Cholesteric-phase flexible liquid crystal display device and preparation method thereof
A liquid crystal display device, flexible liquid crystal display technology, applied in the direction of nonlinear optics, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems that liquid crystal molecules cannot flow freely, the polymer network is irregular, and the mechanical properties are not ideal, so as to achieve low cost and good performance. The effect of improving photoelectric performance and mechanical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. The following description is only for demonstration and explanation, and does not limit the present invention in any form.
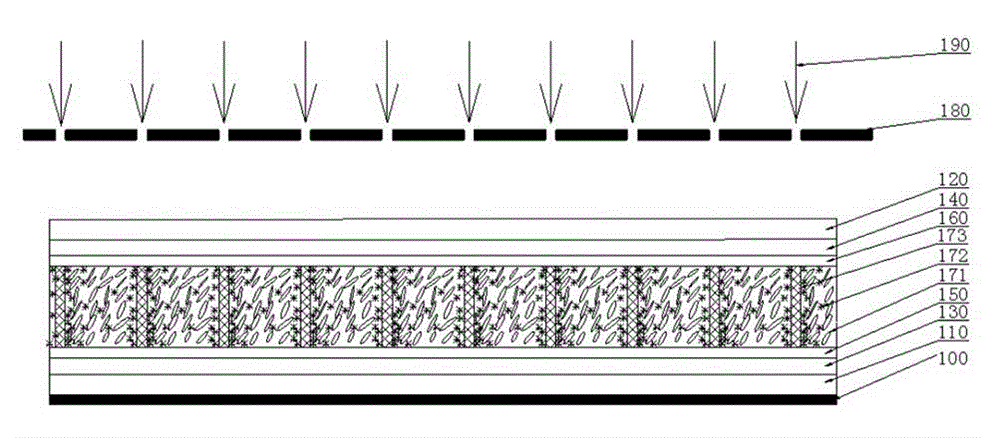
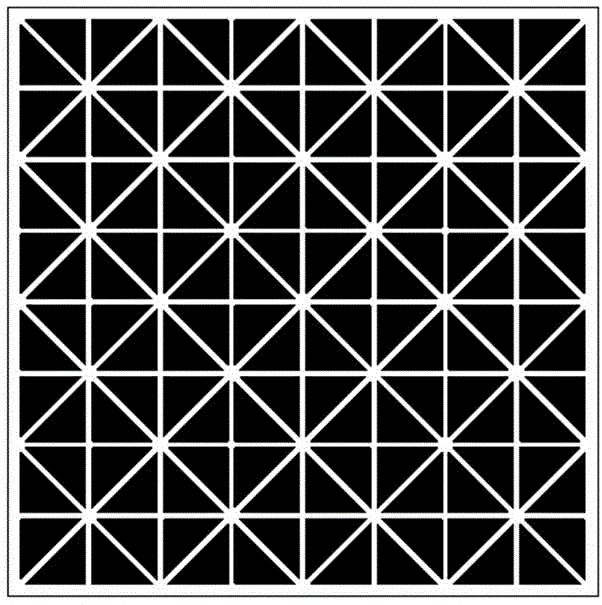
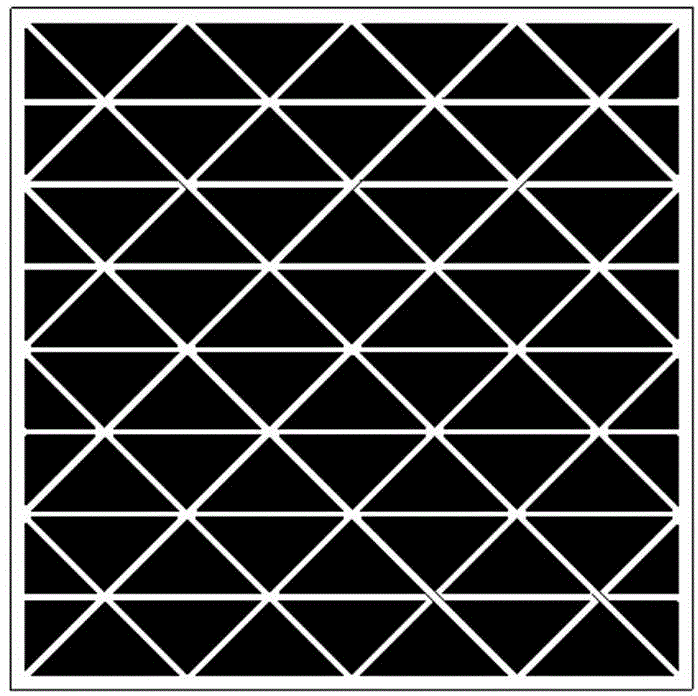
[0033] The cholesteric flexible liquid crystal display device comprises a light absorbing layer, a first flexible substrate, a second flexible substrate, a first electrode, a second electrode, a first alignment layer, a second alignment layer, and a liquid crystal mixture layer. The first electrode, the second The two electrodes are both transparent electrodes that can transmit light. In addition, the device also includes a photomask, and ultraviolet light acts on the flexible liquid crystal display device through the photomask; the liquid crystal mixture layer is a liquid crystal mixture with a special structure polymer wall Layer, the liquid crystal mixture layer with a special structure polymer wall is arranged between ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com