Health water dispenser
A water dispenser, a healthy technology, applied in water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, sterilization/microdynamic water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult strength, toxic and side effects, and reduce power consumption , The effect of low redox potential and improved sterilization and purification capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
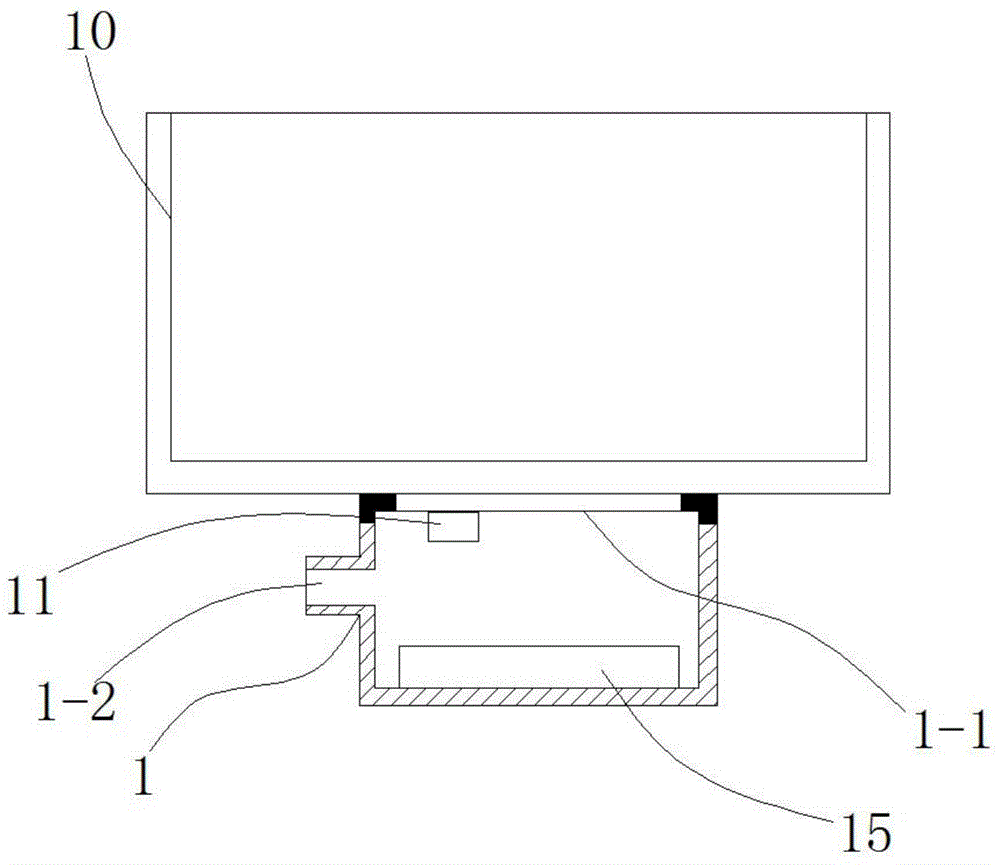
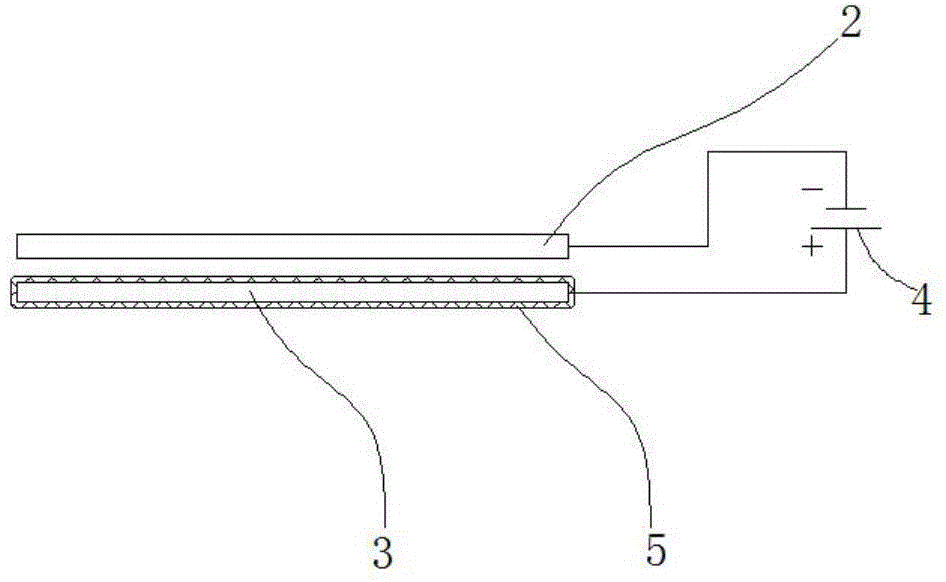
[0040] The health water dispenser of the present embodiment, as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the water dispenser is provided with a drain seat 10, and the bottom of the drain seat 10 is provided with a water container 1, and the water container 1 is provided with a water inlet 1-1 and a water outlet 1-2, and the water inlet 1-1 and the drain seat 10 The bottom water hole is connected, and the water outlet 1-2 is connected with the water outlet hole of the water dispenser; a sterilizing device 15 is provided in the water container 1, and the sterilizing device 15 includes a pair of negative electrodes 2 and positive electrodes 3 and is used for feeding the negative electrode 2 and the positive electrode 3. An electrolysis power supply 4 powered by the anode electrode 3 .
[0041] Such as figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, a water-permeable membrane 5 is provided between the cathode 2 and the anode 3, and the water-permeable membrane 5 is close to the anode 3 and cov...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The healthy water dispenser of the present embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, and the difference from the first embodiment is that the distance δ between the water-permeable diaphragm 5 and the negative electrode 2 in this embodiment is 0 mm, that is, the water-permeable diaphragm 5 is closely attached to the cathode electrode 2 at the same time. On the cathode electrode 2 and the anode electrode 3. The water-permeable diaphragm 5 still adopts a PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with an average hydrophobic pore diameter of 0.03 micron and a thickness of 0.1 mm.
[0056] The water dispenser of the present embodiment is carried out water electrolysis test, and experimental condition is identical with embodiment one, and electrolysis time is 20 minutes, and two kinds of experimental results are as follows table 2:
[0057] Table 2
[0058]
[0059] The following conclusions can be drawn from the analysis of the experimental results:
[0060] 1) With...
Embodiment 3
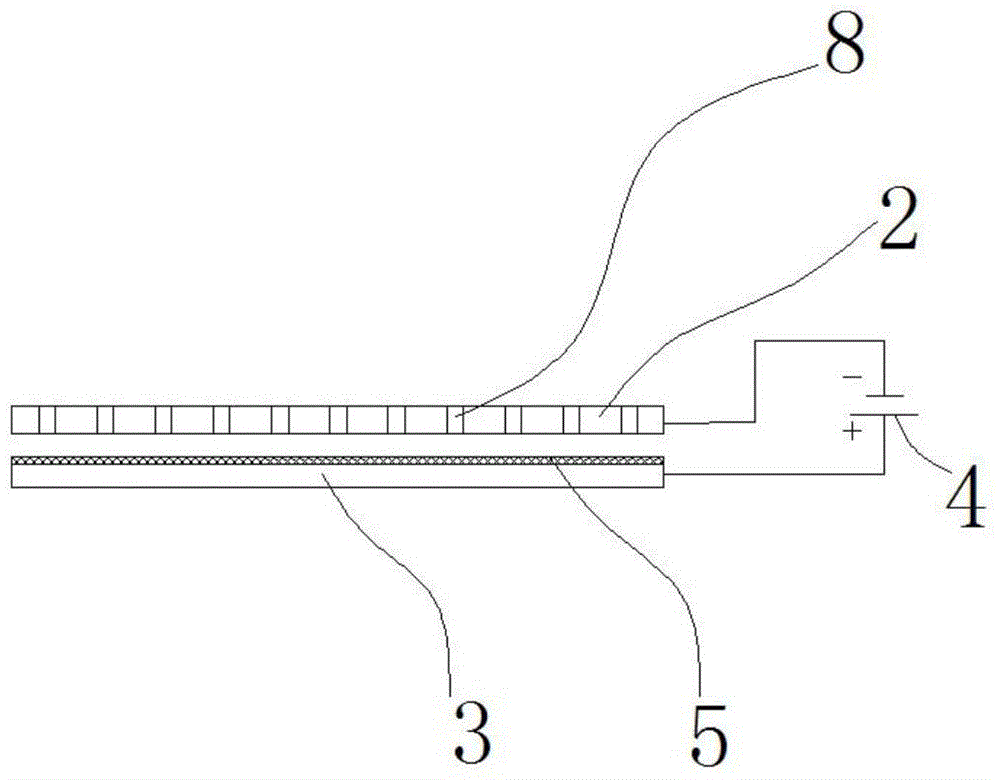
[0063] The healthy water dispenser of the present embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, as image 3 As shown, the changes different from the first embodiment are: 1) a first through hole 8 is opened on the negative electrode 2, and the diameter of the through hole is 1 mm; 2) the water-permeable diaphragm 5 covers part of the surface of the positive electrode 3 (the positive electrode 3) the distance δ between the water-permeable diaphragm 5 and the cathode 2 is 2 mm.
[0064] The healthy water dispenser of this embodiment is subjected to water electrolysis experiment. In this embodiment, 24 first through holes with a diameter of φ1mm are evenly distributed on the negative electrode. Other experimental conditions and detection methods are the same as in Embodiment 1. The experimental results are as follows 3:
[0065] table 3
[0066]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com