Artificial cochlea acoustic nerve conductive electrode array capable of sensing music melodies
A cochlear implant and electrode array technology, applied in ear therapy, medical science, prosthesis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
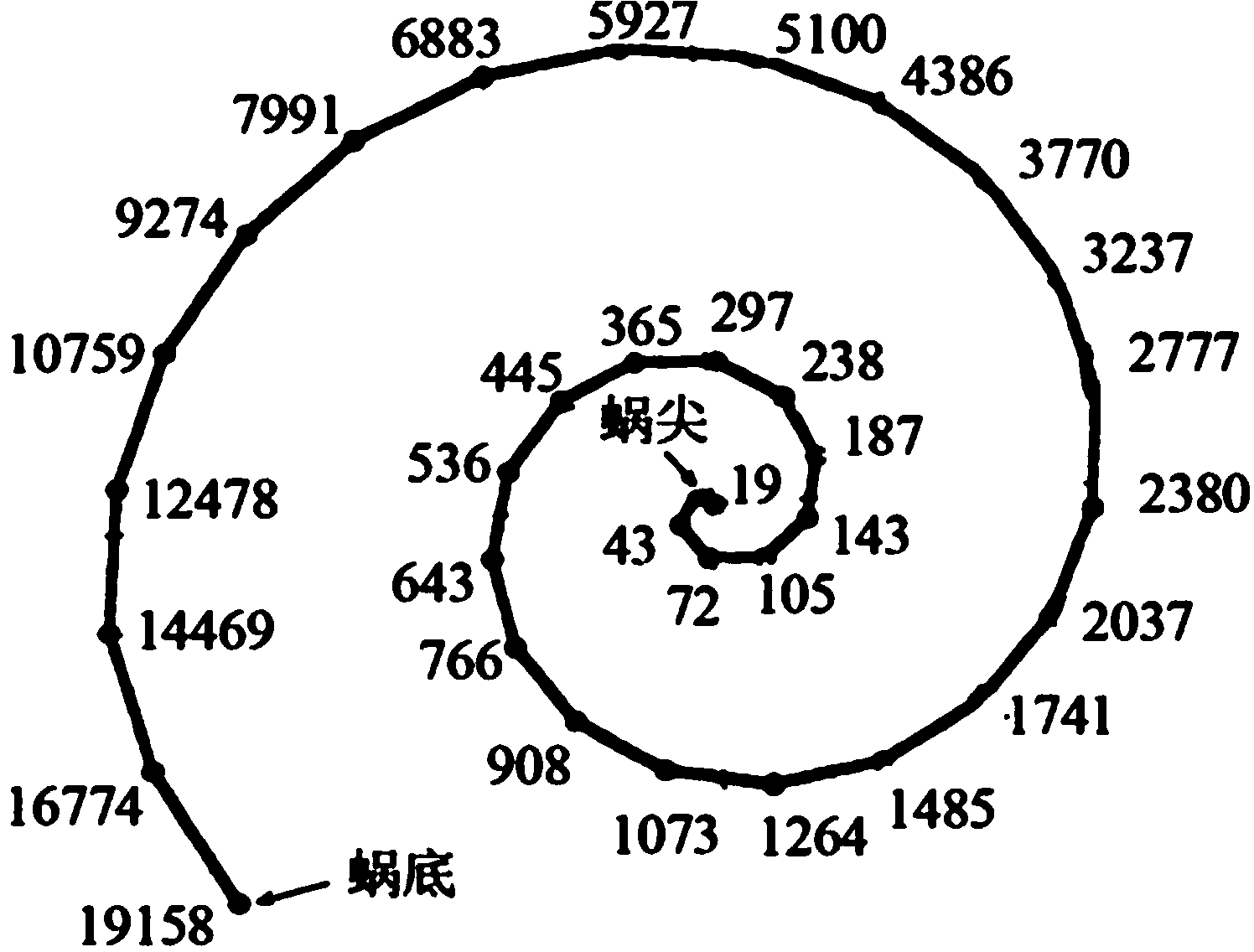
[0206] Different positions on the human cochlear basilar membrane respond to different sound frequency signals such as figure 1 , which is the cochlear position-frequency topology map, which is an important theoretical basis for cochlear implant frequency (or position) encoding.
[0207] It can be known from music knowledge that the pitch of music has seven scales of C D E F G A B, that is, "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7" in musical notation, which is an octave, and all musical pitches can be divided into ten. Octave. The minimum resolution pitch difference of the pitch is one semitone. If the semitone is used as the unit, the fundamental frequency comparison table of all notes is shown in Table 2.
[0208] Table 2 Music "note-fundamental frequency" comparison table (in semitone intervals, unit: Hz)
[0209]
[0210]
[0211] If the music melody information is completely and accurately expressed, so that the cochlear implanter can perceive the music melody, in theory, the positi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com