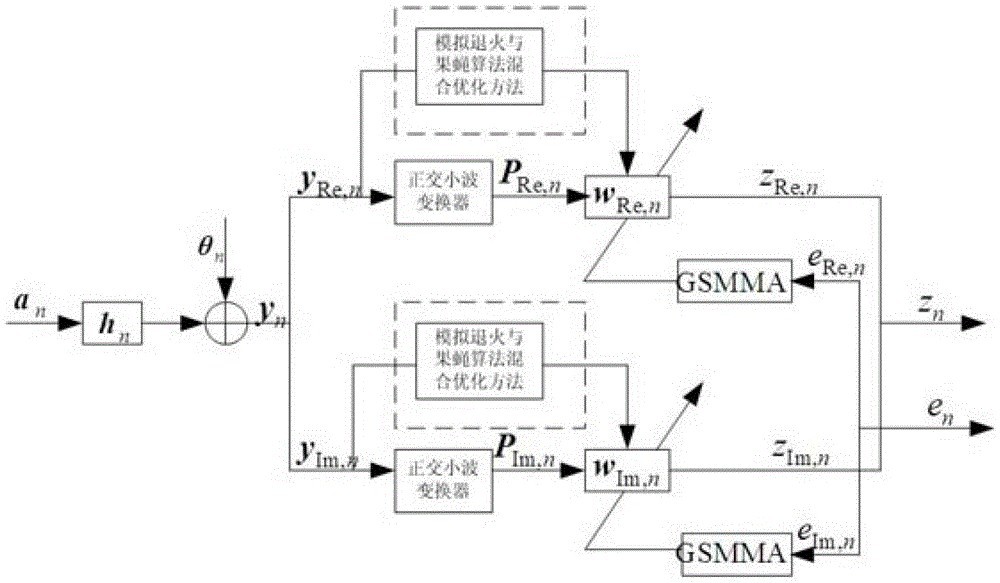
Simulated Annealing and Drosophila Hybrid Optimal Wavelet Generalized Discrete Multimodal Blind Equalization Method
A technology of multi-mode blind equalization and simulated annealing, which is applied to baseband system components, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, etc., can solve problems such as weak global search ability, poor initial value robustness, and slow convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
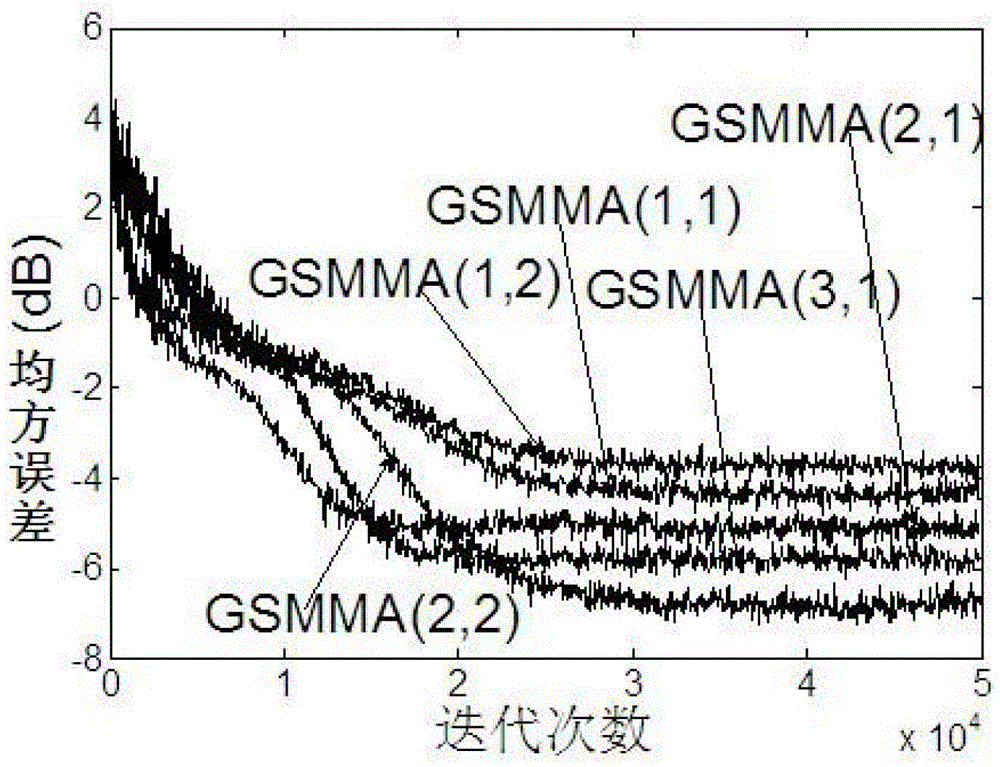
[0124] Using two-path underwater acoustic channel h=[0.3132,-0.1040,0.8908,0.3134], the transmitted signal is 256QAM; the equalizer weight is 16; the signal-to-noise ratio is 35dB; the center tap is used for initializing; other parameter settings are shown in Table 1. As shown, the results of 600 Monte Carlo simulations are shown in Figure 2:
[0125] Table 1 Simulation parameter settings
[0126] p,q value p=1,q=1p=1,q=2p=2,q=1p=2,q=2p=3,q=1
[0127] Simulation step size 0.0000420.00000820.0000040.000000030.0000004
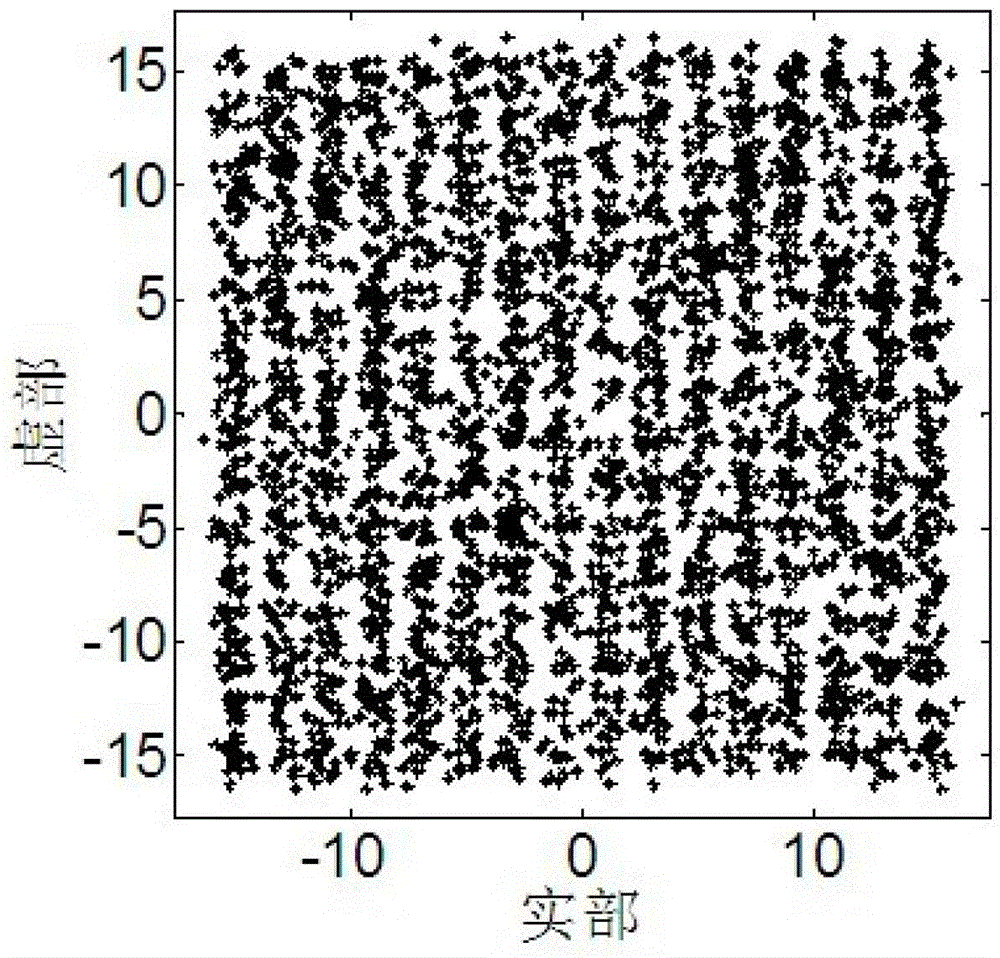
[0128] Figure 2 shows that GSMMA can achieve high-order QAM signal equalization, and when p=2 and q=2, GSMMA has the best equalization effect. Figure 2a It can be seen that when p=2 and q=2, the mean square error of GSMMA is the smallest, the mean square error curve is the smoothest, and the convergence trend is the most stable. Figure 2b to Figure 2f The comparison of the output signal diagrams with different values of p and q shows that when p=2, q=2, the output co...
Embodiment 2
[0129] [Embodiment 2] 256QAM signal optimization and equalization example
[0130] Channel h=[0.005,0.009,-0.024,0.854,-0.218,0.049,-0.016]; transmit signal is 256QAM; equalizer weight is 16; signal-to-noise ratio is 35dB; p=2,q=2; population Scale 500; Drosophila initialization position vector [-0.05,0.05]; Drosophila population iteration step value [-0.01,0.01]; GSMMA and WT-GSMMA are initialized with a center tap; the initial temperature of simulated annealing is T=30; temperature Cooling coefficient α=0.89; k=1; other parameter settings, as shown in Table 2, 400 Monte Carlo simulation results, as shown in Figure 4.
[0131] Table 2 Simulation parameter settings
[0132]
[0133] Figure 3a It shows that for high-order QAM signals, the method SAFOA-WT-GSMMA of the present invention has stability and applicability, and the steady-state error is the smallest, about 7.6dB, which is 2dB lower than FOA-WT-GSMMA, WT-GSMMA and GSMMA respectively. , 3dB and 3.8dB; the fastest convergenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com