A zero-voltage control circuit for tiny signals
A zero-voltage control and micro-signal technology, applied in the control field, can solve the problems of circuit interference, high input signal requirements, and inability to perform zero-voltage for micro-signals, and achieve the effect of zero-voltage control and high detection accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
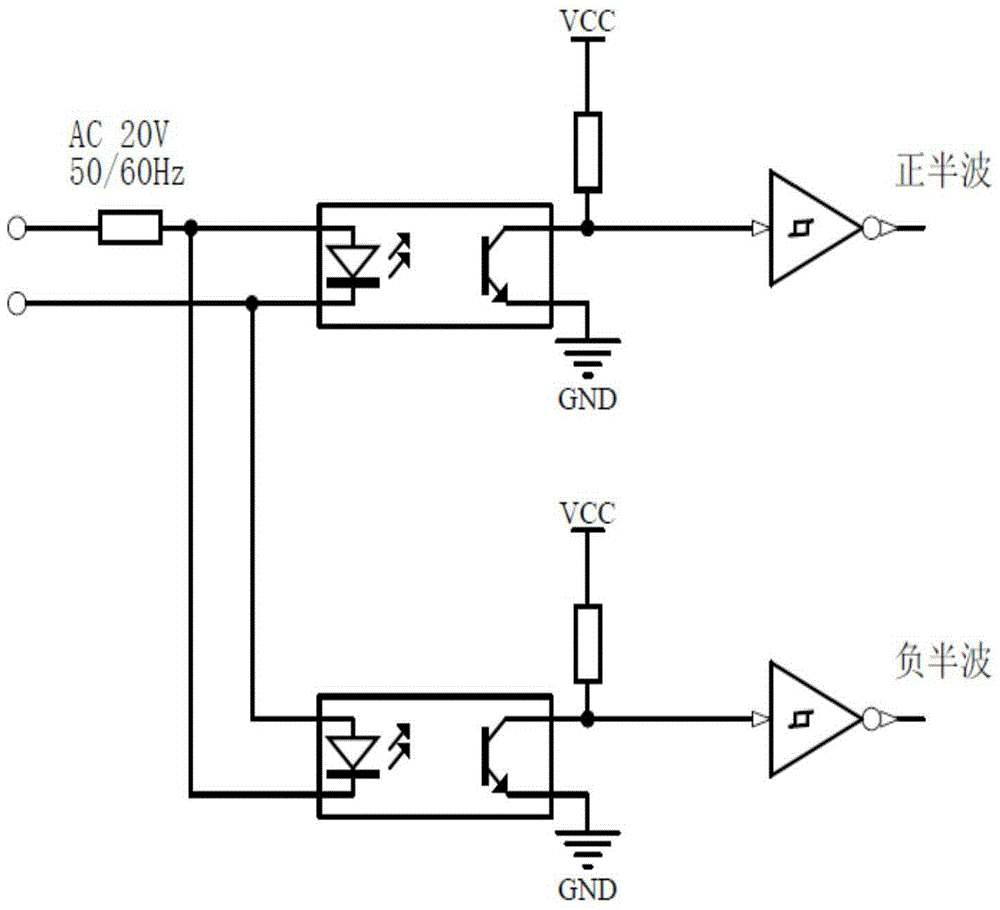
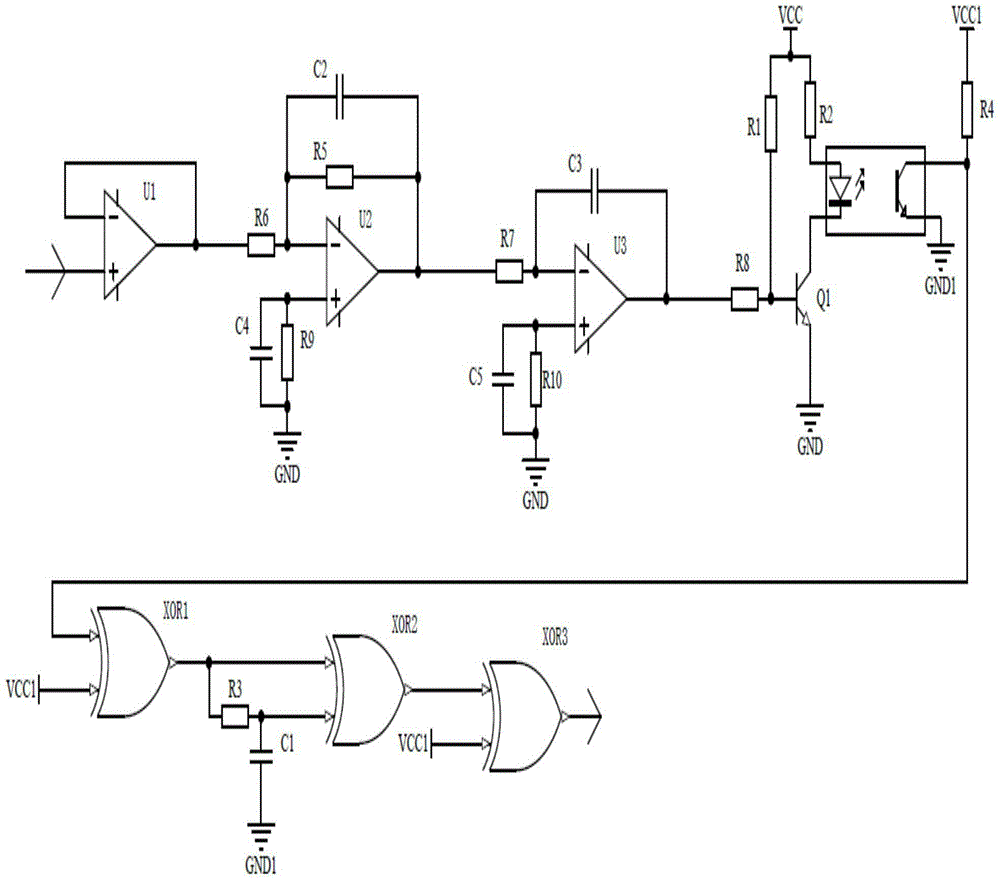
[0019] Such as figure 1 As shown, the zero voltage control circuit for tiny signals of the present invention includes:
[0020] The first operational amplifier U1, the second operational amplifier U2, the third operational amplifier U3, the first resistor R1, the second resistor R2, the third resistor R3, the fourth resistor R4, the fifth resistor R5, the sixth resistor R6, the seventh resistor Resistor R7, eighth resistor R8, ninth resistor R9, tenth resistor R10, first capacitor C1, second capacitor C2, third capacitor C3, fourth capacitor C4, fifth capacitor C5, first transistor Q1, first XOR gate XOR1, second XOR gate XOR2, third XOR gate XOR3, optocoupler, first power supply Vcc and second power supply Vcc1.
[0021] The first operational amplifier U1 constitutes a voltage follower, thereby forming an anti-interference isolation protection device for isolating the input signal from the signal source circuit and eliminating the influence of the zero-voltage control circui...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com