Human gene promoter identification method and system
An identification method and promoter technology, applied in the field of promoter identification, can solve the problem of low identification rate of gene promoters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flow chart of a human gene promoter identification method disclosed in the embodiment of this application.
[0071] like figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0072] Step 101: receiving a sample set composed of multiple sample gene sequences;
[0073] Step 102: Count the cytosine and guanine CG preference characteristics of each sample gene sequence separately to obtain statistical results;
[0074] Specifically, the number of cytosine C (Cytosine) and guanine G (Guanine) CG in each sample gene sequence is counted. If the ratio of C and G numbers in the entire sample gene sequence of CG is greater than a certain value, the sample gene is considered Sequences have a preference feature for CG, otherwise there is no CG preference feature.
[0075] Step 103: divide all sample gene sequences into two categories according to the statistical results, one category has the CG preference feature, and the other category does not have the CG...
Embodiment 2
[0087] In this embodiment, we will introduce the specific implementation process of each step in the first embodiment in detail.
[0088] First, define a sample set consisting of multiple sample gene sequences as:
[0089] where x i ∈R L ,y i ∈ {"promoter", "exon", "intron", "3′UTR"}, N is the number of samples, L is the length of the sample gene sequence.
[0090] It should be noted that the 3'UTR is the untranslated region at the 3' end of the gene sequence.
[0091] Next, we count the cytosine and guanine CG preference characteristics of each sample gene sequence, specifically:
[0092] For each sample gene sequence x i The ratio of cytosine C and guanine G content is counted, and the sample set after statistics is expressed as:
[0093] in no C is the number of occurrences of cytosine C in the sample gene sequence, n G Indicates the number of occurrences of guanine G in the sample gene sequence.
[0094] Through the statistics of CG preference characteristic...
Embodiment 3
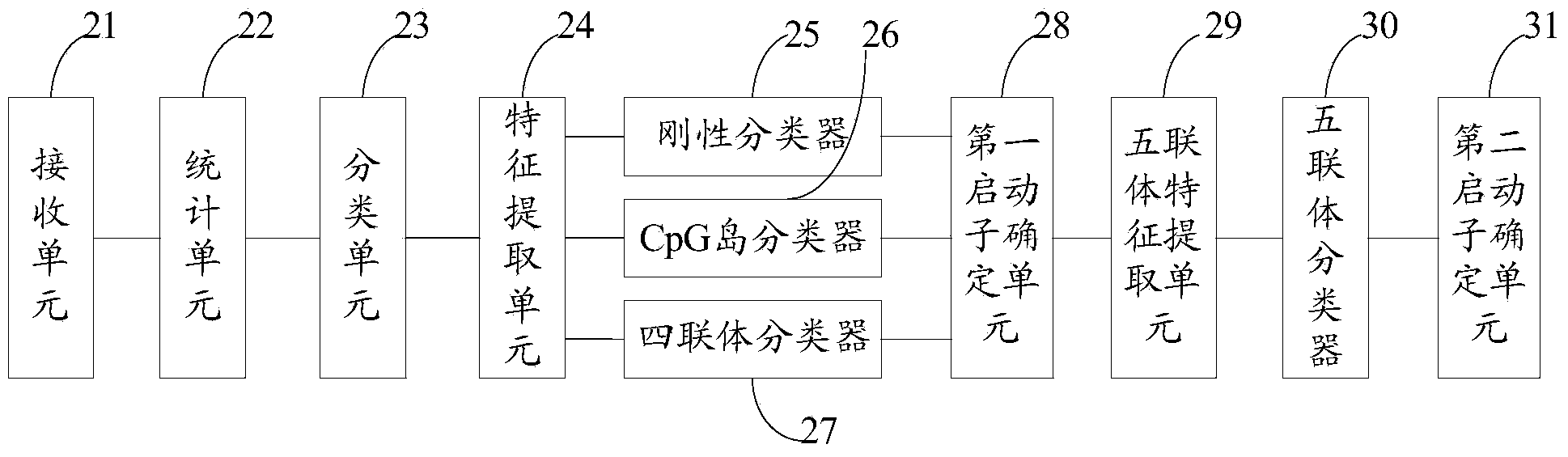
[0132] see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a structural diagram of a human gene promoter recognition system disclosed in the embodiment of this application.
[0133] like figure 2 As shown, the system includes:
[0134] A receiving unit 21, configured to receive a sample set composed of a plurality of sample gene sequences;
[0135] The statistics unit 22 is used to separately count the cytosine and guanine CG preference characteristics of each sample gene sequence to obtain statistical results;
[0136] A classification unit 23, configured to divide all sample gene sequences into two categories according to the statistical results, one category has the CG preference feature, and the other category does not have the CG preference feature;
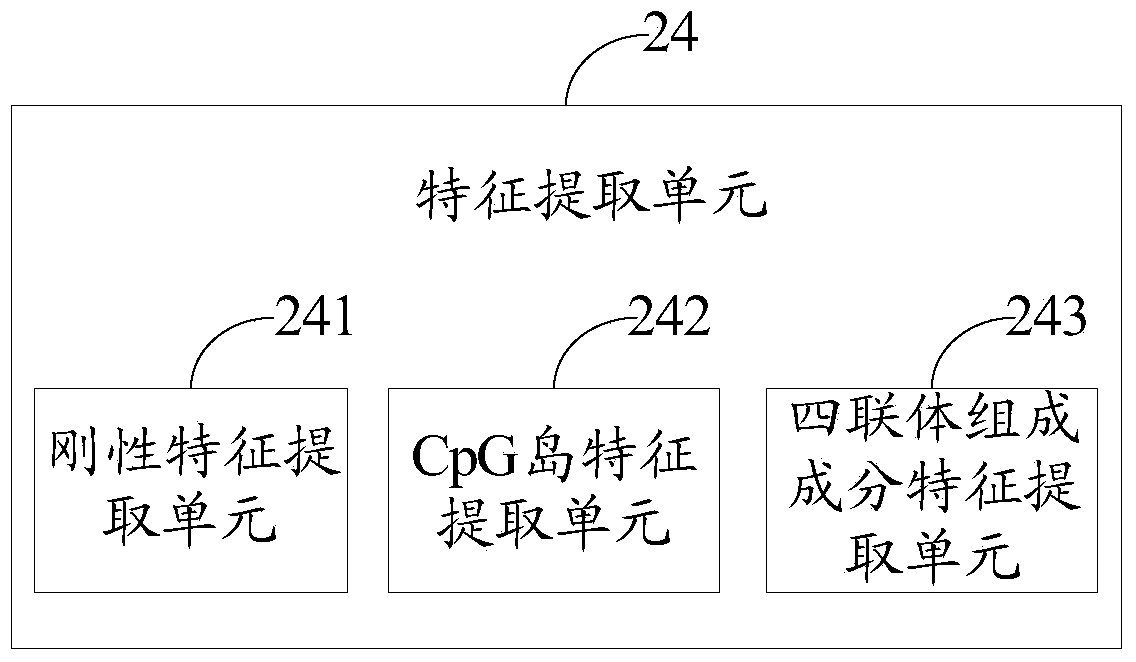
[0137] The feature extraction unit 24 is used to extract the rigidity feature, CpG island feature and quadruple composition feature of each sample gene sequence for each type of sample gene sequence after division;
[0138] A rigid classi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com