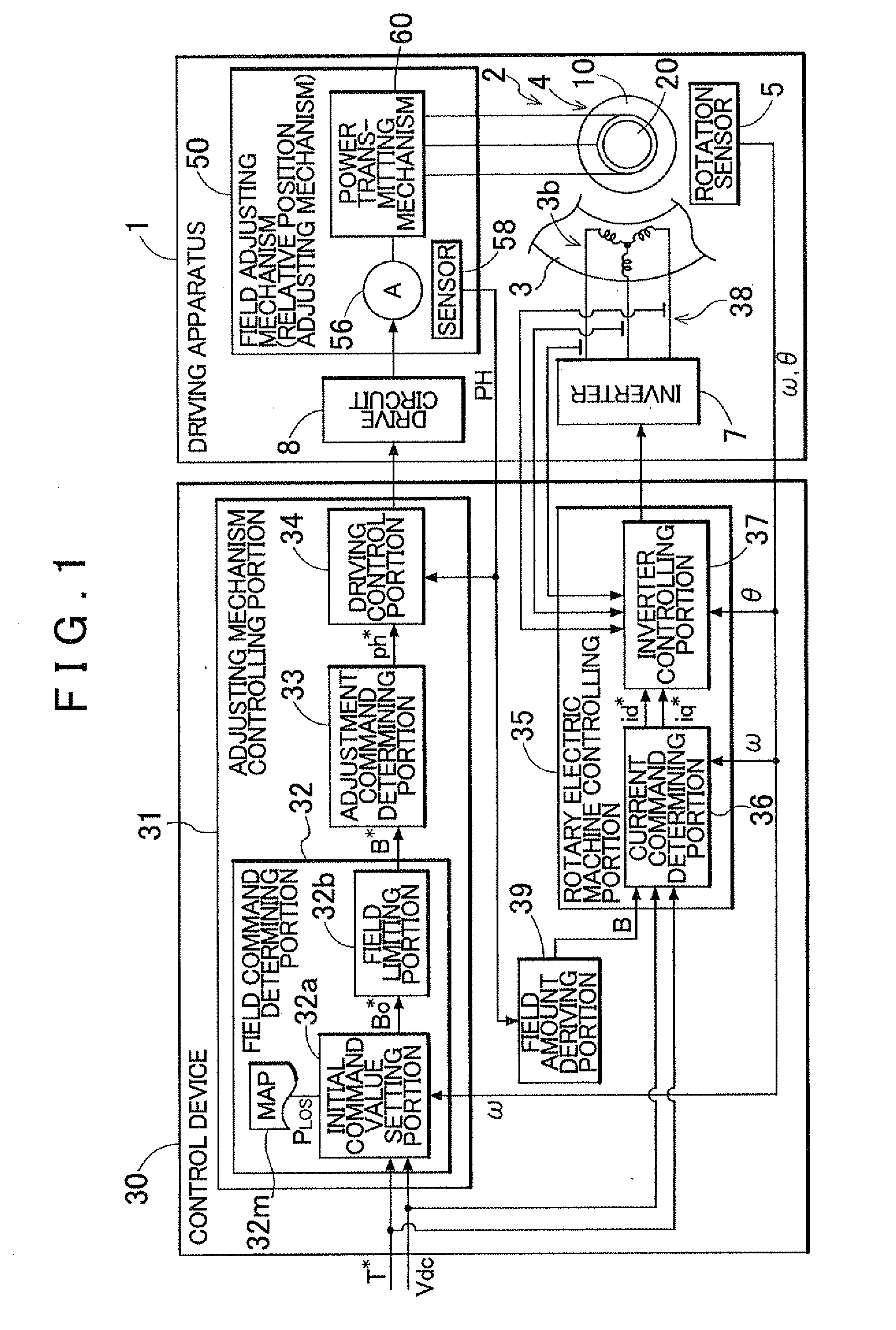
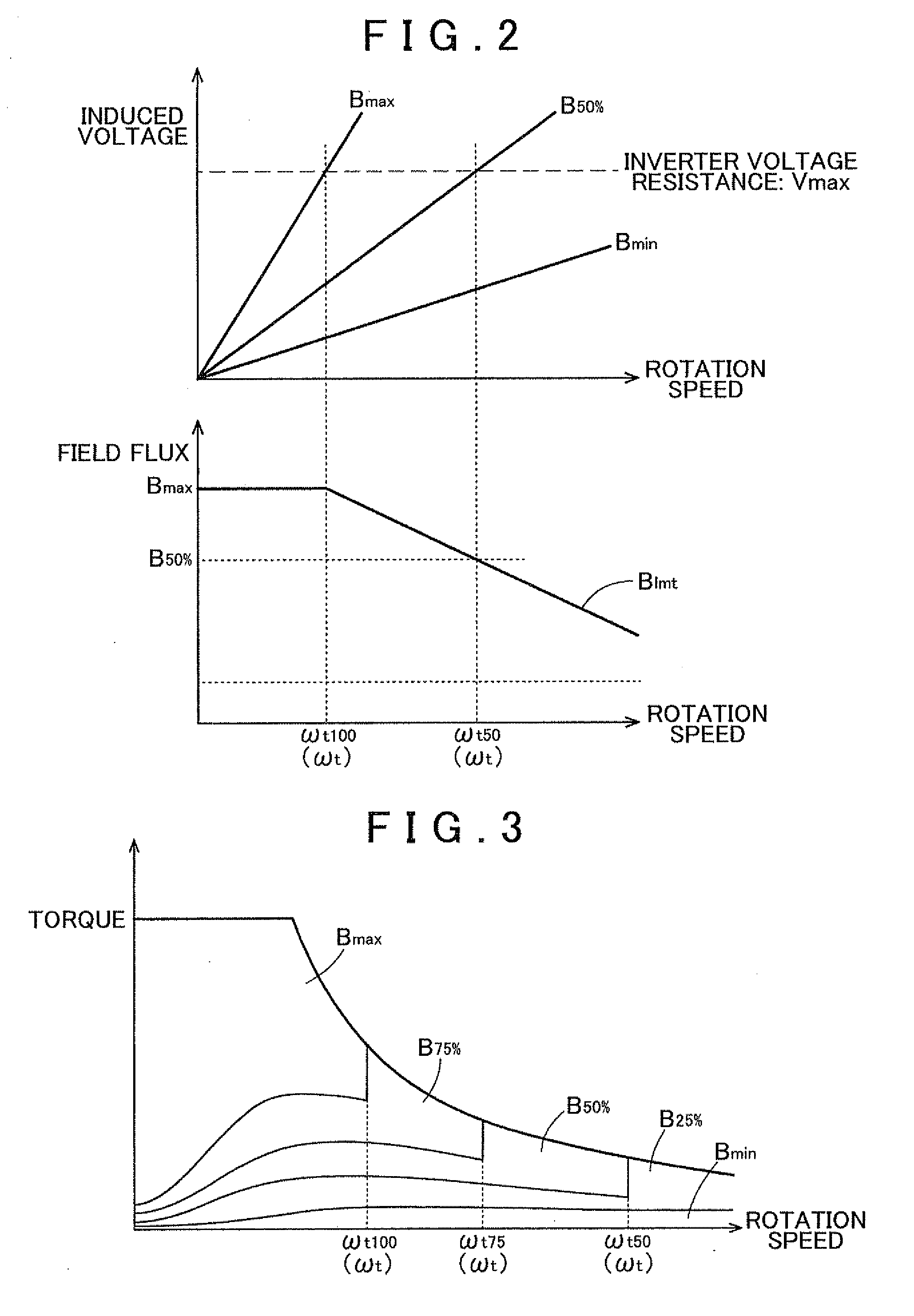
Control device of a driving apparatus
InactiveUS20120081054A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric machine
A control device for a driving apparatus configured with a rotary electric machine having a rotor with a permanent magnet and a stator having a coil. A field adjusting mechanism is configured to change a field flux supplied by the rotor, and an inverter is connected to the coil. A field command determining portion is configured to determine a field command value that serves as a target for the field flux that is adjusted by the field adjusting mechanism, based on at least a rotation speed of the rotor, with a field limiting value, that is set according to the rotation speed of the rotor within a range in which induced voltage that is induced in the coil will not exceed a voltage resistance of the inverter, as an upper limit.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
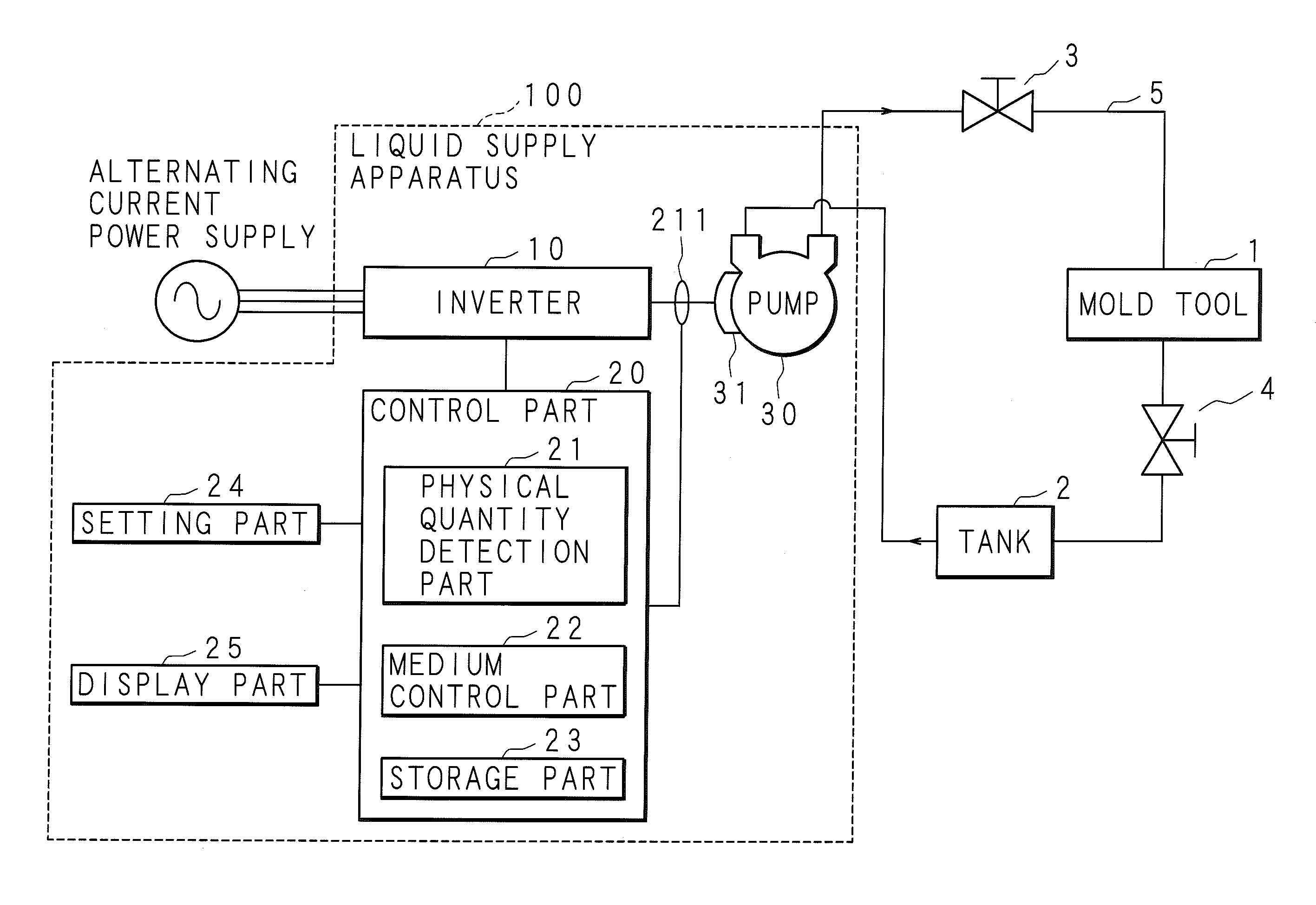
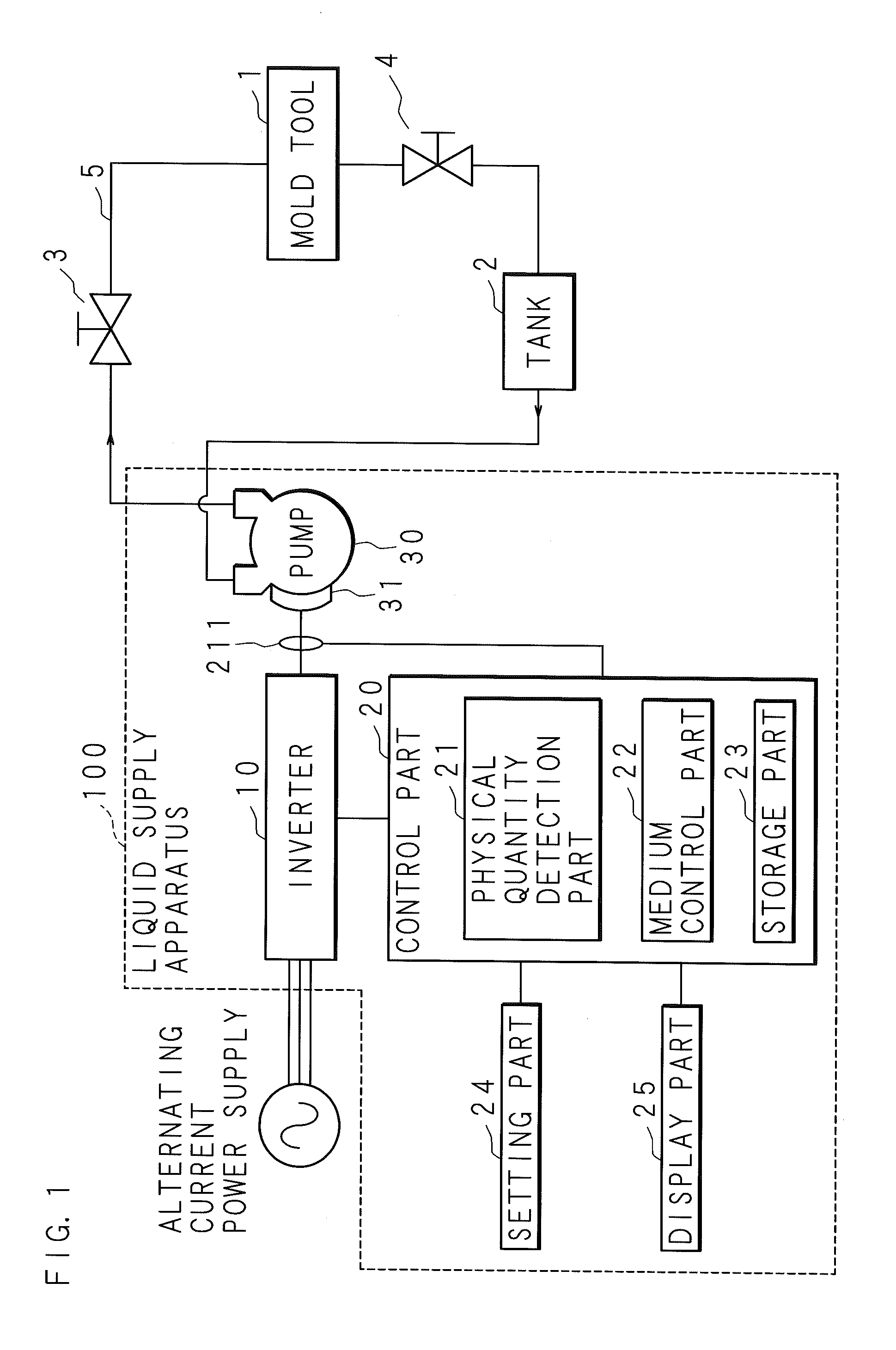
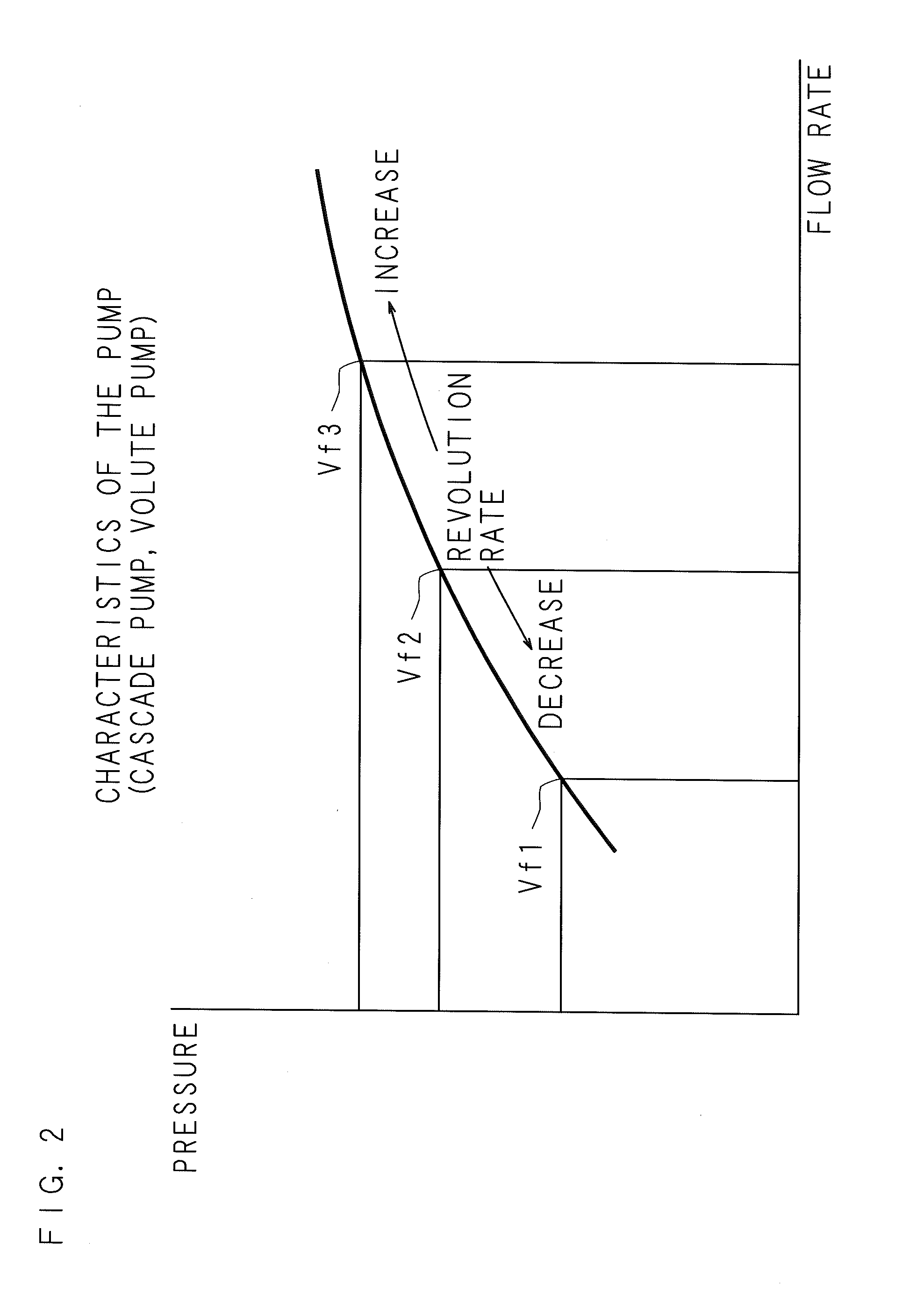
Liquid Supply Apparatus
InactiveUS20150370262A1Reduce flow rateReduce frequencyValve arrangementsFluid pressure control using electric meansMedia controlsEngineering
The liquid supply apparatus includes: an inverter converting the frequency of an alternating-current power supply; a pump including an electric motor driven by the inverter; a control part; and the like. The control part includes a physical quantity detection part, a medium control part, and the like. The physical quantity detection part detects a physical quantity concerning the output of the inverter. On the basis of the physical quantity detected by the physical quantity detection part, the medium control part controls at least one of the flow rate and the pressure of the liquid supplied by the pump.
Owner:MATSUI MFG
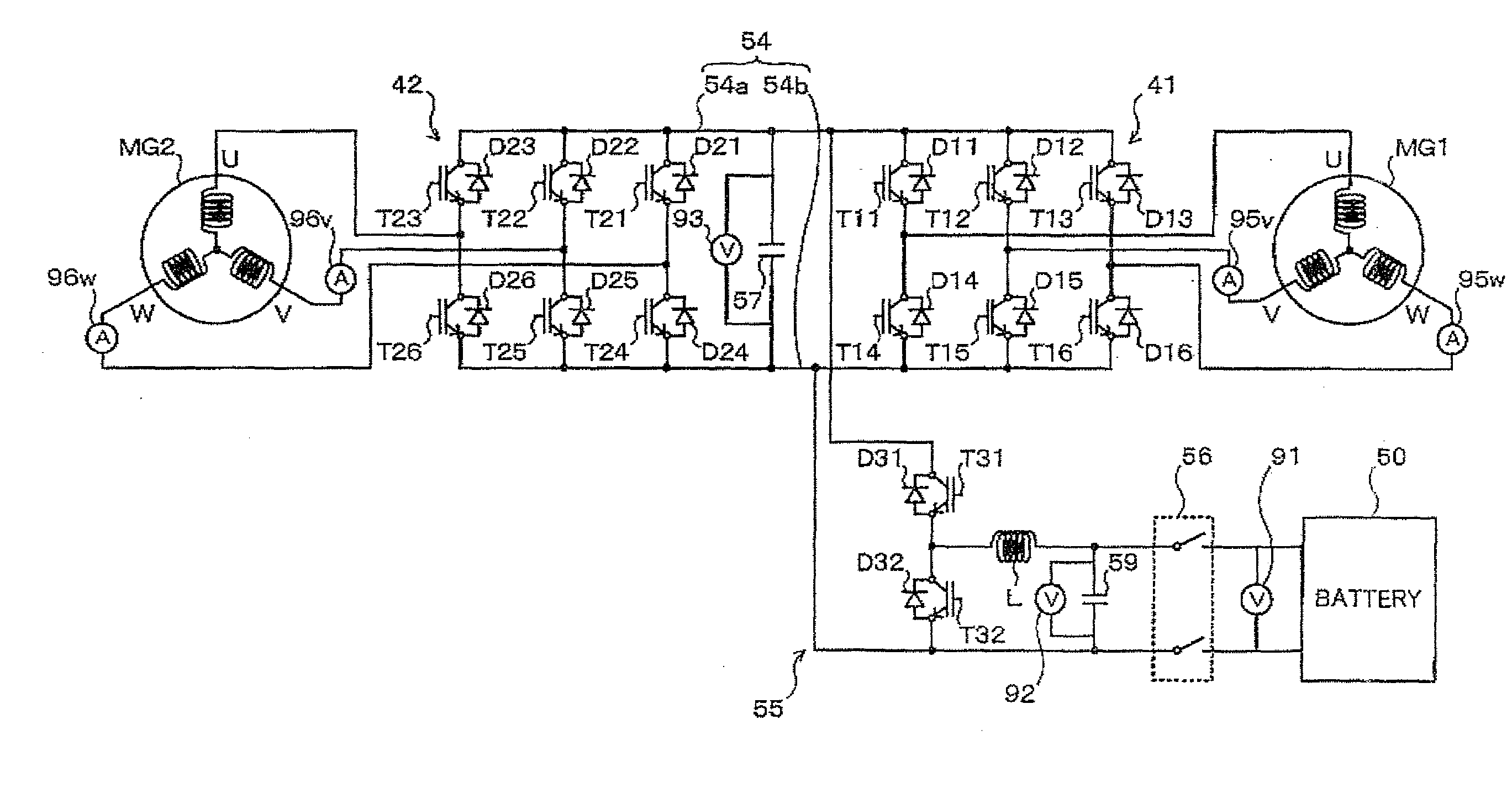
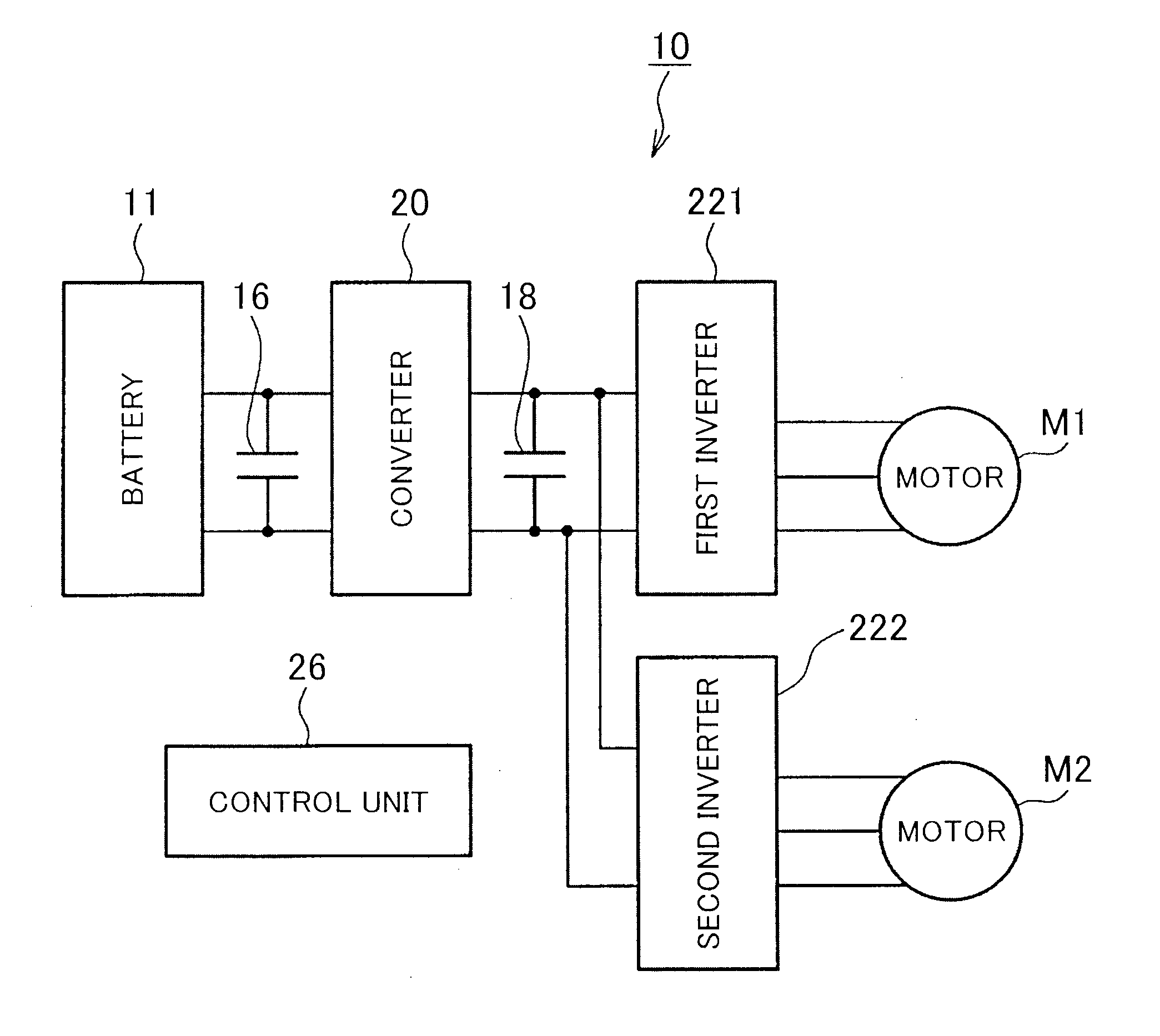
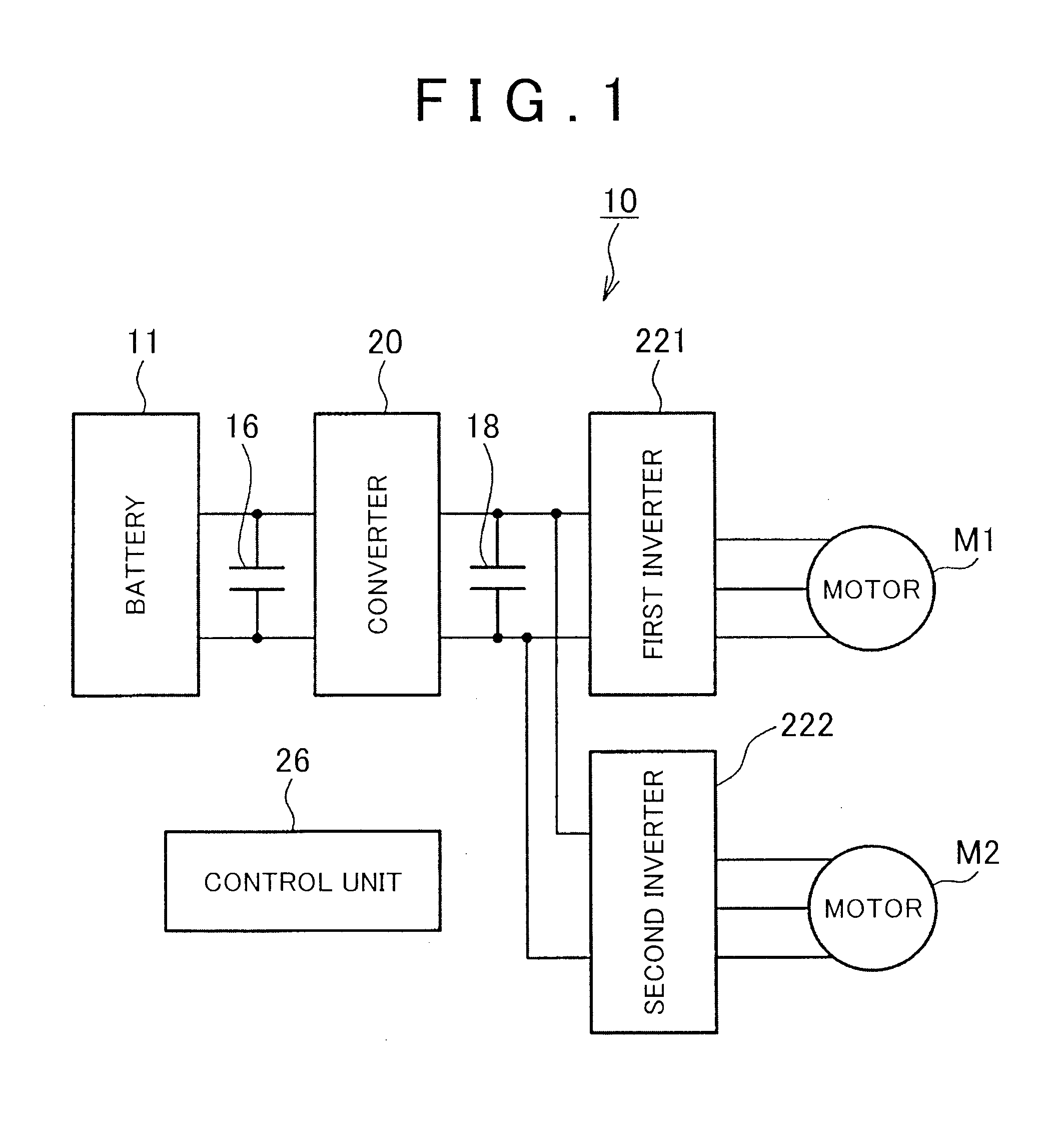
Motor control system
ActiveUS20140225536A1Vector control systemsMultiple dynamo-motor startersControl systemAlternating current
A motor control system includes: a converter; two inverters; two alternating-current motors; and a control unit. The control unit is configured to control the system voltage by feedback of a current phase of a current vector of motor current of each of the motors on a d-q coordinate plane so that rectangular wave control of at least one of the first and second motors is performed in a state where the current phase is an optimal current phase, wherein the control unit selects, as a subject of the feedback, the current phase of one of the motors that is larger than the other motor in system voltage deviation obtained based on the current vector.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
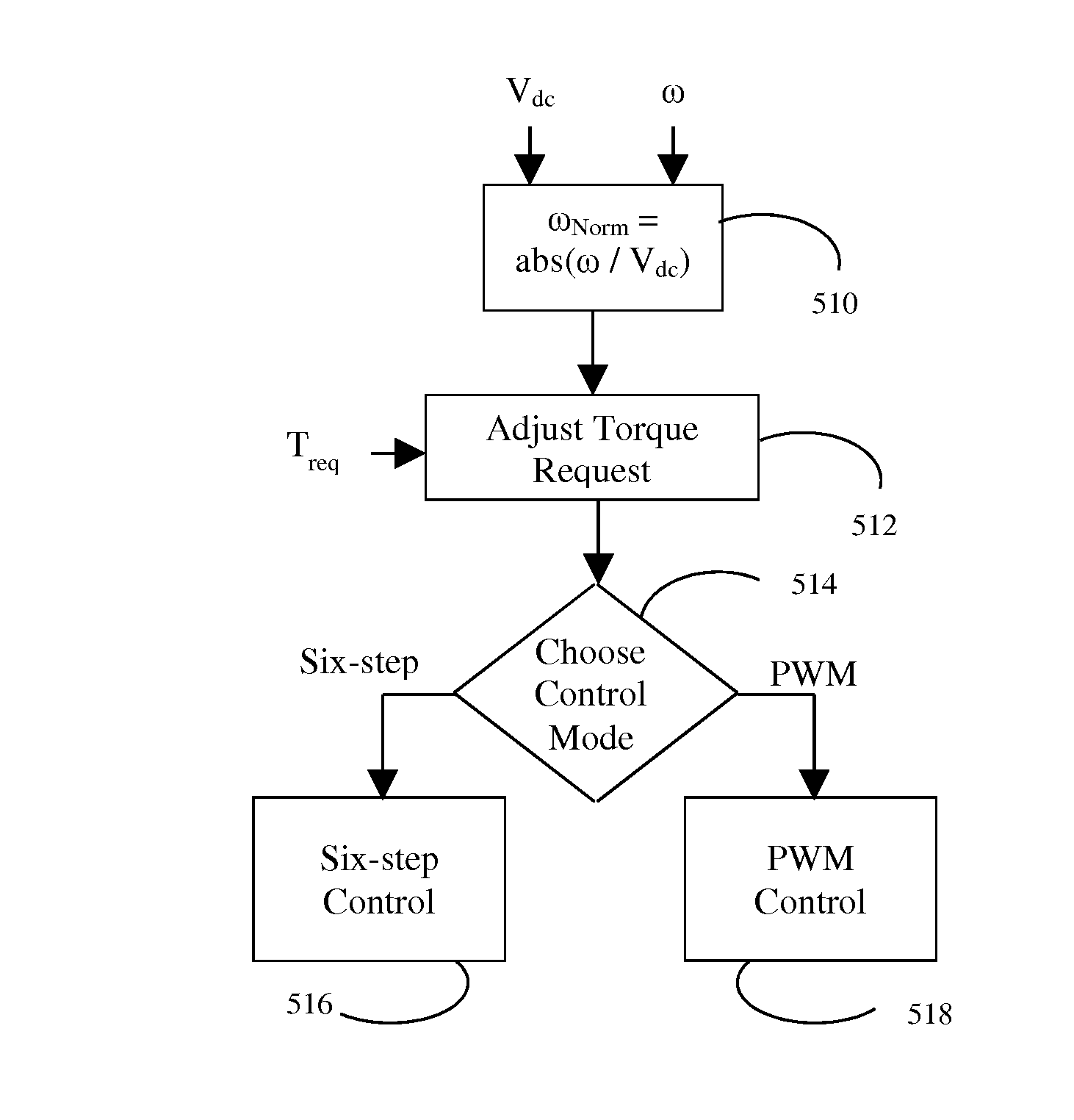
Electric motor torque control
ActiveUS20140070738A1Hybrid vehiclesSynchronous motors startersPermanent magnet synchronous motorEngineering
A vehicle includes one or more inverter-fed electric machines such as permanent magnet synchronous motors. In response to a torque request, a controller issues commands to an inverter calculated to cause the motor to produce the requested torque. A method of operating the inverter may determine the commands based on the ratio of rotor speed to inverter input voltage, reducing the approximation error associated with multi-dimensional lookup tables. When the speed and voltage vary while maintaining a constant ratio and constant torque request, the issued commands produce a winding current in the electrical machine with constant direct and quadrature components.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
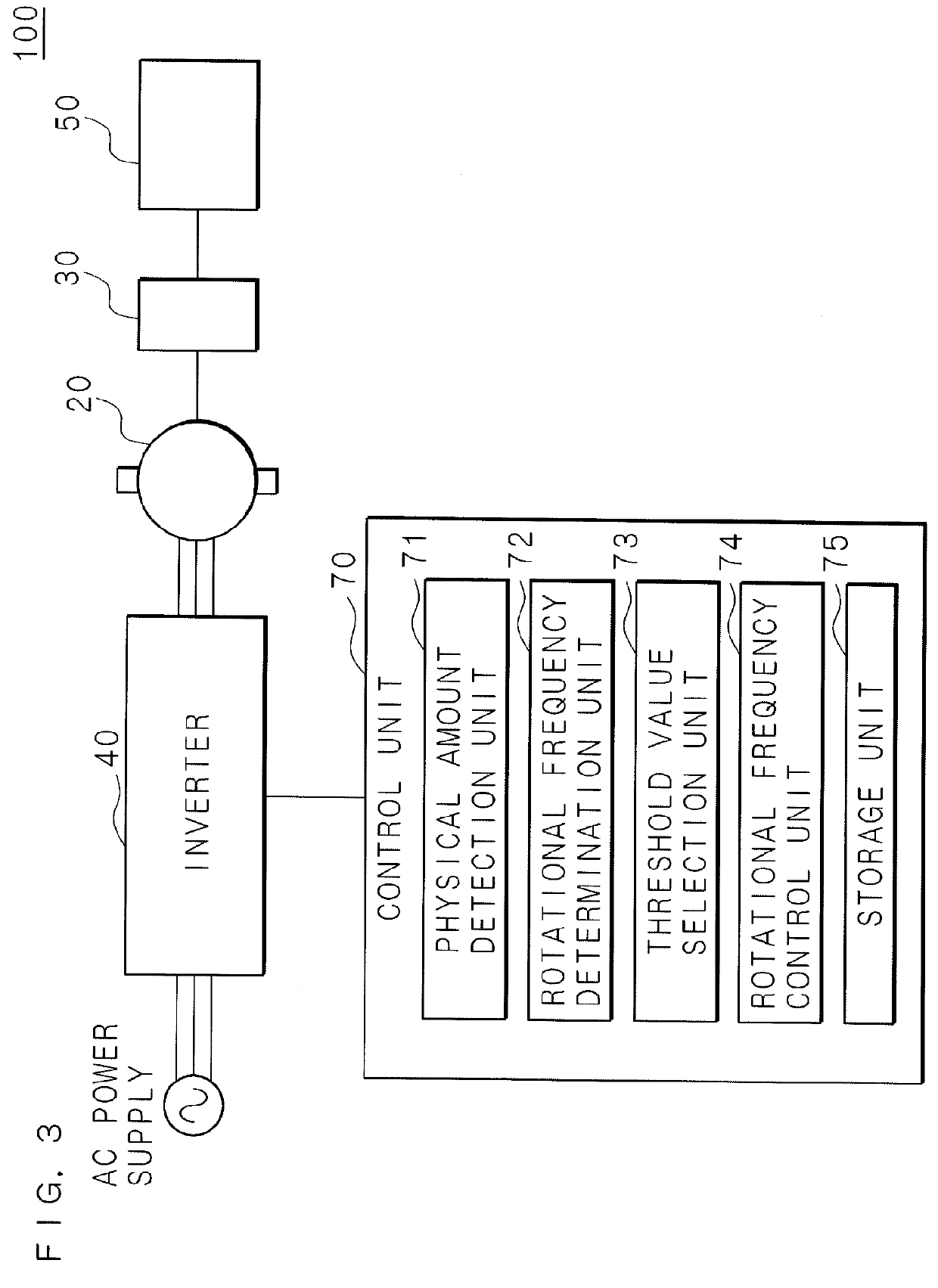
Drive control device, electrical apparatus and drive control method
ActiveUS9337764B2Low costSimple configurationElectronic commutation motor controlMotor control for low load efficiencyControl theoryRotational frequency
A drive control device is provided with a physical amount detection unit which detects the physical amount pertaining to the output of a motor, a rotational frequency determination unit for determining whether the rotational frequency of the motor is equal to or greater than a base rotational frequency, a threshold value selection unit for selecting a threshold value for the physical amount in accordance with the determination result of the rotational frequency determination unit, and a rotational frequency control unit for controlling the rotational frequency of a rotating shaft in accordance with the magnitude relationship between the detected physical amount and the selected threshold value.
Owner:MATSUI MFG
Electric motor driving device and vehicle equipped with the same
InactiveUS8896252B2Increase powerSynchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlPower flowTransverter
An electric motor driving device that drives an electric motor including a field winding, a rotor and a stator, wherein the rotor and the stator each form a field pole by passing a field current through the field winding, includes: a power supply device; a converter including a reactor that at least partially serves as the field winding shared with the electric motor, and configured to receive a voltage from the power supply device to carry out voltage conversion between first and second power lines and to pass the field current through the field winding during voltage conversion operation; an inverter configured to convert a direct-current power received from the converter to an alternating-current power for driving the electric motor; and a controller controlling the converter so that a current flows through the field winding in the same direction both during power running and regeneration of the electric motor.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS9742318B2Increase powerShorten the timeMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectric machineControl system
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
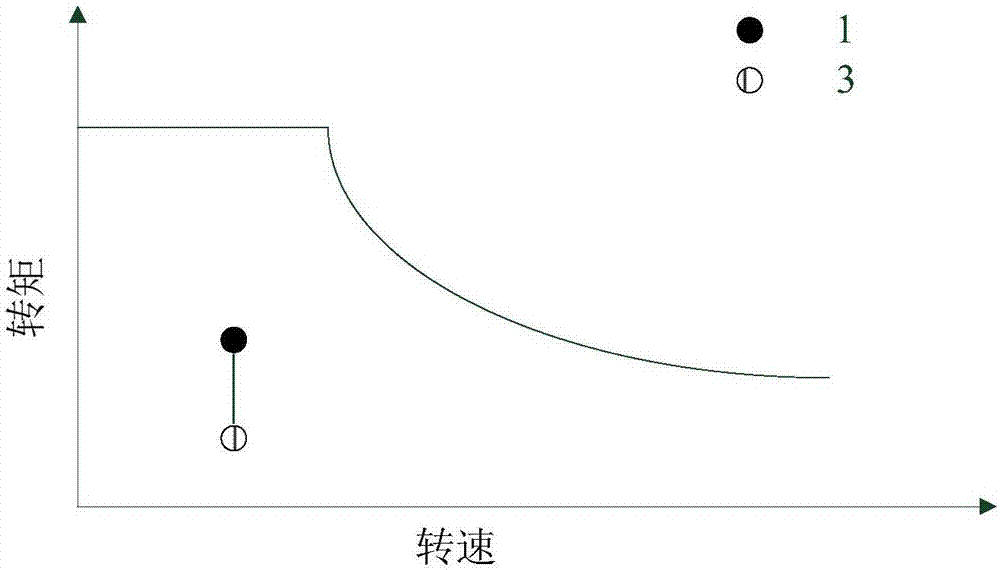
Method for adjusting high-efficiency region of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN107342667ASave energyImprove efficiencySpeed controllerElectric devicesSynchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention discloses a method for adjusting the high-efficiency region of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The method specifically comprises the steps of: revealing the internal relationship between a high-efficiency point and a surrounding point, proving the optimal proportion of copper loss, iron loss and permanent-magnet eddy-current loss in the motor when the high-efficiency point moves towards different directions, and thus, summarizing the method for adjusting the high-efficiency region. The method is applied to the permanent-magnet motor in any form; the high-efficiency region can be adjusted to the working point dense region of the motor under different operation working conditions according to design requirements; the high-efficiency region and the operation working condition of an electric automobile can be effectively combined; therefore, the energy consumption is reduced; and the endurance mileage of the electric automobile is increased.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
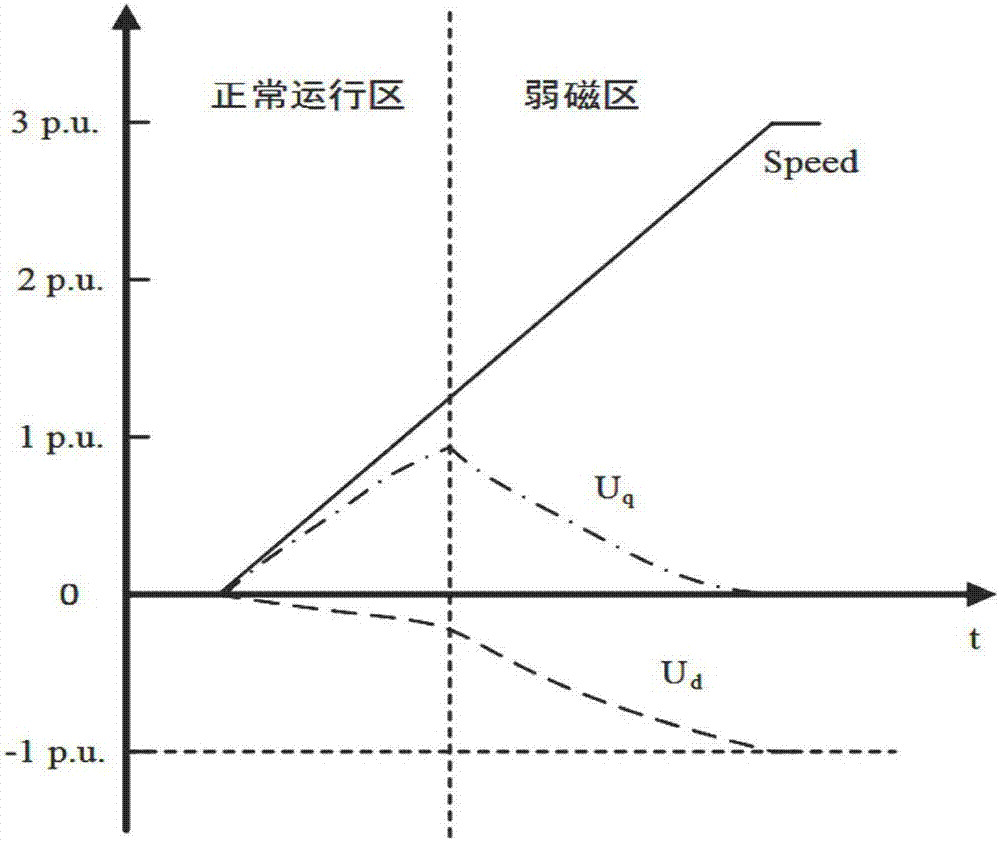
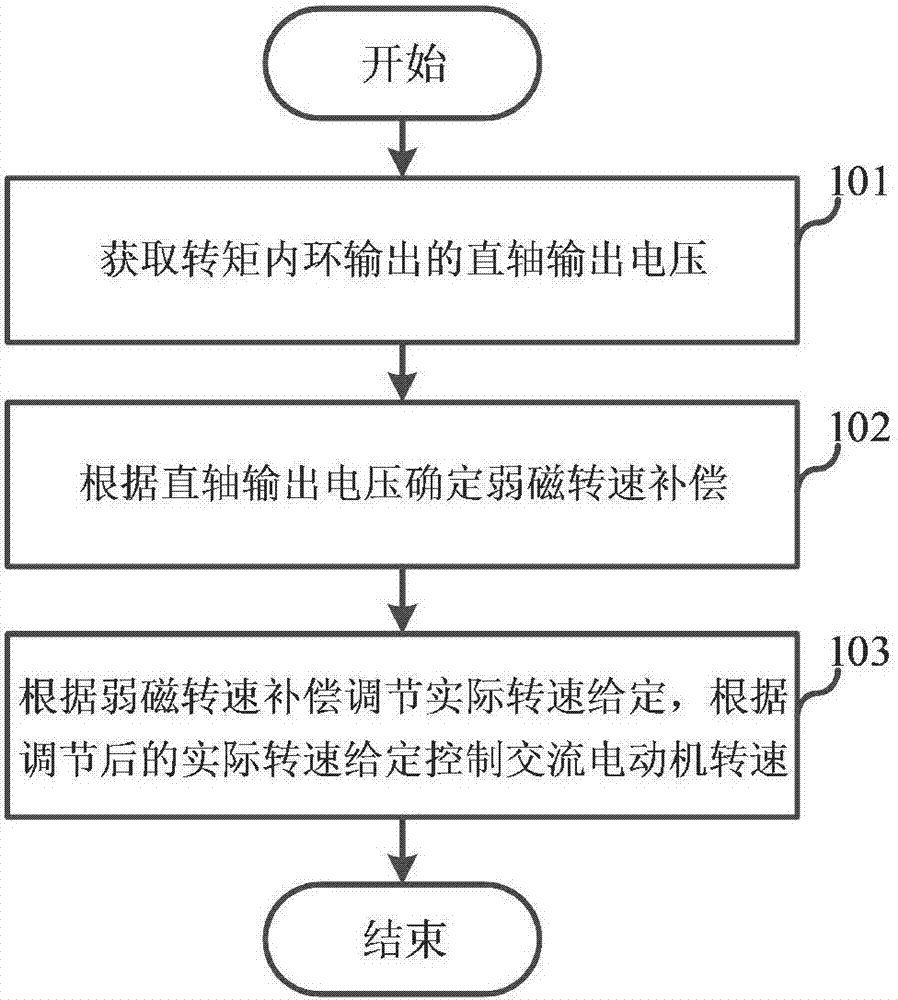
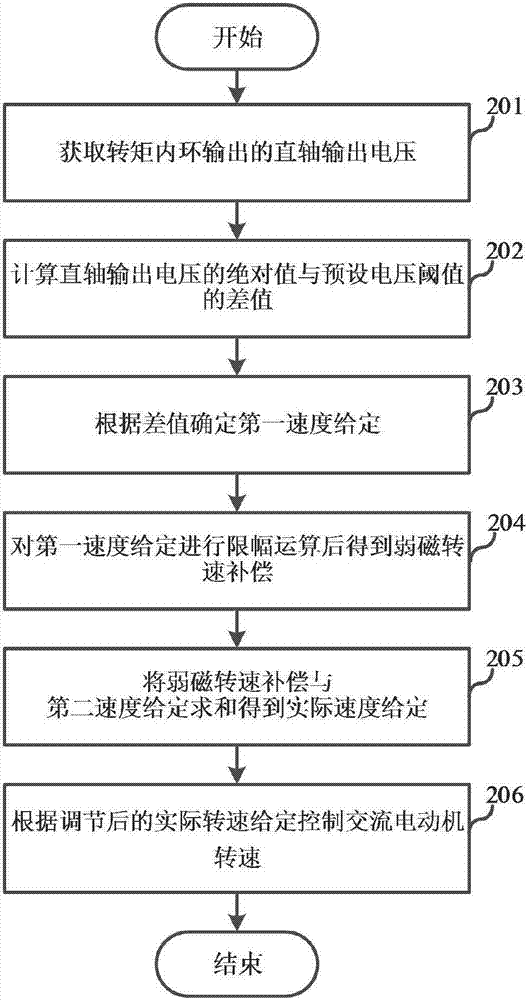
Weak magnetic control method and device for running speed of AC motor
ActiveCN107104621AAvoid getting out of controlImprove stabilityMotor control for high speedAutomatic controlAC motor
The invention relates to the technical field of automatic control, and discloses a weak magnetic control method and device for a running speed of an AC motor. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a direct-axis output voltage output from a torque inner ring; determining weak magnetic rotational speed compensation according to the direct-axis output voltage; and adjusting an actual given rotational speed according to the weak magnetic rotational speed compensation, and controlling the rotational speed of the AC motor according to the adjusted actual given rotational speed. According to the method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the weak magnetic rotational speed compensation is determined by acquiring the direct-axis voltage, the actual given rotational speed after the weak magnetic rotational speed compensation is adjusted according to the weak magnetic rotational speed compensation so as to further control the rotational speed of the AC motor; and therefore, during deep weak magnetic running of the motor, the rotational speed of the AC motor is controlled according to the actual given rotational speed after the weak magnetic rotational speed compensation, and meanwhile, the working stability of the motor is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI STEP ELECTRIC +1
Calibration method and control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor, and bench test control system
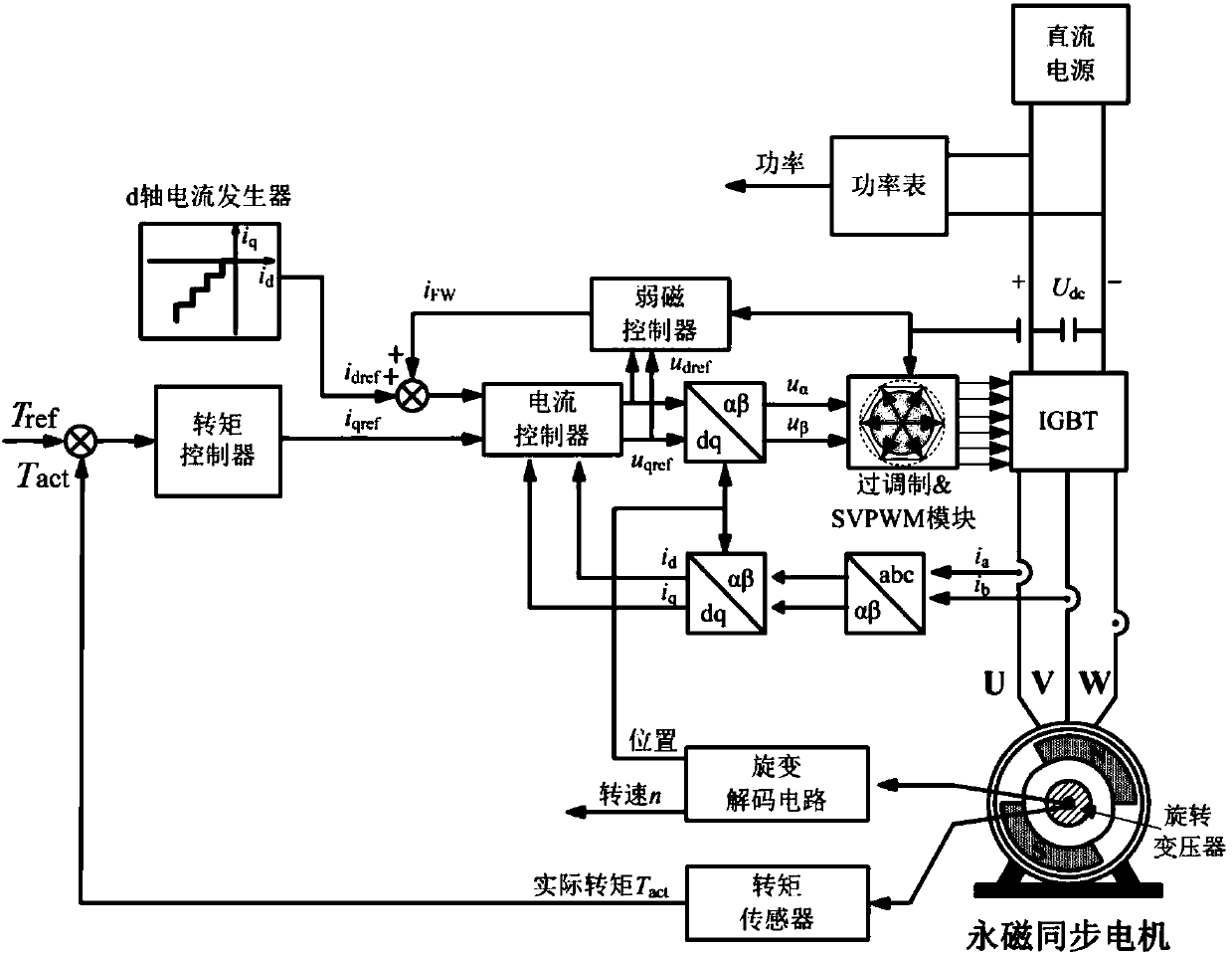
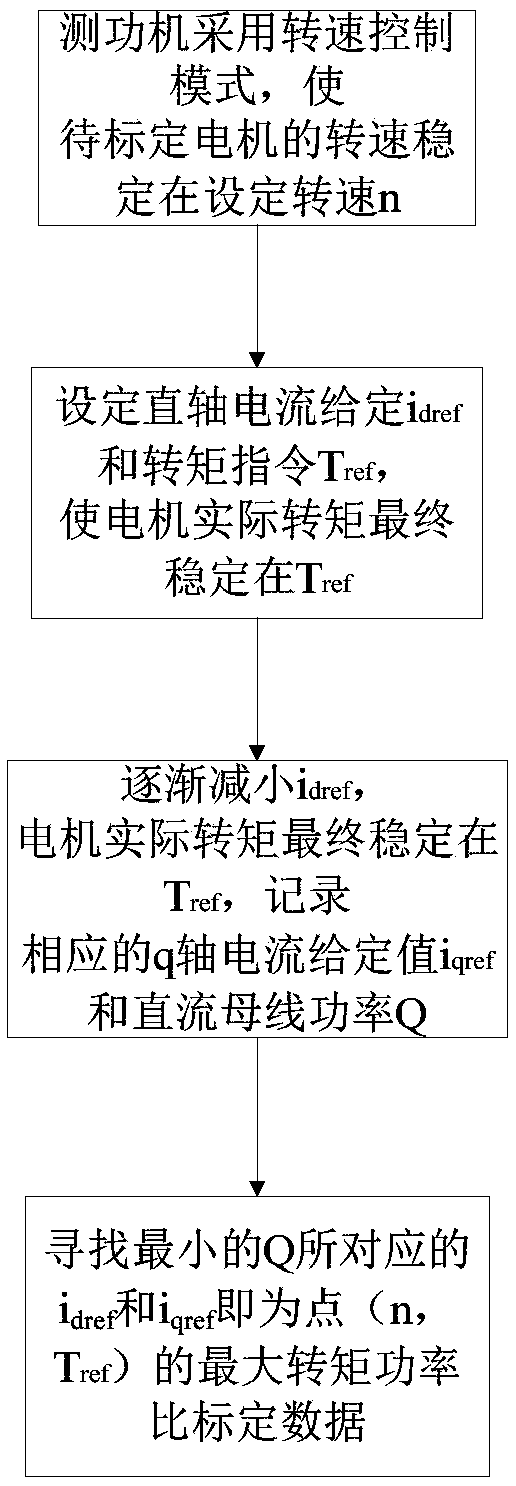
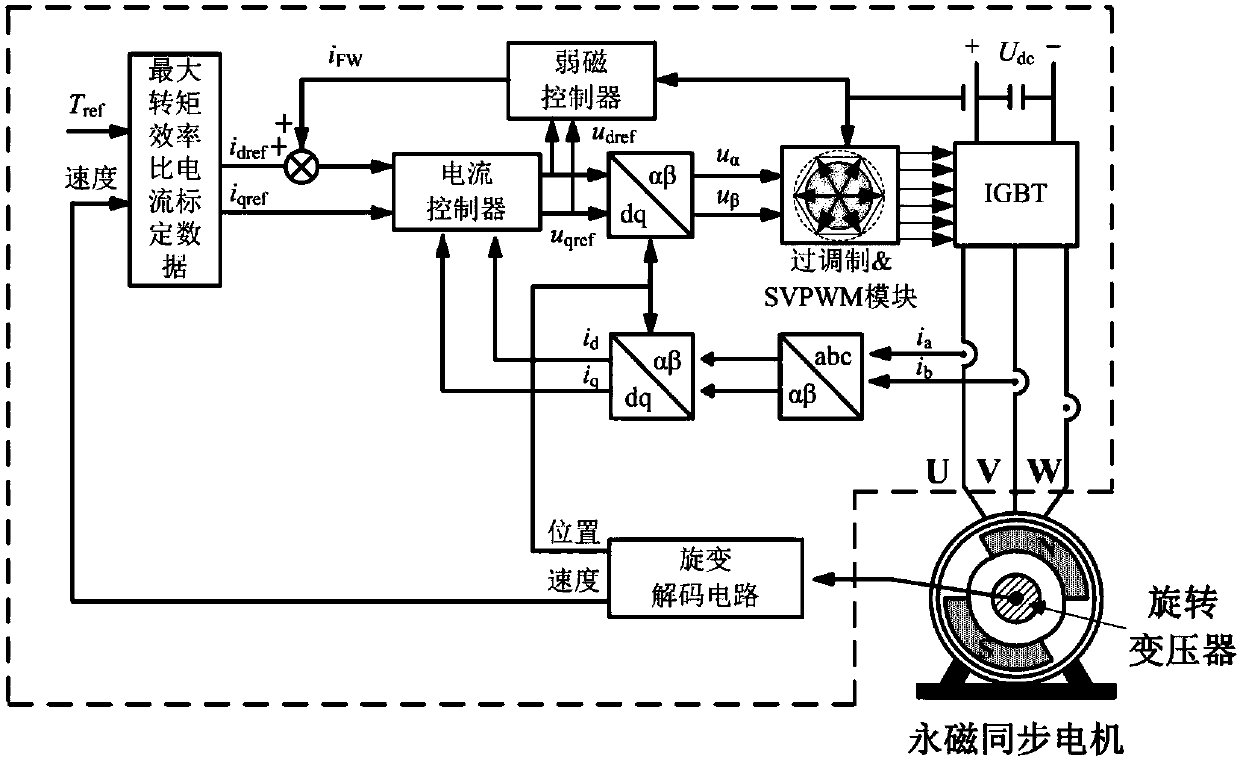
ActiveCN110289792AEasy to controlBalanced Iron ConsumptionElectric motor controlMotor control for high speedMaximum torqueElectric machine
The invention relates to a calibration method and a control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and a bench test control system. The calibration method comprises the steps of: enabling a dynamometer to use a rotational speed control mode in order to stabilize the rotational speed of a motor to be calibrated at a set rotational speed n; enabling the motor to be calibrated to use a torque control mode, setting a d-axis current given value idref1 and a torque instruction value Tref, and after the motor operates stably, recording the corresponding q-axis current given value iqref1 and the DC bus power Q1; giving a d-axis current given value idrefj, 2 <= j <= n, idref1 > idref2 > ...> idrefn, and under each idrefj, recording the corresponding iqrefj and Qj after the motor runs stably; searching for the idrefj and iqrefj, corresponding to the minimum Qj, as the maximum torque power ratio calibration data corresponding to the Tref and n; and repeating the above processes to obtain maximum torque power ratio calibration data corresponding to different torque instruction values and the rotational speeds. The method, by calibrating the maximum torque power ratios corresponding to different torque instruction values and rotational speeds, finally realizes the control of a motor system and achieves the highest system efficiency.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUTONG BUS CO LTD
Inverter control system
InactiveUS20130278189A1Low arithmetic loadSmall sizeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPower inverterPower flow
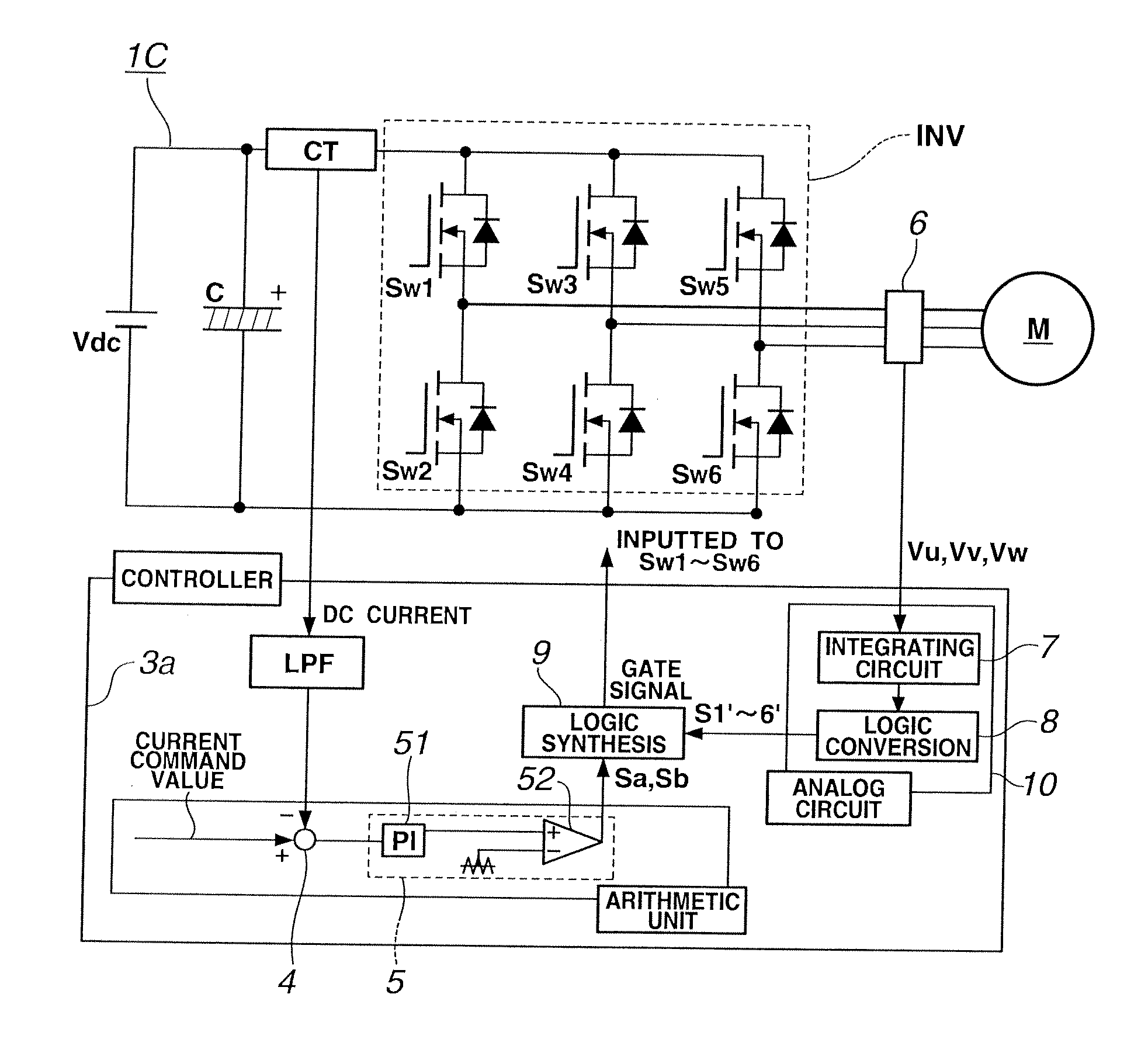
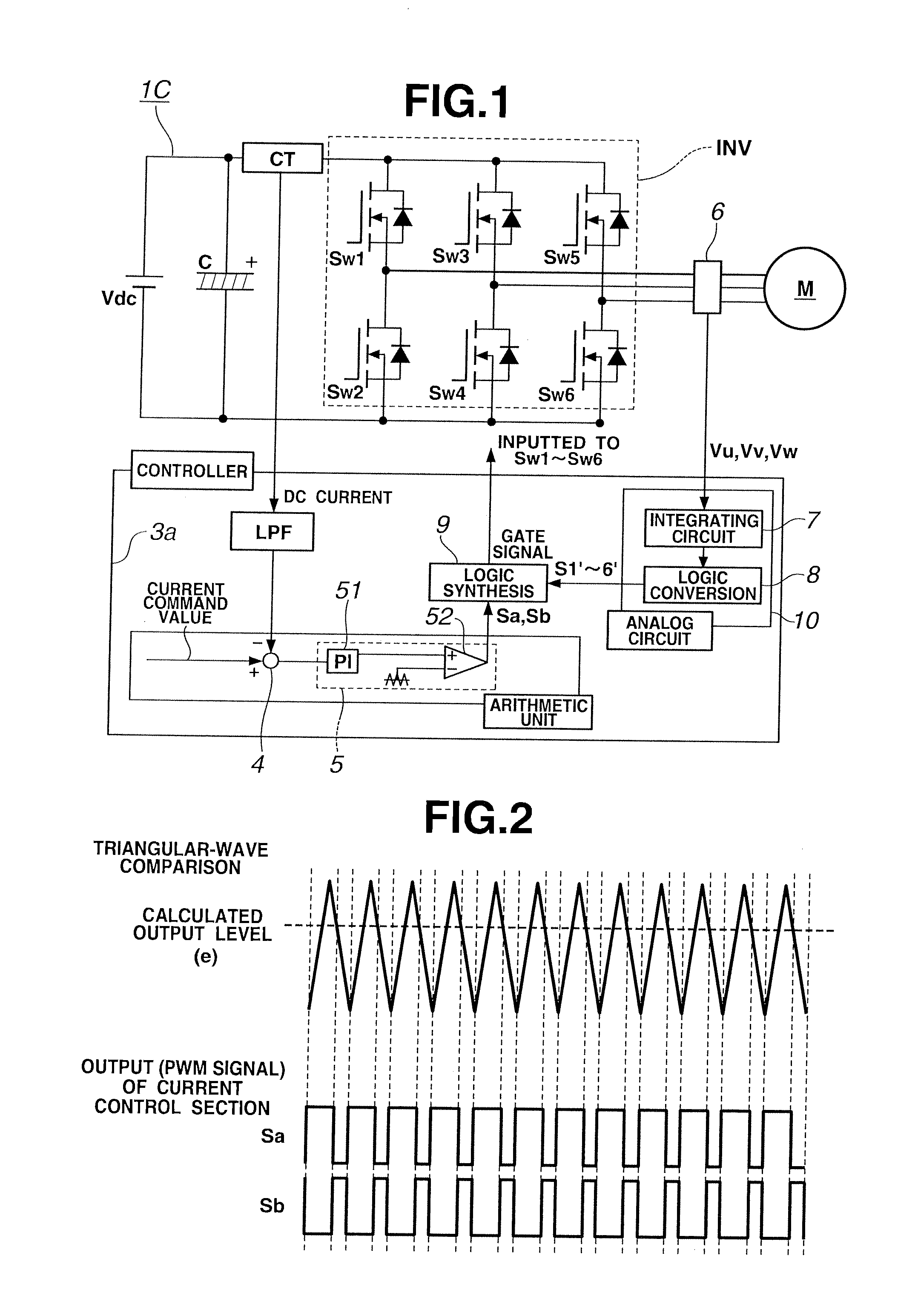
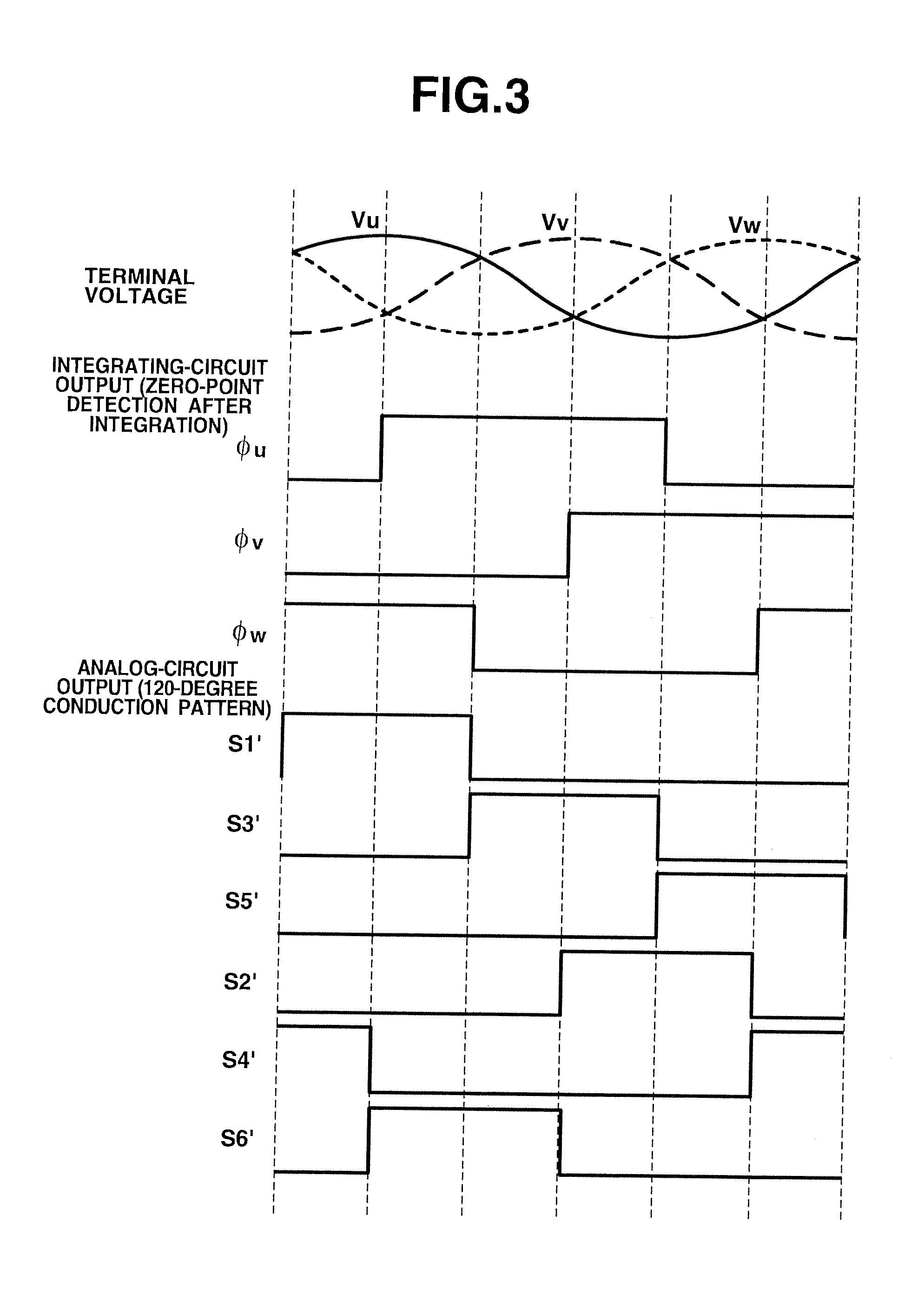
A LPF extracts DC component of a current detection value of an inverter input current. A subtracting section 4 calculates a difference between a current command value and the DC component of the current detection value. A current controller 5 produces two-phase PWM signals Sa and Sb complementary to each other, from the current difference. Further, an integrating circuit 7 integrates output terminal voltages Vu, Vv and Vw of the inverter to convert the output terminal voltages Vu, Vv and Vw into a magnetic-flux information Φu, Φv and Φw. A logic conversion section 8 converts the magnetic-flux information Φu, Φv and Φw into 120-degree conduction patterns S1′-S6′ to output the 120-degree conduction patterns S1′-S6′. Then, a logic circuit section 9 executes a logic synthesis between the PWM signals Sa and Sb and the 120-degree conduction patterns S1′-S6′ to output gate signals S1-S6.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Control device for motor drive system and vehicle having same
ActiveCN102859866AReduce the amount of field weakening currentImprove efficiencyVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor driveControl theory
A control device (200) for a motor drive system (100) including an AC motor (MG1) having a magnet on a rotor, a converter (120) and an inverter (130), generates a boost command value for the converter (120) on the basis of a torque command value of the AC motor (MG1). The control device (200) determines whether weak field control, which increases the current in the direction in which the magnetic force supplied to the AC motor (MG1) from the inverter (130) is diminished, is to be implemented, on the basis of the boost command value and the drive status of the AC motor (MG1). If weak field control is to be implemented, and the absolute value of the torque command value is smaller than a threshold value, the control device (200) will further increase the generated boost command value. As a result of doing so, the level of the weak field current can be reduced, thereby improving the efficiency of the motor drive system (100).
Owner:DENSO CORP
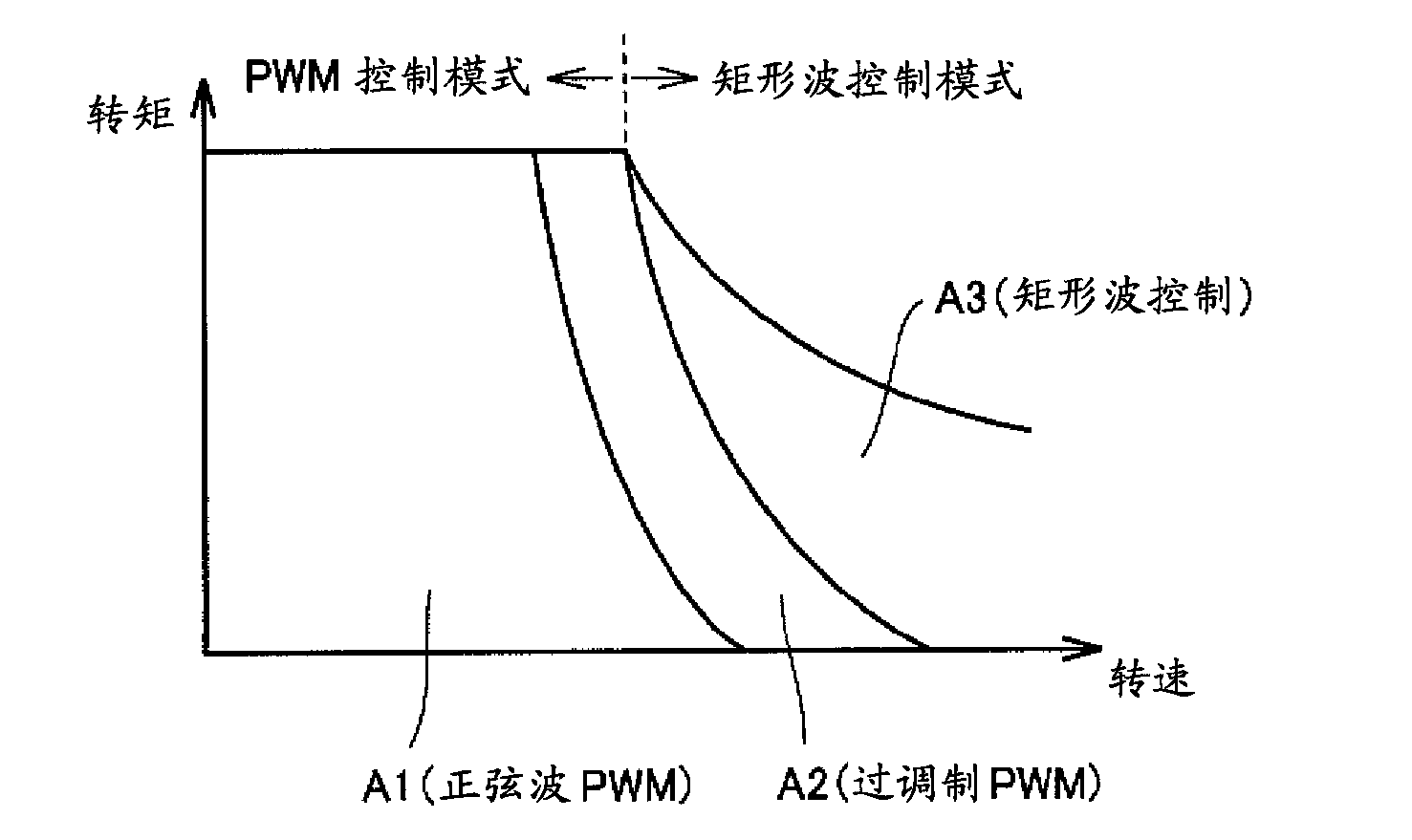
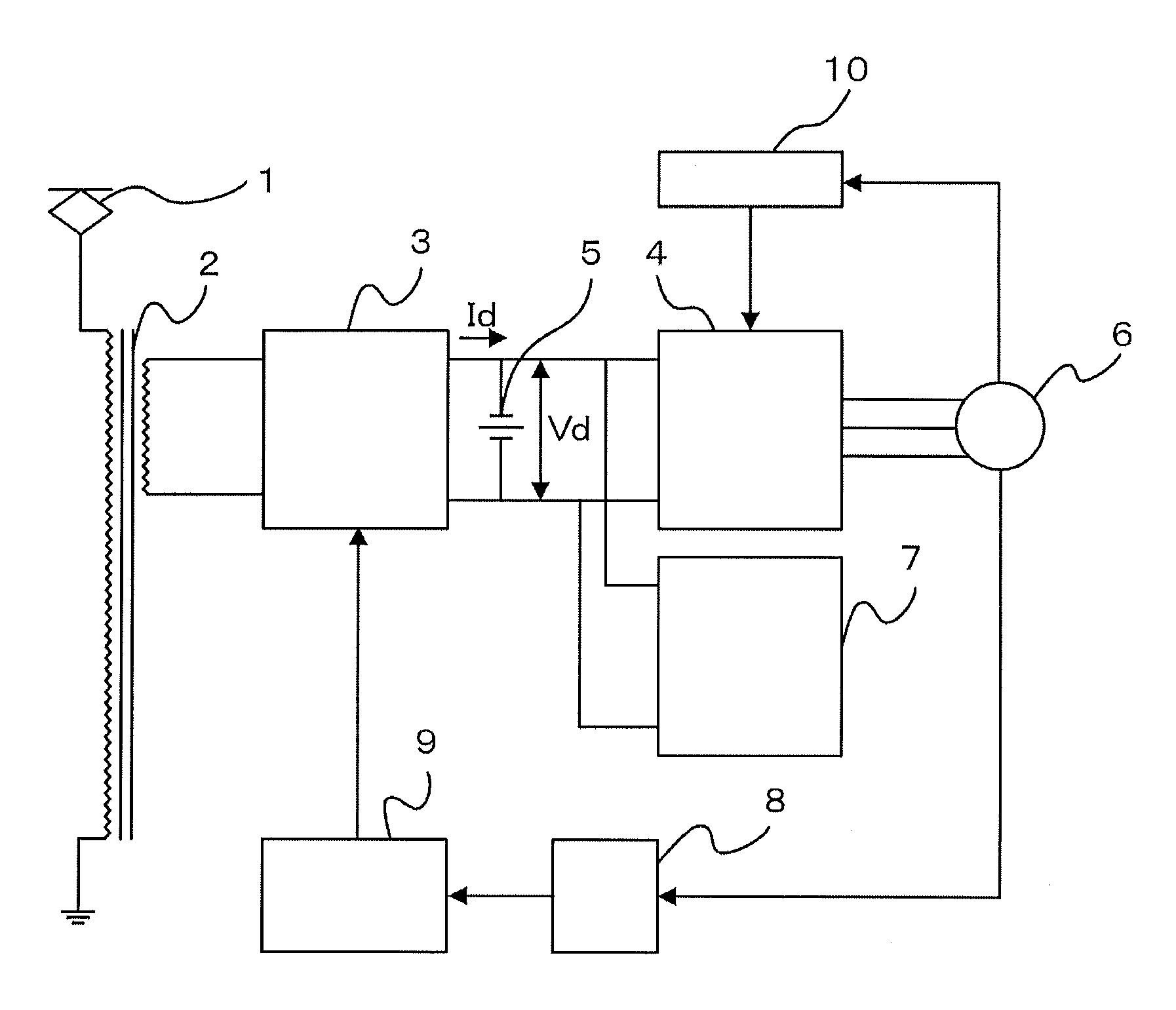
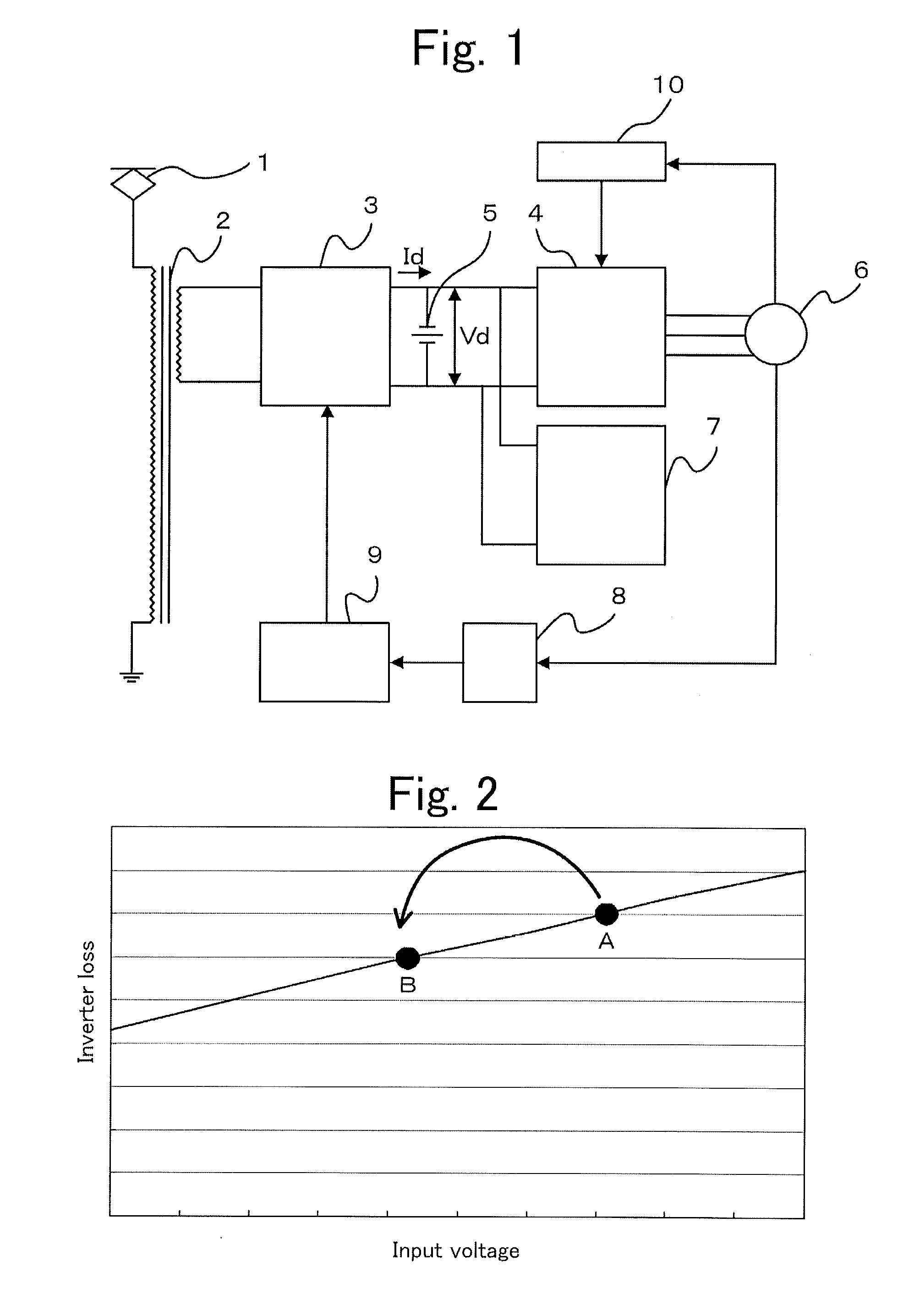
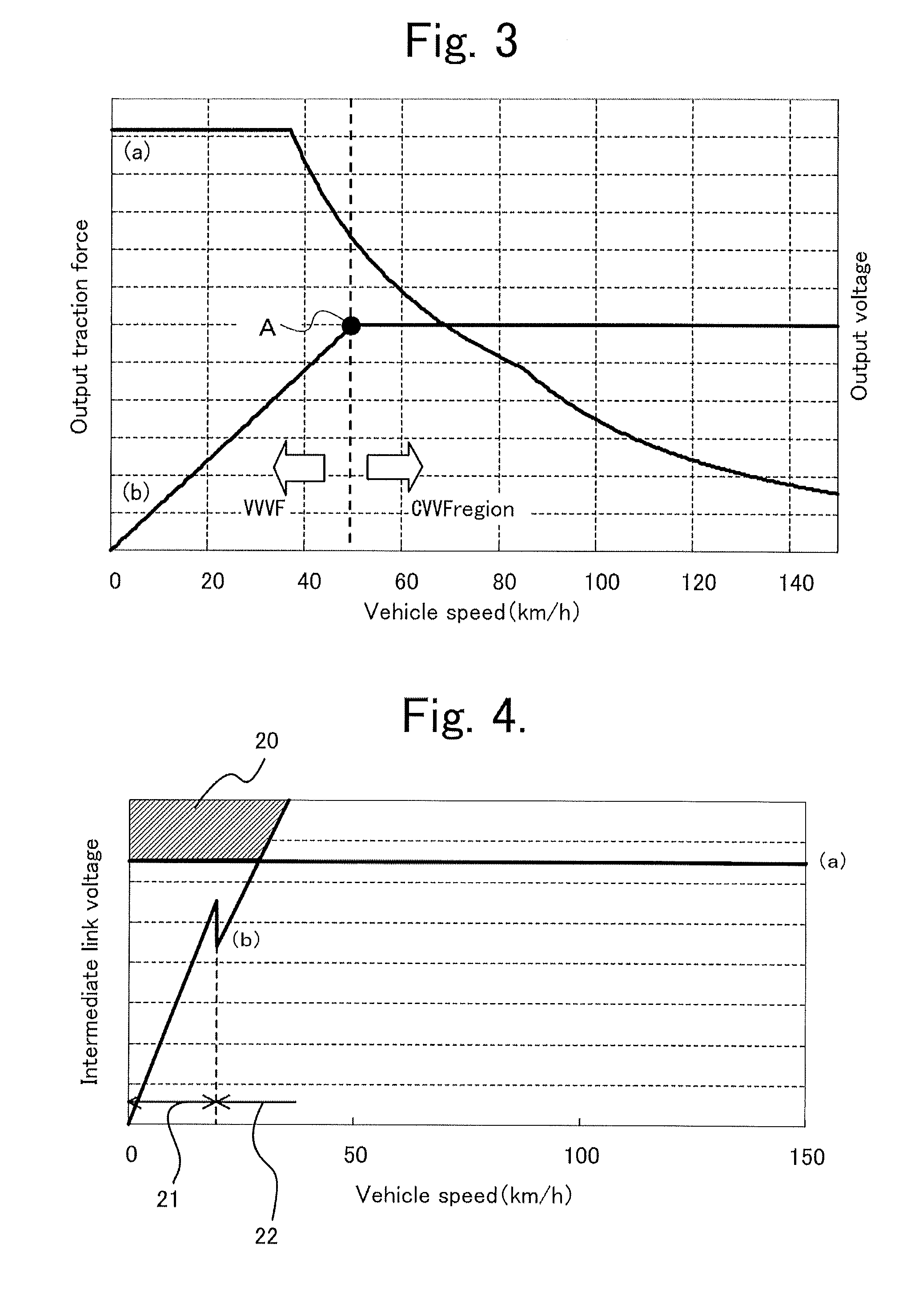
Propulsion control apparatus
ActiveUS20120296507A1Power supply lossReduce lossesDigital data processing detailsRailway vehiclesLow speedEngineering
In a configuration in which an auxiliary power supply is connected to an intermediate link circuit of a main conversion unit, intermediate link voltage as input voltage of the auxiliary power supply is set at higher voltage depending on the main conversion unit as a main unit, and loss generated in a main circuit element of the auxiliary power supply increases; therefore, a problem has occurred that a cooling unit has to be increased in size. The main conversion unit recognizes a low-speed and stop state by monitoring a vehicle speed, and varies the intermediate link voltage corresponding to the vehicle speed; thereby, the loss generated in the main circuit element of the auxiliary power supply is reduced at the low-speed and stop state where cooling ability is decreased; as a result, small sizing and light weighting of the cooling unit is achieved.
Owner:NEXGEN CONTROL SYST LLC
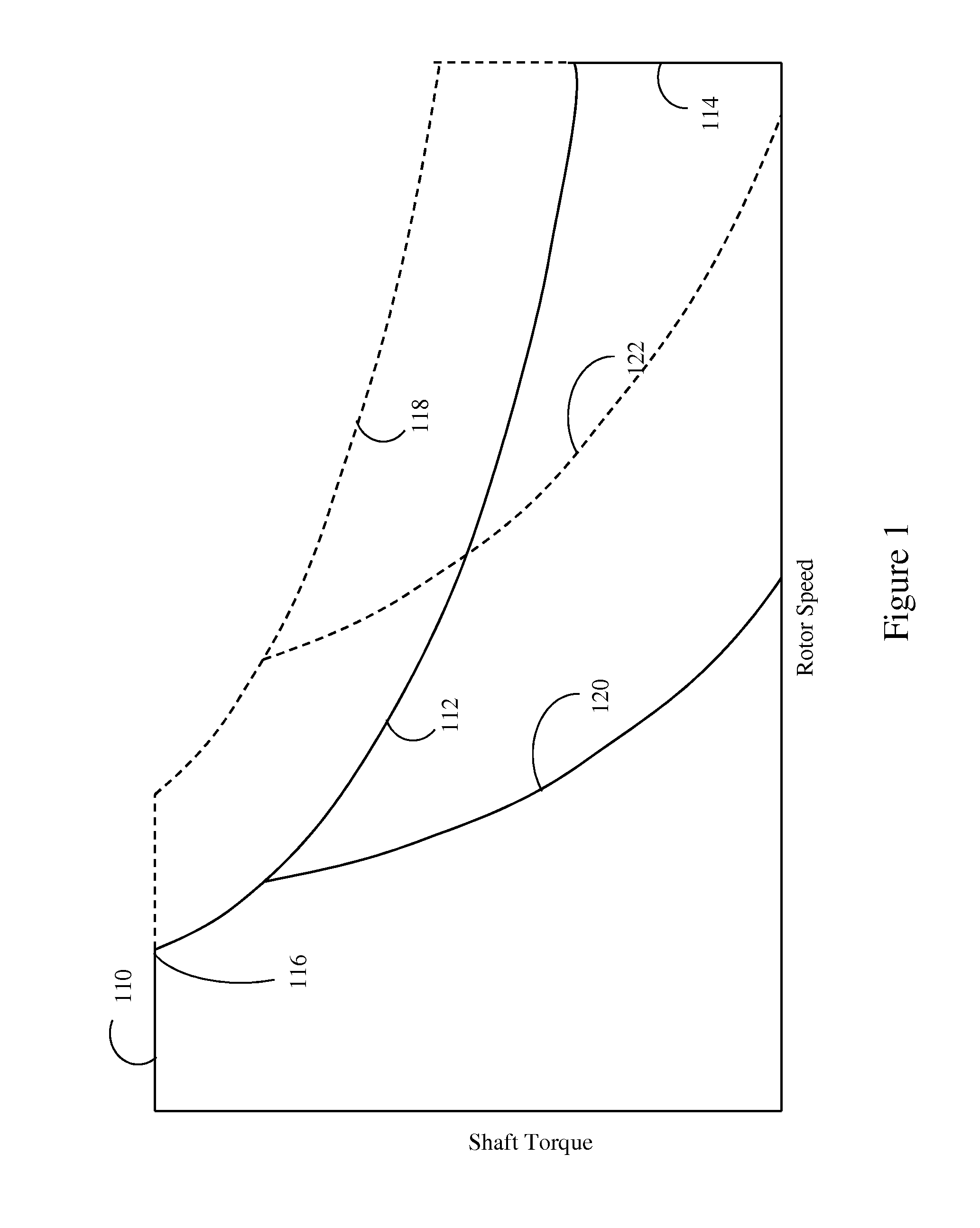
Method for operating a delta wound three-phase permanent magnet brushless motor
ActiveUS7612520B2Reducing complexity and expenseTotal current dropSingle-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlBrushless motorsPhase currents
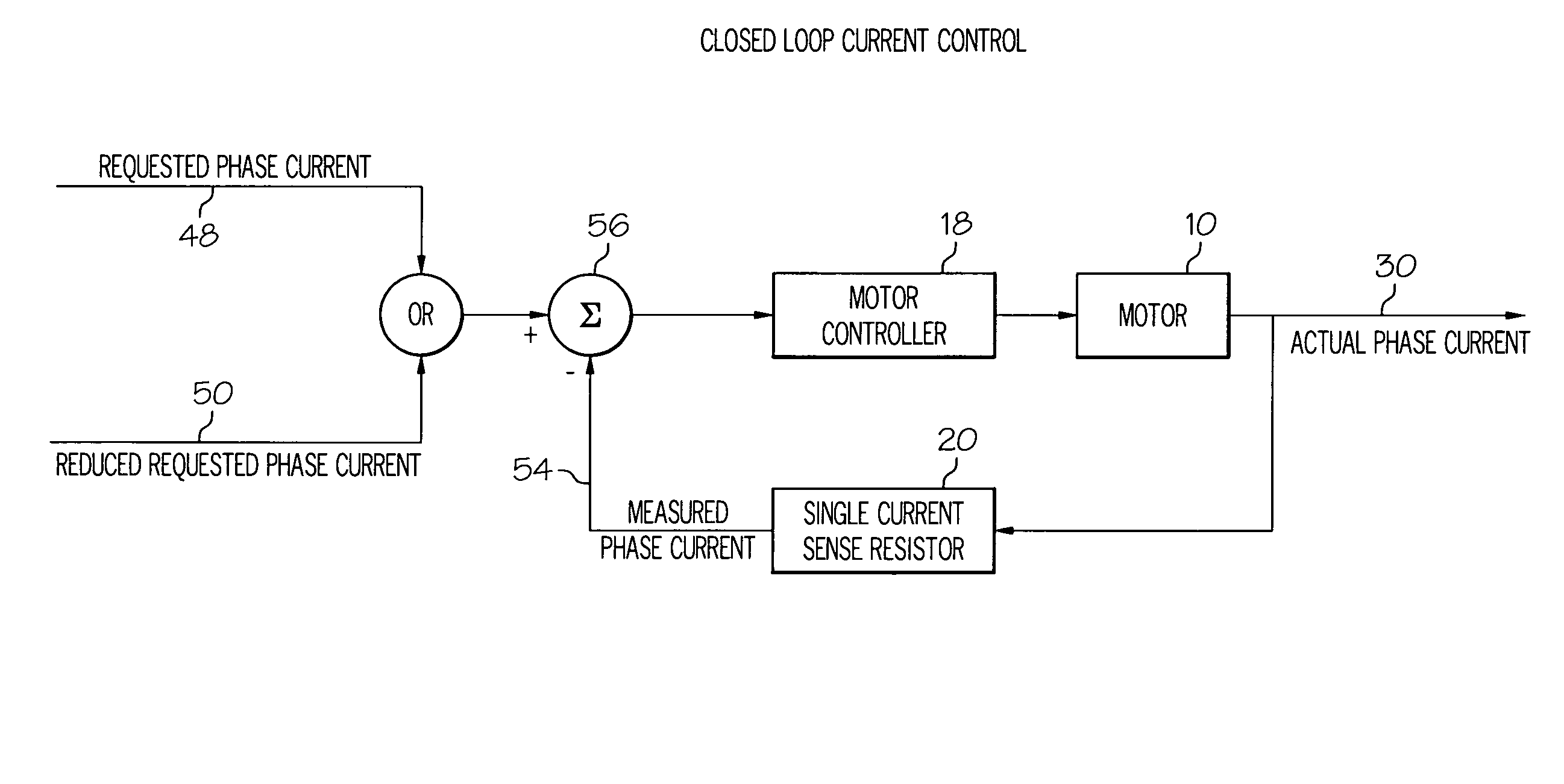
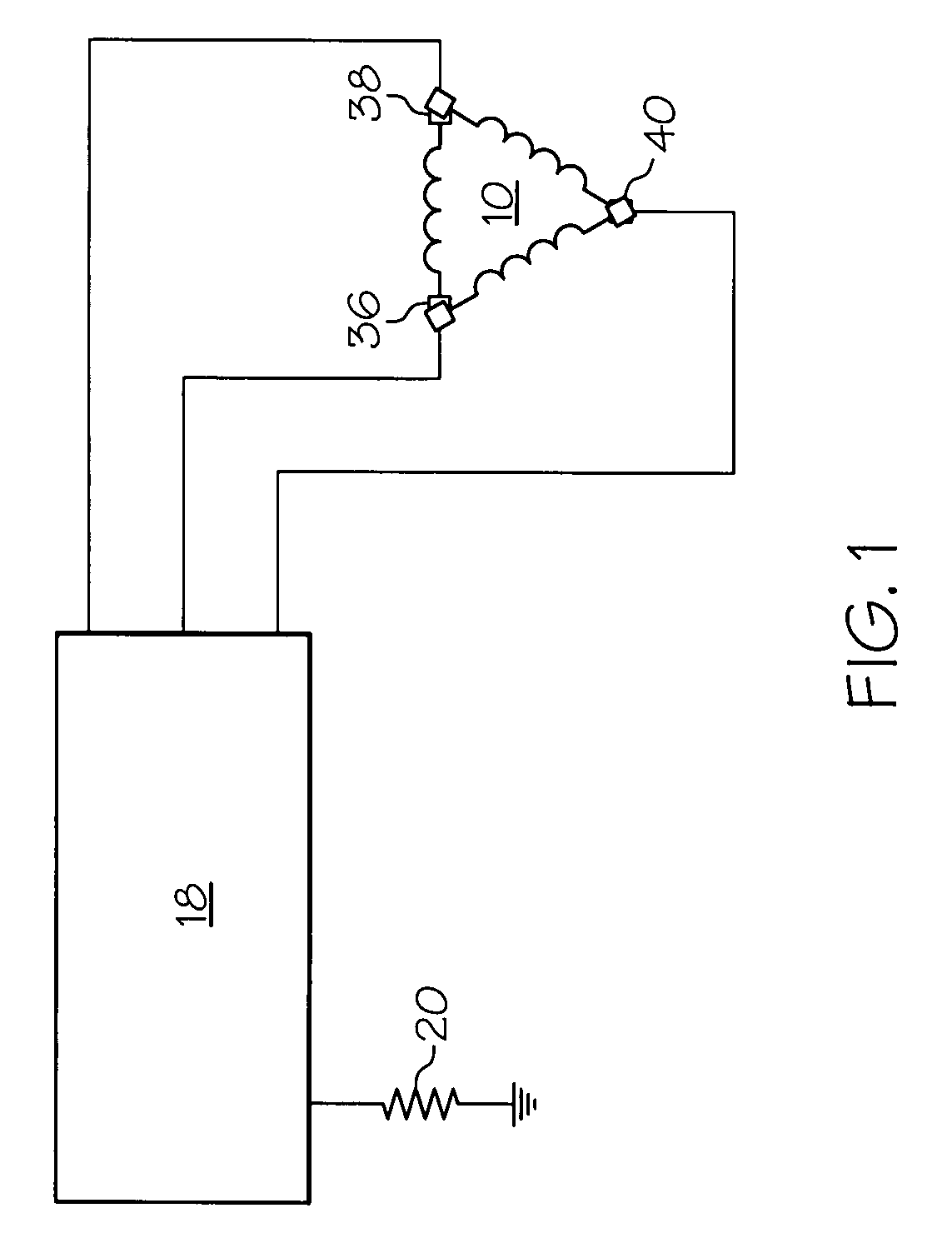
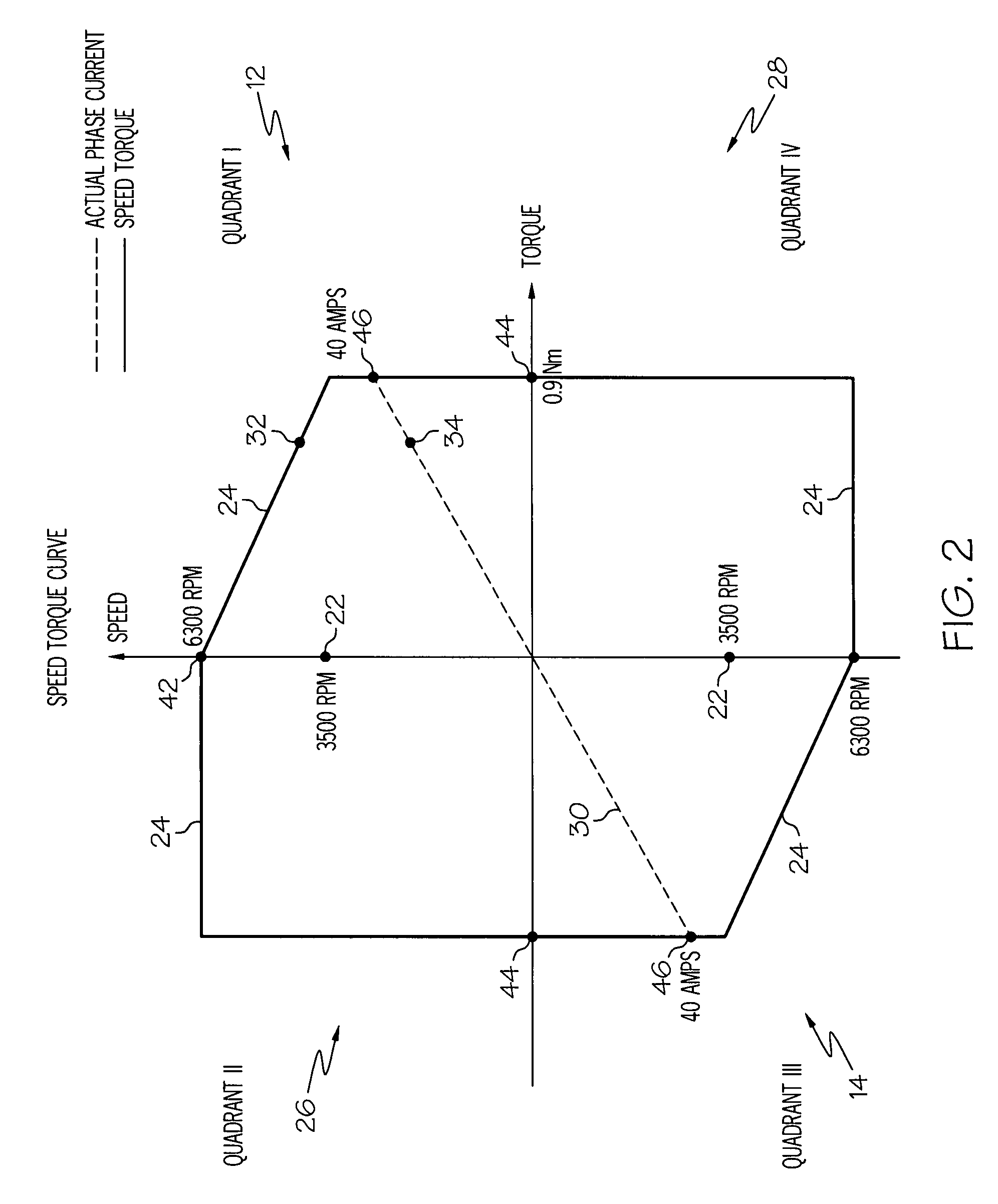
Method for operating a delta wound three-phase permanent magnet brushless motor. A transition speed is determined in a quadrant of a speed versus torque curve above which speed continues to increase while current / torque decreases wherein actual phase current can be controlled in a current control modification manner which reduces requested phase current. The modification manner is determined for a quadrant, wherein a controller can use the modification manner to reduce the requested phase current to control the actual phase current when the speed is above the transition speed. The motor is controlled in a quadrant wherein, when the motor has a speed above the transition speed, the controller reduces the requested phase current in the modification manner and the controller supplies the actual phase current to the motor using the reduced requested phase current and using measured phase current of the motor derived from using a single current sense resistor.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC +1
System and method for dynamic field weakening
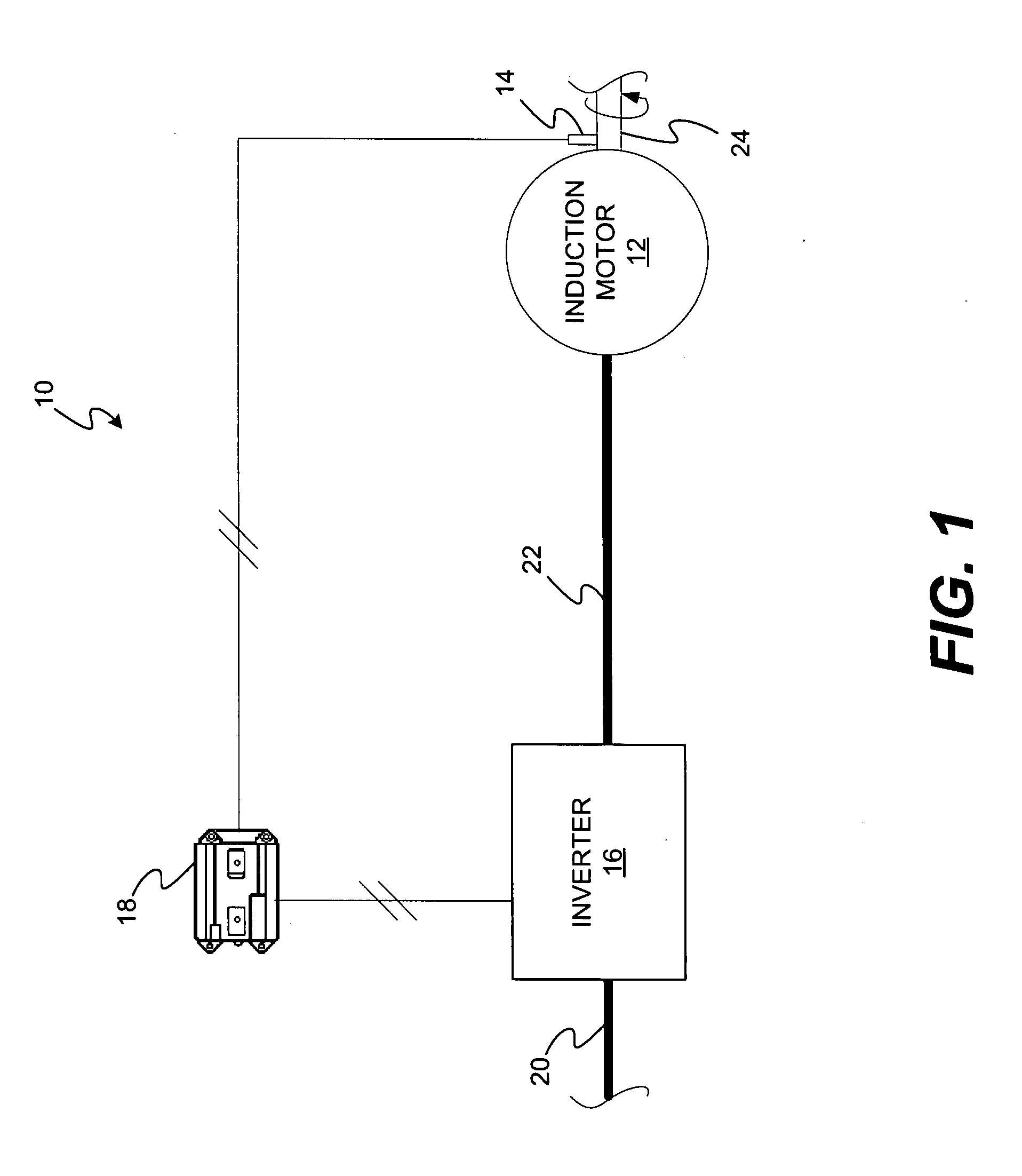
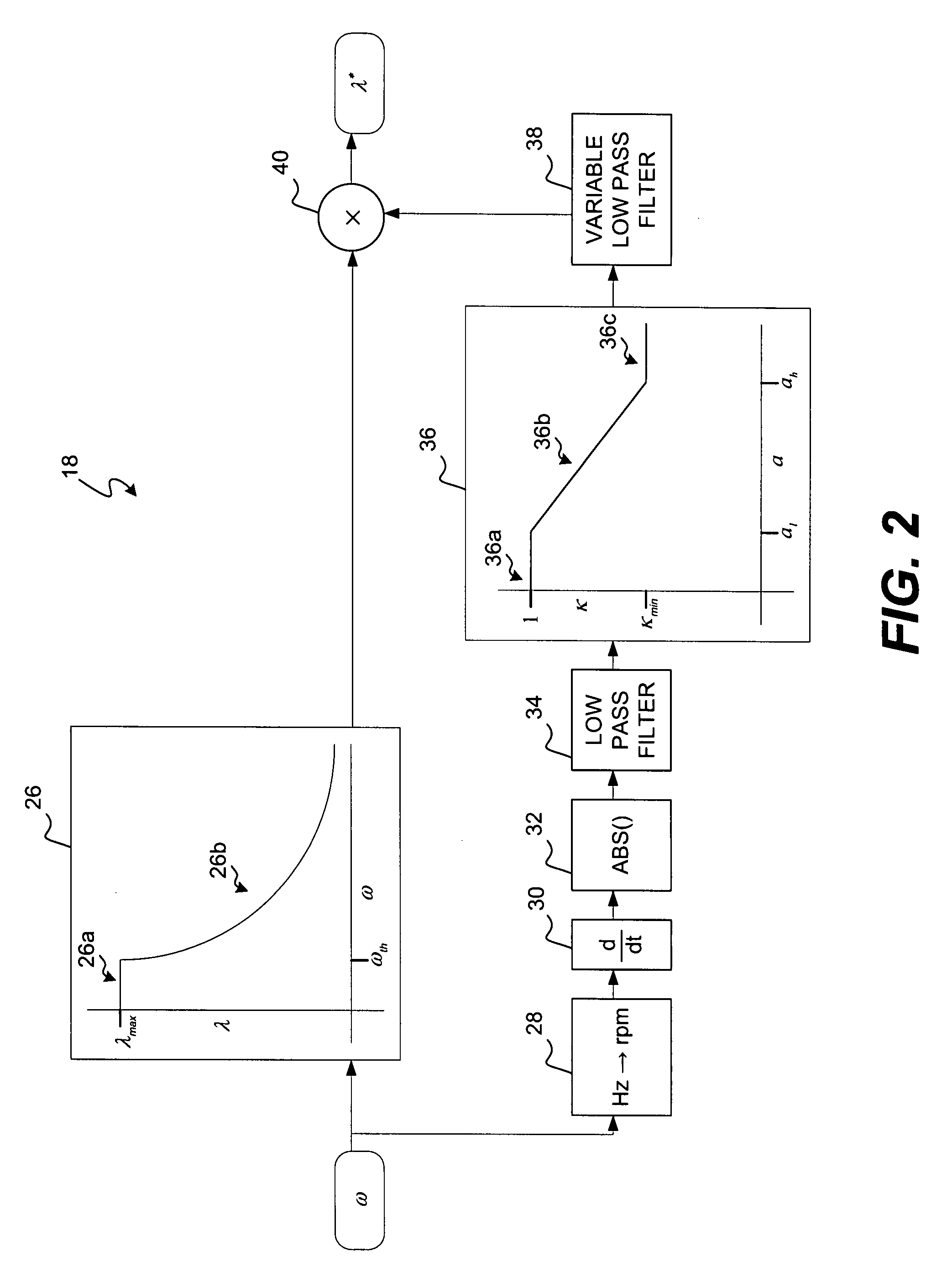
InactiveUS20090001924A1Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersDynamic fieldControl system
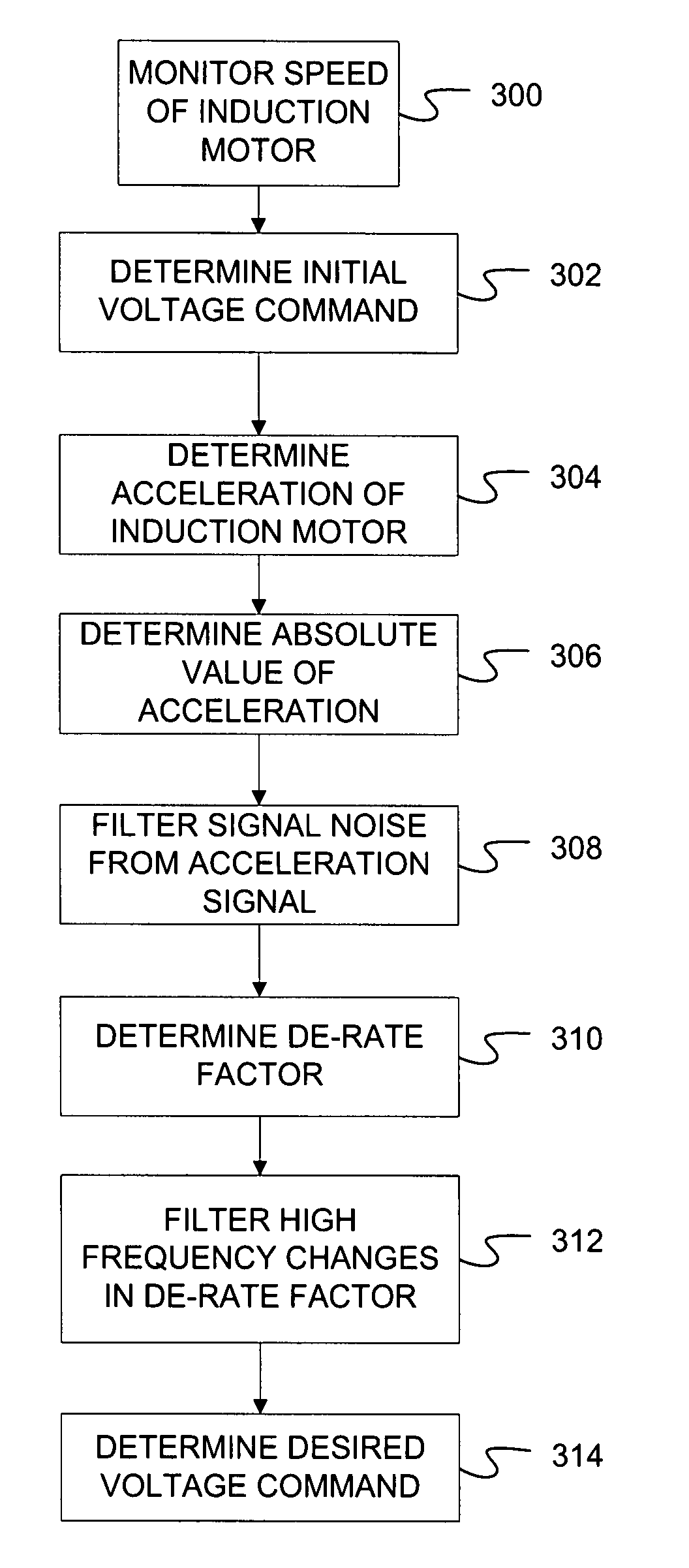
A field weakening control system for use with an induction motor is disclosed. The field weakening control system has a sensing device configured to generate a signal indicative of a speed of the induction motor and a controller. The controller is configured to determine an initial voltage command based on the signal and determine an acceleration of the induction motor based on the signal. The controller is also configured to generate a desired voltage command based on at least one of the initial voltage command and the acceleration.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Popular searches
AC motor angular speed control Dynamo-electric brake control Dynamo-electric gear control Synchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnets Magnetic circuit rotating parts Field or armature current control Dynamo-electric converter control Inorganic material magnetism Electric generator control Metal working apparatus
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com