End products incorporating short-cut microfibers
A technology of microfiber and fiber products, which is applied in the field of fiber products and can solve problems such as increasing manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
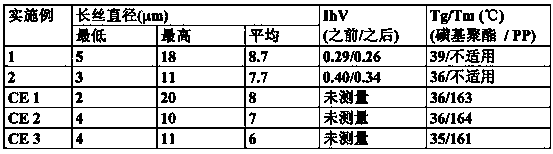
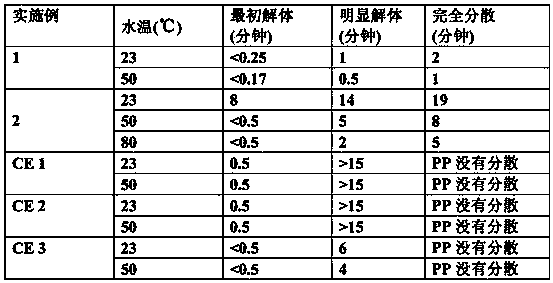
[0365] Containing 76 mol% isophthalic acid, 24 mol% sodium sulfoisophthalic acid, 76 mol% diethylene glycol and 24 mol% 1,4-cyclohexane via an Ih.V. of 0.29 and a Tg of 48°C The sulfopolyester of alkanedimethanol was melt blown onto a cylindrical collector through a nominal 6 inch die (30 holes / inch in the nosepiece) using the conditions shown in Table 1 . No need to insert paper. A soft, handleable, flexible web is obtained that does not block during roll winding. Physical properties are provided in Table 2. As shown by the data in Table 3, small pieces (1” x 3”) of nonwoven fabric were readily dispersed in room temperature (RT) and 50°C water with mild agitation.
[0366] Table 1 - Melt blown conditions
[0367]
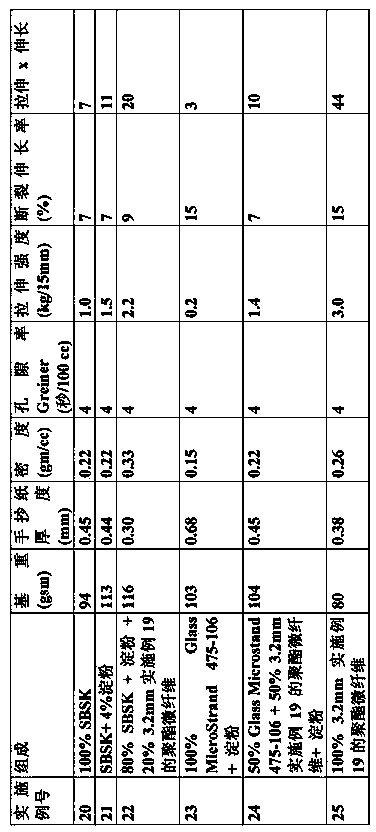
[0368] Table 2 - Physical Properties of Nonwoven Fabrics
[0369]
[0370] Table 3 - Dispersibility of nonwoven fabrics
[0371]
Embodiment 2
[0373] A sulfo group containing 89 mol% isophthalic acid, 11 mol% sodium sulfoisophthalic acid, 72 mol% diethylene glycol and 28 mol% ethylene glycol with an Ih.V. of 0.4 and a Tg of 35°C The polyester was meltblown through a 6 inch die using conditions similar to those in Table 1 . A soft, handleable, flexible web is obtained that does not block during roll winding. Physical properties are provided in Table 2. Small pieces (1” x 2”) of nonwoven fabric dispersed easily and completely at 50°C and 80°C; at RT (23°C), as shown by the data in Table 3, the fabric took longer to fully disperse.
[0374] It was found that the compositions in Examples 1 and 2 could be overblown onto other nonwoven substrates. It is also possible to condense and wrap in place of the shaped or contoured forms used in traditional net collectors. Thus, a circular "roving" or plug form of the web can be obtained.
Embodiment 5
[0380] The PP has a MFR (melt flow rate) of 800. The meltblowing operation was performed on a line with a 24 inch wide die to produce a handleable soft, flexible but non-blocking web with the physical properties provided in Table 2. Small pieces (1” x 4”) of nonwoven fabric disintegrated easily as reported in Table 3. However, due to the insoluble polypropylene component, no fiber is completely water dispersible.
[0381] Example 3
[0382] A circular piece (4" diameter) of the nonwoven fabric made in Example 2 was used as an adhesive layer between two pieces of cotton fabric. The two pieces of cotton were fused together using a Hannifin melt press by applying a pressure of 35 psig at 200°C for 30 seconds. The resulting assembly exhibits exceptionally strong consolidation strength. The cotton substrate tears before the bond or consolidation fails. Similar results were obtained with other celluloses and with PET polyester substrates. Strong consolidation is also produced ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com