Time-interval-based feature identification and fast search method for hotspot path
A hotspot path and feature recognition technology, applied to road network navigators and other directions, can solve problems such as not allowing users to choose the time period they are interested in, unfavorable use of frequency roads, and no online query solution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
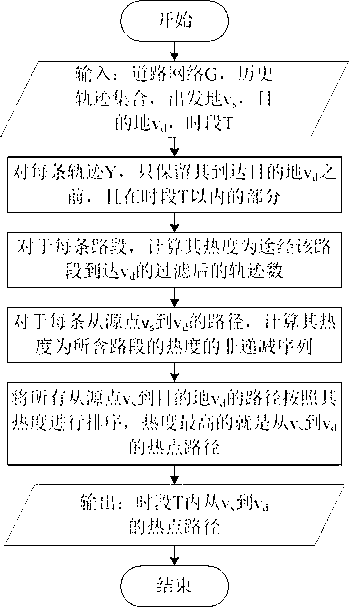
[0092] Embodiments of the present invention provide a feature recognition method for hotspot paths, such as figure 1 shown. Input parameters include: road network G, historical trajectory collection, starting point v s , destination v d , and the period of interest T. Specifically include the following steps:
[0093] a1. For each historical trajectory, only keep its destination v d before (including v d ), and the part within T.
[0094] a2. Calculate the heat of each road section to reach v through this road section d The number of (filtered) historical trajectories for ;
[0095] a3. For each item from v s to v d The path of , the calculation of its heat is a non-decreasing arrangement of the heat of the road section it passes through;
[0096] a4. Change all from v s to v d The paths of all are sorted according to their popularity, and the most popular path is in the time period T, starting from v s to v d hotspot path.
[0097] The historical trajectory acc...
Embodiment 2
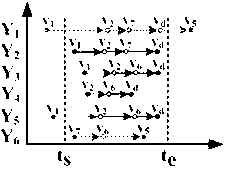
[0116] The embodiment of the present invention provides the basic principle and logical structure of index CFMI. The basic principle of CFMI is to recover a large number of trajectories by reading a small number of dominant trajectories, such as Figure 4 shown. Suppose trajectory Y passes through node v i , with Y (*,vi) Mark trajectory Y to reach v i before (including v i ) sub-trajectories, use Path(Y (*,vi) ) marked Y (*,vi) path passed. For any other path v i The trajectory Y', if either Path(Y (*,vi) ) and Path(Y' (*,vi) ) same, or Path(Y (*,vi) ) is not Path(Y' (*,vi) ), we call Y a node v i dominant trajectory. exist Figure 4 in, v i is a black node in the road network. A total of six trajectories (Y1 to Y6) reach this node. Note that the path traversed by trajectories Y2 and Y3 is included in trajectory Y1, the path traversed by trajectories Y4 and Y5 is contained in trajectory Y6, and the path traversed by Y1 and Y6 before reaching the black node is...
Embodiment 3
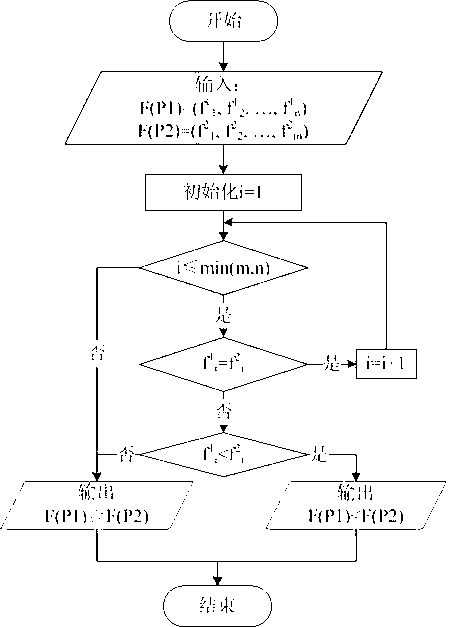
[0129] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method and process for creating a heat map, such as Figure 6 shown. Input road network G(V, E), destination v d And the time period T of interest, the heat map G f The specific steps to create are as follows:
[0130] c1. Use the adjacency matrix FG to represent based on (v s , v d , T) heat map G f , all elements in FG are initialized to 0;
[0131] c2. Look up the index CFMI and return two sets: the track record set TR and the dominant track record set DOM. Among them, the set TR stores all the processes (v d , T) is not empty after filtering (that is, the trajectory has passed v in T d ) trajectory information, including (tid, t start , did, sloc), note that tid is the unique identifier of the trajectory; the set DOM stores the information of the dominant trajectory of all the trajectories in the set TR, including (did, len), where did is the only identifier of the dominant trajectory, and len is the arriva...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com