Pavement repairing method capable of resolving settlement velocity difference between hard soil and soft soil
A technology for road surface repair and hard soil layer, applied in the direction of road, road, bridge maintenance, etc., can solve problems such as the difference in settlement velocity between hard soil layer and soft soil layer, achieve short curing time, reduce construction time, and avoid bridgehead jumping. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
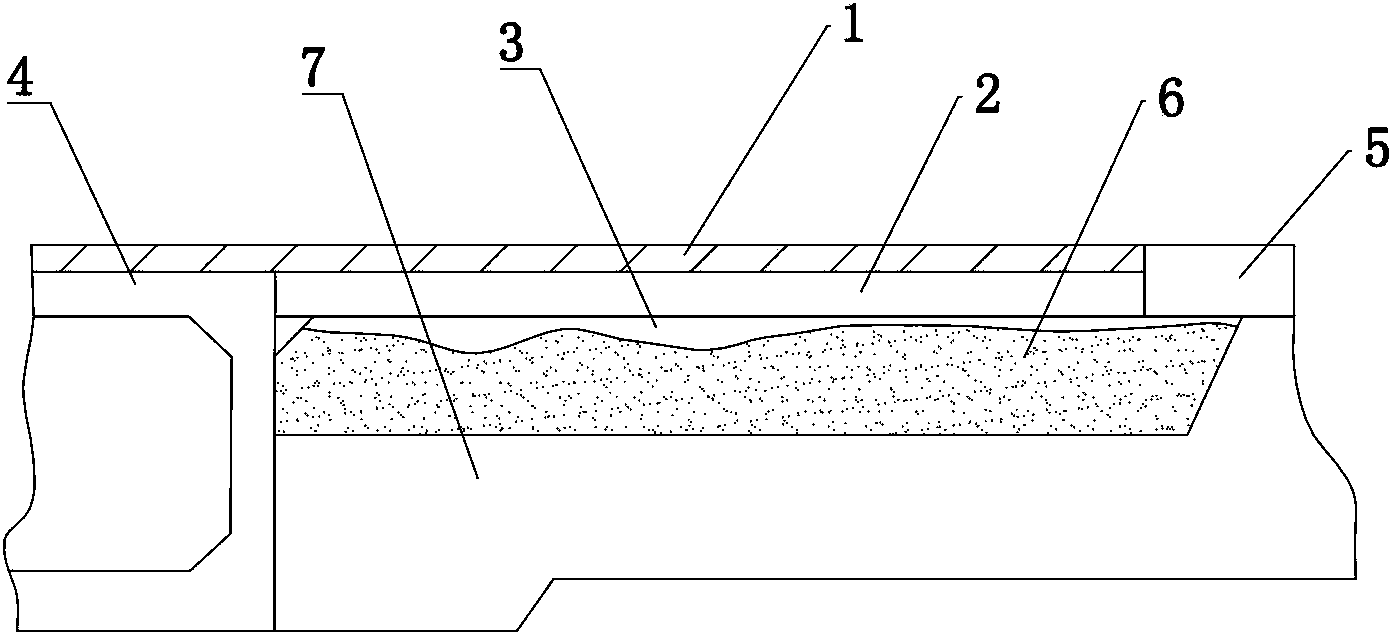
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the damaged bridge generally includes: pavement 1, slab 2, void 3, bridge deck 4, road surface 5, soft soil layer 6, and hard soil layer 7.
[0035] Void generally occurs between the strap 2 and the soft soil layer 6, and the volume of the void will gradually increase with the settlement of the soft soil layer. Since the soft soil layer 6 is higher than the roadbed, it is convenient to drill the soft soil layer 6 from the side. hole.
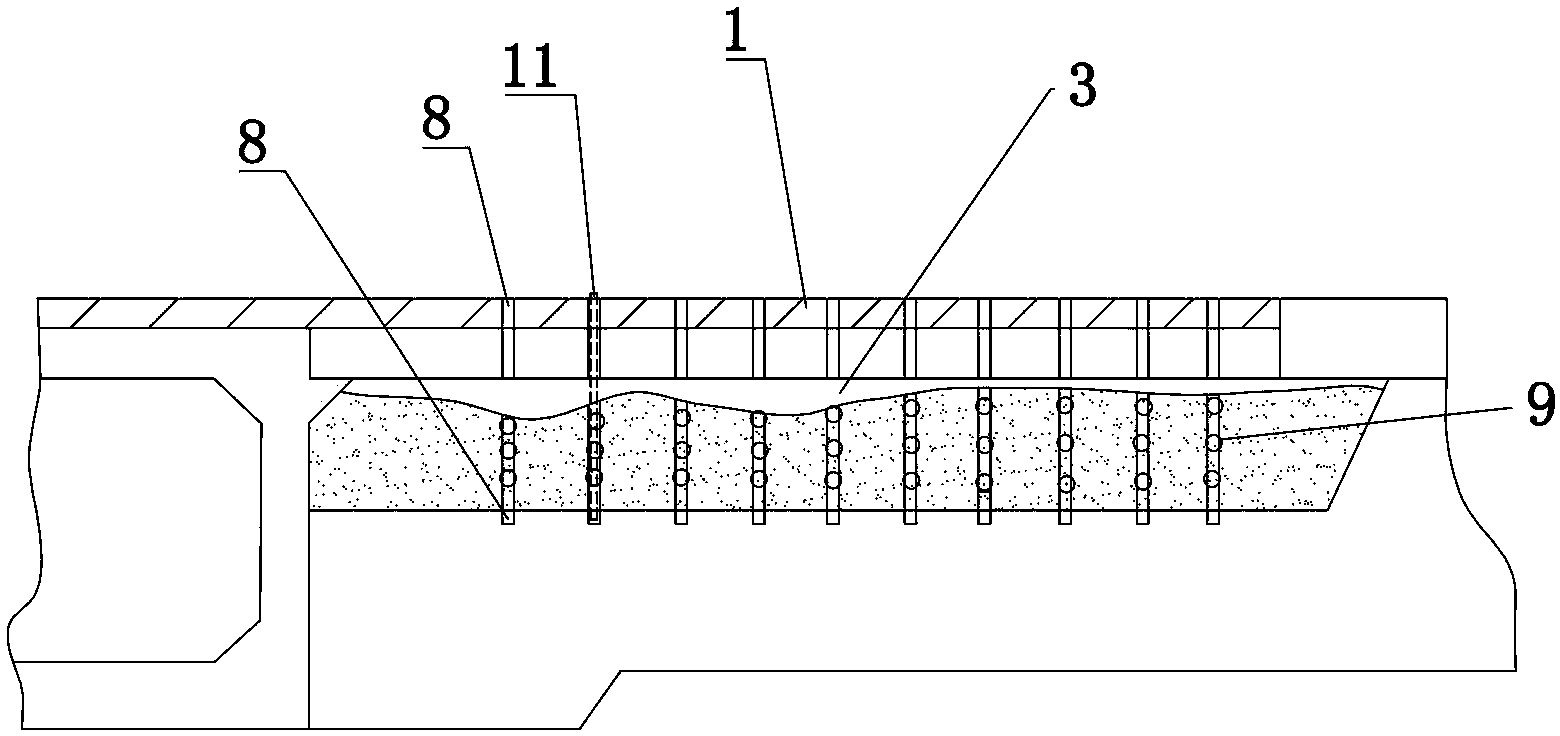
[0036] Such as figure 1 - Shown in 3, a kind of pavement restoration method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Use a three-dimensional detection radar or an ultrasonic detection device to detect the position of the void 3 in the slab of the damaged bridge, mark the position of the void 3 on the surface of the slab 2, and measure the void 3 and the hard soil layer 7 depth;
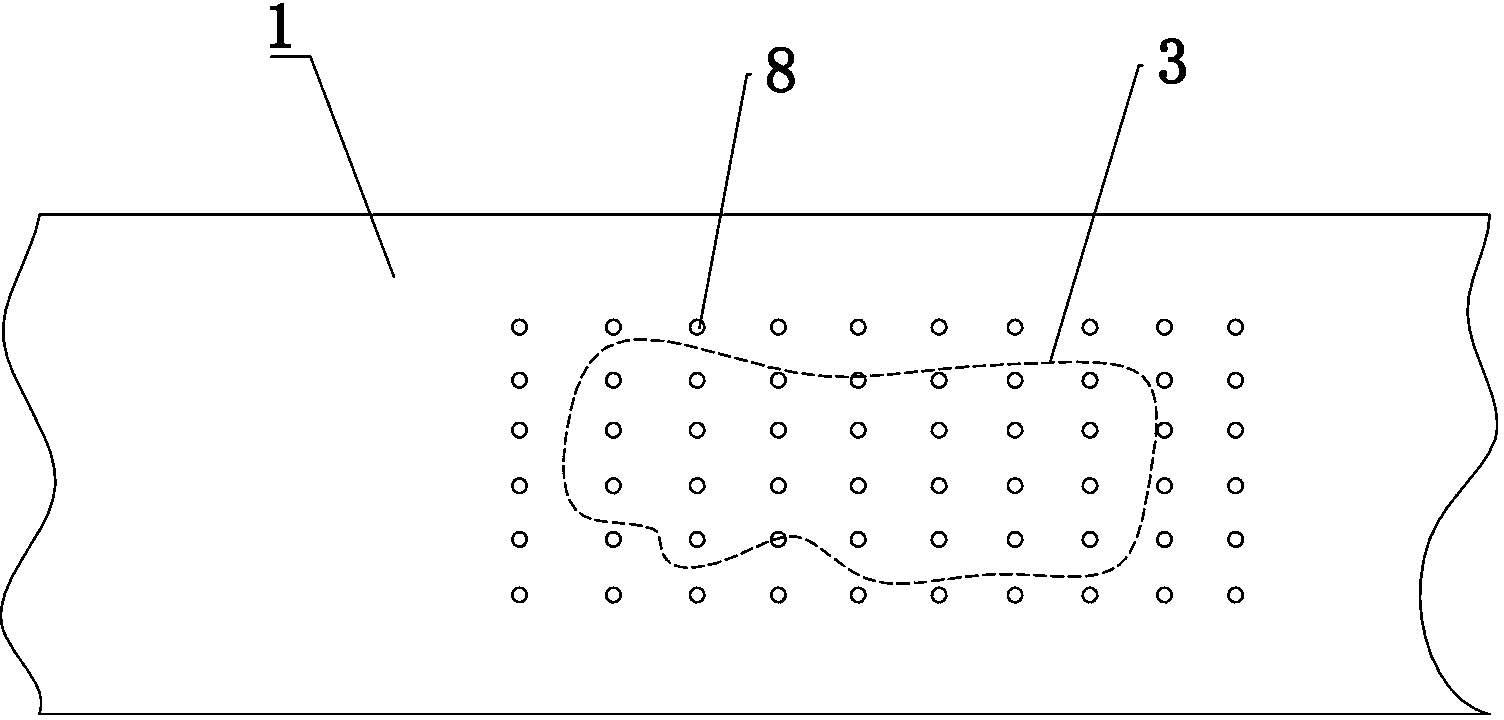
[0038] (2) Mark the position of each grouting hole 8 on the surface of the board 2 above the void 3 an...
Embodiment 2
[0046]The slurry described in the present invention adopts a kind of high-strength foaming resin, and its model is SZ3, and this resin is added in the above-mentioned grouting equipment during grouting, and the viscosity of the resin flowing out from the grouting equipment (exit machine viscosity ) is 100±45mPa·s, the volume of the resin slurry increases continuously in the flow, and its permeability is strong, which is suitable for quickly reaching the empty part or entering the gap, and is suitable for discharging accumulated water under the action of pressure. When the above The slurry can be filled and voided after 3 minutes of injection, and its final strength can be reached after 10 minutes of injection. The compressive strength is ≥20MPa, and the bending strength is ≥15MPa.
[0047] The slurry has the following characteristics:
[0048] (1) The slurry does not contain water, will not shrink when dry, and can densely fill voids; the slurry is flexible and elastic after c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com