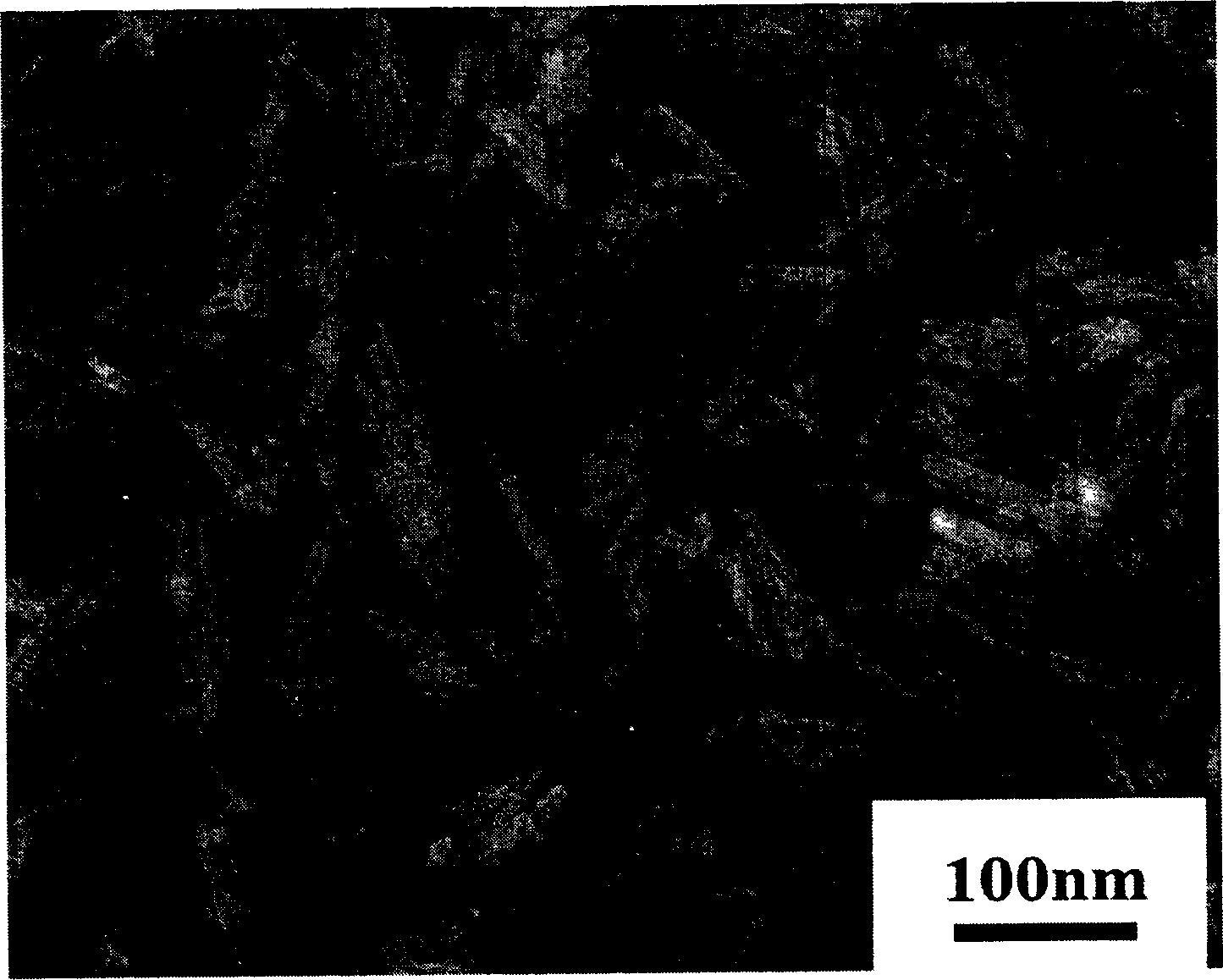
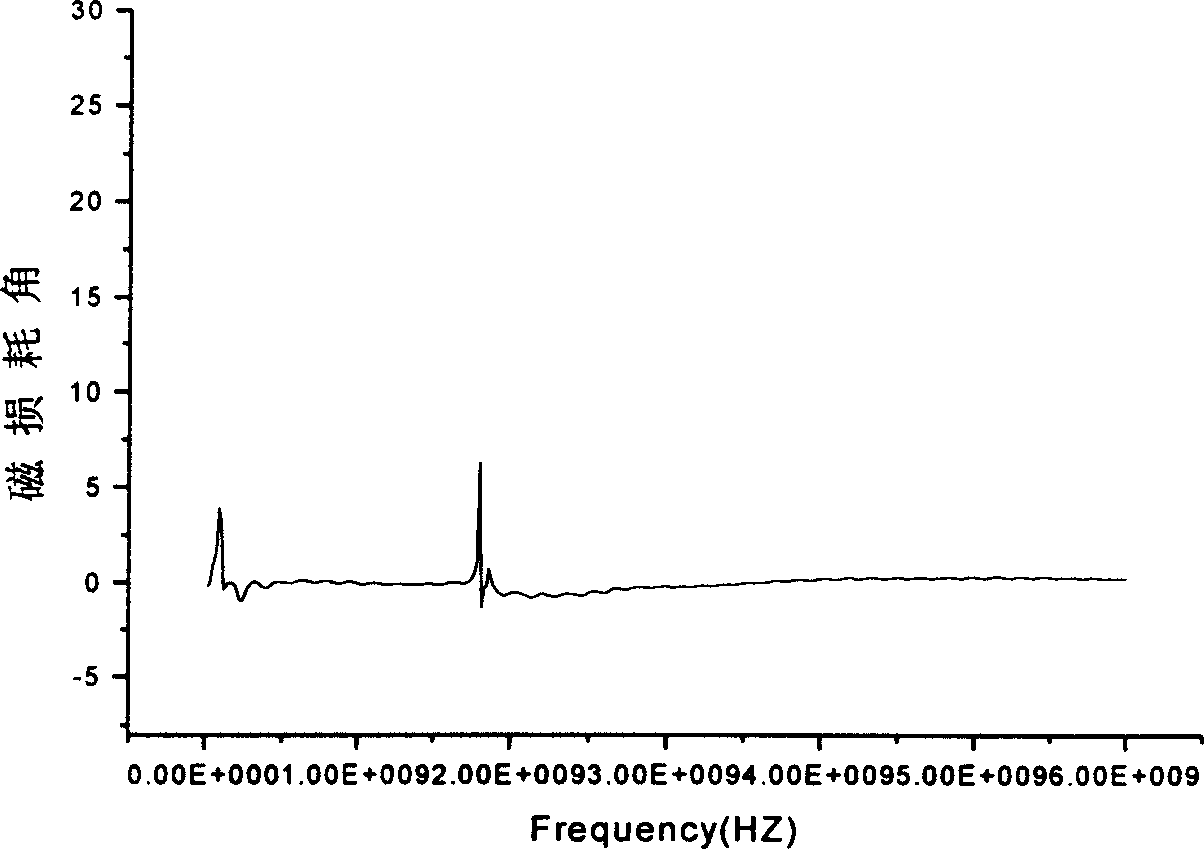
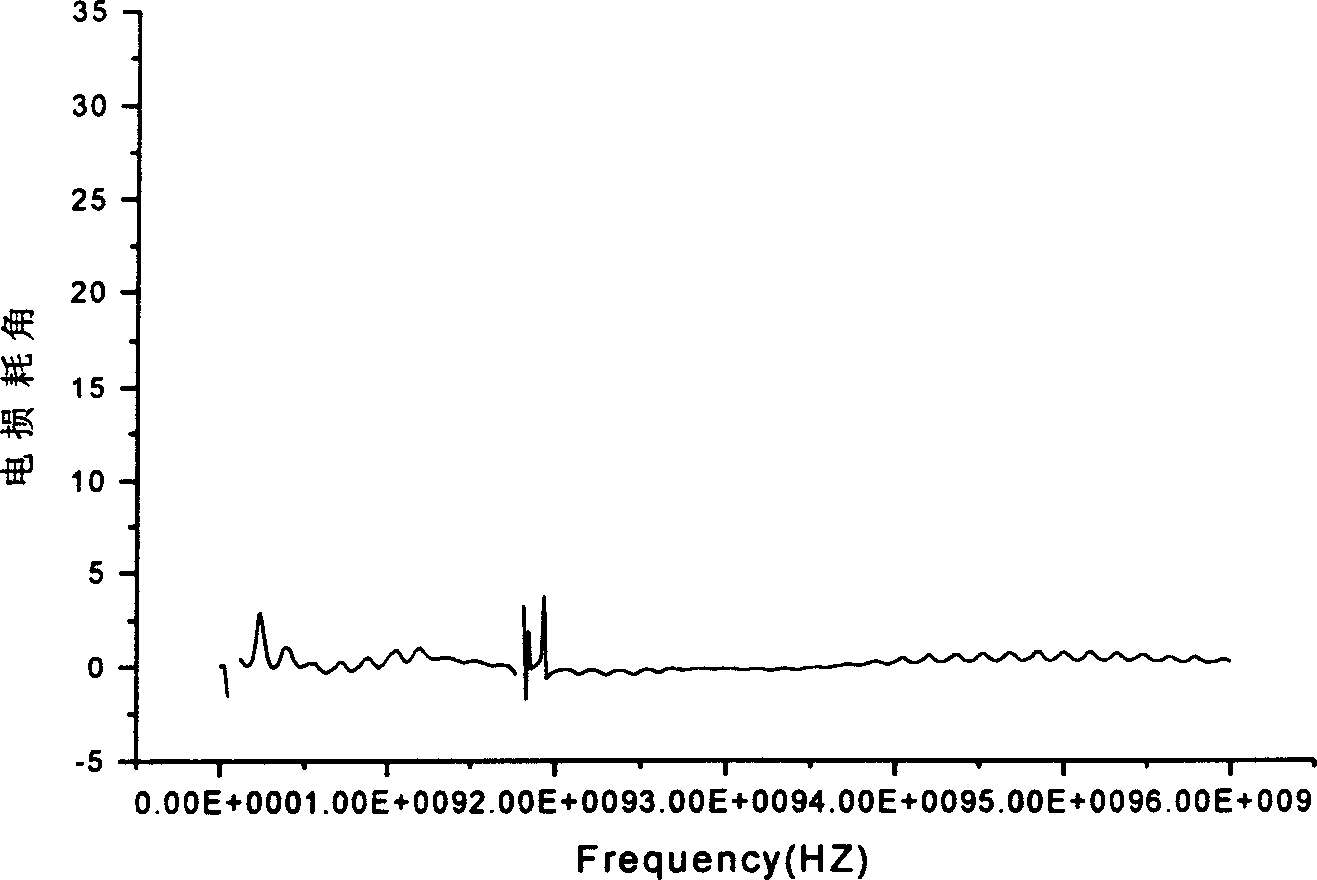
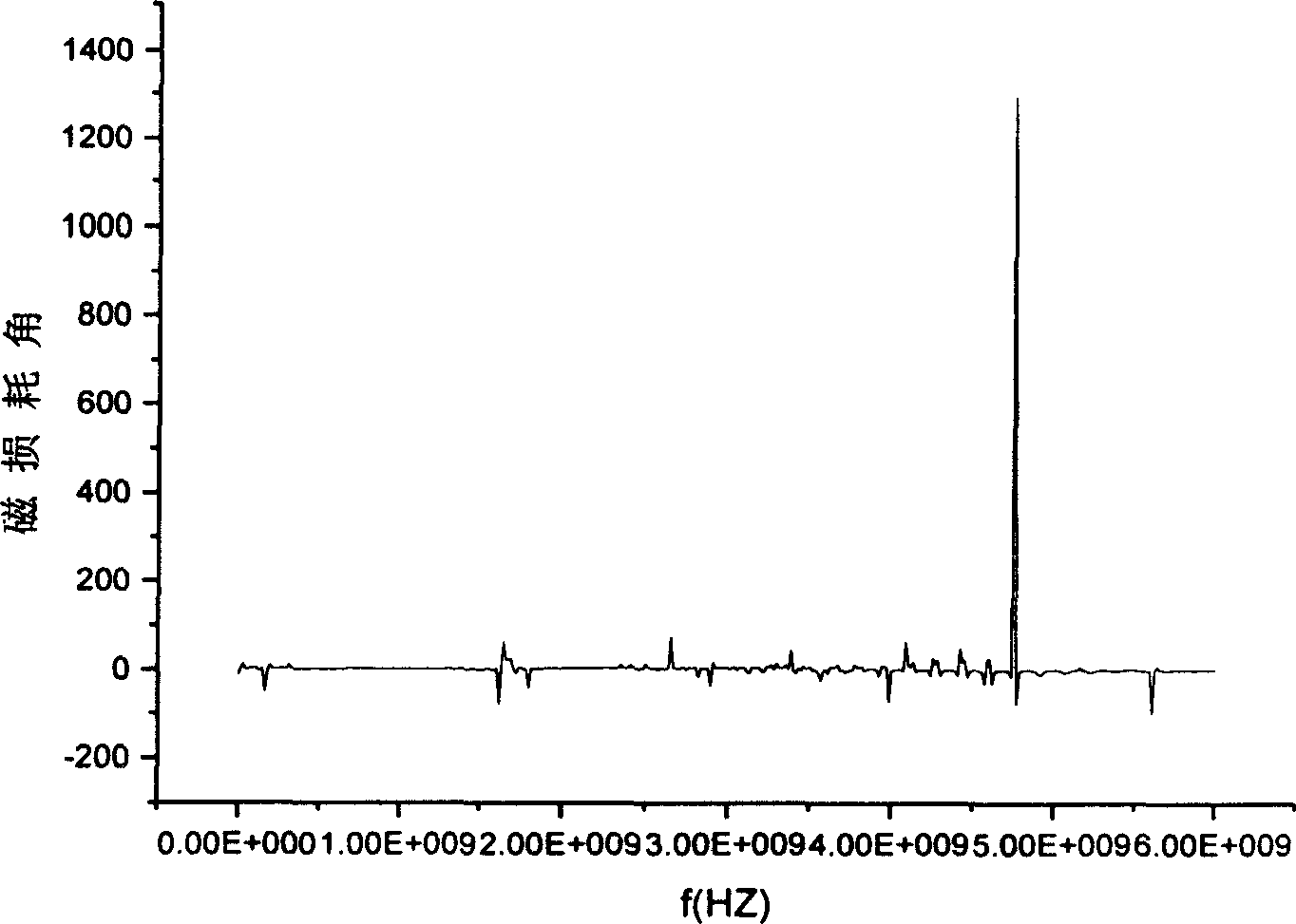
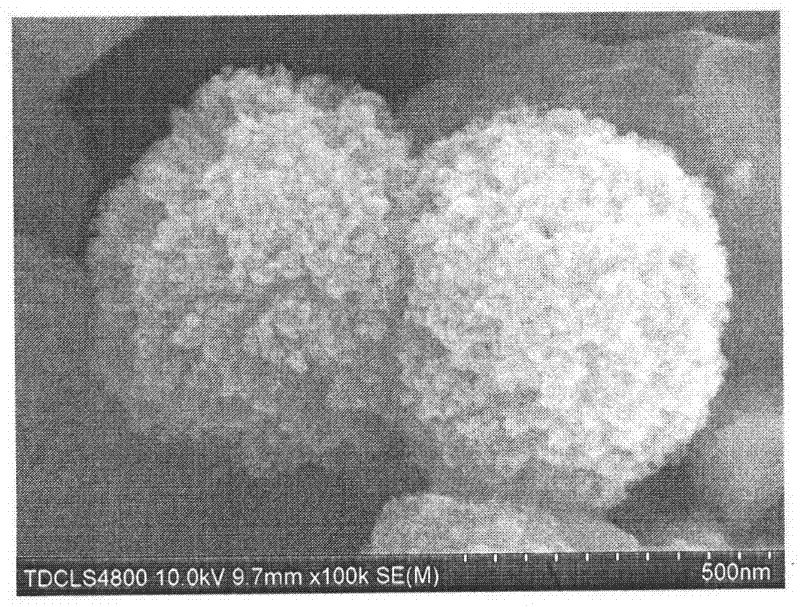
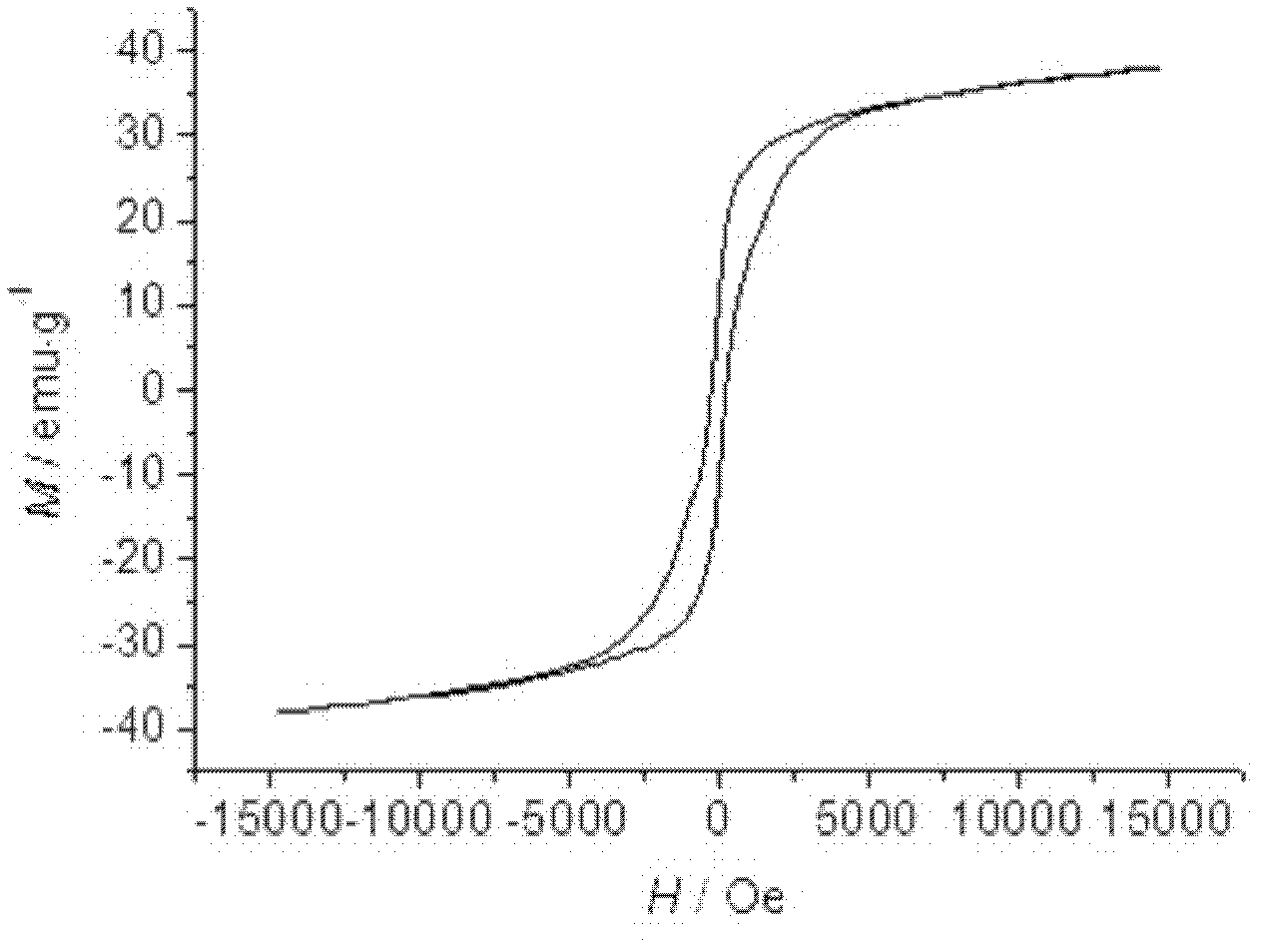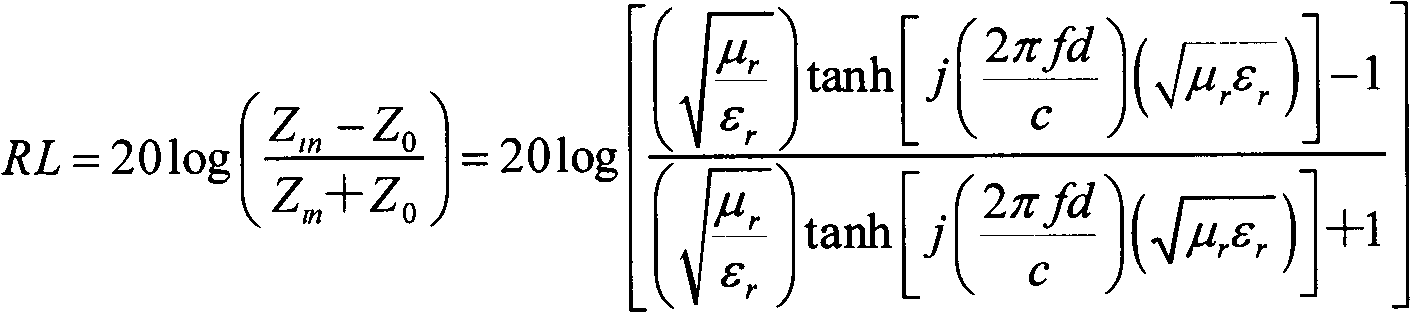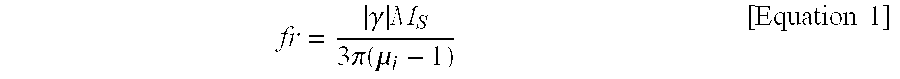Patents
Literature
324 results about "Barium ferrite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
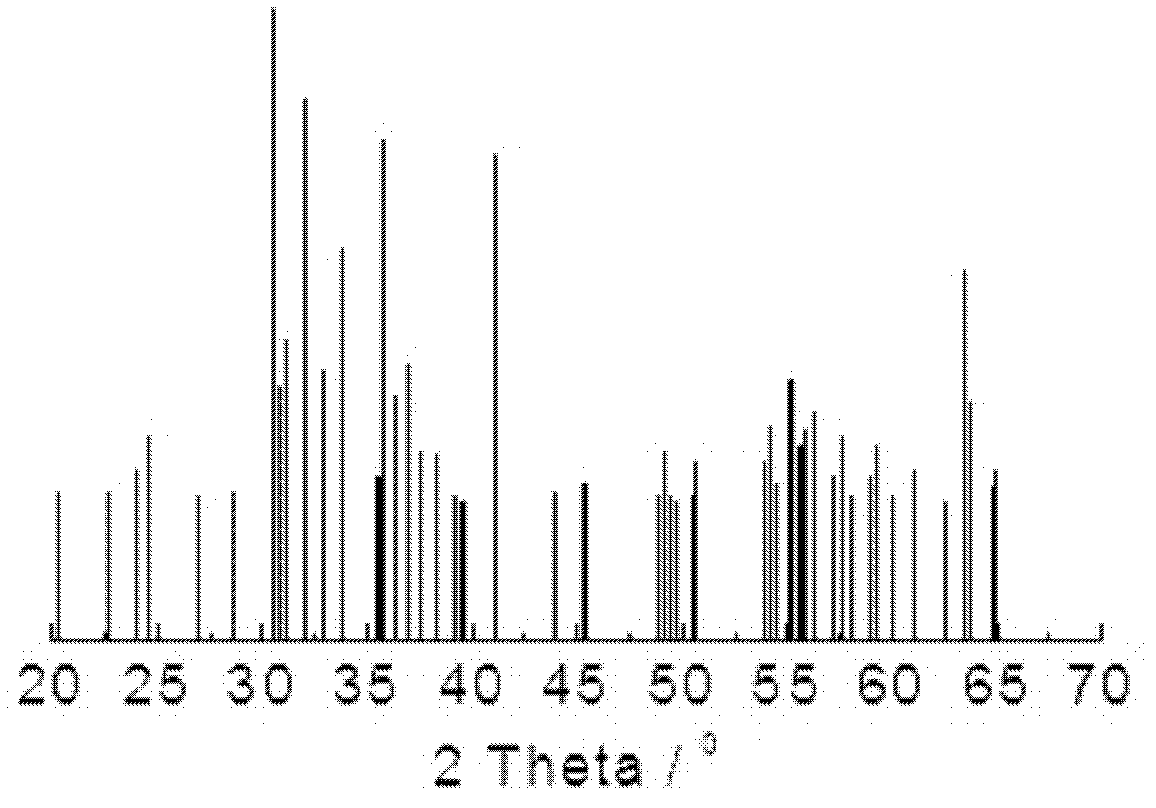
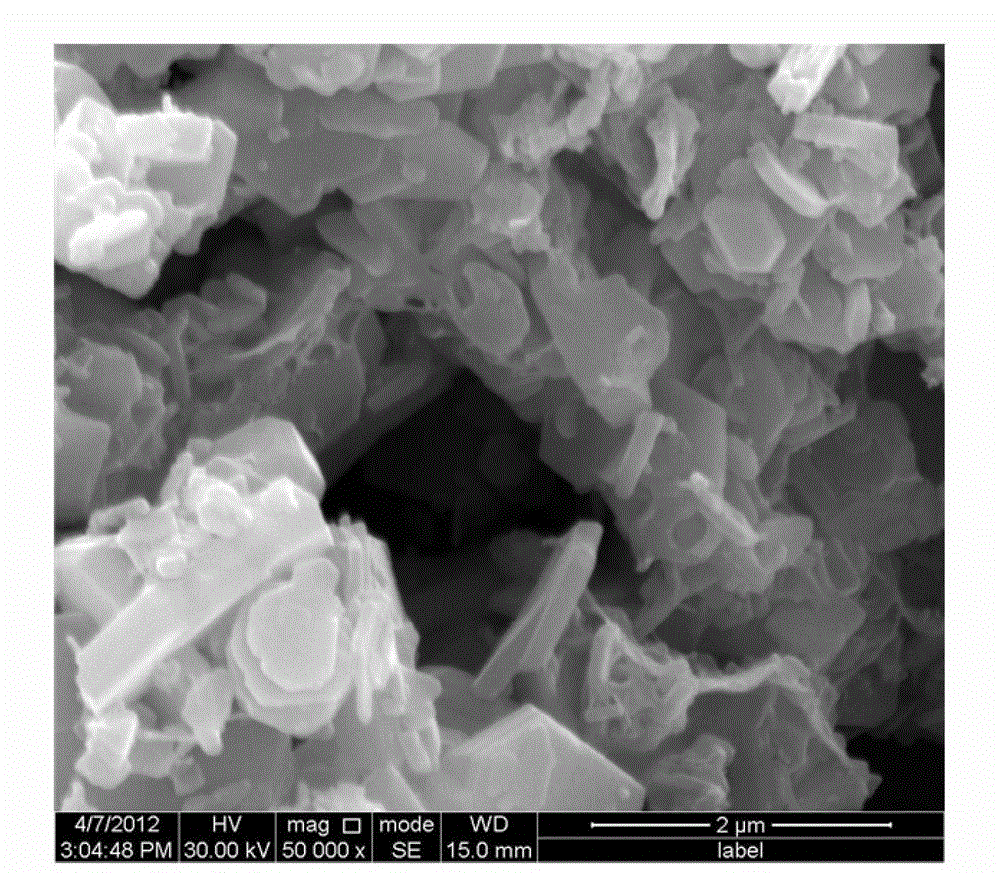
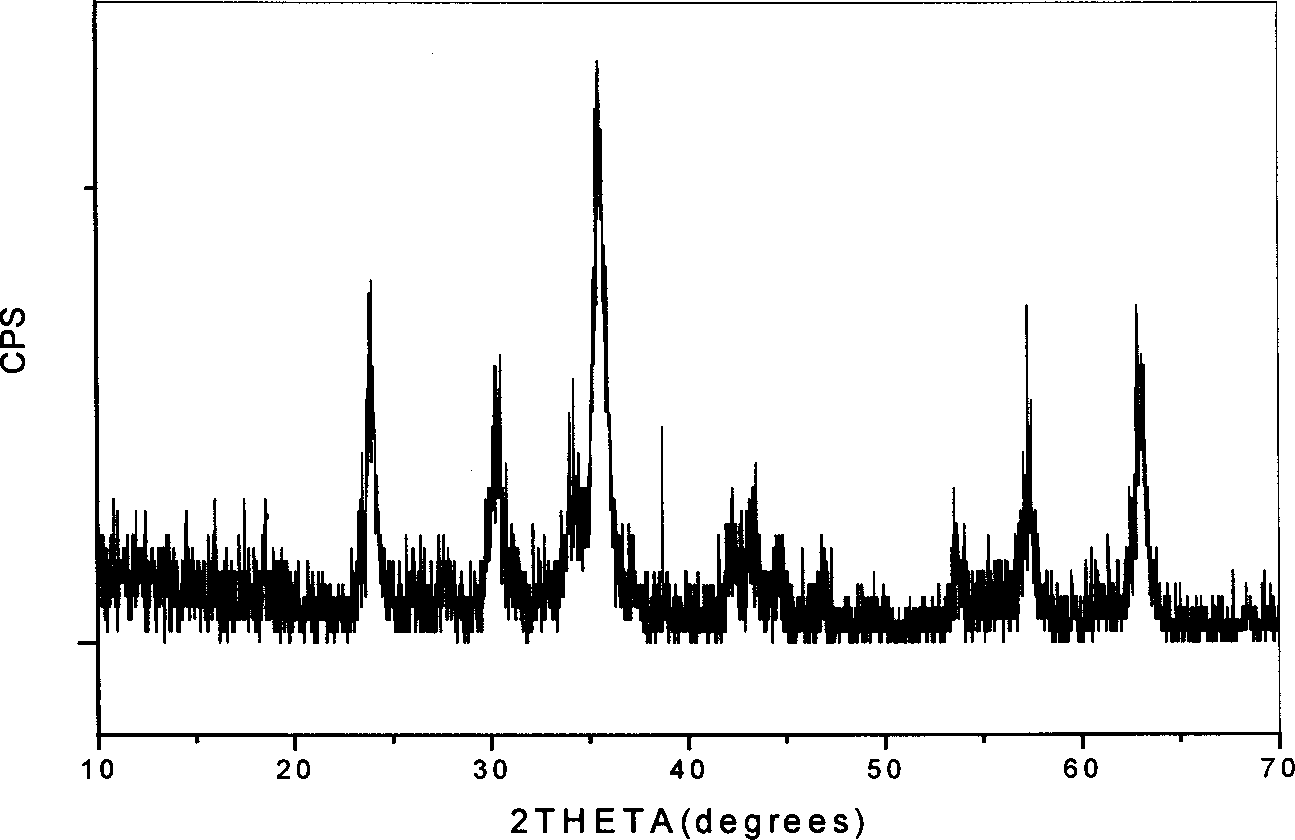
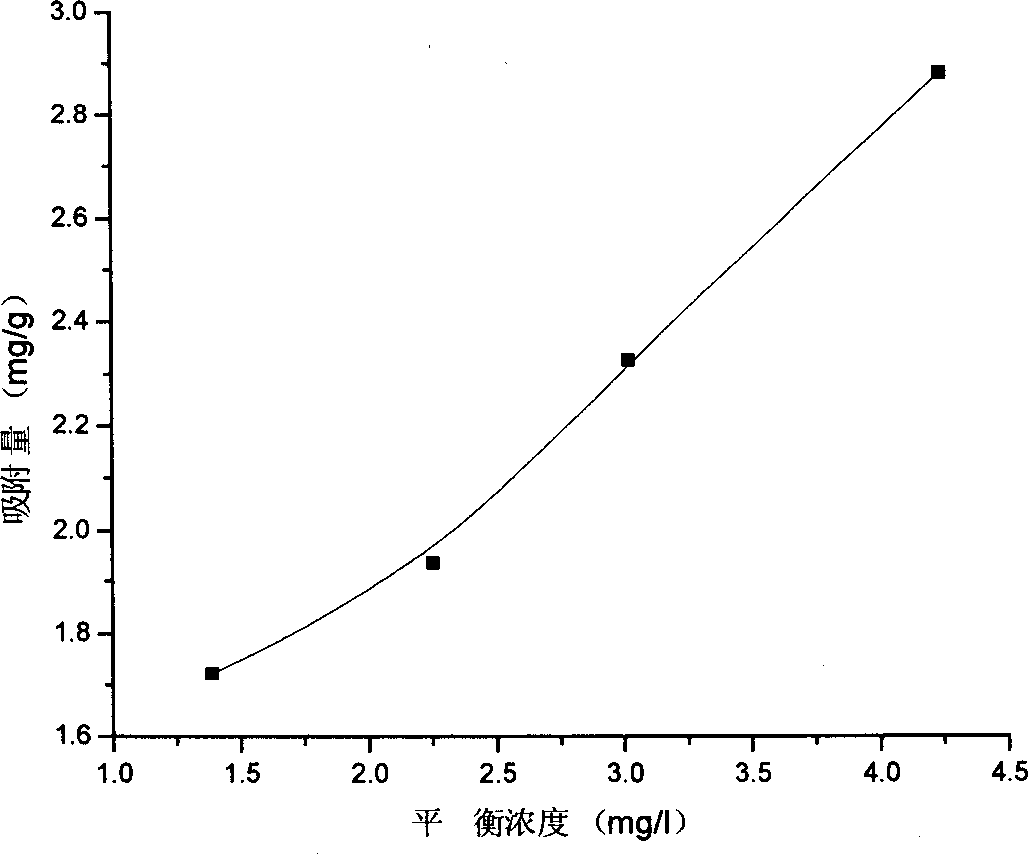
Barium ferrite, abbreviated BaFe, BaM, is the chemical compound with the formula BaFe₁₂O₁₉. This and related ferrite materials are components in magnetic stripe cards and loudspeaker magnets. BaFe is described as Ba²⁺(Fe³⁺)₁₂(O²⁻)₁₉. The Fe³⁺ centers are ferromagnetically coupled. This area of technology is usually considered to be an application of the related fields of materials science and solid state chemistry.
Hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20120177951A1Inhibit drop in thermal stabilityEnsure easeMagnetic materials for record carriersInorganic material magnetismBiological activationMaterials science
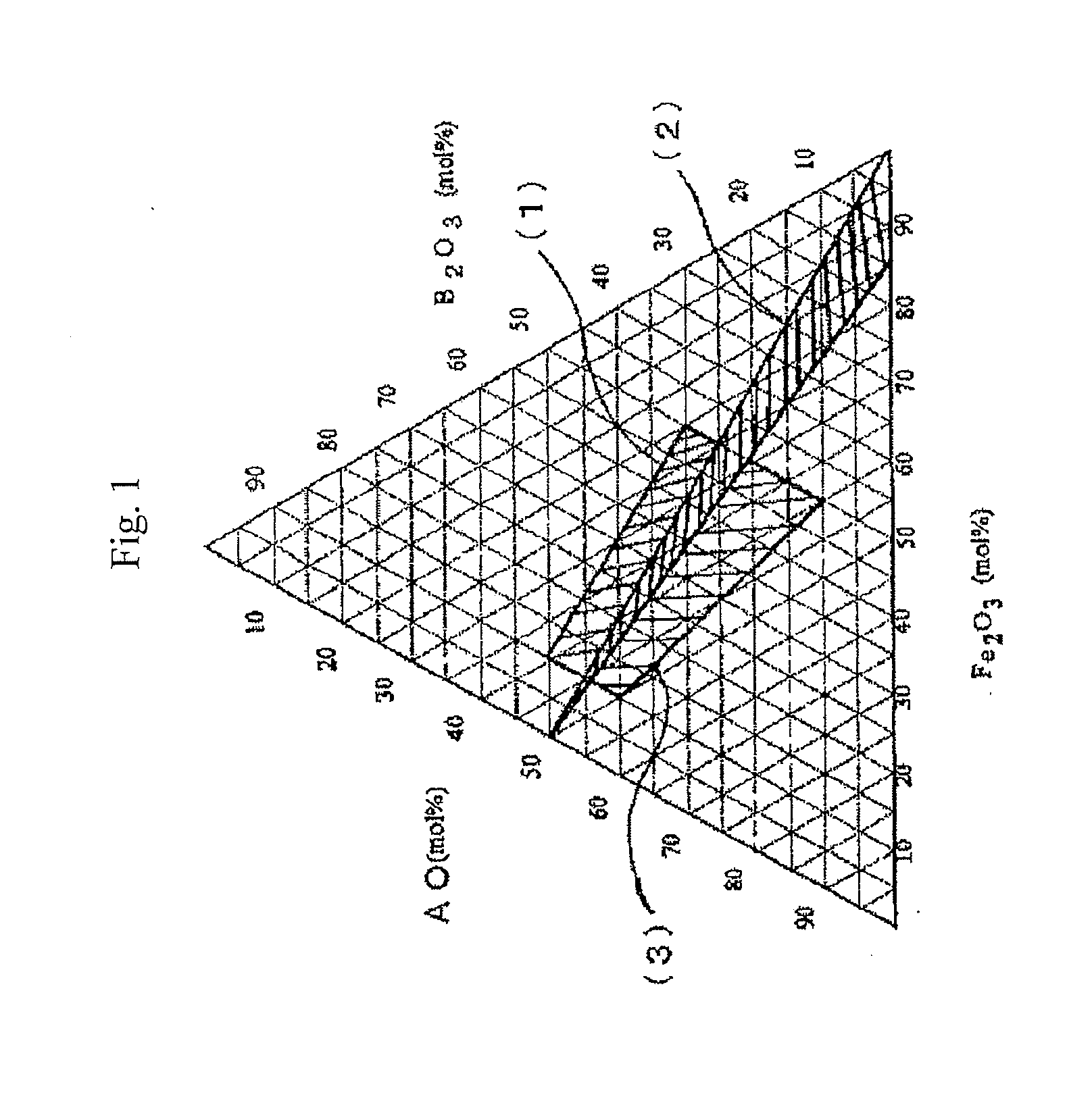
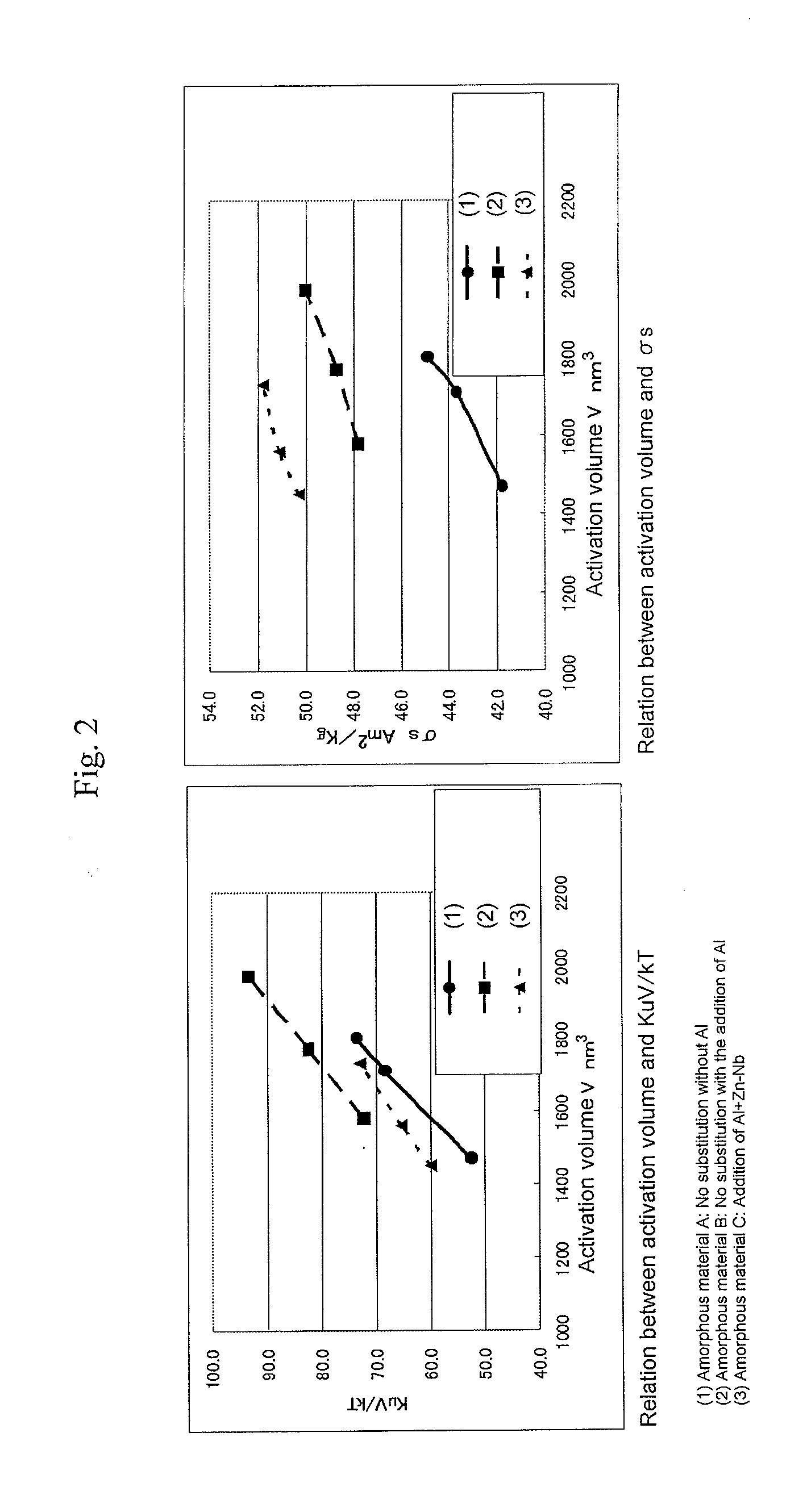
An aspect of the present invention relates to a hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle, wherein, relative to 100 atom percent of a Fe content, an Al content ranges from 1.5 to 15 atom percent, a combined content of a divalent element and a pentavalent element ranges from 1.0 to 10 atom percent, an atomic ratio of a content of the divalent element to a content of the pentavalent element is greater than 2.0 but less than 4.0, and an activation volume ranges from 1,300 to 1,800 nm3.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Novel multi-element structure composite conductive filling material
The invention discloses a multi-element structure composite conductive filling material. A surface of lightweight inorganic powder (hollow glass beads, mica, carbon fibers, flake graphite and the like) is plated with a layer of wave absorbing magnetic material (Ni, Fe, Co, Ni-P, Co-P, Ni-Co-P, Co-W-P, barium ferrite, ferriferrous oxide, carbonyl iron and the like), and then is plated with a layer of conductive material (such as metal of silver, nickel, copper and the like or inorganic oxides of doped tin oxide, doped indium oxide, doped zinc oxide, titanium dioxide and the like), and a novel multi-element structure composite conductive filling material-inorganic powder core / magnetic material coating layer / conductive material coating layer is prepared. The electromagnetic shielding performance of the composite conductive filling materials can be raised further by utilization of wave absorbing performances of the wave absorbing material to electromagnetic waves and the reflection performances of the conductive material to electromagnetic waves. The composite conductive filling material has advantages of light weight, low cost, wide shield frequency band, good shielding properties and the like, and has great application values in the electromagnetic shielding composite material field.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Hexagonal crystal system Y-type ferrite electromagnetic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102674823AFacilitated DiffusionFully contactedInorganic material magnetismCrystal systemHexagonal crystal system
The invention provides a hexagonal crystal system Y-type ferrite electromagnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The material is a Ba2Co2-xZnxFeyO22 (x is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 2, and y is more than or equal to 10 and less than or equal to 14) ferrite material with hexagonal flaky morphology, and is obtained by uniformly mixing reactants and a reaction medium and calcining, wherein the reactants at least comprise a barium source, an iron source and a cobalt source; the reaction medium is one kind of chlorate or a mixture of two kinds of chlorate; the molar ratio of various elements in the reactants is that the ratio of Ba to Fe is 2:(10-14), and the ratio of Ba to Co is 2:(0-2); and the ratio of the mass of the reaction medium to the total mass of the reactants is (1-4):1. The invention has the advantages that the morphology of ferrite powder particles can be well controlled; inorganic molten salt is taken as the reaction medium, and the reactants are quickly dispersed and fully contacted in the molten salt by utilizing the dissolution of the reactants in the molten salt so as to reduce reaction temperature and improve reaction rate; the molten salt runs through generated barium ferrite particles in the reaction process, so the mutual agglomeration among the particles can be stopped; and the process is simple, the product is high in purity, the resultant temperature is low, the mechanical ball milling is not required, the doping is avoided, and the particle size distribution is narrow.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
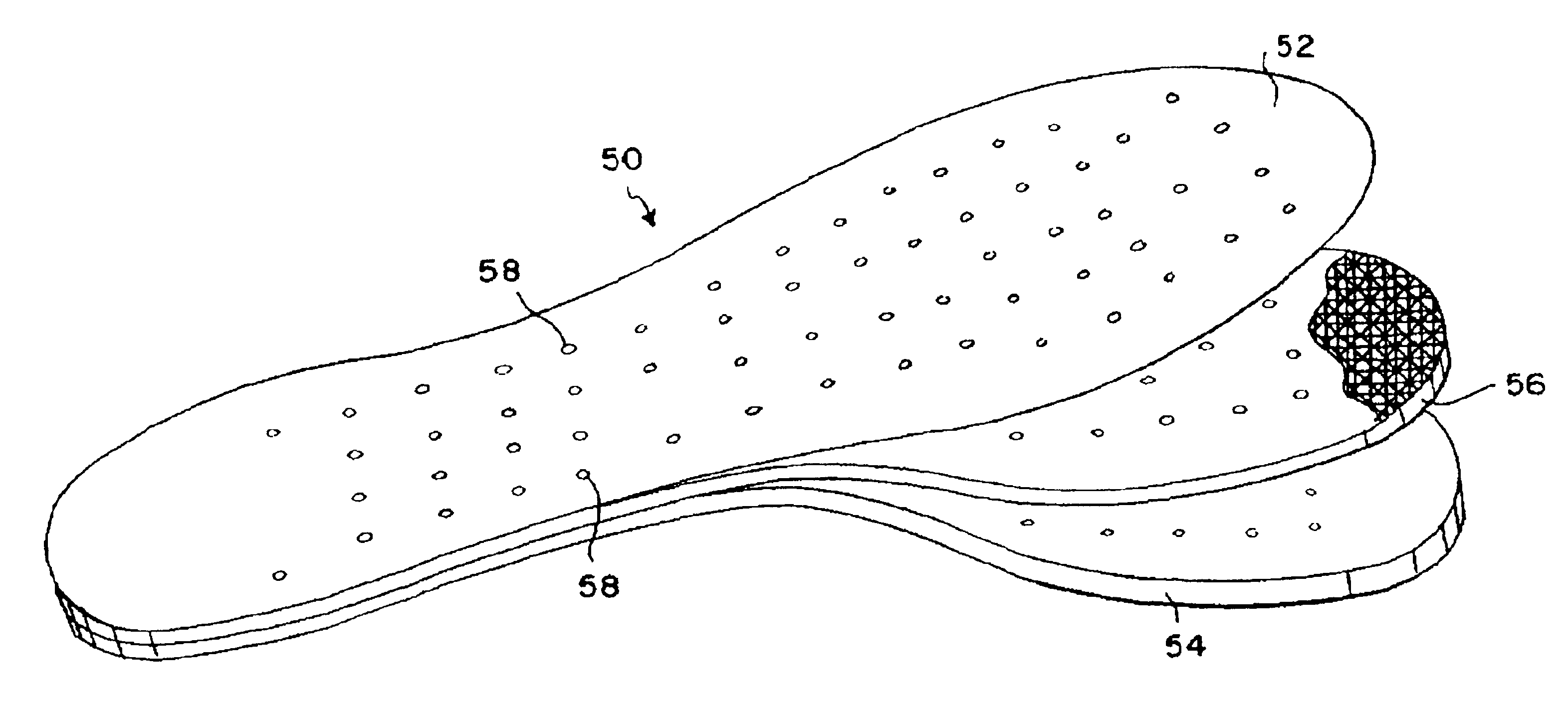
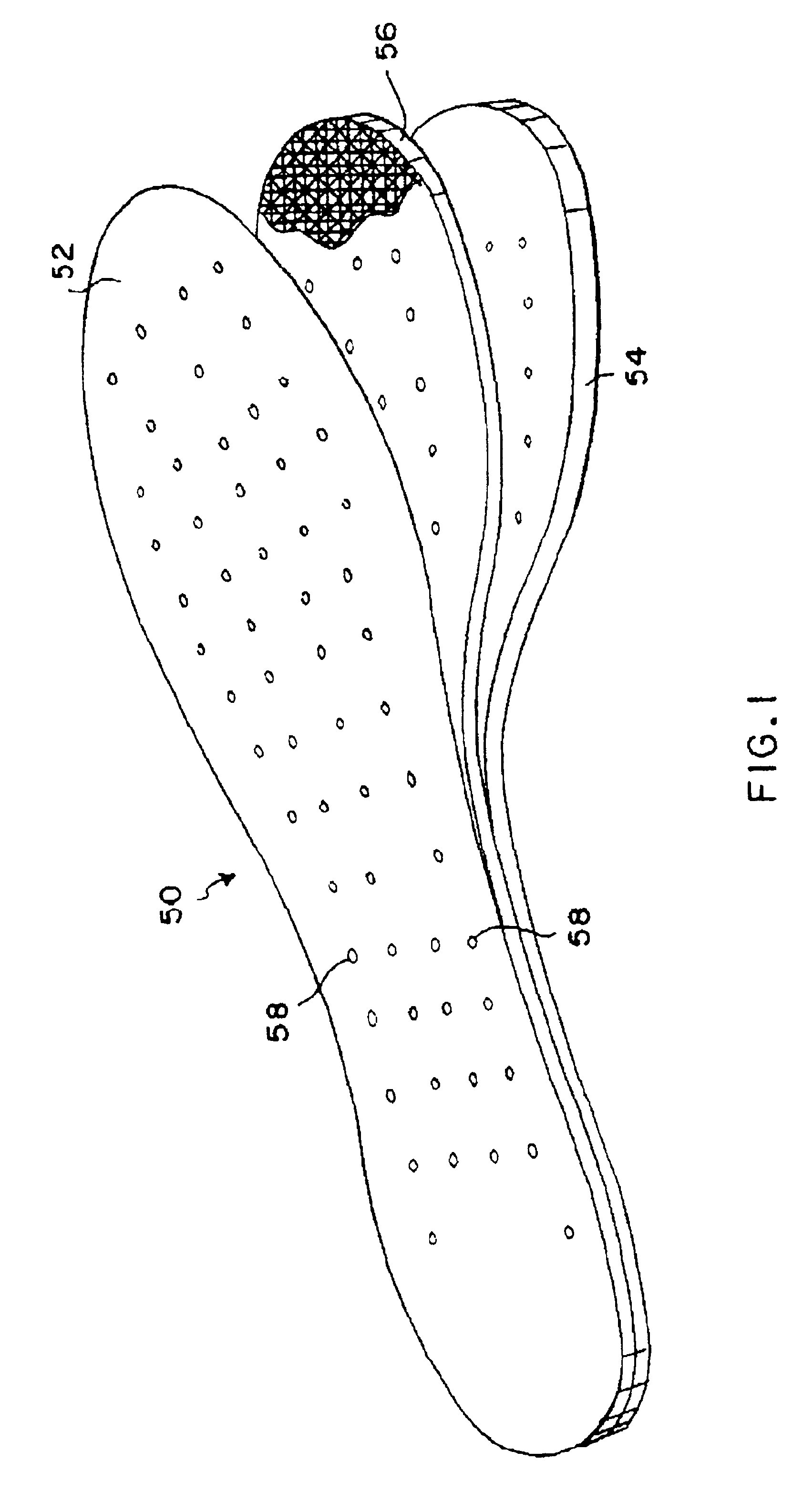
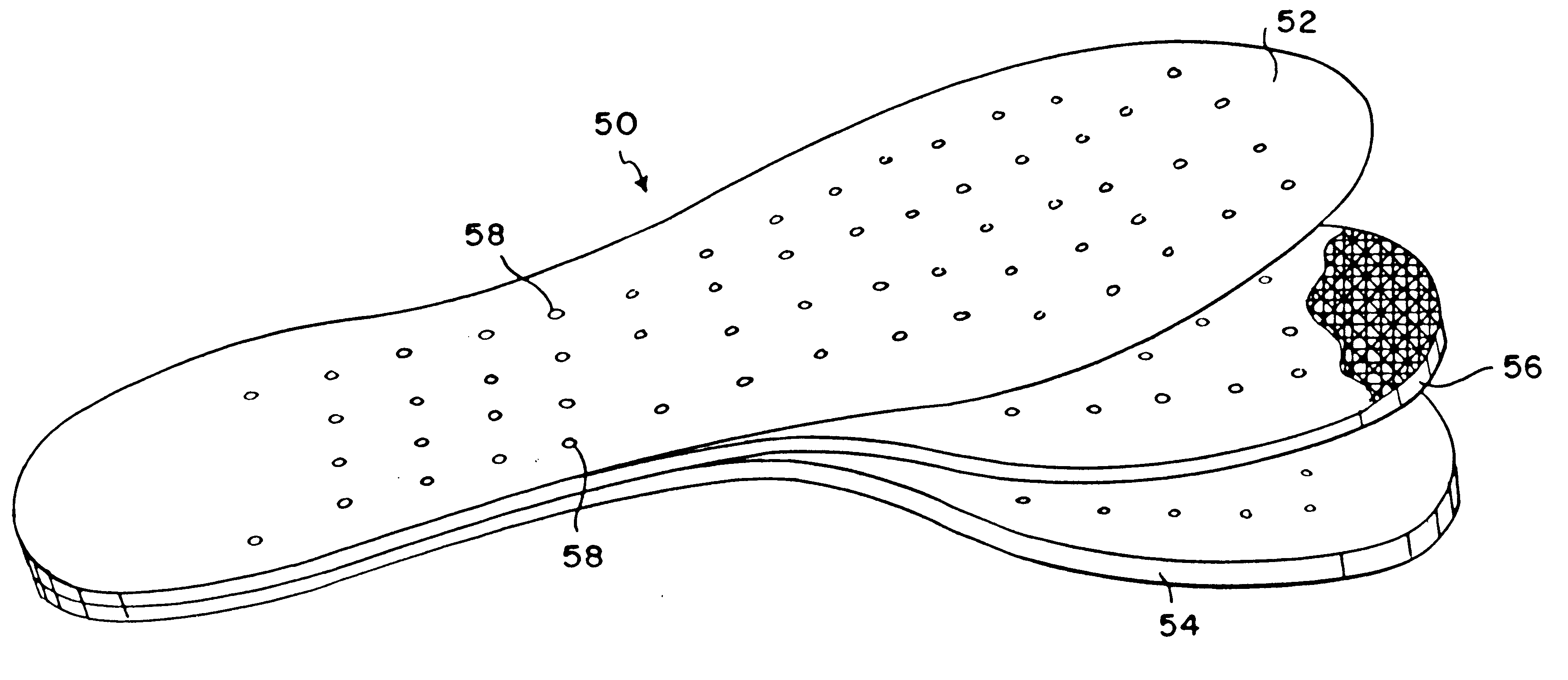
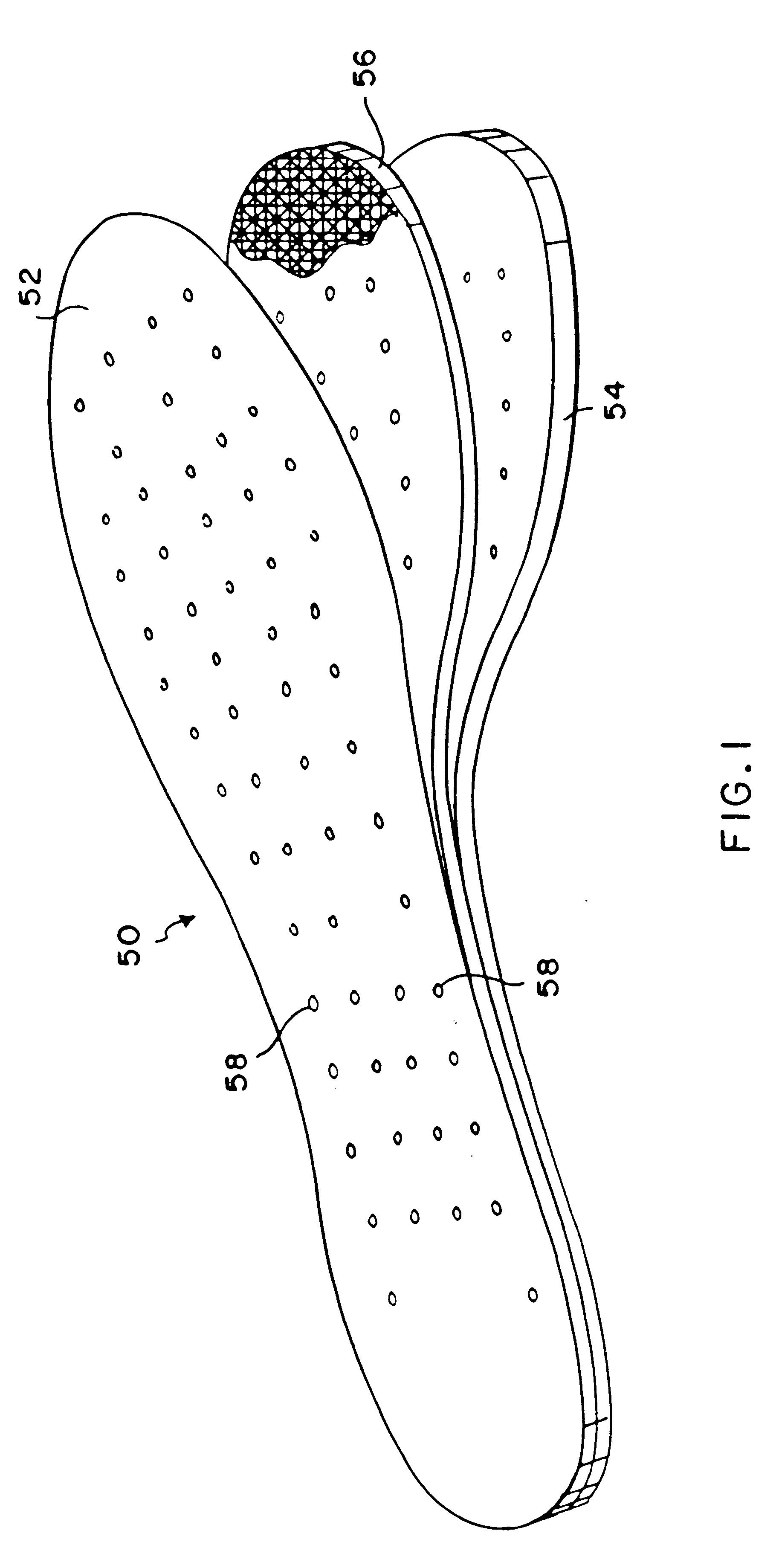
Flexible magnetic insole and method of manufacture
A magnetic insole provides cushioned magnetotherapy for the soles of a wearer's feet. A laminated insole in the general shape of a foot is inserted into a shoe to provide magnetotherapy to the wearer's foot adjacent the sole. Collateral therapeutic effects may be effected as such magnetotherapy may affect the nerve endings in the foot and collateral, corresponding, or related tissue structures in the body. A flexible magnetic core provides alternating magnetic fields in a regular pattern thereby to provide magnetotherapy to the foot. A cushioning base acts as an underpad for the magnetic insole in order to provide greater comfort and cushioning for the user's foot. The flexible magnetic core is constructed by mixing strontium ferrite, barium ferrite, or other strongly ferromagnetic material and with an elastic binder such as neoprene.
Owner:NYUU MAGUNETEIKUSU
Graphite/barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102876288AAvoid Toxic HazardsImprove absorbing performanceOther chemical processesCvd graphenePrepared Material
The invention provides a preparation method of a graphite / barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material, relating to a preparation method of a graphite-loaded magnetic particle barium ferrite. The invention aims to solve the problem that toxicity hazards exist in the existing graphite / Fe3O4 composite preparation processes. The method comprises the following steps: I. preparing the graphite oxide aqueous dispersion liquid; II. preparing the barium ferrite suspension; III. carrying out ultrasonic treatment; IV. carrying out hydrothermal treatment; and V. carrying out washing and drying treatment. The material and the preparation method have the following advantages: I. the operation cost and the operation difficulty are reduced, nonhazardous operation is achieved, and the material has the advantage of environment friendliness; and II. the prepared material has excellent wave-absorbing property and has good application prospect in the field of electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. The preparation method is mainly used for preparing the graphite / barium ferrite composite wave-absorbing material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
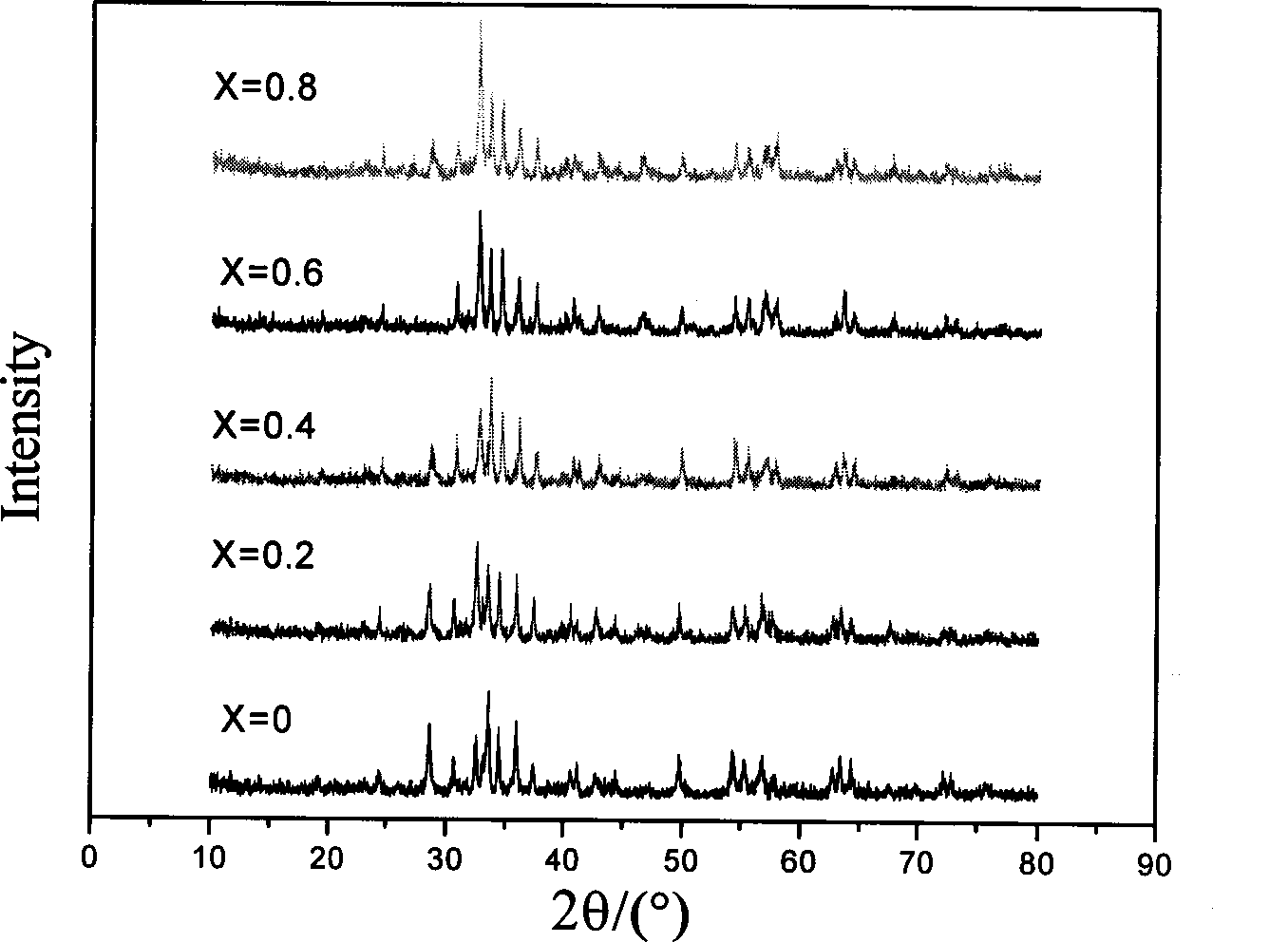
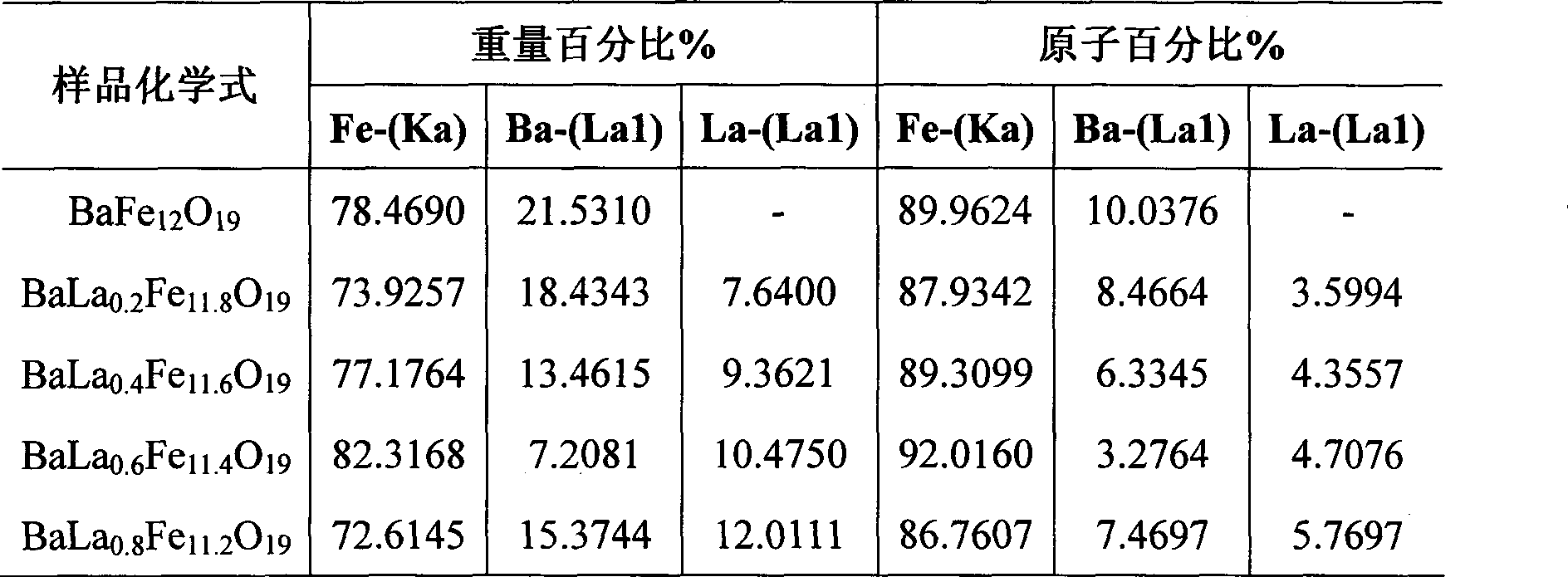
Preparation method of lanthanum-doped barium ferrite-polyaniline composite material microwave absorbent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lanthanum-doped barium ferrite-polyaniline composite material microwave absorbent. Lanthanum-doped barium ferrite is prepared from nitrate of barium, ferrum and lanthanum and an aniline monomer which serve as main raw materials by a sol gel-self-propagating method; and a lanthanum-doped barium ferrite-polyaniline composite is prepared by an in-situ chemical oxidation method. Due to organic composition of the lanthanum-doped barium ferrite and the polyaniline, advantages of the two components can be maintained; electromagnetic parameters of a material can be cut; microwave absorption frequency band is widened; the material density is reduced; absorption efficiency is improved; comprehensive properties are improved; the problems of high thickness, heavy weight, narrow frequency band, low absorbability and the like of the single ferrite wave-absorbing material are solved; thin, light, wide and strong requirements of a wave-absorbing coating are met; and the lanthanum-doped barium ferrite-polyaniline composite material microwave absorbent is an ideal and high-performance microwave absorbent.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
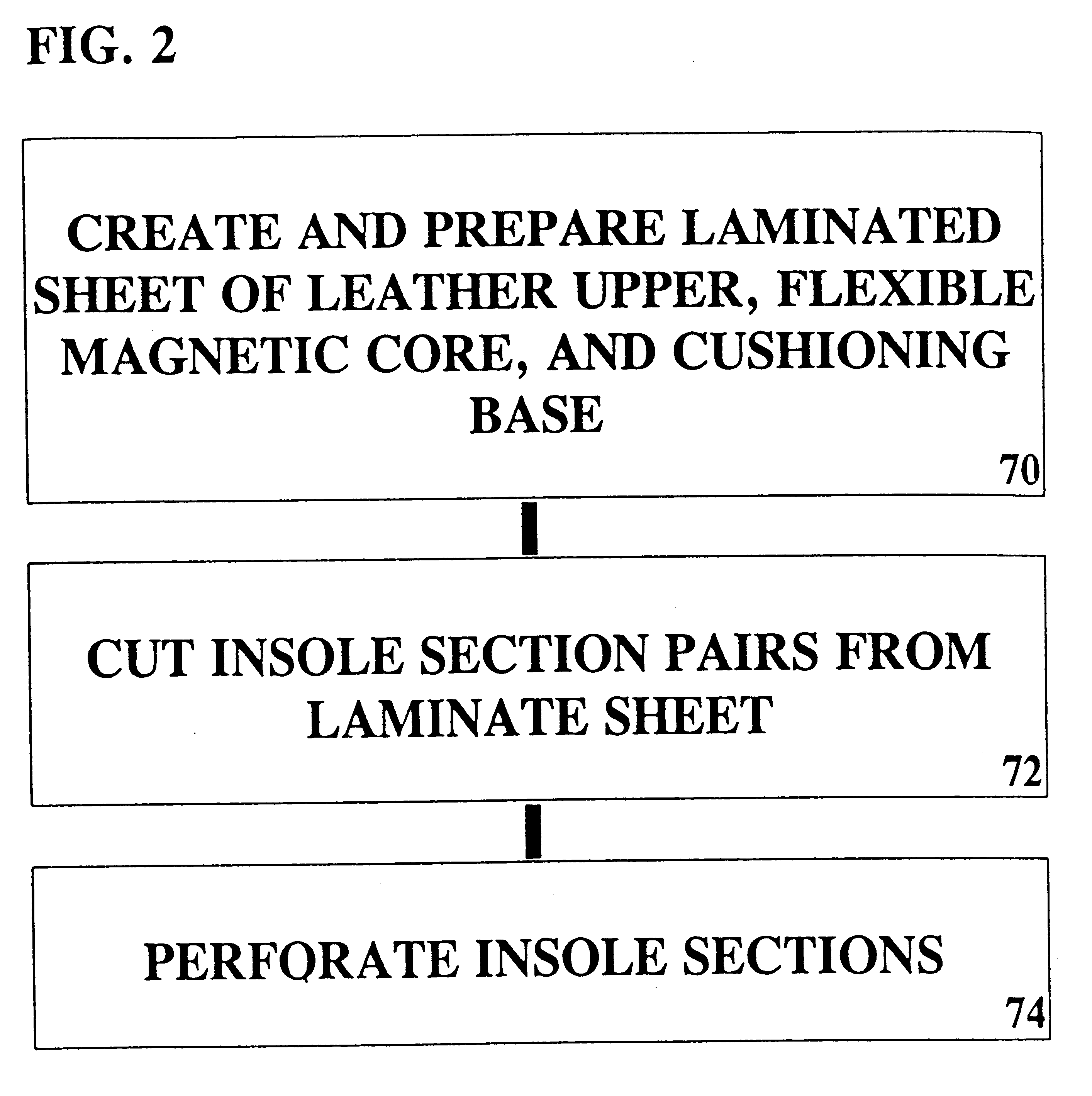
Flexible magnetic insole
A magnetic insole provides magnetotherapy for the soles of a wearer's feet. A laminated insole in the general shape of a foot is inserted into a shoe to provide magnetotherapy to the wearer's foot adjacent the sole. Collateral therapeutic effects may be effected as such magnetotherapy may affect the nerve endings in the foot and collateral, corresponding, or related tissue structures in the body. A leather upper is used to bear the abrasion between the foot and the magnetic insole. A flexible magnetic core provides alternating magnetic fields in a regular pattern thereby to provide magnetotherapy to the foot. A cushioning base acts as an underpad for the magnetic insole in order to provide greater comfort and cushioning for the user's foot. The flexible magnetic core is constructed by mixing strontium ferrite, barium ferrite, or other strongly ferromagnetic material and with an elastic binder such as neoprene. Additional minor constituents are also added to aid processing. The ferromagnetic material-elastic mixture is mixed together on a two (2) roll rubber mill as is known in the art, pigged, calendared, magnetized, and cut to size. The resulting sheet may then be laminated on its top side by leather upper material and on the bottom side by cushioning material so as to provide a three (3) layer laminated sheet from which magnetic insoles of the present invention may be cut and perforated.
Owner:NYUU MAGUNETEIKUSU
Method of one-step synthesis of hexagonal barium ferrite nanometer crystal by microwave-assistant sol-gel spontaneous combustion
InactiveCN101559982AUniform particle sizeImprove distribution uniformityIron compoundsQuick FreezeSingle crystal
The invention provides a preparation method of one-step synthesis of hexagonal barium ferrite (BaFe12O19) nanometer crystal by microwave-assistant sol-gel spontaneous combustion process. The technical scheme comprises the following steps: 1) nitrate Ba(NO3)2 and Fe(NO3)3 are taken as the raw materials; water solution with certain concentration is prepared according to barium ferrite chemometry; citric acid, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, urea, glucose and glycol and other organic reagents or compound thereof are taken as complexing agent of metal ion and hydrocarbon fuel required by sol-gel spontaneous combustion; ammonium nitrate and ammonium hydroxide are in addition added to adjust content of systematic oxidizer and PH value; even sol is formed by complexation. 2) xerogel which with desirable residual moisture content is prepared by using liquid nitrogen quick-freezing sol and vacuum condensation drying process. 3) the xerogel is compressed to form a block which is put into a quartz reaction chamber with microwave absorptive character; the xerogel is induced for spontaneous combustion in a microwave field, single-phase barium ferrite nanometer crystal is synthesized in one step which is precise in components and even in granule size; the invention can be used to prepare quasi-single crystal texture millimeter wave gyromagnetic ferrite.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Barium titanate and barium ferrite composite powder with nucleus shell structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102093045AStrong Magnetoelectric Coupling CoefficientFully coveredBarium titanateFerromagnetism
The invention discloses barium titanate and barium ferrite composite powder with a nucleus shell structure and a preparation method thereof. The powder is ferroelectric-ferromagnetic multifunctional composite powder with a nucleus shell structure, wherein ferroelectric powder barium titanate serves as a nucleus; a controllable-thickness ferromagnetic shell layer made from barium ferrite is arranged outside the nucleus; and the thickness of a shell layer is adjustable between 10 nanometers and 100 nanometers. The preparation method of the powder is a uniform co-precipitation out-phase coating method. In a co-precipitation process, urea is taken as a precipitant, any surface modification on barium titanate is not required, the nucleus is coated fully by the shell layer, and independent shell layer particles do not exist in a product. The method has the advantages of low cost, easiness and convenience in operating, simple equipment, wide application range and suitability for mass production.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A method for synthesizing high-performance barium ferrite with molten salt as flux and reaction medium
The invention relates to a preparation method of barium ferrite material. A method for synthesizing high-performance barium ferrite with molten salt as flux and reaction medium is characterized in that it comprises the following steps: 1) ferric oxide and barium carbonate are pressed by Fe3+: Ba2+ in a mol ratio of 10 to 12: 1. Weighing and mixing to obtain the reactant; 2) weighing NaCl and KCl according to the molar ratio of NaCl and KCl to be 1:1 and mixing to obtain the mixed salt; 3) according to the total mass of the mixed salt / total mass of the reactant=1~6, Mix the reactant with the mixed salt, ball mill and dry it, put it into a corundum crucible with a cover and place it at 750°C-1100°C for calcination for 1-3h; 4) After the reaction, cool down to room temperature naturally, wash and dry to obtain barium iron Oxygen. The method has the characteristics of simple process and low synthesis temperature, and the obtained barium ferrite has excellent performance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Lanthanum doped nano barium ferrite film and method of manufacturing the same
The invention relates to a lanthanum doping nanometer barium ferrite thin film and a preparation method thereof, which is technically characterized in that the prescription is as follows: 1.48 g / 100 ml to 1.60 g / 100 ml of glycol, 2.51 g / 100 ml to 2.71 g / 100 ml of citric acid, 1.74 g / 100 ml of iron nitrate, 0.125 g / 100 ml of barium nitrate and 0.03 g / 100 ml to 0.125 g / 100 ml lanthanum nitrate. The preparation method is that the iron nitrate, the barium nitrate, the lanthanum nitrate, and the like, serve as raw materials to prepare a forerunner body the forerunner body of the lanthanum doping nanometer barium ferrite in a sol-gel method; sol-gel method; clean silicon dioxide serves as a support base, the iron nitrate, the barium nitrate and the lanthanum nitrate serve as main salt, the citric acid serves as complexing agent, the glycol serves as complexing agent assist, and the soakage-drawing method is adopted to make the film. The method has the advantages of simple process flow and low cost; the method is convenient for preparing the thin film on bases with different shapes, the lanthanum doping nanometer barium ferrite thin film with high purity is obtained, and the thin film can be used for preparing magnetic recording materials and absorbing materials.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
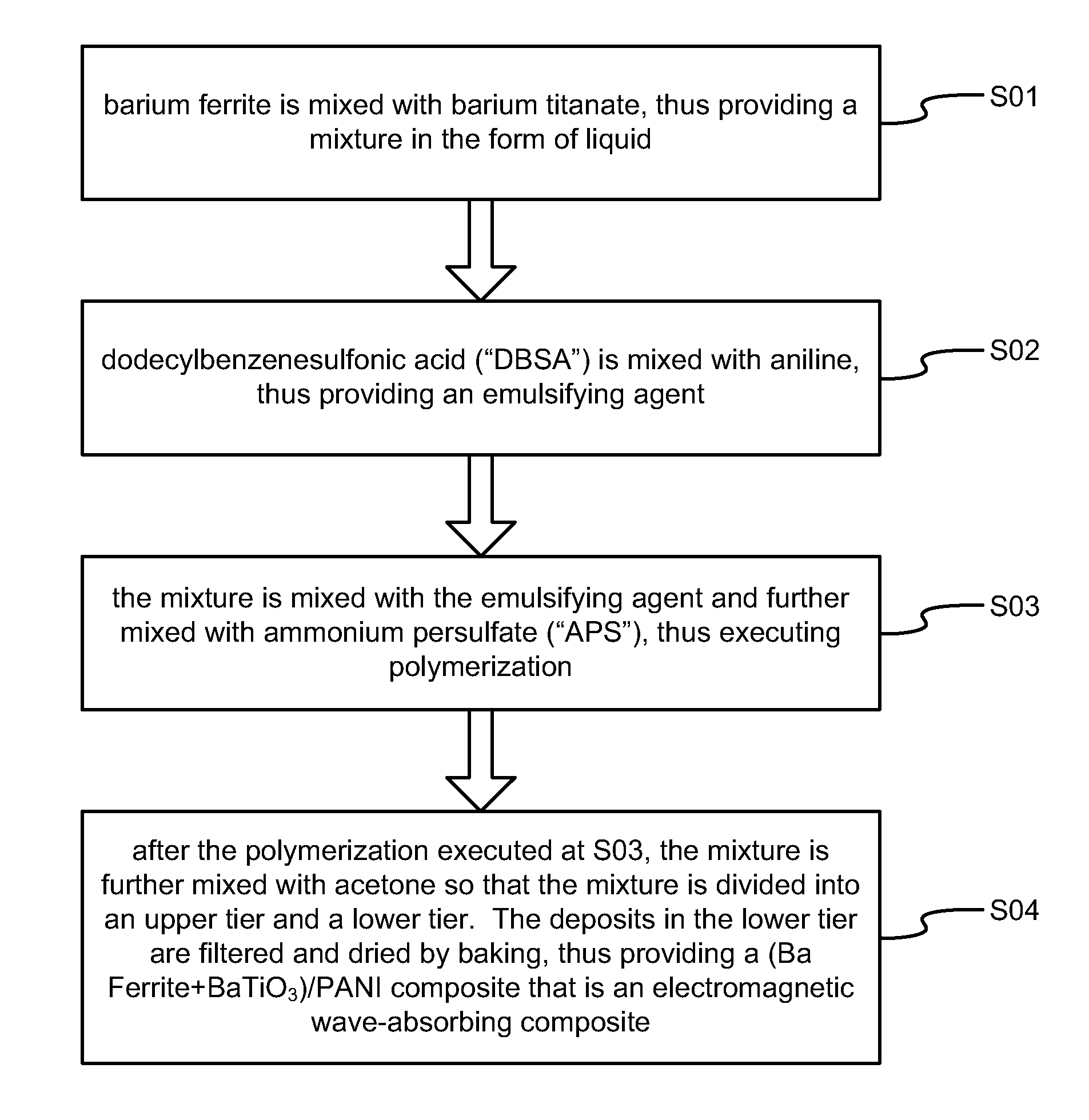
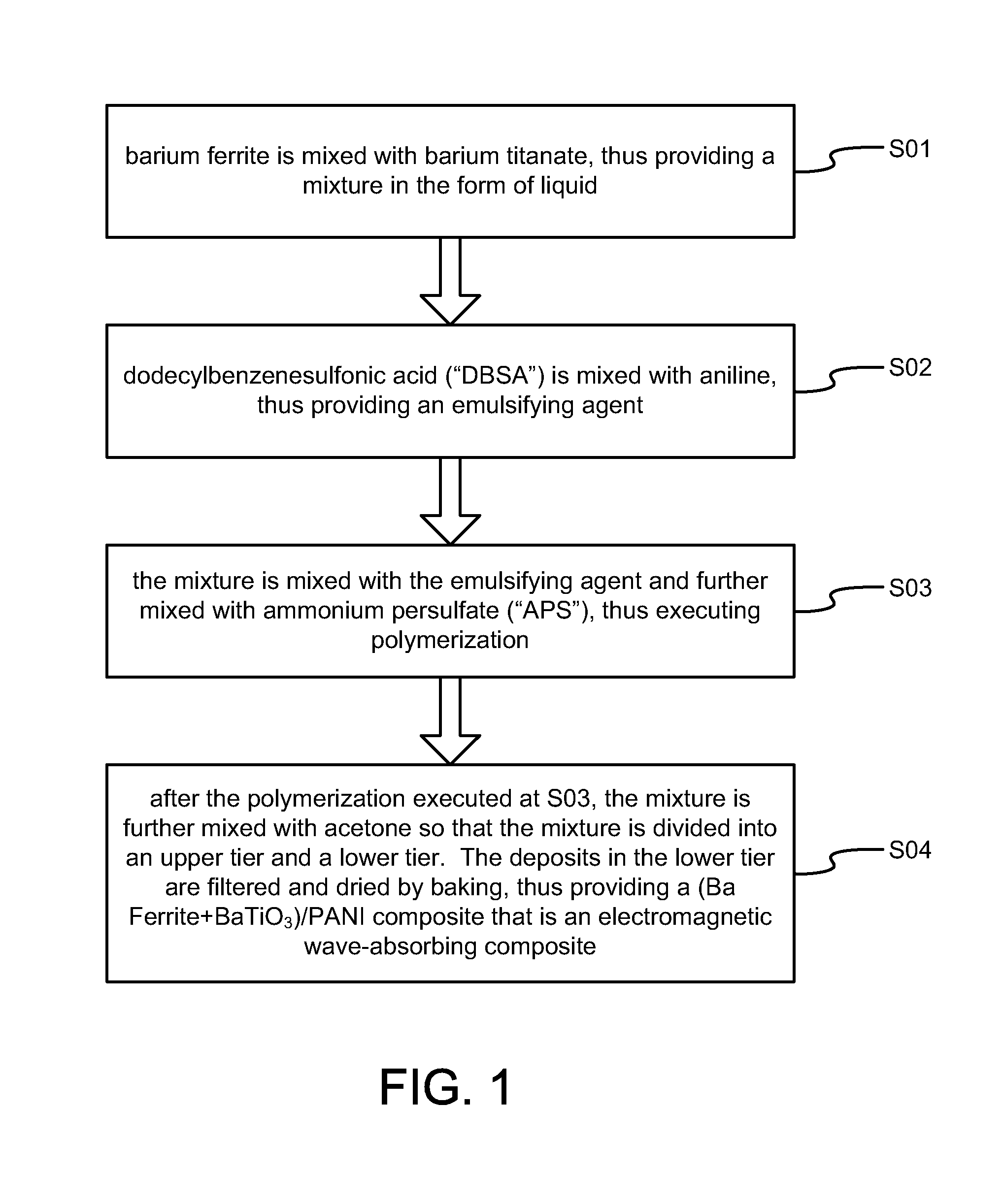
Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Material
Disclosed is an electromagnetic wave-absorbing composite. To make the electromagnetic wave-absorbing composite, barium ferrite (BaFe12O19) and barium titanate (BaTiO3) are added into aniline during polymerization of the aniline. Thus, a core-shell structure is formed. The core-shell structure includes a magnetic / dielectric core and a conductive shell for covering the magnetic / dielectric core.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Method of raising permanent magnetic ferrite residual magnetization by adding additive
InactiveCN1414575AImprove remanenceHigh energy productInorganic material magnetismStrontiumSilicon dioxide
An additive to be used for raising the residual magnetism of ferrite in permanent magnetism adds an additive of raising the residual magnetism with the molecular formula of MxSiyO2, where X=1=4, y=0-2, Z=2-6 in addition to add calcium carbonate and 1-4 additives of kaolin silica, aluminium oxide and boracic acid to increase its coercive force in the secondary process during production course of strontium ferrite or barium ferrite, where X, Y and Z can be decimal and M is one or more kinds of mixtures of Fe, Pr, Nd, Mn, Sr and C. With the same raw material, by use of the additive of MxSiyO2 ofthe present invention, the residual magnetism can be raised by 50-150 Gs based on 3600-4100 Gs.
Owner:BGRIMM TECH CO LTD +2
Catalyst for degrading water organic pollutant by microwave
InactiveCN1765494AImprove absorbing performancePromote degradationWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMicrowaveNetwork structure
The invention belongs to the technique for preparing the catalyst of sewage treatment, especially relating to a catalyst which can degrade the organic pollutant via microwave. The preparing method comprises: compounding the soluble barium and ferric salt with the gel polymer ligand in the network structure; arranging the leading body of gel polymer in the vacuum or protective atmosphere furnace to be thermal dissociated in the 200-500 Deg. C to attain the powder leading body; thermal processing it in 600-1000 Deg. C to attain the foamed material compounded with barium ferrite and pyrolysis carbon. The inventive catalyst uses the foamed material as carrier which has stronger ability to absorb organic pollutant with high catalytic activity. And said preparing method is simple and easy while the prepared catalyst has better property.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Flexible magnetic sheet systems
InactiveUS20100028667A1Efficient and inexpensiveDuplicating/marking methodsSynthetic resin layered productsHigh energyStrontium
Flexible magnetic sheets made with high-energy strontium ferrite and oriented magnetic particles of strontium ferrite and barium ferrite, such as to decrease thickness while maintaining a strong magnetic energy as well as flexibility.
Owner:MAGNUM MAGNETICS
Titanium-doped barium ferrite ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a titanium-doped barium ferrite ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. Densification sintering of the ceramic material is achieved through titanium doping, and electron hopping and a nonuniform conduction structure are formed through the replacement of iron ions to titanium ions. The ceramic has high residual magnetization, and great dielectric constant can be produced by utilizing the nonuniform conduction structure. The preparation method of the titanium-doped barium ferrite ceramic comprises the following steps of: preparing a ceramic precursor through a citrate sol-gel method, and then molding and sintering at high temperature to obtain the titanium-doped barium ferrite ceramic, wherein the molar ratio of titanium to barium is controlled between 0.4 and 0.8; and the molar ratio of iron to barium is between 11.6 and 11.2. According to the titanium-doped barium ferrite ceramic material and preparation method thereof, the process is simple, the cost is low, and meanwhile extremely high dielectric constant, high saturation magnetization and residual magnetization can be obtained. The residual magnetization acts as an important multifunctional material and can be used for developing preparation of relative electronic components.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
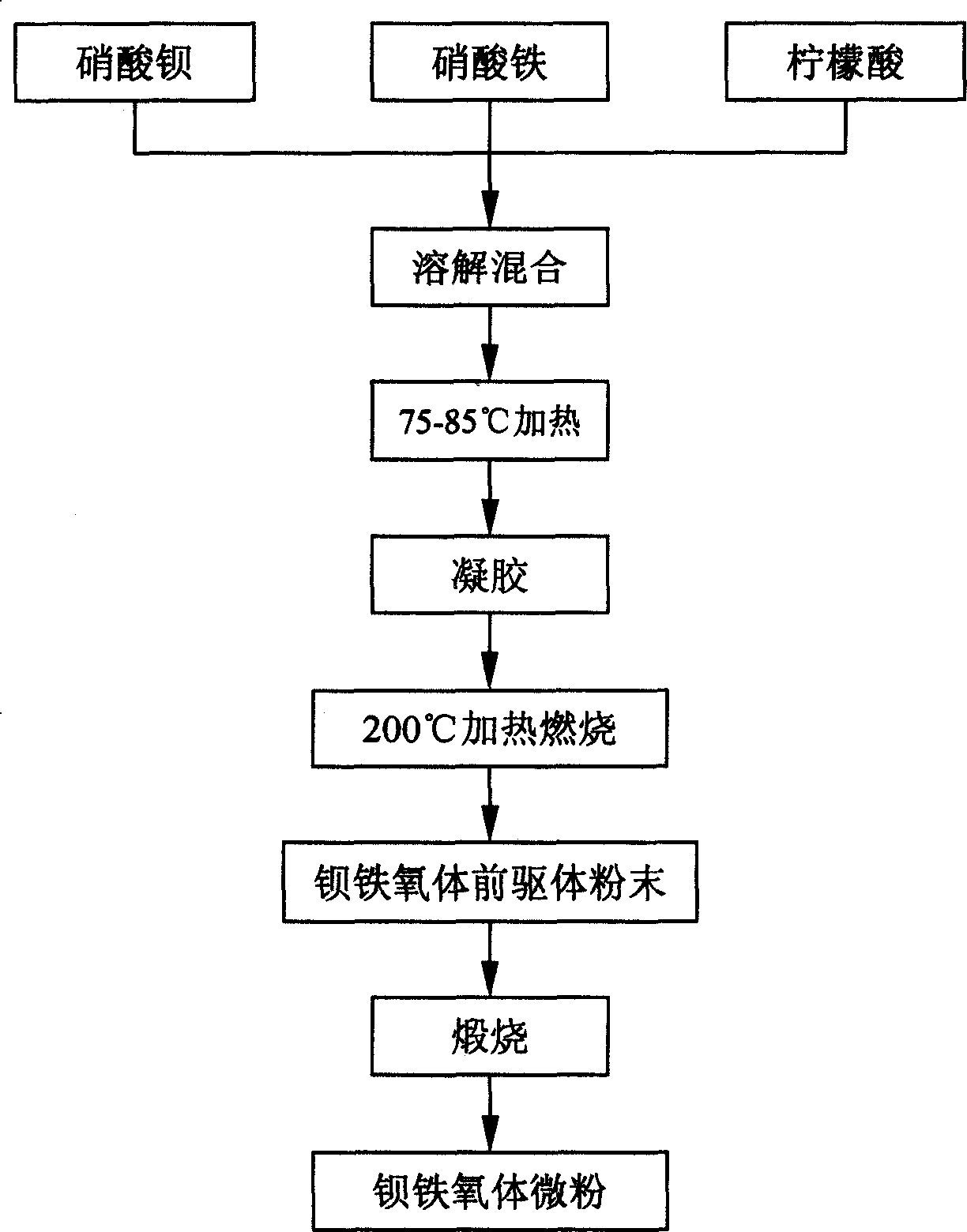
Process for synthesizing barium ferrite micro powder by self combustion method
The self-combustion process of synthesizing fine barium ferrite powder includes the following steps: 1) compounding 0.125-0.25 M barium nitrate solution, compounding 0.125-1.0 M ferric nitrate solution, and mixing via stirring to obtain mixed solution an of molar Fe / Ba ratio in 12; 2) mixing citric acid with mixed solution A to obtain mixed solution B with the molar ratio between nitrate radical and citric acid of 1 to 1-3 through stirring, regulating pH value with acid or alkali to 7.5-8.5, heating at 75-85 deg.c to evaporate for 8-12 hr to form gel; 3) evaporating water of the gel and self-spreading combustion in electric furnace at 200 deg.c to form powder precursor; and 4) calcining the powder precursor at 600-700 deg.c for 2-4 hr to obtain the fine barium ferrite powder. The present invention has the features of low synthesis temperature, high product purity and small average grain size.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
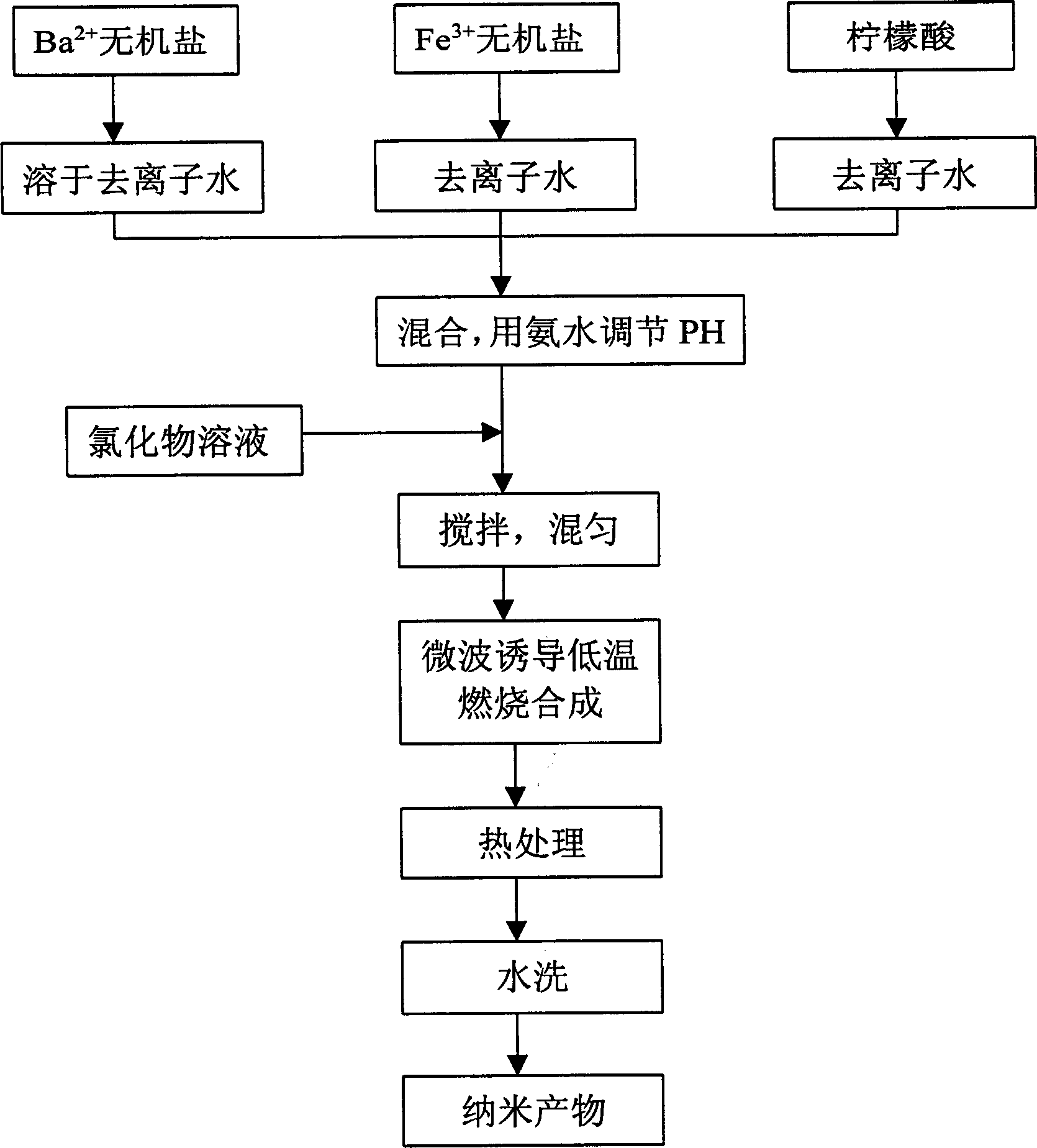
Process for synthesizing nano barium ferrite powder by microwave induction and low-temp combustion
InactiveCN1378996AThe process is simple and convenientReduce energy consumptionInorganic material magnetismPotassiumHeat treating
A process for synthesizing nanometre BaFe12O19 powder includes such steps as proportionally mixing the inorganic salt (nitrate or carbonate) of Ba2+ or Fe3+, citric acid and chloride (potassium chloride, sodium chloride, or their combination in mol ratio of NaCl / KCl=1:0.5-1.5), microwave inducing, low-temp. combustion for 2-10 min, heat treating under 900 deg.c for 0.2-10 hr and water washing to obtain nanometre hexagonal crystal of BaFe12O19. Its advantages are simple process, low energy consumption, and regulatable magnetic performance of product.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
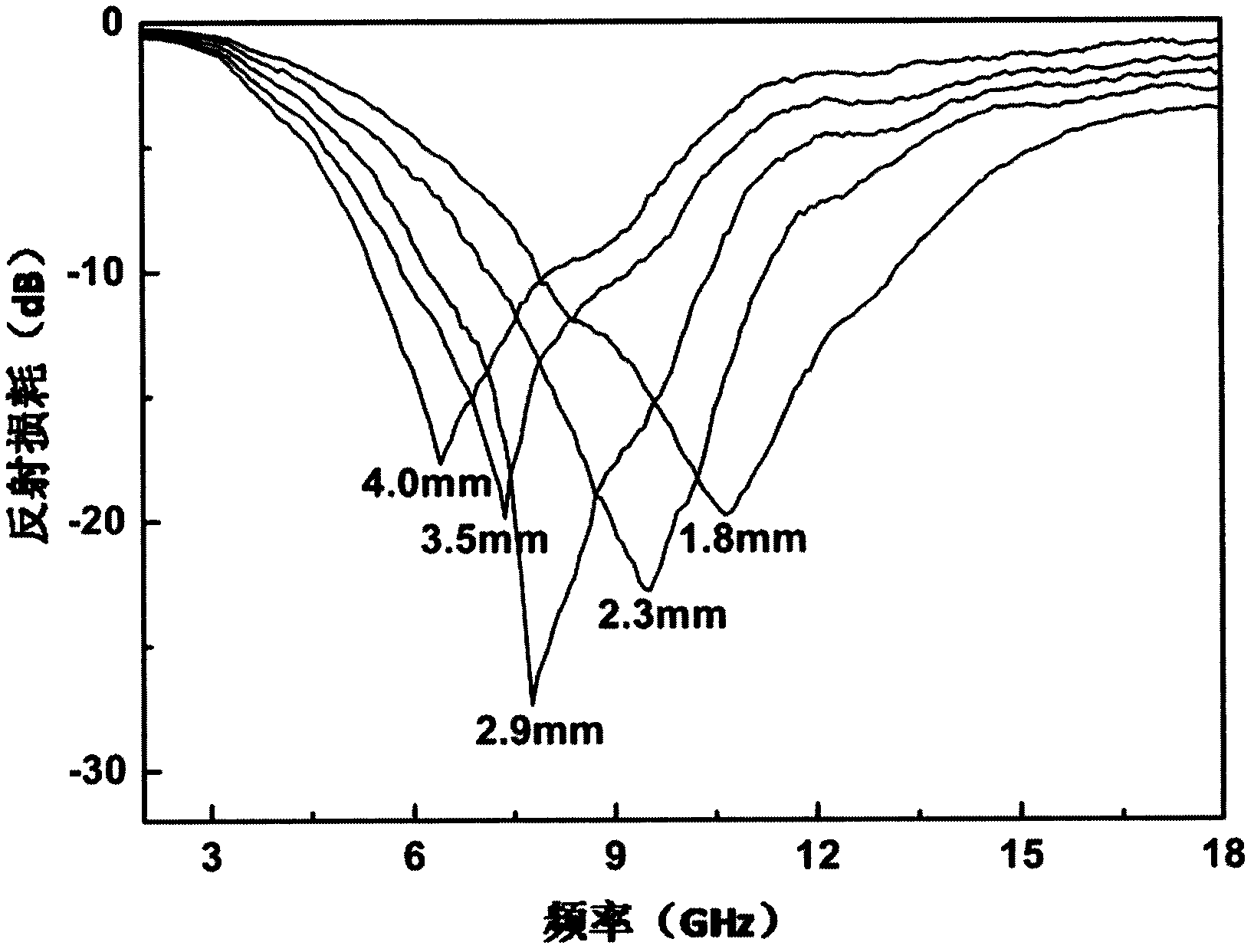
Zirconium-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104030667AApplication frequency band wideningMatching Thickness ReductionOther chemical processesBarium nitrateElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a zirconium-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing material having a chemical formula of BaFe12-xZrxO19, wherein x is 0.3-0.5, zirconium-doped barium ferrite is a polycrystalline powder, and Fe<3+> and Fe<2+> exist in the barium ferrite simultaneously. A preparation method comprises the preparation steps: mixing barium nitrate, iron nitrate and zirconium nitrate, adding deionized water, and dissolving into a nitrate solution; placing EDTA in deionized water, and dissolving into an EDTA solution; adding the nitrate solution into the EDTA solution, heating, drying, and thus obtaining a dry gel; and sintering the dry gel to obtain a zirconium-doped barium ferrite powder, then grinding, and thus obtaining the zirconium-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing material. The wave-absorbing material has the characteristics of thin matching thickness and wide wave-absorbing frequency band, can be used for a wave-absorbing coating layer, and can have wide applications in the electromagnetic shielding and stealth fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cerium-doped nanometer barium ferrite thin film and method for making same
InactiveCN101452756AImprove absorbing performanceAdjust the magneticMagnetic layersCerium nitrateCerium nitrate hexahydrate
The invention relates to a cerium-doped nanometer barium ferrite film and a preparation method thereof. The film is characterized in that the formula comprises 1.48 to 1.60g / 100ml of glycol, 2.51 to 2.71g / 100ml of citric acid, 1.74g / 100ml of ferric nitrate, 0.125g / 100ml of barium nitrate, and 0.04 to 0.125g / 100ml of cerium nitrate. The preparation method comprises: a crystalline nanometer barium ferrite film is prepared on a quartz substrate; the cerium-doped nanometer barium ferrite film with high purity is obtained through the optimization of preparation technology; and the film can be used for preparing magnetic recording materials and wave-absorbing materials. The method has the advantages that the method has simple process flow and low cost, is convenient for preparing films on various substrates with different shapes, is easy to obtain an uniform and multi-component oxide film, is easy for quantitative doping, and can effectively control the constituents and a microscopic structure of the film.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
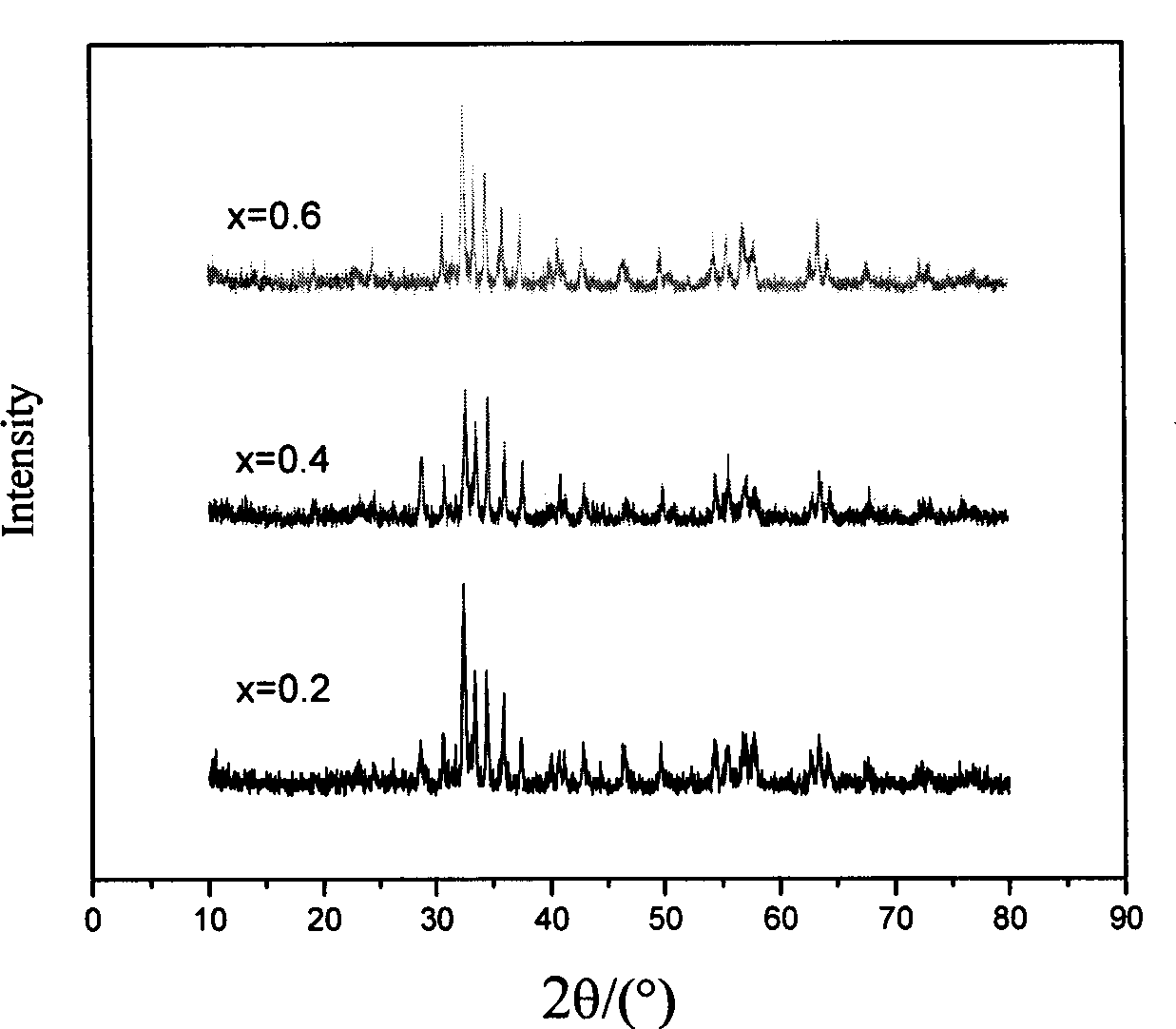
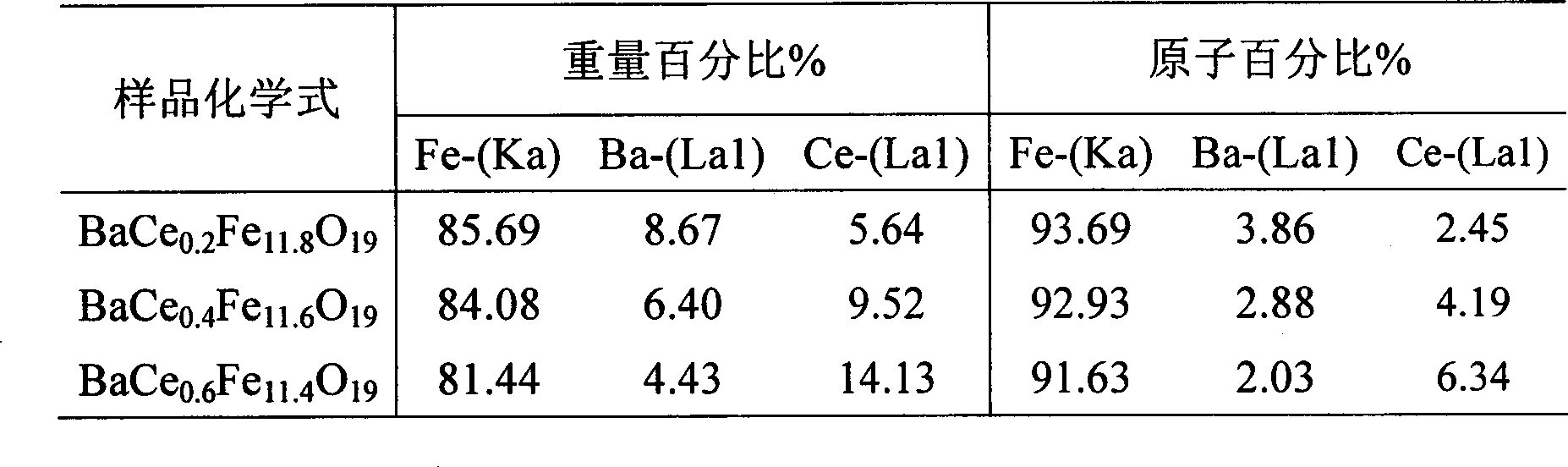
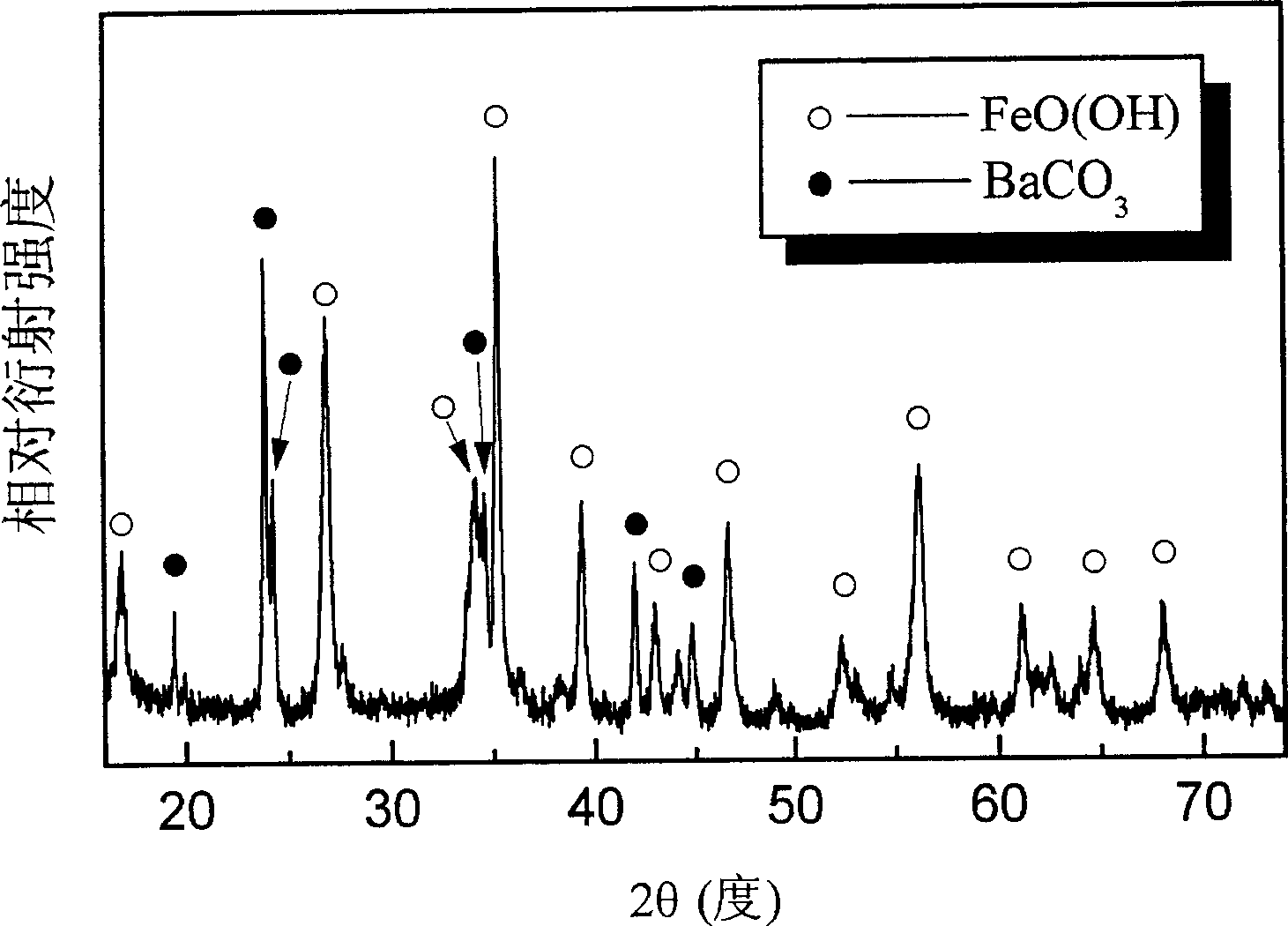
Hexagonal sheet-like barium ferrite magnetic nanometer powder preparation method
InactiveCN1880272ACalcination temperature is lowShort calcination timeHigh volume manufacturingHigh density
A preparing method of hexagonal piece barium ferrite nanometer magnetic powder includes: the predecessor body composed with the mixture of powdered BaCO3 and FeO(OH) powder the fineness of which belongs to nanometer is burnt for hexagonal piece barium ferrite nanometer magnetic powder. The optimal fineness of powered BaCO3 is nanometer and optimal nanometer FeO(OH) powder is the spindly FeO(OH) powder. The invention is suitable for application of perpendicular magnetic recording medium of high density and microwave absorber. The invention has the outstanding advantages as follows: well energy conservation effect for low calcinations heat and short calcinations time; high purity and good crystal model; simple process, low level demand for production facility, that is suitable for mass production in industry.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of graphene oxide/barium ferrite wave-absorbing material
InactiveCN104449561AHeating evenlyAvoid high temperature calcination processOther chemical processesBarium nitratePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a novel material for absorbing electromagnetic waves, and in particular relates to a preparation method of a graphene oxide / barium ferrite wave-absorbing material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: forming a sol from analytically pure barium nitrate Ba(NO3)2 and ferric nitrate Fe(NO3)3 with a graphene oxide water solution by taking citric acid and ethylene glycol as a compound complexing agent; continuously heating and stirring the sol to form a gel; and igniting the gel by virtue of microwave-assisted auto-combustion to further prepare the graphene oxide / barium ferrite wave-absorbing material. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and controllable in process, uniform in temperature distribution of the entire system through microwave field heating, and meanwhile, the preparation method can be used for greatly shortening reaction time and greatly improving the wave-absorbing performance of a barium ferrite material with the doping of the graphene oxide.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUEDA NEW MATERIAL TECH
Composite wave absorbing material and production thereof
InactiveCN1644546AWide absorption frequency rangeRadiation-absorbing paintsCITRATE ESTERFerrite thin films
A composite wave-absorbing material and its production are disclosed. The multi-hole glass phase micro-particle surface is coated by barium ferrite thin film, the mass ratio of multi-hole glass phase and ferrite is 0.1-10:1. The barium ferrite layer is produced on multi-hole glass phase micro-particle surface by citrate sol-gel method. The absorbing frequency range of composite material is wider than the barium ferrite. It can be used for electromagnetic wave absorbing material of aircraft and building coating.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Environment-friendly halogen-free ferrite composite magnetic material
InactiveCN102832005AImprove magnetic propertiesImprove mechanical propertiesInorganic material magnetismAdhesivesElastomerThermoplastic
The invention provides an environment-friendly halogen-free ferrite composite magnetic material, which comprises a bonding agent and ferrite magnetic powders; the bonding agent comprises at least one of PBE (propylene basic elastomer), TPO (thermoplastic polyolefin elastomer), POE (polyolefin elastomer) or acrylic acid rubber; the ferrite magnetic powders comprise strontium ferrite magnetic powders or barium ferrite magnetic powders, a mass percentage of the strontium ferrite magnetic powders or barium ferrite magnetic powders in raw materials is 50-94 percent, and a diameter-thickness ratio of the strontium ferrite magnetic powders or barium ferrite magnetic powders is (1.0-4.0):1. The adopted bonding agent is a halogen-free bonding agent, belonging to environment-friendly materials, environmental problems caused by halogens such as CPE (chlorinated polyethylene) or PVC (polyvinylchloride) do not exist, sulfide precipitating materials produced by NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) sulfide process do not exist as well, leftover bits and pieces of the bonding agent can be recycled, and thus the production cost is lowered; and the process for producing the composite magnetic material is simpler, and the magnetic property and the mechanical performance of the produced composite magnetic material are better.
Owner:BGRIMM TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing BaFe12O and BaTiO3 multiplayer nano compound film/powder
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Composite wave-absorbing material of zinc oxide-coated barium ferrite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102504759AImprove absorbing performanceStable structureOther chemical processesDistillationBarium nitrate
The invention discloses a composite wave-absorbing material of zinc oxide-coated barium ferrite and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of wave-absorbing materials. The composite wave-absorbing material comprises zinc oxide-coated barium ferrite particles. The preparation method for the composite wave-absorbing material comprises the following steps: preparing ferric nitrate, barium nitrate and citric acid into a solution in molar ratio; regulating the pH value of the solution; performing drying by distillation until gel is generated; then heating for an auto-igniting process reaction; roasting to obtain the barium ferrite particles; dissolving zinc acetate into diethylene glycol, and adding a polyvinylpyrrolidone surface active agent to prepare a solution 1; adding a barium ferrite powder to the solution 1 in ferrum-zinc molar ratio; and reacting at certain temperature to obtain a zinc oxide-coated barium ferrite powder. The invention has the advantages that the preparation process is simple, and the production cost is low. The prepared composite wave-absorbing material of the zinc oxide-coated barium ferrite has excellent wave-absorbing performance, a stable structure and good dispersion property.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Magnetic nano composite film and its method for preparing sol-gel
InactiveCN1588593ACounteract internal stressNo microcracksNanostructure manufactureMagnetic film to substrate applicationComposite filmElectromagnetic shielding
The invention is a nano complex film and its sol-gel preparing method, firstly making a TiO2 sol and a barium ferrite precursor sol, respectively, then mixing them to make stable mixed sols in different mass proportions, adopting a rotating method to coat a substrate (like a quartz glass plate), making drying and thermal treatment to obtain a microcrack-free complex film. It belongs to a nano complex film and a crystal particle size less than 100 nm; it also belongs to an inorganic film and has a wide range of use temperature. It has higher magnetic property and has a wide application prospect in the fields of magnetic recording, electromagnetic screening, wave absorption coating, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Barium ferrite composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103184033AHigh sintering activityCalcination temperature is lowOther chemical processesCombustionSolvent
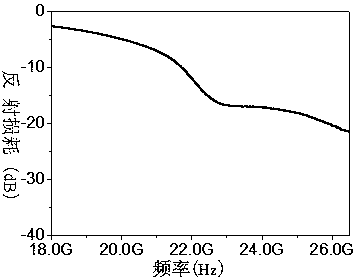
The invention discloses a preparation method of a barium ferrite composite material, which comprises the following steps: (1) well mixing an aqueous solution containing Ba2+ and an aqueous solution containing Fe3+ to obtain a mixed solution, mixing with citric acid, adjusting the pH value to 6.5-7.5, mixing with nanometer silica powder, dispersing uniformly, volatilizing the solvent to obtain wet gel, wherein the using amount of the nanometer silica powder is 0.5-10 wt% of the mass of the barium ferrite composite material; (2) drying the wet gel, performing self-propagating combustion, removing citric acid to obtain a precursor, calcining the precursor, and cooling to obtain the product. The preparation method of the invention is simple in process, high in precursor calcining activity, and low in calcining temperature; the prepared barium ferrite composite material is uniform in components, good in dielectric properties, good in wave absorption performance in high frequency range, and high in continuous bandwidth below -20 dB.
Owner:NINGBO SHANSHAN NEW MATERIAL TECH +1
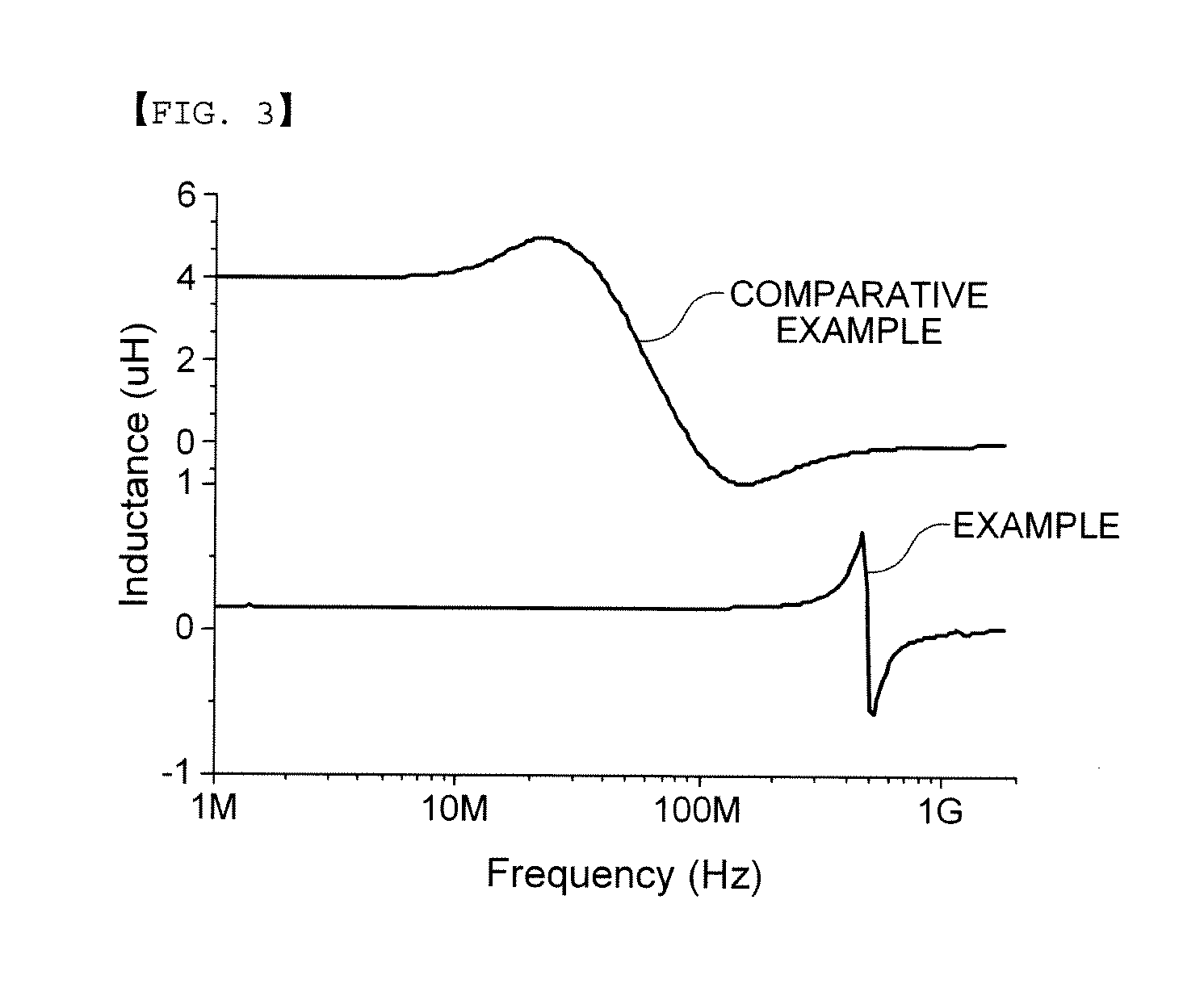
Ferrite composition for high frequency bead and chip bead comprising the same
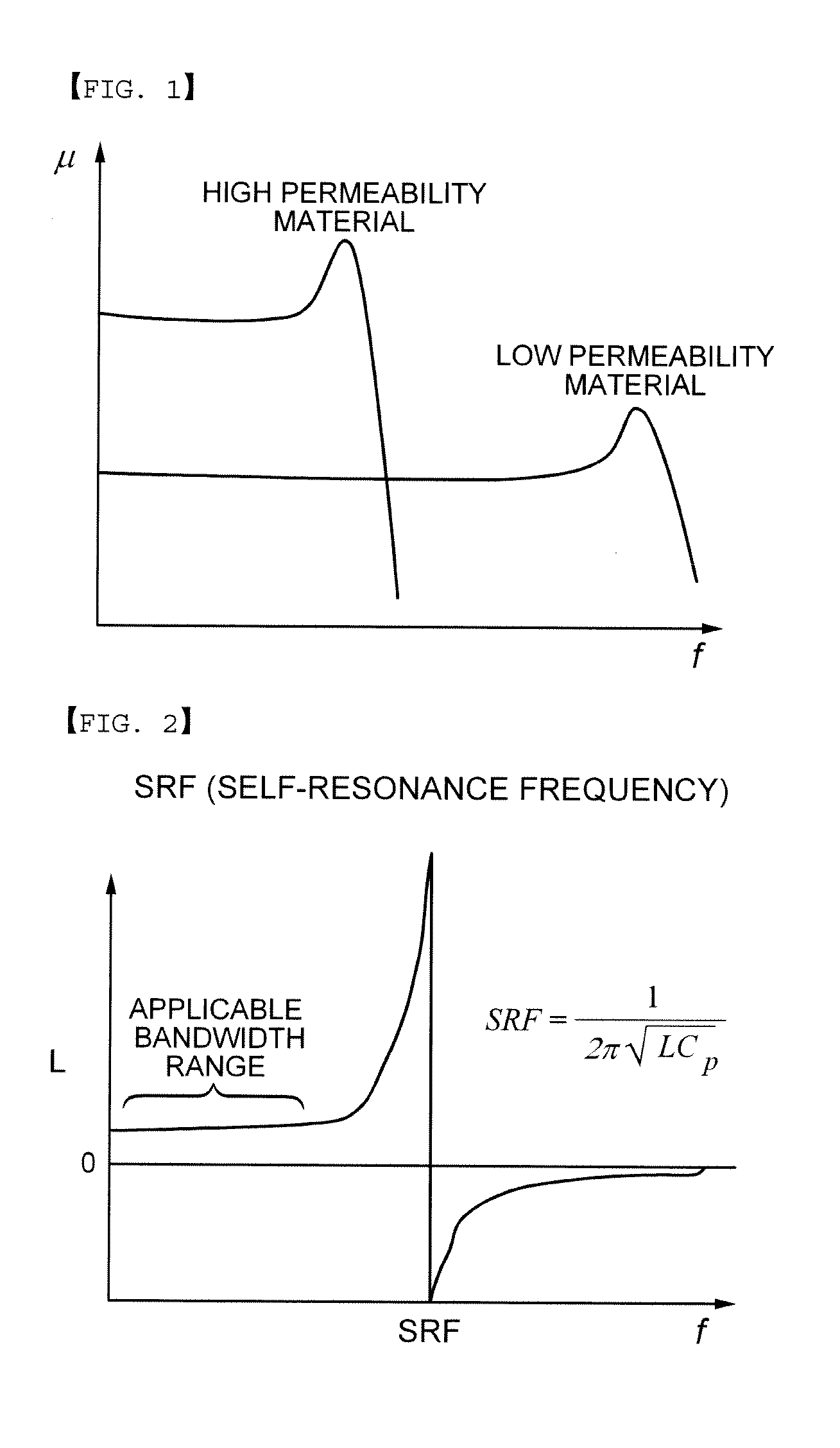
Disclosed herein are a ferrite composition for a high frequency bead in that a part of Fe in M-type hexagonal ferrite represented by BaFe12O19 is substituted with at least one metal selected from a group consisting of 2-valence, 3-valence and 4-valence metals, as well as a chip bead material using the same.According to embodiments of the present invention, the dielectric composition is characterized in that a part of Fe as a constituent of M-type hexagonal barium ferrite is substituted by other metals, to thus decrease a sintering temperature to 920° C. or less without using any additive for low temperature sintering. Moreover, because of high SRF properties, the inventive composition is applicable to a multilayer type chip bead used at a high frequency of more than several hundreds MHz and a magnetic antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Zirconium and titanium-co-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing powder material and preparation method therefor
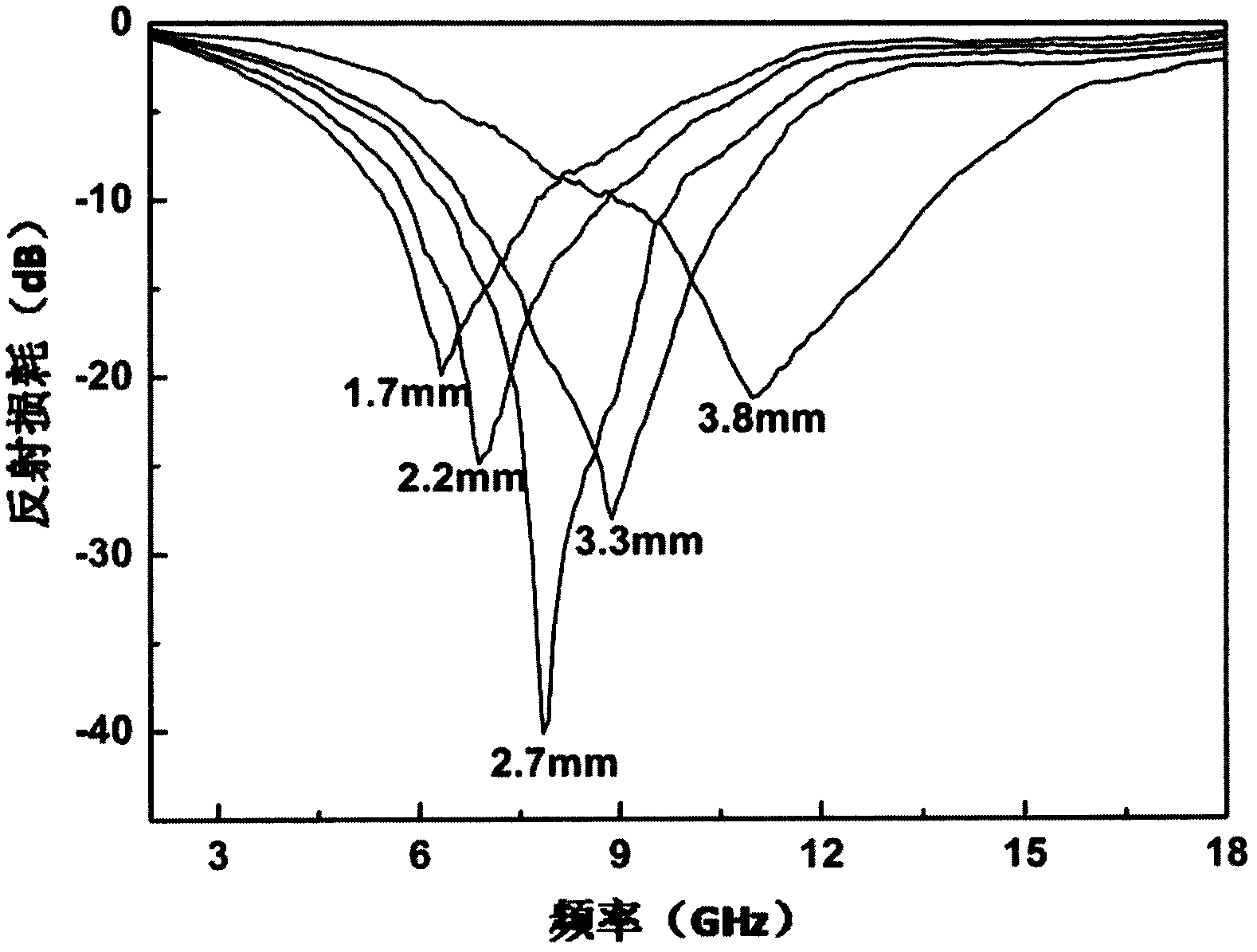
ActiveCN104844182AReduce the heterosexual fieldAbsorbing frequency modulation range widenedReflection lossElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a zirconium and titanium-co-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing powder material. The chemical formula is BaFe(12-x)ZrxTixO19, wherein x is equal to 0.2-0.4. The zirconium and titanium-co-doped barium ferrite is single-phase polycrystalline powder, and Fe<3+> and Fe<2+> exist in the barium ferrite at the same time. A preparation method comprises the following step of preparing the zirconium and titanium-co-doped barium ferrite wave-absorbing powder material by virtue of a self-propagating combustion method which is combined with ball-milling and a sequential secondary vacuum high-temperature thermal treatment process. The wave-absorbing material disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being strong in absorption loss, wide in wave absorbing bandwidth, thin in match thickness and wide in modulated wave-absorbing frequency range. The effective wave absorbing bandwidth is controlled in a frequency range of 18-40GHz, double absorption peaks appear, the maximum absorbing bandwidth can reach 16GHz, the optimum match thickness is just about 1mm, and the optimum reflection loss RL value at the special frequency can reach about -48dB. The barium ferrite wave-absorbing powder material is simple in preparation process, can be used for a wave-absorbing coating, and can be widely applied to the fields of electromagnetic shielding and stealth.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com