Overheating protection circuit for power transistor
A technology of overheating protection circuit and power transistor, which is applied in the direction of output power conversion device, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of power transistor base pulling down.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
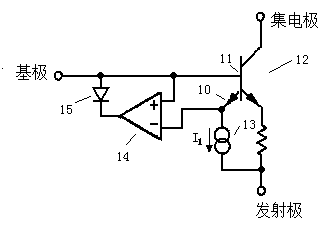
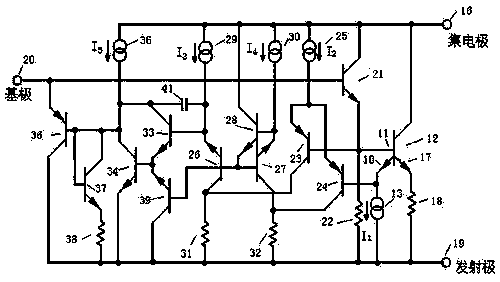
[0013] Simplified schematic of a power transistor with its sense emitter and thermal control circuitry such as figure 1 shown. The sensing emitter 10 and the power transistor 12 share a base 11 . A current source biases the sense emitter at a current I 1 , so that the emitter-base potential is zero at the desired extreme temperature. The operational amplifier 14 acts as a controller. When the potential of the sense emitter 10 is lower than the potential of the base 11, the output of the op amp is high and is prevented by a diode 15 from coupling to the base circuit. If the sense emitter potential rises to the base potential, the output potential of the op amp will drop, absorbing the drive to the base through this diode. It is convenient to zero the sensing potential at extreme temperatures. A non-zero value would require a reference voltage to be generated at the input circuit of the op amp. If protecting the power transistors was the only consideration, the design of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com