Rotor for rotating electric machine, rotating electric machine, and method for manufacturing rotor for rotating electric machine
A technology for rotating electrical machines and rotors, applied in the manufacture of motor generators, stator/rotor bodies, and electric components, etc., can solve problems such as hindering labor saving, improving productivity, and complicated operation time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0087] Hereinafter, the rotor of the rotating electric machine according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
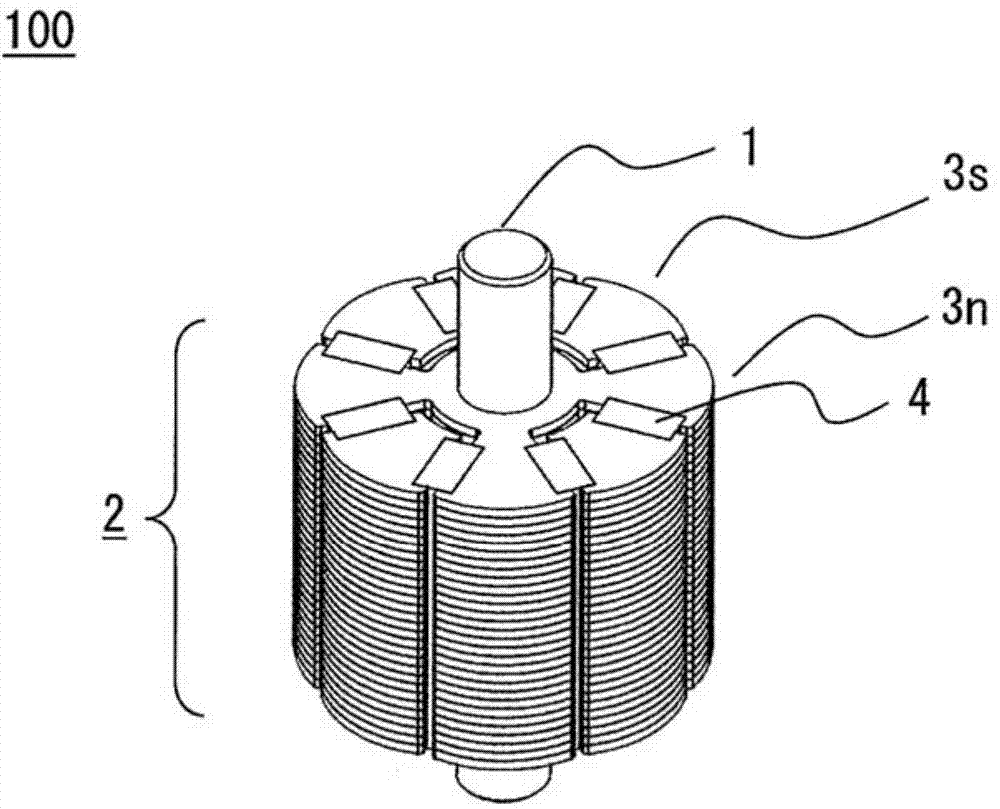
[0088] figure 1 It is an oblique view of the rotor 100.
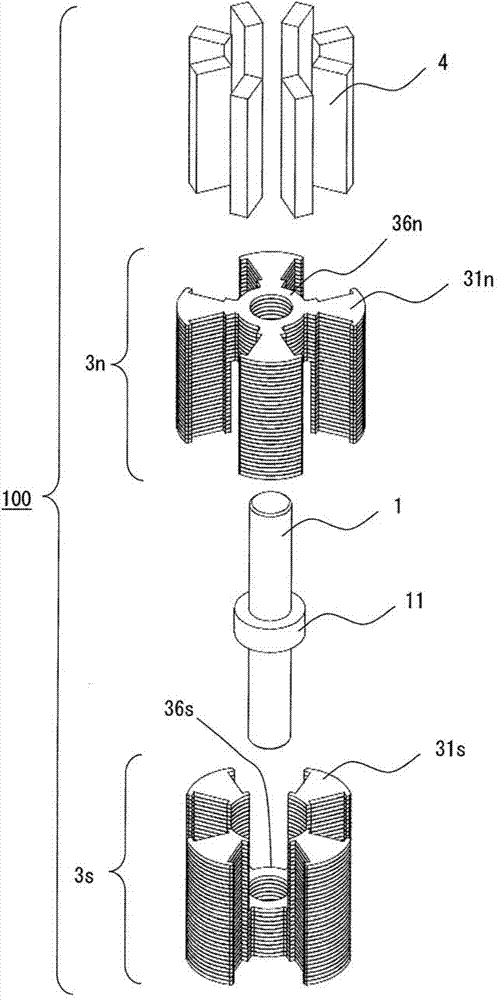
[0089] figure 2 It is an exploded perspective view of the rotor 100.
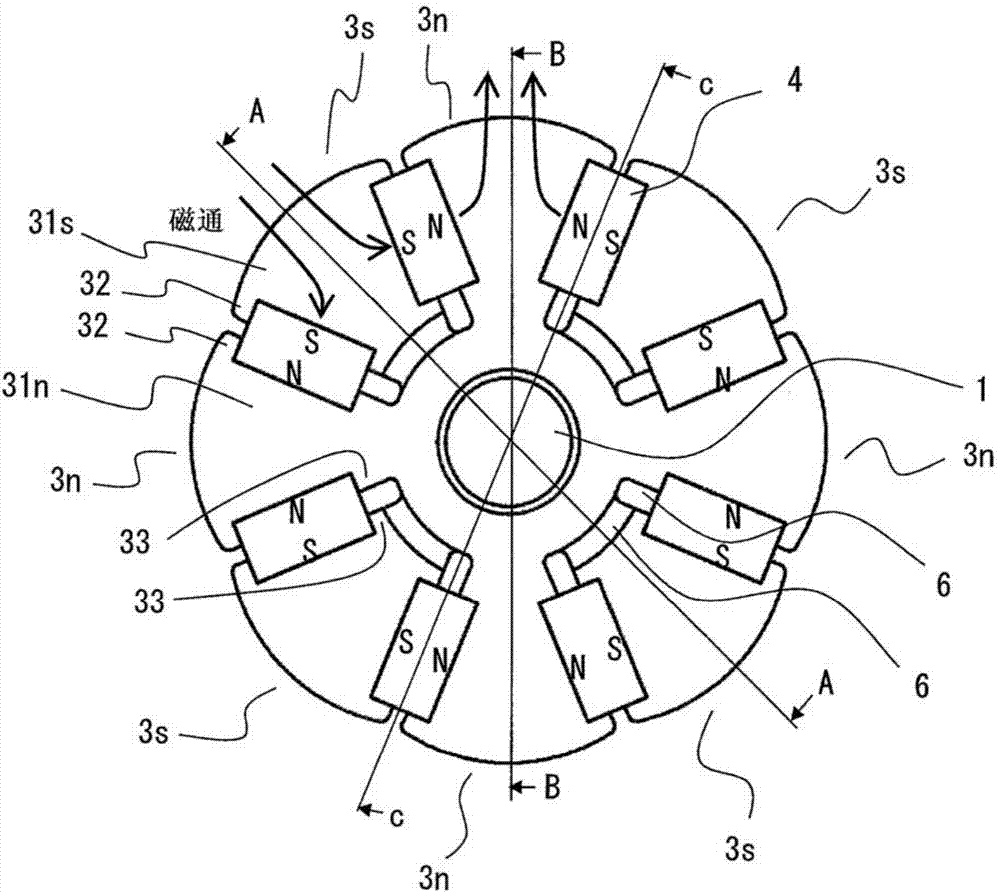
[0090] image 3 It is a top view of the rotor 100.
[0091] Figure 39 It is a cross-sectional view of the electric motor 50 (rotating electric machine).
[0092] In such Figure 39 The rotor 100 used in the motor 50 (rotating electric machine) shown is an N-pole integrated laminated core 3n and an S-pole integrated laminated core 3s, a non-magnetic rotating shaft 1, and the circumference of the rotating shaft 1 is alternately magnetized in the circumferential direction A plurality of permanent magnets 4 (first permanent magnets) are combined and configured.
[0093] Hereinafter, in this specification, the N-pole integrated laminated core 3n and the S-pole integrated laminated core 3s are desig...
Embodiment approach 2
[0142] Hereinafter, with reference to the drawings, the rotor of the rotating electric machine according to the second embodiment of the invention of the present application will be described centering on the parts different from the first embodiment.
[0143] Components with the same reference numerals as those described in the first embodiment basically indicate the same components
[0144] Picture 10 It is a cross-sectional view of the rotor 200.
[0145] The rotor 200 is a non-magnetic rotating shaft 201 with a non-magnetic collar 211 inserted as an independent member to constitute a member having the same shape as the rotating shaft 1 of the first embodiment.
[0146] By forming the structure as described above, it is possible to reduce the amount of expensive non-magnetic material used compared to Embodiment 1.
[0147] In addition, it is possible to adopt an assembly sequence in which the N-pole integrated laminated core 3n, the non-magnetic collar 211, and the S-pole integrated...
Embodiment approach 3
[0149] Hereinafter, with reference to the drawings, the rotor of the rotating electric machine according to the third embodiment of the invention of the present application will be described centering on the different parts from the second embodiment.
[0150] Components with the same reference numerals as those described in Embodiment 1 or 2 basically indicate the same components.
[0151] Picture 11 It is a cross-sectional view of the rotor 300.
[0152] Picture 12 Yes Picture 11 Enlarged view of the main part.
[0153] In the rotor 300, a cylindrical permanent magnet 311 (second permanent magnet) is inserted into a non-magnetic rotating shaft 201 to constitute a rotor having the same shape as the rotating shaft 1 of the first embodiment.
[0154] Such as Picture 12 As shown, the permanent magnet 311 is magnetized so that the N pole is arranged on the side in contact with the laminated ring-shaped connecting portion 36n of the N-pole integrated laminated core 3n, and the N pole is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com