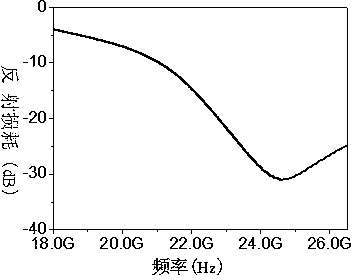
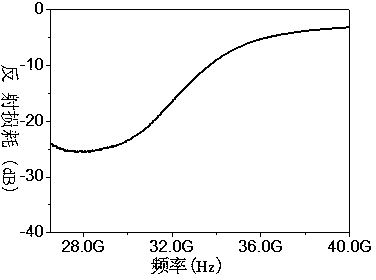
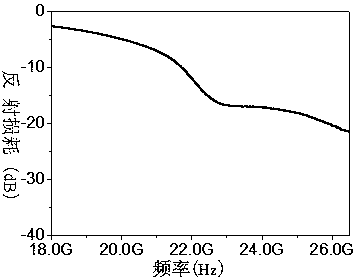
Zirconium-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
A technology of barium ferrite and wave-absorbing materials, which is applied in the field of zirconium-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing materials and its preparation, can solve the problem that barium ferrite has a small dielectric loss value, which is not conducive to the popularization and application of materials, modulation and Problems such as application capacity limitations, to achieve the effect of low cost, reduced matching thickness, and widened application frequency band
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1) Mix barium nitrate, iron nitrate and zirconium nitrate at a molar ratio of 1:11.5:0.5, add deionized water and stir for 3 h to dissolve to obtain a nitrate solution, in which the total molar concentration of barium nitrate, iron nitrate and zirconium nitrate is 1.5mol / L;
[0024] 2) Put EDTA in deionized water, stir at 80°C until completely dissolved, the molar concentration of EDTA is 0.5mol / L, then adjust the pH value to 5 with ammonia water to obtain EDTA solution;
[0025] 3) Add the nitrate solution to the EDTA solution drop by drop, where the molar ratio of EDTA to the total amount of metal ions in the nitrate solution is 5:1, and continue heating and stirring at 80°C to obtain a sol; dry the obtained sol at 100°C , to obtain a fluffy xerogel;
[0026] 4) Put the dry gel in a muffle furnace, keep it at 230°C for 4.5 hours, then raise the temperature to 460°C at a rate of 3°C / min and keep it for 4.5 hours, then raise the temperature to 800°C at a rate of 5°C / m...
Embodiment 2
[0031] 1) Mix barium nitrate, ferric nitrate and zirconium nitrate at a molar ratio of 1:11.6:0.4, add deionized water and stir for 3.5 h to dissolve to obtain a nitrate solution, in which the total molar concentration of barium nitrate, ferric nitrate and zirconium nitrate is 2.0mol / L;
[0032] 2) Put EDTA in deionized water, stir at 85°C until completely dissolved, the molar concentration of EDTA is 1.0mol / L, and adjust the pH value to 6 with ammonia water to obtain EDTA solution;
[0033] 3) Add the nitrate solution to the EDTA solution drop by drop, the molar ratio of EDTA to the total amount of metal ions in the nitrate solution is 5:1, and continue heating and stirring at 85°C to obtain a sol; dry the obtained sol at 140°C, Obtain a fluffy xerogel;
[0034] 4) Put the dry gel in a muffle furnace, keep it at 240°C for 3 hours, then raise the temperature to 470°C at a rate of 4°C / min and keep it for 3 hours, then raise the temperature to 700°C at a rate of 10°C / min and k...
Embodiment 3
[0039] 1) Mix barium nitrate, ferric nitrate and zirconium nitrate at a molar ratio of 1:11.7:0.3, add deionized water and stir for 4 h to dissolve to obtain a nitrate solution, in which the total molar concentration of barium nitrate, ferric nitrate and zirconium nitrate is 2.5mol / L;
[0040] 2) Put EDTA in deionized water, stir at 90°C until completely dissolved, the molar concentration of EDTA is 1.5mol / L, then adjust the pH value to 7 with ammonia water to obtain EDTA solution;
[0041] 3) Add the nitrate solution dropwise to the EDTA solution, the molar ratio of EDTA to the total amount of metal ions in the nitrate solution is 5:1, and continue heating and stirring at 90 °C to obtain a sol; dry the obtained sol at 120 °C, Obtain a fluffy xerogel;
[0042] 4) Put the dry gel in a muffle furnace, keep it at 250°C for 1.5 hours, then raise the temperature to 480°C at a rate of 5°C / min and keep it for 1.5 hours, then raise the temperature to 600°C at a rate of 10°C / min and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com