3D Needle Localization Using 2D Imaging Probes
An imaging system, defined technology, applied in application, ultrasound/acoustic/infrasonic image/data processing, echo tomography, etc., can solve problems such as no transducer, unknown needle position, loss of original target plane, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
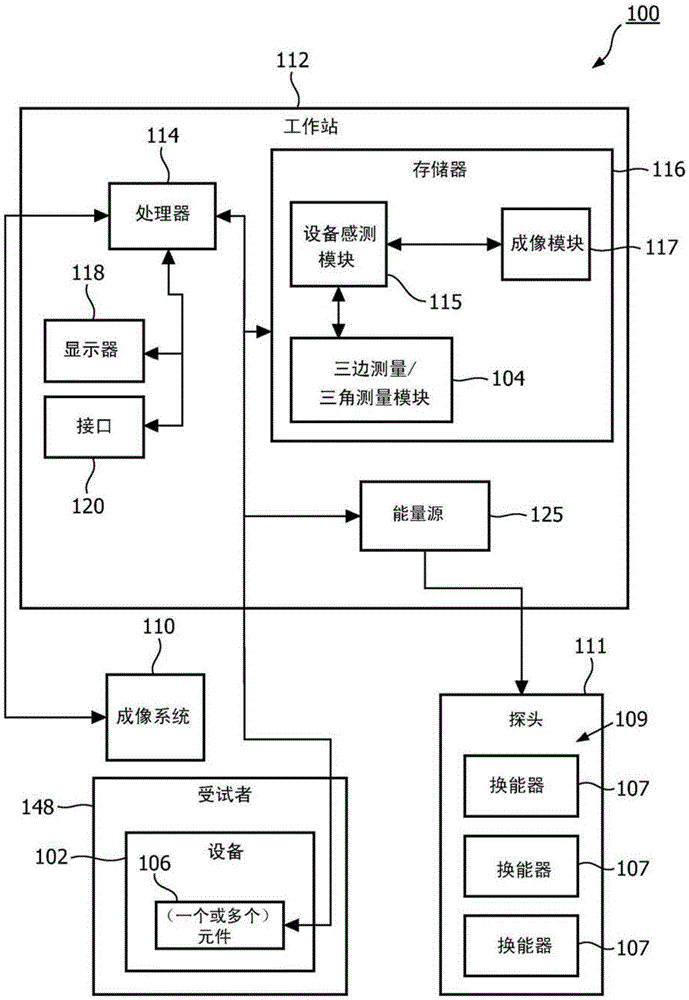
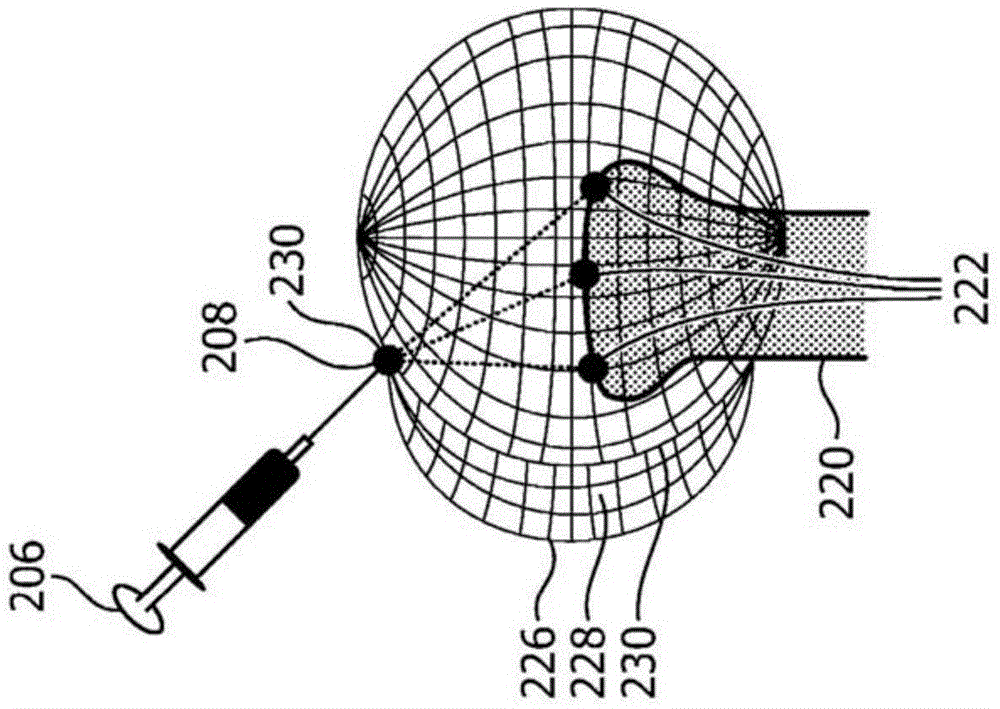
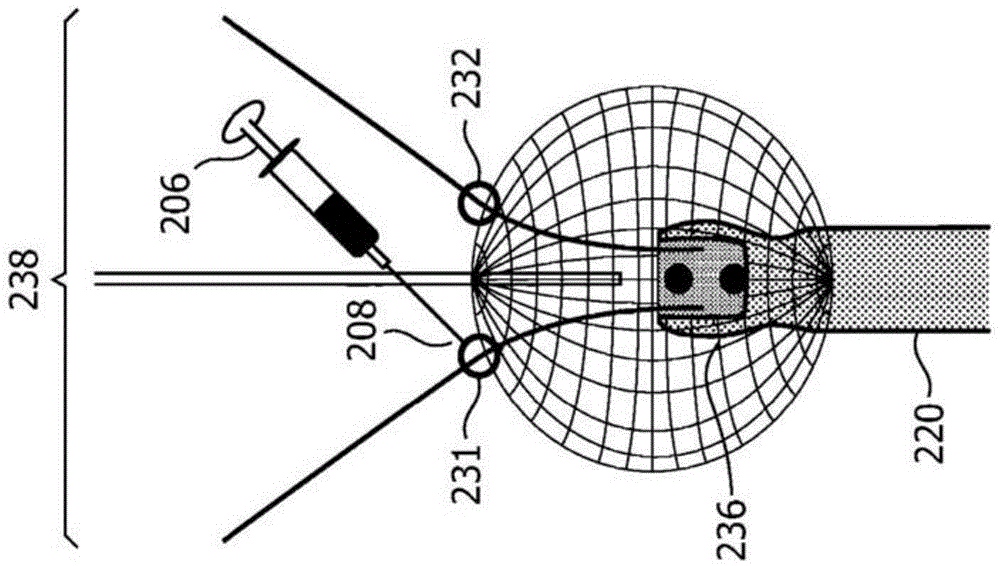
[0017] In accordance with the present principles, simultaneous imaging of the target plane, relative position, and trajectory (eg, of target anatomy relative to the target plane) of the medical device is required to avoid problems associated with losing images of out-of-plane needles during procedures. In a broad range of clinical interventions, two-dimensional (2D) visualization of the needle relative to the anatomy is achieved using a one-dimensional (1D) ultrasound probe. However, needle and tool positions cannot be assessed when they are located outside the imaging plane. The present systems and methods are provided to track and visualize out-of-plane needles without losing the target anatomy image. In one embodiment, this is accomplished using a simple one-dimensional (1D) probe (for 2D imaging) or a two-dimensional (2D) probe for 3D imaging. Also provided are methods for assessing the 3D position of a needle relative to the imaging plane using a 1D array.
[0018] Embe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com