RFID (radio frequency identification) reader based on adaptive smart antennae
A smart antenna and reader technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve problems such as limited effective identification area, unrecognized tags, lost tags, etc., to improve the degree of digitization and self-adaptive ability, expand the effective identification area, and increase the maximum identification effect of distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the invention or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only For some embodiments of the present invention, those skilled in the art can also obtain other designs according to the drawings without paying creative labor.
[0028] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but the embodiments of the present invention are not limited thereto.
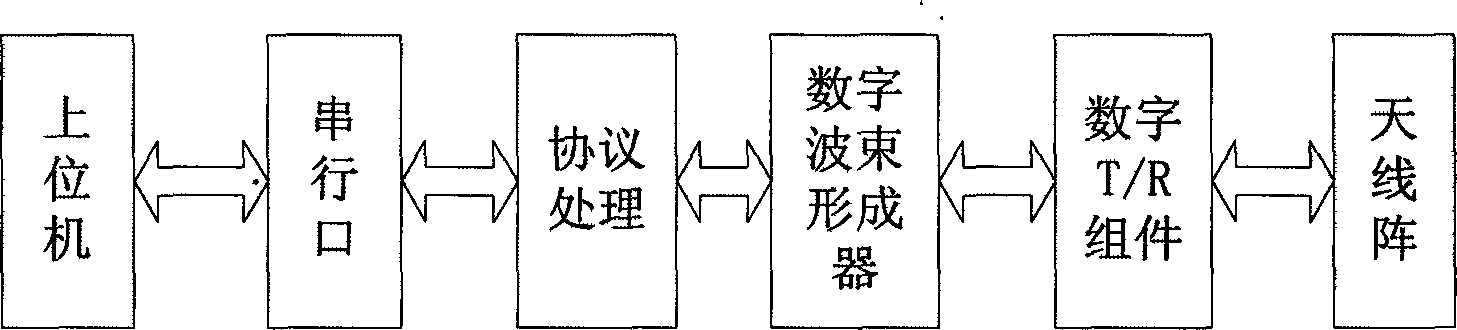
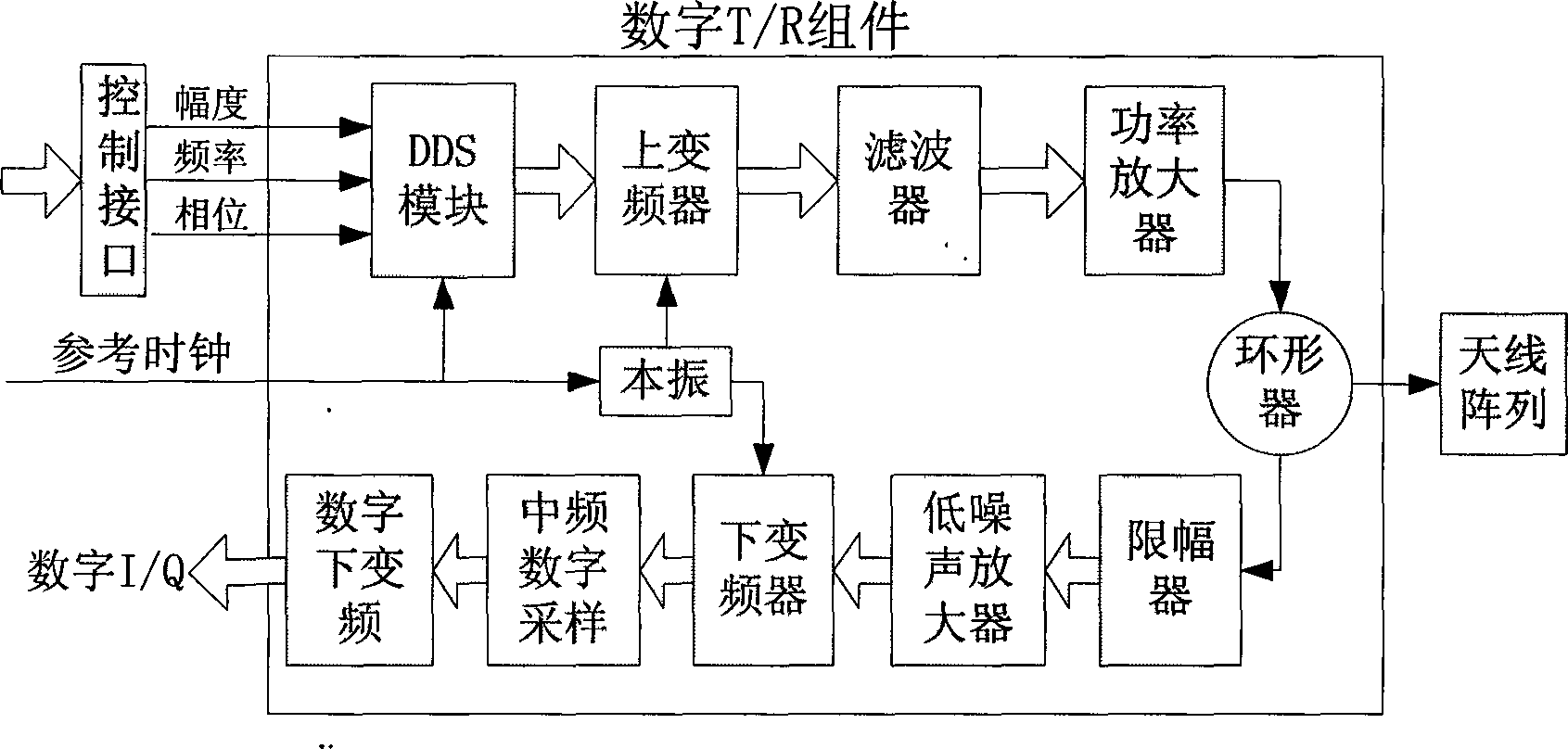
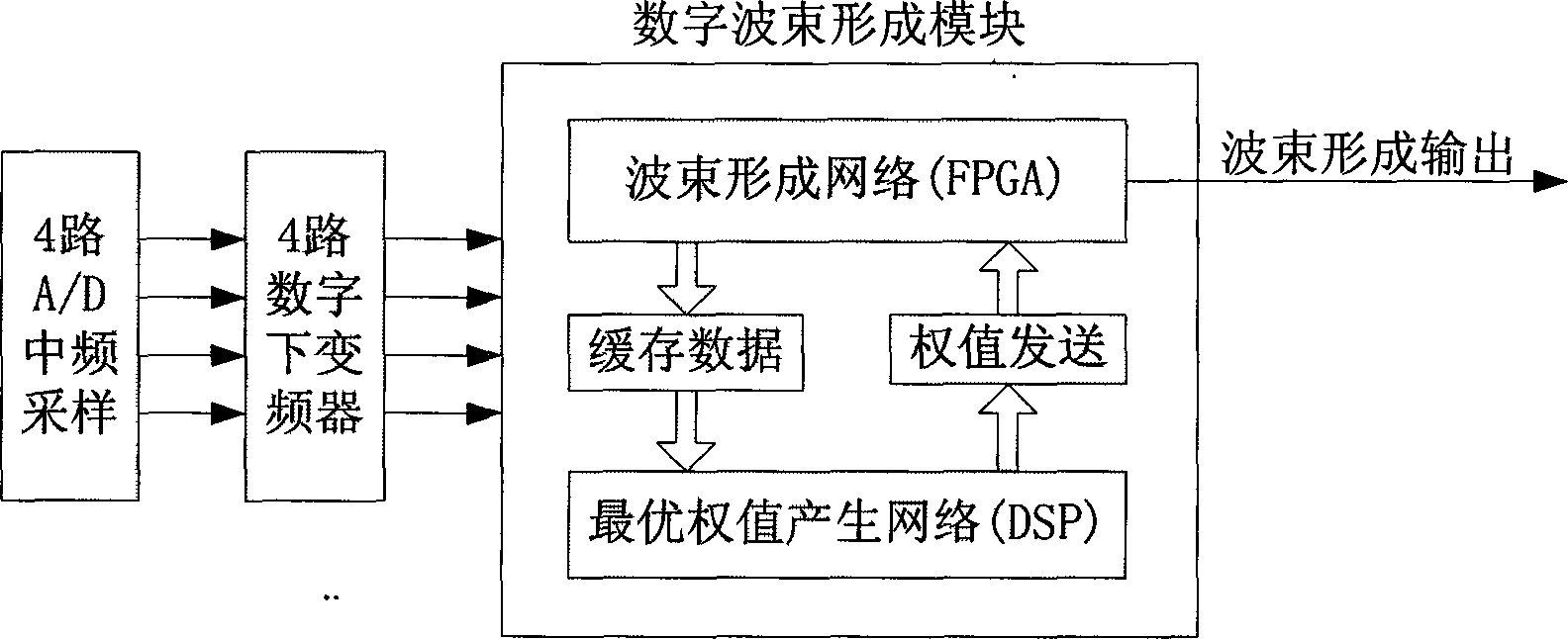
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the reader includes a protocol processing module, a digital beamformer, a digital transmission / reception component (T / R component) and an antenna array composed of multiple antenna...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com