Composite wave-absorbing material of zinc oxide-coated barium ferrite and preparation method thereof
A composite wave-absorbing material, barium ferrite technology, applied in the field of wave-absorbing materials, can solve problems such as unsuitable microwave absorbing materials, achieve excellent wave-absorbing performance, low production cost, and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
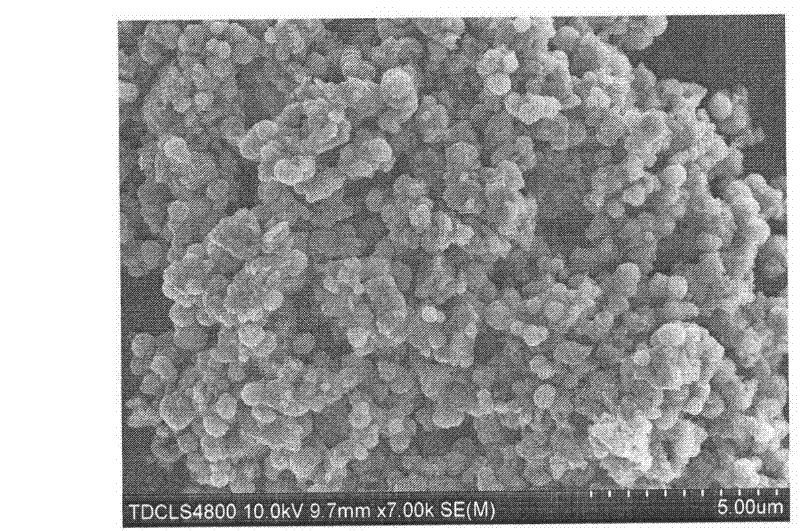
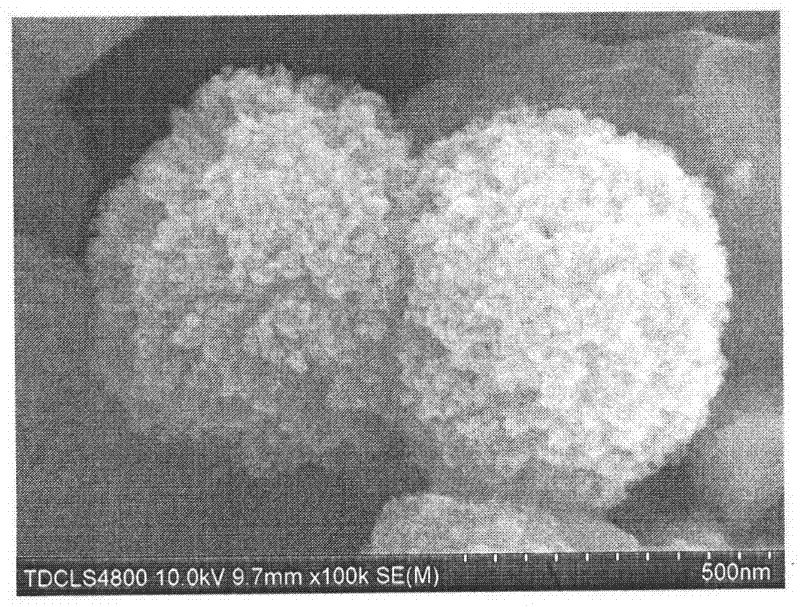
[0015] Weigh 18g of citric acid, dissolve it in 100ml deionized water, and prepare a citric acid solution; weigh 22g of ferric nitrate and 1.3g of barium nitrate and dissolve it in the citric acid solution, and adjust the pH of the solution to 7 with ammonia water. Put the above solution in a drying oven and dry it at 80°C until it becomes jelly, heat the jelly to 200°C and burn it to react to obtain the product and grind it, heat treatment at 800°C for 2 hours, and obtain barium with an average particle size of 0.9 μm Ferrite powder. Weigh 3.00 g of zinc acetate, 0.5 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and mix with 80 ml of diethylene glycol, then weigh 3.00 g of ground barium ferrite and add it to the above mixed solution for ultrasonication for 20 minutes. The above-mentioned mixture was introduced into a three-necked flask with an argon gas and a condenser, followed by argon gas for 30 minutes to remove the air in the system, and the system was slowly heated to 200° C. and kept for ...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Weigh 9.0 g of citric acid, dissolve it in 50 ml of distilled water, and prepare a citric acid solution; weigh 11.0 g of ferric nitrate, and dissolve 0.65 g of barium nitrate in the citric acid solution, and adjust the pH value to 9 with ammonia water. Put the above solution in a drying oven at 80°C and dry until it becomes jelly, heat the jelly to 200°C and burn it to react, collect the product, grind it thoroughly and heat it at 800°C for 2 hours to obtain barium with an average particle size of 0.9 μm Ferrite powder. Weigh 1.5 g of zinc acetate, 0.25 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 40 ml of diethylene glycol and mix to prepare a solution, then weigh 1.5 g of ground barium ferrite and add it to the above mixed solution for ultrasonication for 20 minutes. The above-mentioned mixture was introduced into a three-necked flask with an argon gas and a condenser, followed by argon gas for 30 minutes to remove the air in the system, and the system was slowly heated to 200° C. a...
Embodiment 3
[0019] Weigh 18g of citric acid, dissolve it in 100ml of distilled water, and prepare a citric acid solution; weigh 22g of ferric nitrate, and dissolve 1.3g of barium nitrate in the citric acid solution, and adjust the pH value to 7 with ammonia water. Put the above solution into a drying oven and dry it at 80°C until it becomes a jelly, heat the jelly to 200°C and burn it to react to obtain 20g of BaFe 12 o 19 The powder was ball milled for 5 hours and then heat-treated at 800°C for 2 hours to obtain barium ferrite powder with an average particle size of 0.6 μm. Weigh 1.5 g of zinc acetate, 0.5 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone and mix with 80 ml of diethylene glycol, then weigh 2.5 g of ground barium ferrite and add it to the above mixed solution for ultrasonication for 20 minutes. The above mixture was introduced into a three-necked flask with argon gas and a condenser, and argon gas was passed for 30 minutes to remove the air in the system, and the system was slowly heated to 200...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com