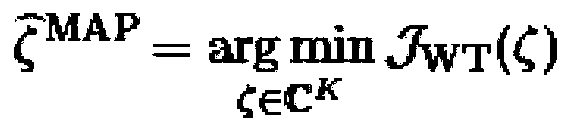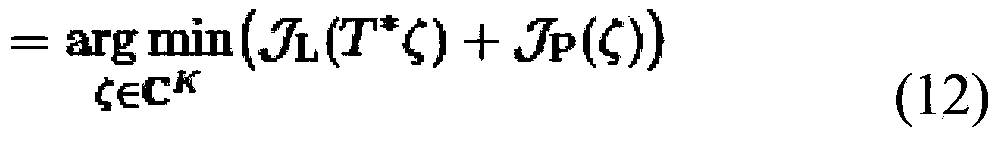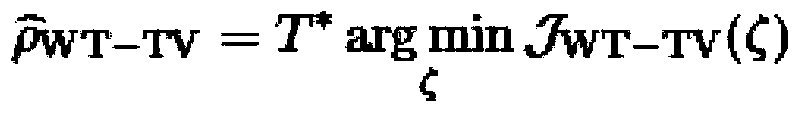Method for performing parallel magnetic resonance imaging
A technology of magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance imaging, which is applied in the direction of measuring magnetic variables, measuring devices, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of high reduction factor being infeasible and so on.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0058] Before describing the present invention in detail, some basic facts about pMRI, especially SENSE, need to be reviewed.
[0059] MRI is an imaging technique that can be performed in 2D (two-dimensional) or directly in 3D (three-dimensional) depending on the associated RF pulse design. In the 2D case, adjacent slices are used to cover the volume. Since this method enables faster k-space scanning, PMRI can be used in both cases regardless of its resolution (ie in 2D or 3D). For brevity, only the 2D case is shown in the following.
[0060] A bank of C-coils is used to measure the spin density p into the object under study, eg the brain in the patient's head. Image acquisition is based on a specific imaging sequence; in an exemplary embodiment of the invention, anatomical MRI is based on a 3DMPRAGE sequence, whereas the involved functional MRI is performed using 2D echo planar imaging (EPI). The following description will focus on the 2D case; then, the signal d received ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com