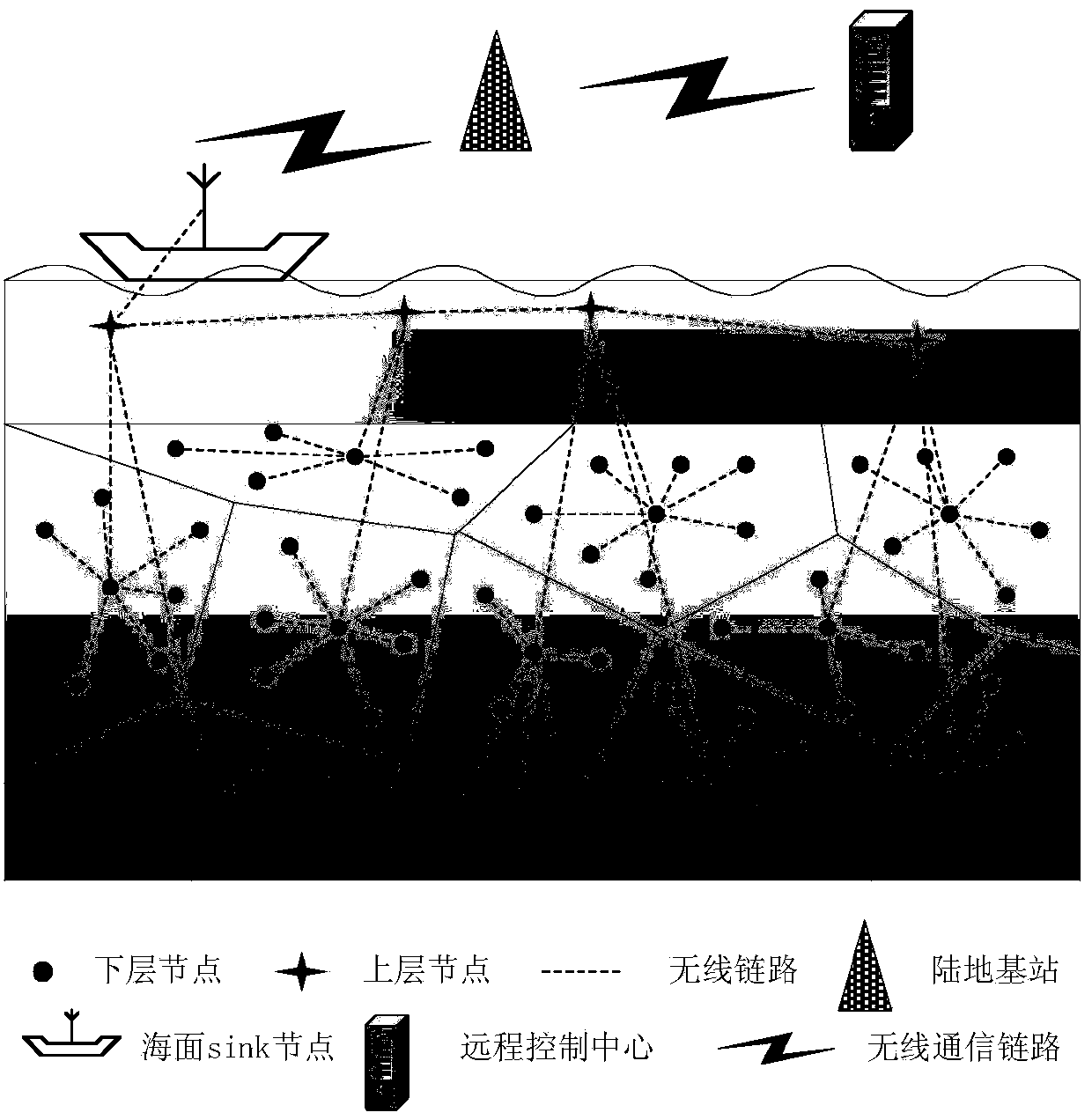
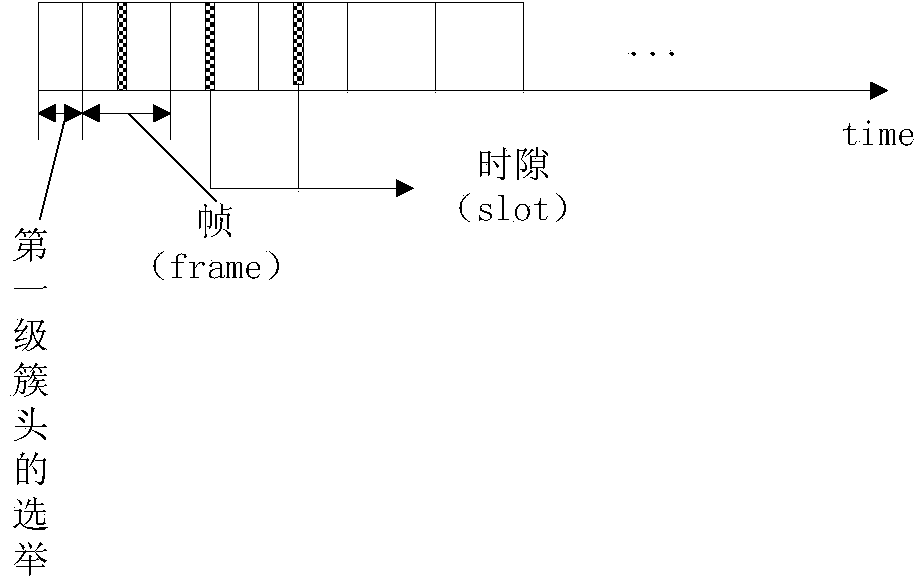
Two-stage isomerism clustering underwater wireless sensor network and routing method thereof
A wireless sensor and sensor node technology, applied in network topology, wireless communication, advanced technology, etc., can solve problems such as power consumption limitation, low transmission speed, and long delay of acoustic channel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
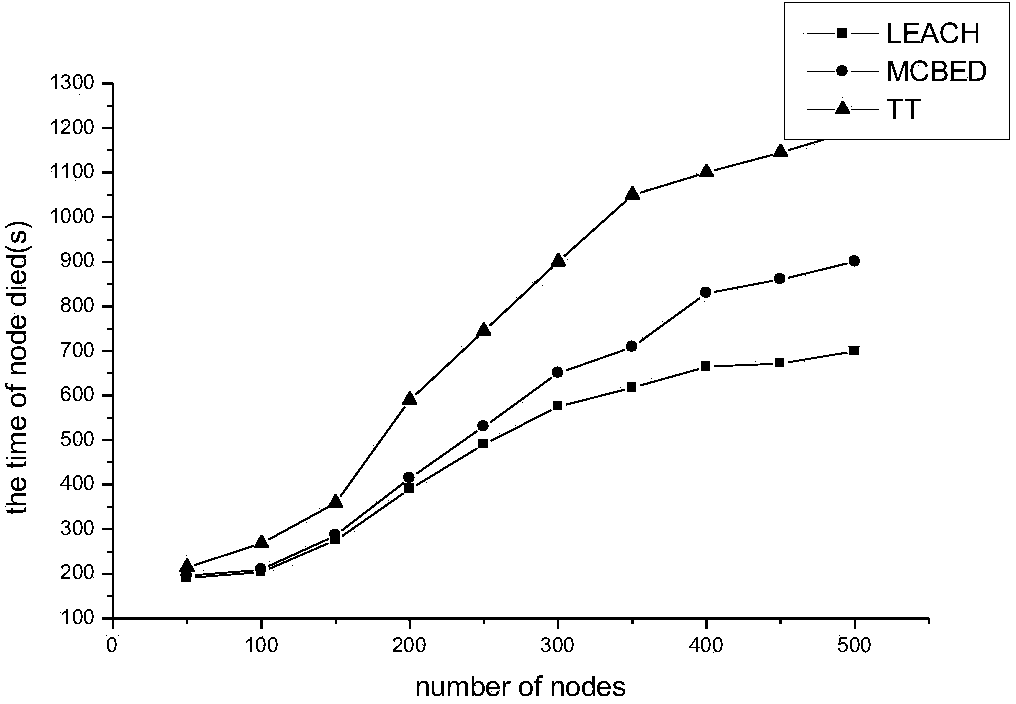
[0085] Embodiment 1: The scale of nodes is 500, and the data packet size is 500 Bytes. After experimental verification, the experimental results are as follows image 3 shown. From image 3 It can be seen from the figure that compared with the LEACH and MCBED protocols, when the node scale is large, the "TT" protocol makes the node's energy consumption more balanced.
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2: 500 nodes are randomly distributed in the monitoring area, and one Sink node is deployed far away from the monitoring area, and the data packet size is 500 Bytes. Experimental results such as Figure 4 shown. From Figure 4 It can be seen that with the increase of the "round number" of periodic clustering, the number of surviving nodes in the "TT" protocol is more than the number of surviving nodes in the LEACH protocol and the MCBED protocol in the period with the same "round number". want more. That is to say, the "TT" protocol increases the "number of rounds" to reach this state. Compared with LEACH and MCBED protocols, "TT" has significantly longer network survival time, and the first node dies later. This shows that "TT" achieves the purpose of balancing node energy consumption and prolonging the network survival time.
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3: 500 nodes are randomly distributed, and the initial energy of the nodes is 2J, and one of the secondary cluster head nodes is selected for observation. Experimental results such as Figure 5 shown. From Figure 5 It can be seen that because the "TT" protocol adopts the form of inter-cluster routing, the energy consumption of the cluster head of the "TT" protocol is less than the energy consumption of the cluster head nodes in the LEACH and MCBED protocols.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com