A method to reduce active power loss of doubly-fed induction wind turbine
A wind turbine, double-fed induction technology, applied in wind power generation, single grid parallel feeding arrangement, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the reliability and service life of the double-fed induction wind turbine, without considering the active power loss of the wind turbine, double-fed induction Problems such as large active power loss of wind turbines can improve calculation efficiency and engineering application value, facilitate safe and economical operation, and improve energy conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
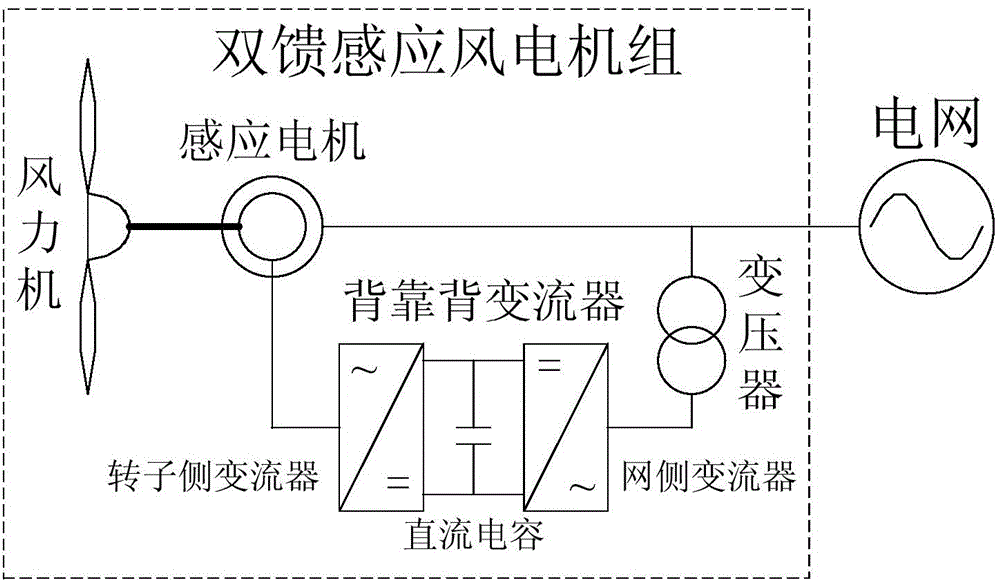
[0041] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the composition of doubly-fed induction wind turbine includes: wind turbine, induction motor, back-to-back converter composed of rotor-side converter, grid-side converter and DC capacitor, and transformer. The induction motor includes rotor and stator. The wind energy captured by the wind turbine is converted into electric energy and injected into the grid through the induction motor. The rotor converter is connected to the rotor of the induction motor to adjust the rotor speed and the reactive output of the stator; differential power and emit or absorb reactive power; the doubly-fed induction wind turbine is connected to the grid, and accepts grid active power dispatching and reactive power dispatching.
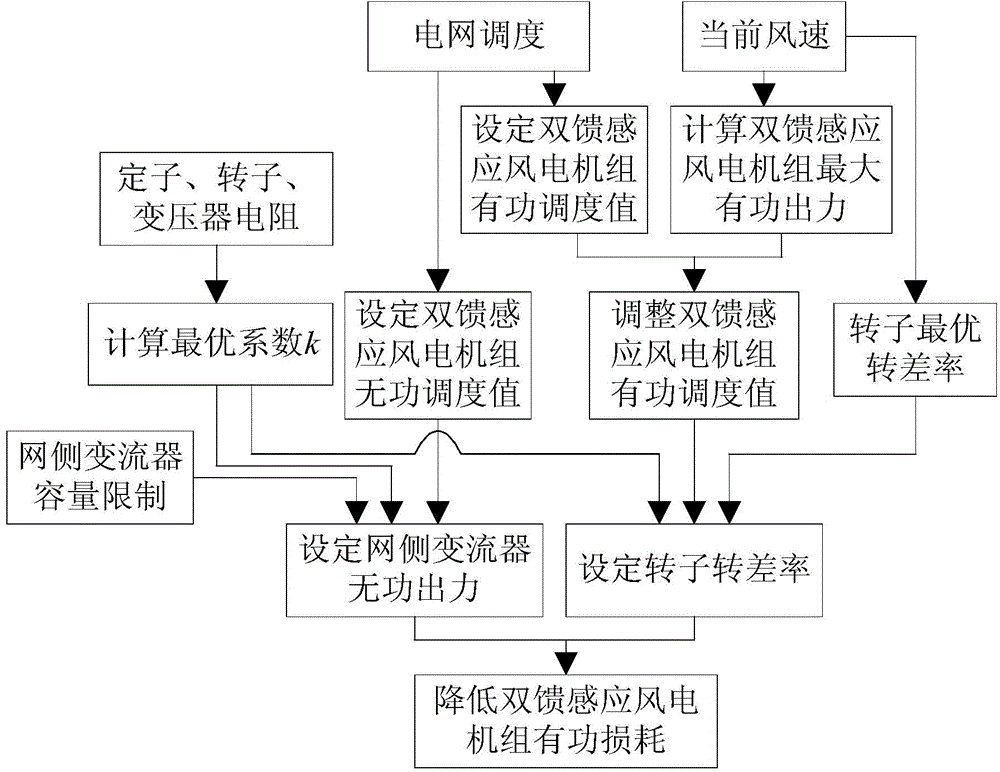
[0042] see figure 2 , a method for reducing active power loss of doubly-fed induction wind turbines is carried out as follows:
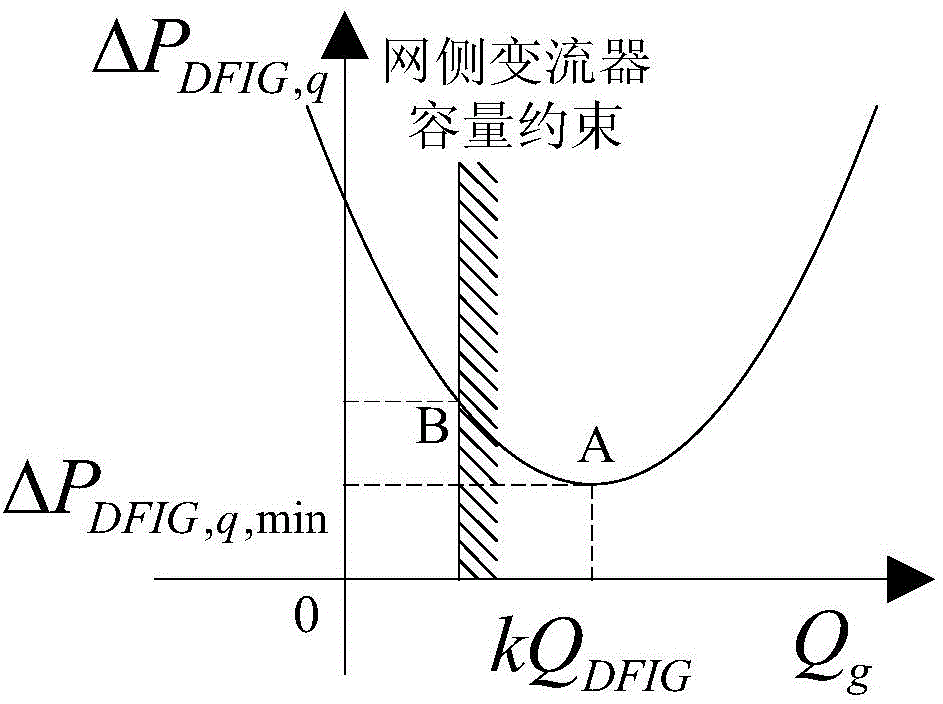
[0043] 1) Set the reactive output Q of the doubly-fed induction wind turbine dispatched by the gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com