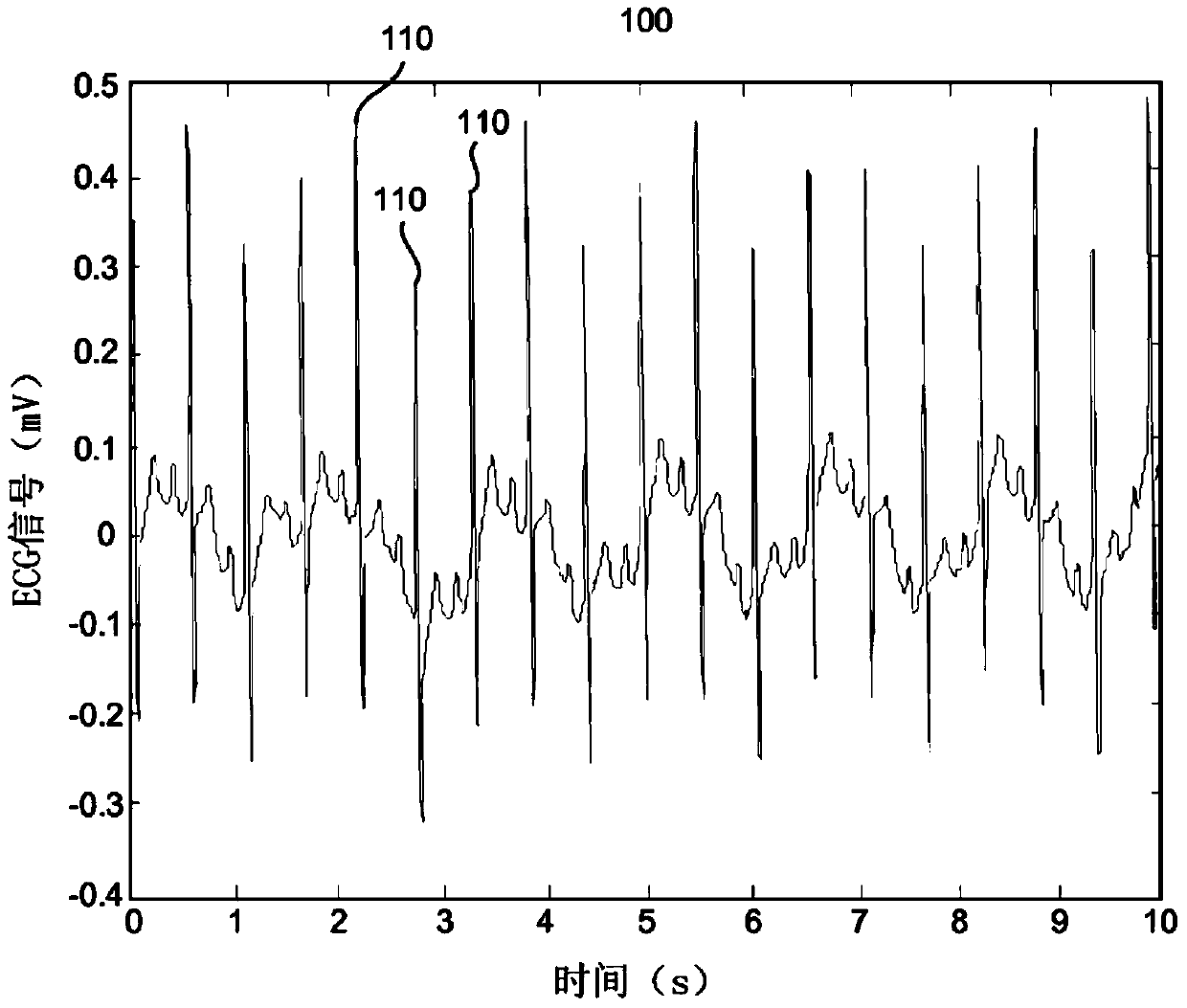
Electrocardiogram baseline removal
An electrocardiogram and baseline technology, applied in medical science, diagnosis, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete filtering of baseline changes, calculation errors, etc., and achieve the effect of easy implementation and reduced distortion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
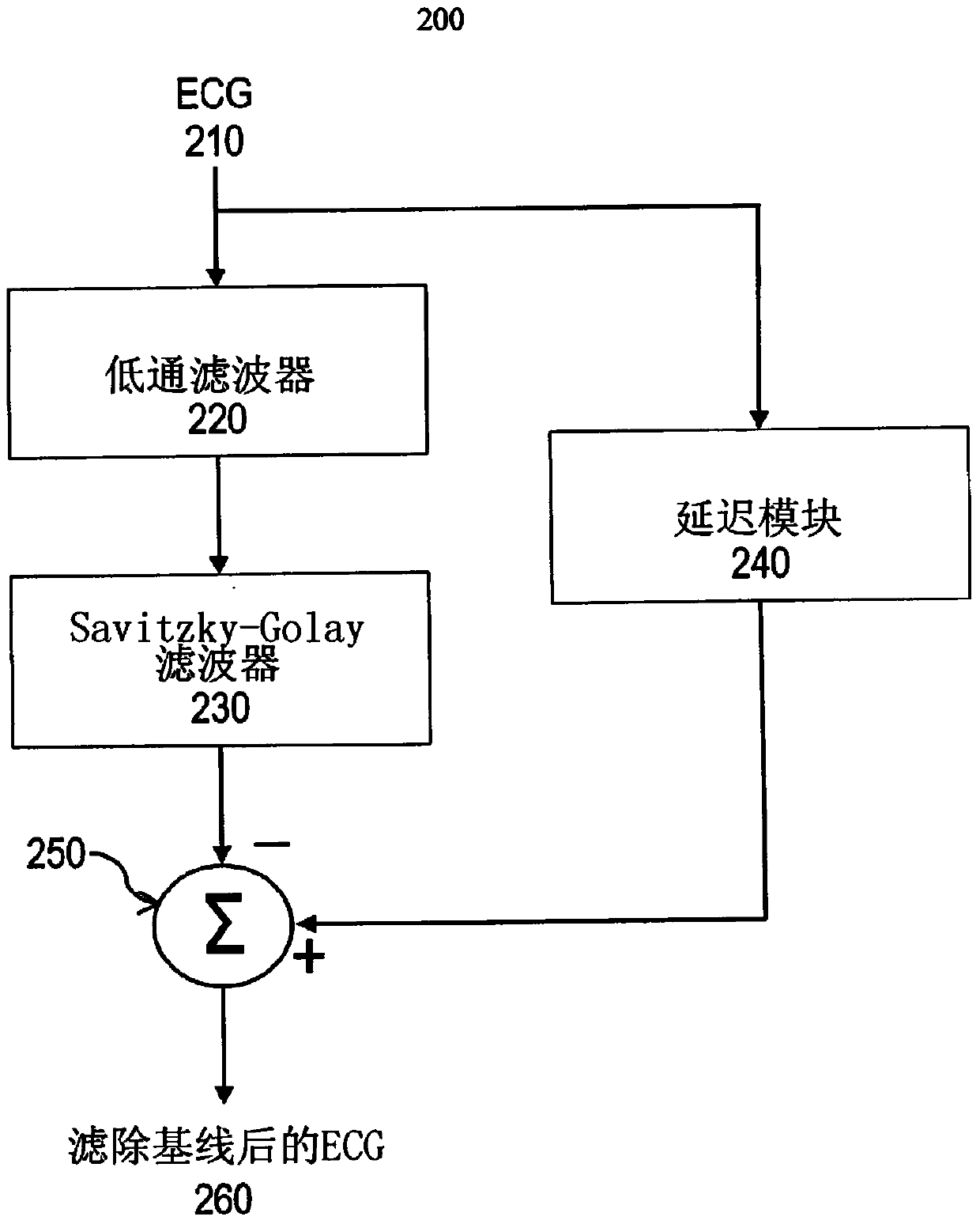
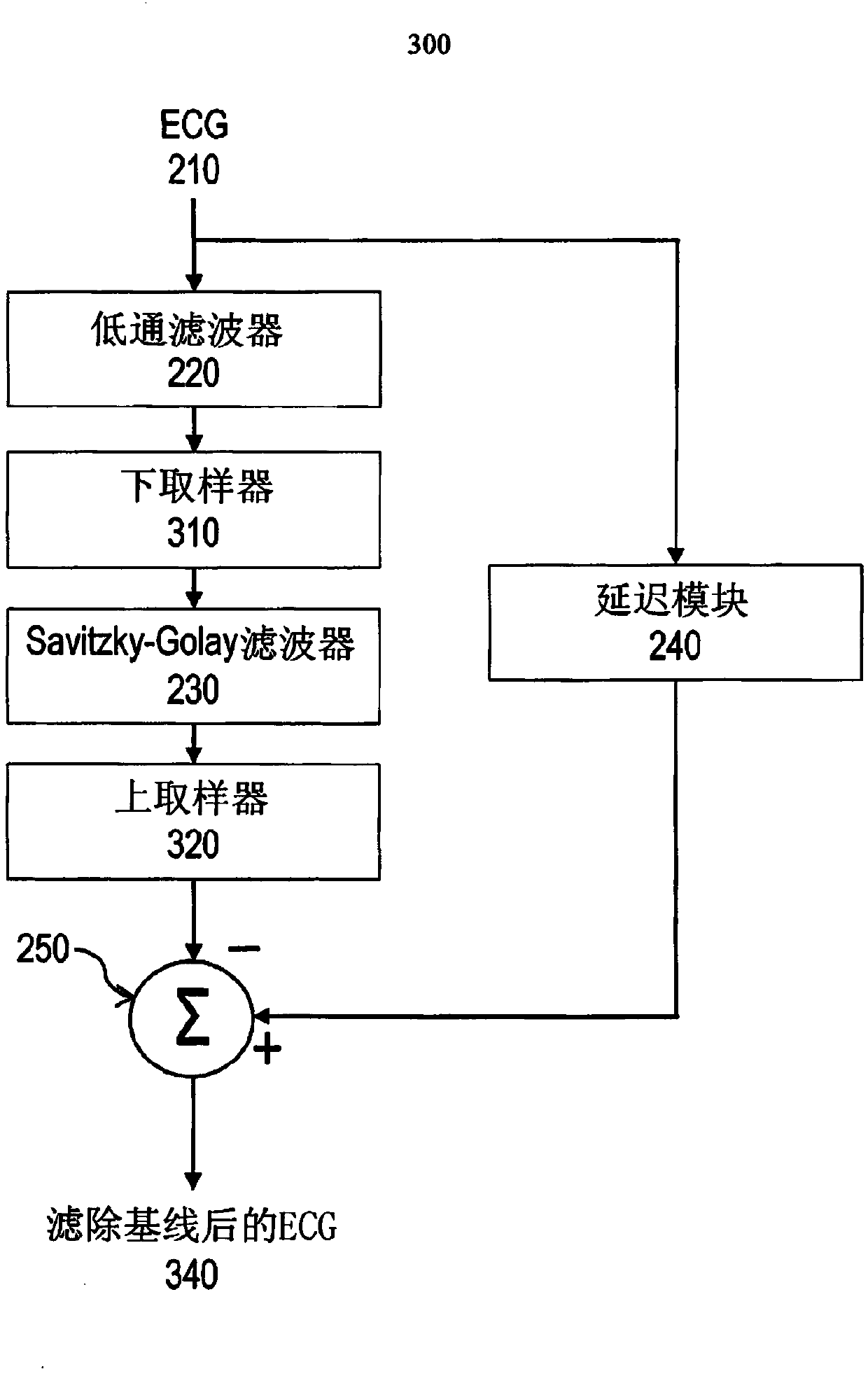
[0025] figure 2 System diagram 200 is a system diagram 200 for an ECG baseline change filtering system. The input ECG 210 is passed to a low pass filter 220 to produce a filtered signal whose high frequency components are filtered out. The filtered signal is then passed to a Savitzky-Golay (SG) filter 230 , which produces an estimate of the baseline change of the input ECG 210 . The SG filter is a filter that performs a local polynomial regression (of degree k) on a series of values (of at least k+1 points) to determine a smoothed value for each point. One advantage of this method is that it preserves characteristics of the distribution, such as relative maxima, minima, and width, which are often "flattened" by other adjacent averaging techniques such as moving averages, for example. ECG 210 may also be passed to delay module 240 to be delayed in time (eg, time shifted). The delay can compensate for any delay introduced by the processing of the low-pass filter 220 and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com