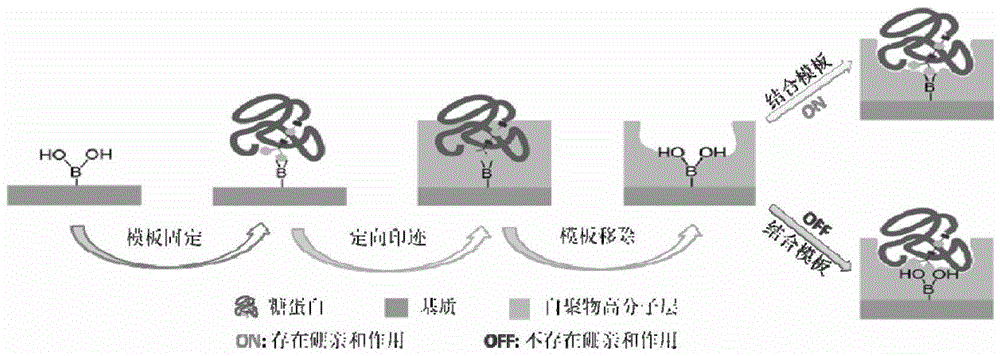
A controllable and versatile method for directional surface imprinting and applications of the resulting molecularly imprinted polymers
A molecular imprinting and surface imprinting technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, ion exchange, ion exchange regeneration, etc., can solve problems such as poor controllability and versatility, and achieve large binding capacity, fast binding and analysis speed, and imprinting efficiency. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Preparation of polymer-modified glass flakes
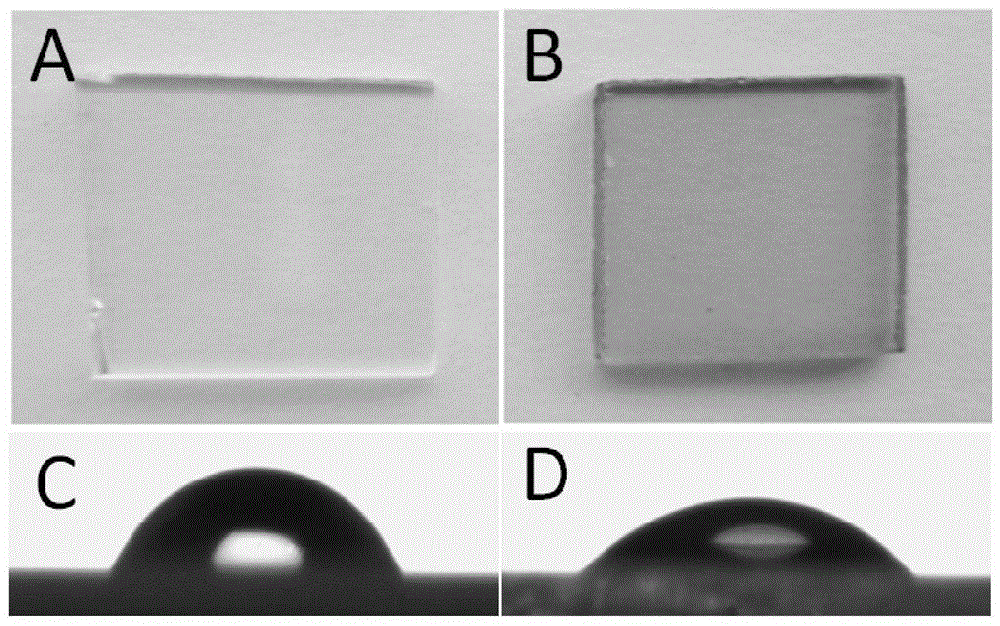
[0031] First prepare the pre-polymerization solution: the pre-polymerization solution is a 0.1M, pH8.5 phosphate buffer containing 2.0mg / mL dopamine, 1.6mg / mL m-aminophenylboronic acid and 1.2mg / mL ammonium persulfate. After the pre-polymerization solution is mixed evenly, glass flakes are added, and polymer-modified glass flakes can be obtained by self-polymerizing at room temperature for 24 hours. The result is as figure 2 b. with untreated glass ( figure 2 A) Contrast, showing a noticeably darker color.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Contact Angle Test of Polymer Modified Glass Sheets
[0033] The cleaned untreated glass piece and the glass piece obtained in Example 1 were dried and used for the contact angle test respectively. The results are as follows figure 2 C, 2D. Among them, the contact angle of the polymer-modified glass sheet was 38.9°, and that of the untreated glass sheet was 66.1°. Obviously, the polymer-modified glass flakes are more hydrophilic.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: the investigation of the relationship of polymer thickness with time
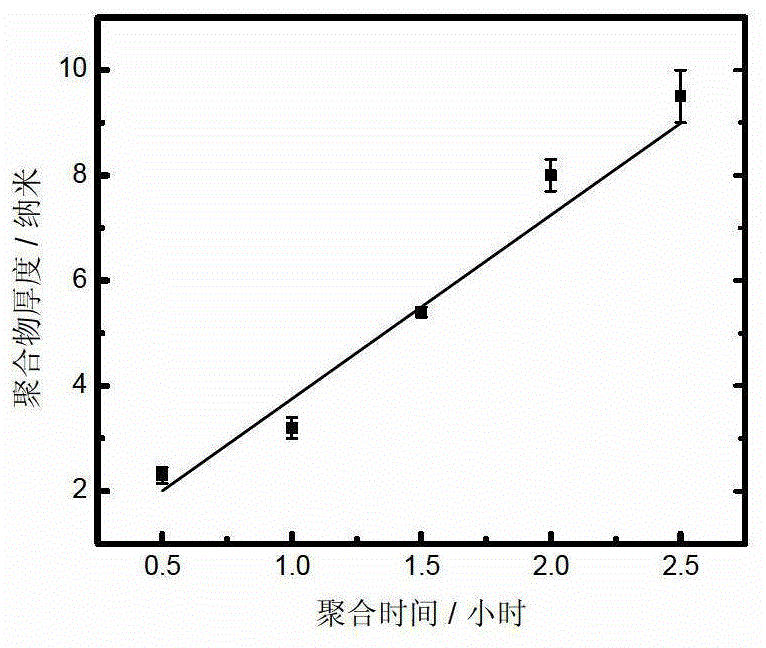
[0035] Place a group of clean glass slides in 0.1M, pH 8.5 phosphate buffer containing 2.0mg / mL dopamine, 1.6mg / mL m-aminophenylboronic acid and 1.2mg / mL ammonium persulfate, and control the polymerization time respectively for 0.5h, 1.0h, 1.5h, 2.0h and 2.5h. The aggregate thickness was then characterized by atomic force microscopy (AFM). The result is as image 3 . In the figure, the linear correlation coefficient r2=0.95, and the slope s=3.5±0.4nm / h, which shows that the thickness of the polymer has a good linear correlation with the time growth, which provides a guarantee for the controllability of this technology.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com