Method for synthesizing alpha-ketoglutaric acid by reinforcing Yarrowia lipolytica
A technology of Yarrowia lipolytica and ketoglutaric acid, which is applied in the field of metabolic engineering and can solve the problems of low concentration of target metabolites and low production intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
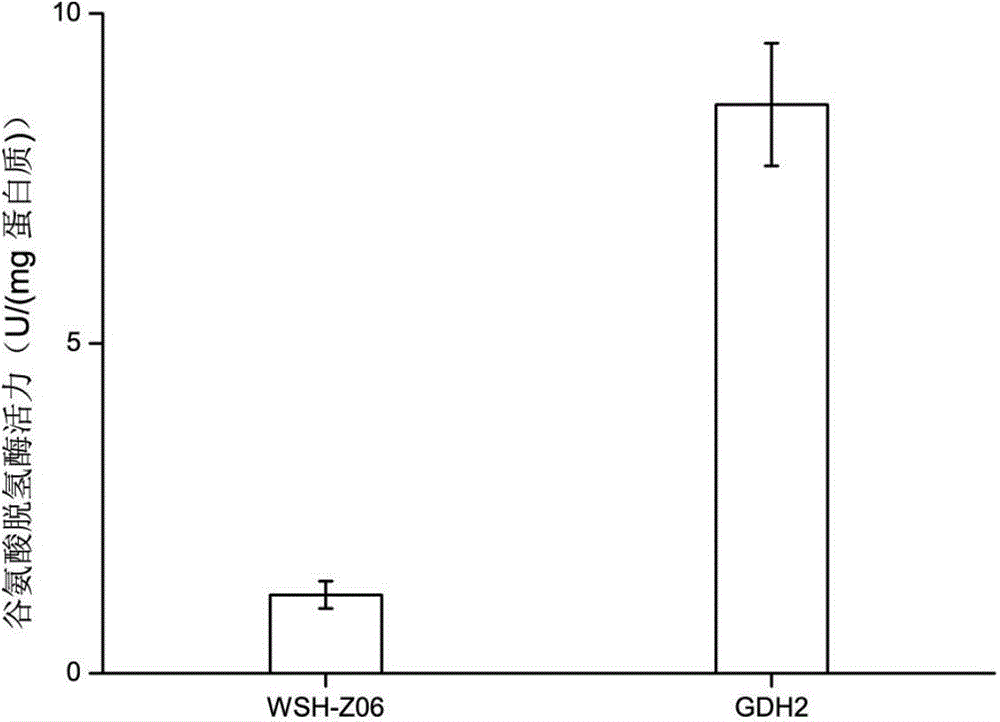
[0039] Example 1 Effect of overexpression of glutamate dehydrogenase on bacterial cell growth
[0040] (1) Construct the integrated expression vector used for expressing the target gene: amplify the hygromycin phosphotransferase hph gene, the nucleotide sequence of the hph gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, using the restriction endonuclease Stu I and Simultaneously process the amplified hph gene and p0 plasmid with Hind III, and connect the two digested products to obtain an integrated expression vector p0(hph) containing hygromycin transphosphoryl transferase as a selection marker; (2) construct a recombinant integrated expression vector Plasmid: According to the sequence published by NCBI (derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, GeneID: 851311), the open reading frame sequence encoding glutamic acid dehydrogenase encoding gene GDH2 was fully chemically synthesized, and the restriction endonucleases Sfi I and Not I were used to cut GDH2 The open reading frame and the integrated ex...
Embodiment 2
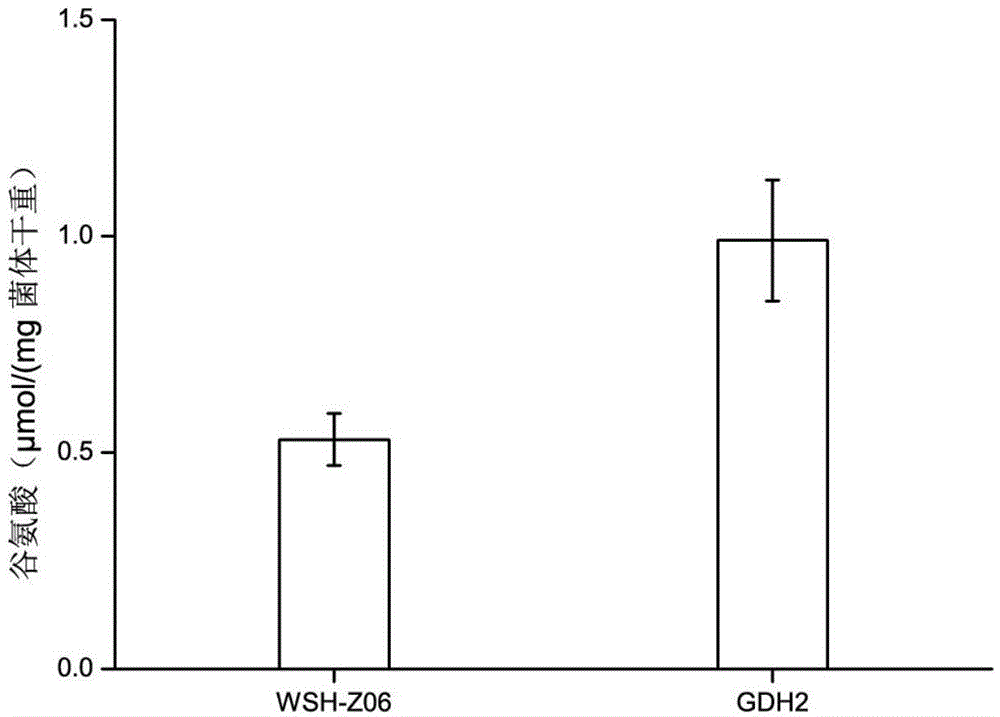
[0044] Example 2 Adding L-methionine imine to strengthen intracellular glutamate supply
[0045] Inoculate the wild-type Y.lipolytica WSH-Z06 cells and the recombinant strain Y.lipolytica-GDH2 into a 500ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml of fermentation medium at the same time, culture at 28°C and 200rpm for 96h, collect the cells by centrifugation, and follow the previous method. The glutamic acid content in the cells of the two strains was determined by the method described above. Compared with wild-type Y.lipolytica WSH-Z06, the glutamic acid content in recombinant strain Y.lipolytica-GDH2 cells ranged from 0.53μmol / (mg·dry weight of bacteria) to 0.99μmol / (mg·dry weight of bacteria) ( image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
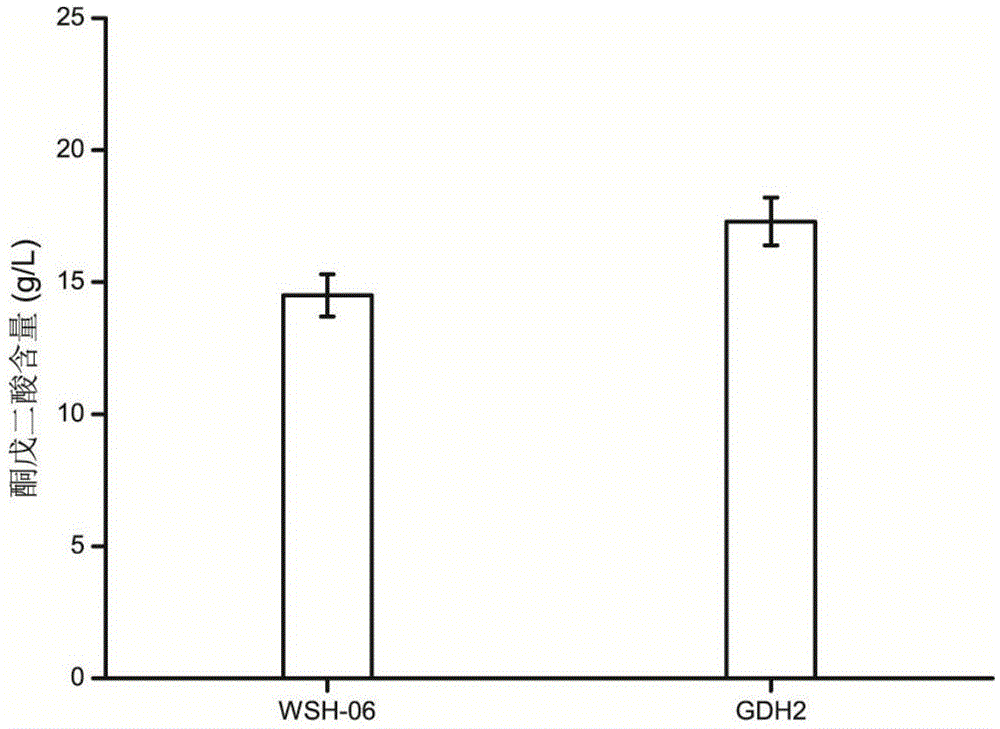
[0046] Example 3 Regulation of Intracellular Amino Acid Metabolism Enhances α-Ketoglutarate Accumulation
[0047] The wild-type Y.lipolytica WSH-Z06 strain and the recombinant strain Y.lipolytica-GDH2 were simultaneously inoculated in a 500ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml fermentation medium according to the method for producing α-ketoglutarate as described before, and L-methionine was added Imine was fermented at 28°C and 200rpm for 144h to compare the accumulation of α-ketoglutarate accumulated outside the cells. It was found by comparison that the intracellular glutamate supply and glutamate metabolism were strengthened to produce α-ketoglutarate at the same time, the catalytic activity of glutamate dehydrogenase in the recombinant strain Y.lipolytica-GDH2 was significantly increased, and the extracellular accumulation α-ketoglutarate from 14.5g·L -1 Rise to 19.2g·L -1 ( Figure 4 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com