Application of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (ACAT2) inhibitor in liver cancer growth inhibition
A cholesterol acyl and acyl coenzyme technology, applied in the fields of biomedicine and pharmacy, can solve the problems of unsuccessful liver cancer intervention and unclear molecular mechanism of liver cancer.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
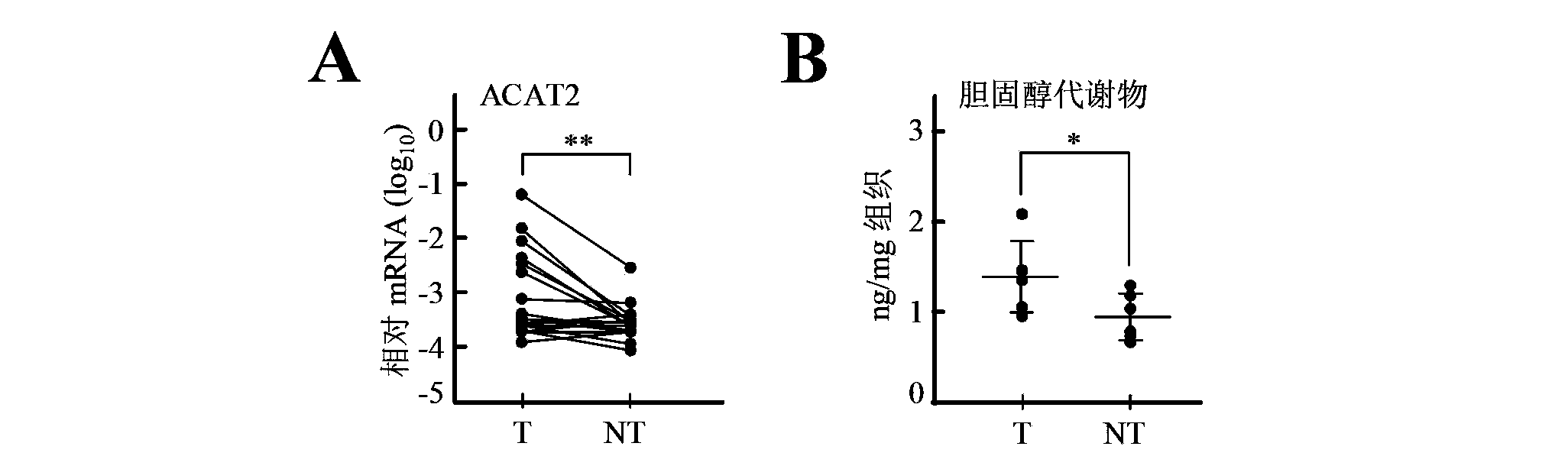
[0136] High expression of ACAT2 in human liver cancer tissues is associated with accumulation of cholesterol metabolites
[0137] In this example, the inventors used 19 pairs of cancer tissues and paracancerous tissues of liver cancer patients to first detect the mRNA level of ACAT2 gene and perform statistical analysis.
[0138] The results showed that, compared with the adjacent tissue cells, the mRNA level of ACAT2 gene in liver cancer tissue cells was significantly increased ( figure 1 A). Next, the levels of cholesterol metabolites in liver cancer and adjacent tissue cells were detected. The results showed that the levels of cholesterol metabolites in 6 pairs of liver cancer tissues were significantly higher than those in adjacent tissues ( figure 1 B).
[0139] The above results indicated that the high expression of ACAT2 gene in liver cancer tissues was related to the accumulation of cholesterol metabolites.
Embodiment 2
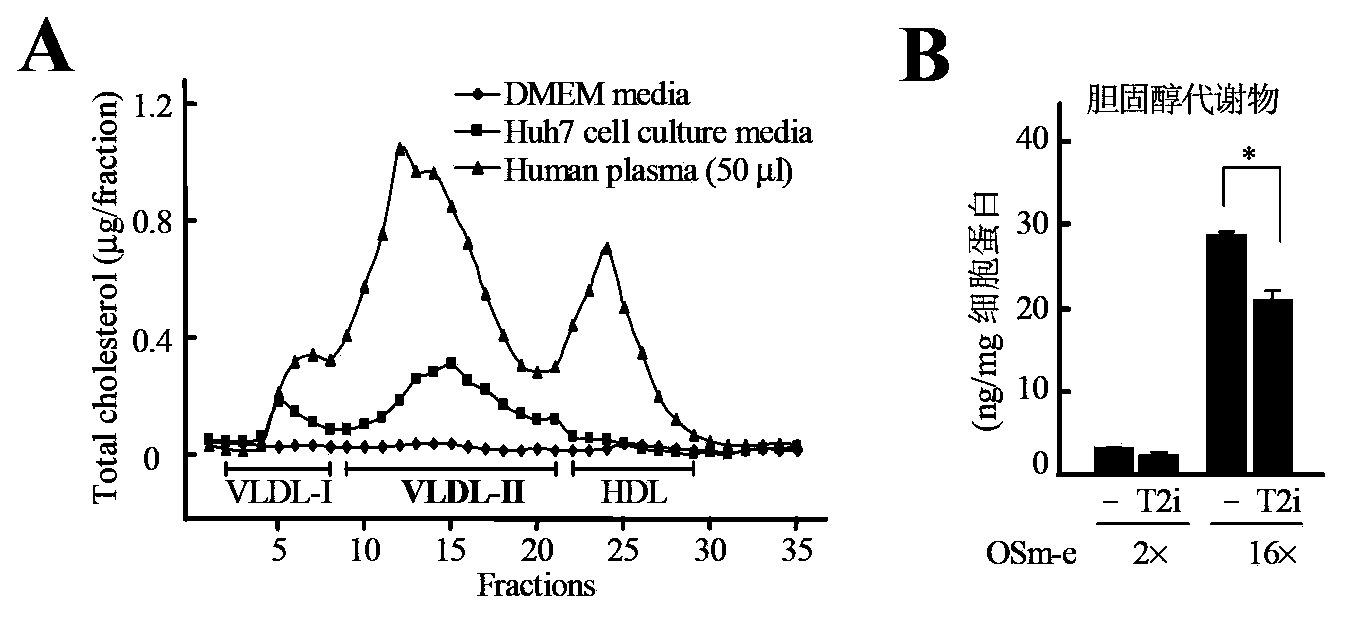
[0141] ACAT2 is involved in the secretion and efflux of cholesterol metabolites in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
[0142] In order to study the role of ACAT2 in the metabolism of cholesterol metabolites in liver cancer cells, the inventors detected intracellular and secreted cholesterol metabolites (27- and 24-hydroxycholesterol) in the liver cancer cell line Huh7 under the condition of exogenously delivering high amounts of cholesterol metabolites (27- and 24-hydroxycholesterol). Extracellular cholesterol metabolite content. After the lipoprotein secreted by Huh7 cells was separated by FPLC, the content of cholesterol metabolites was detected by GC-MS.
[0143] The results showed that the liver cancer cells Huh7 could secrete three kinds of lipoproteins (named VLDLI, VLDLII and HDL in turn), and the determination of the total cholesterol content showed that the cholesterol was mainly distributed in the VLDLII component ( figure 2 A); Furthermore, the treatment of ACAT2 inh...
Embodiment 3
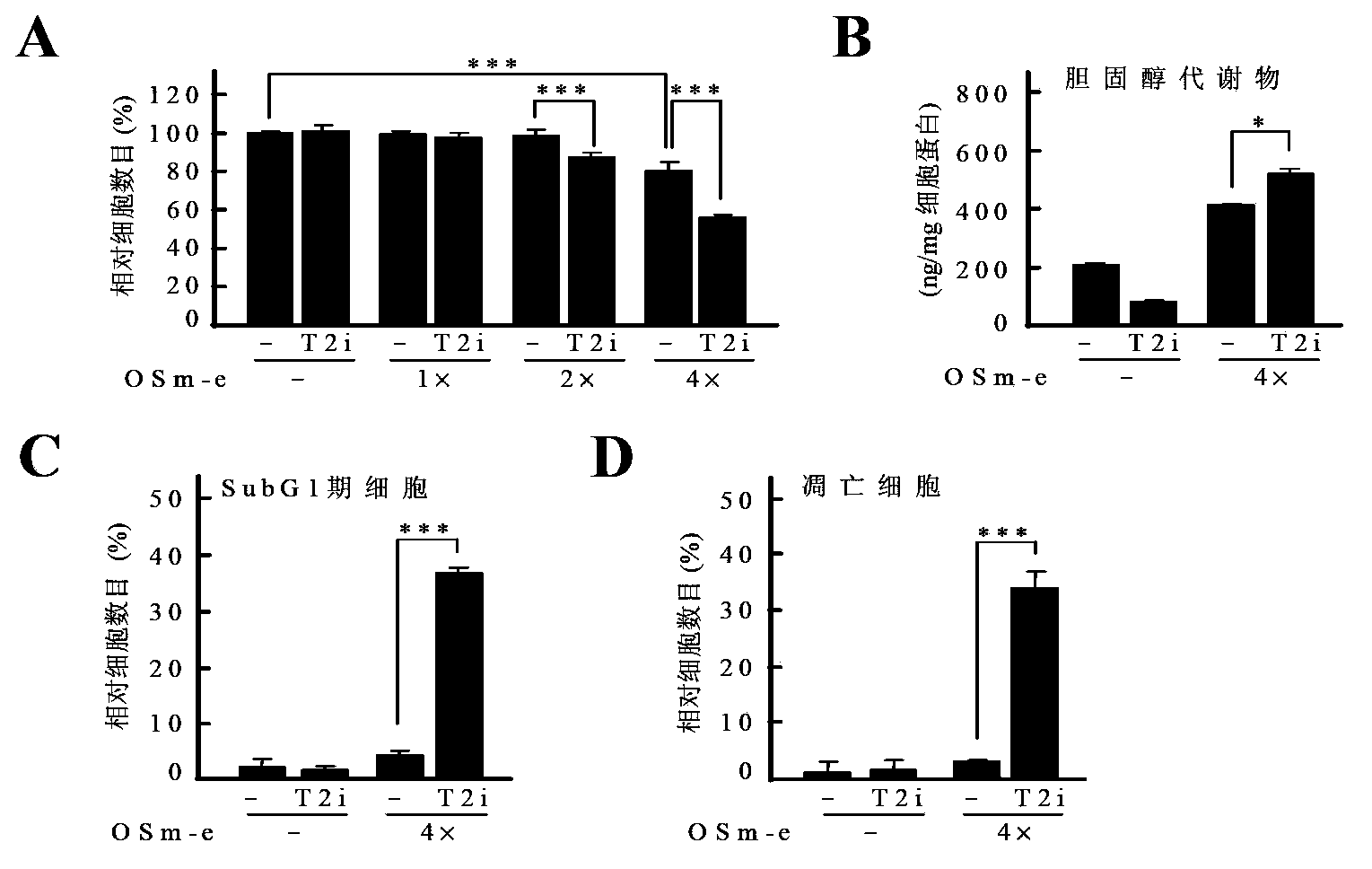
[0146] Combination of ACAT2 inhibitors and cholesterol metabolites can inhibit the growth of liver cancer cells
[0147] In this example, the inventors studied the role of ACAT2 inhibitors in inhibiting the growth of liver cancer cells.
[0148] The results of growth experiments showed that ACAT2 inhibitor had little effect on the growth of Huh7 cells under the condition of no exogenous delivery of cholesterol metabolites; while under the condition of exogenous delivery of mixture of cholesterol metabolites 27- and 24-hydroxycholesterol, with With the increase of its concentration (2× to 4×), cholesterol metabolites significantly inhibited the growth of Huh7 cells, and the combination with ACAT2 inhibitors significantly increased the inhibitory effect of cholesterol metabolites on the growth of Huh7 cells ( image 3 A).
[0149] Analysis of the content of cholesterol metabolites in Huh7 cells showed that under the condition of exogenous delivery of a mixture of cholesterol me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com