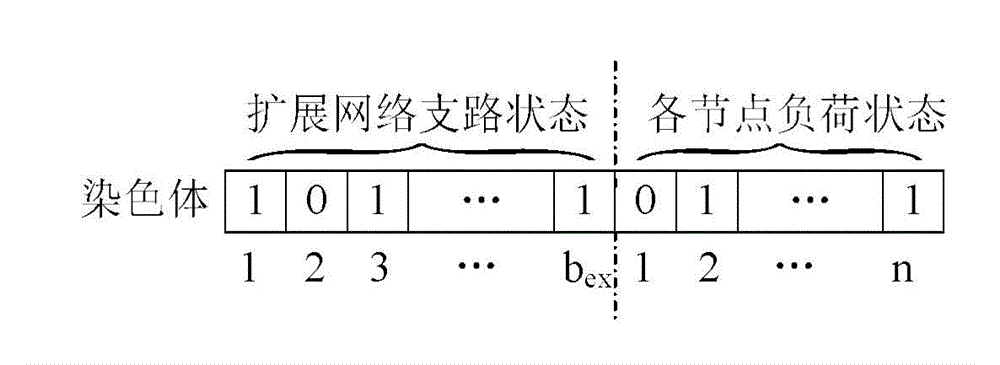
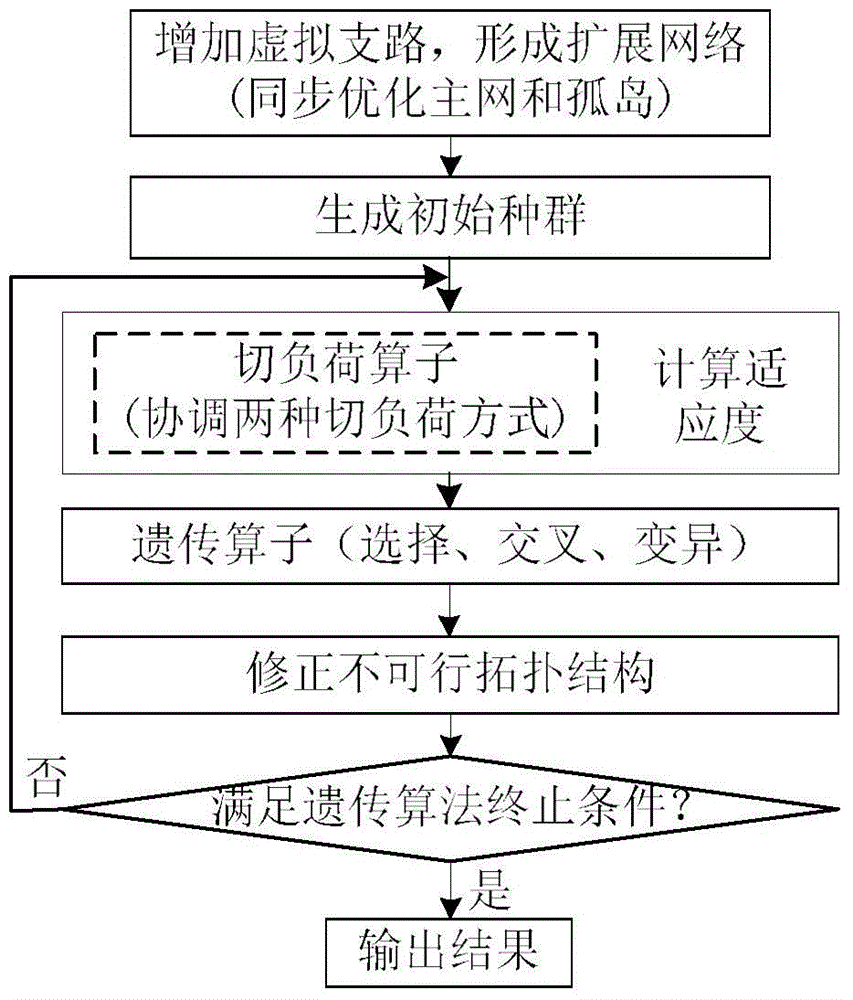
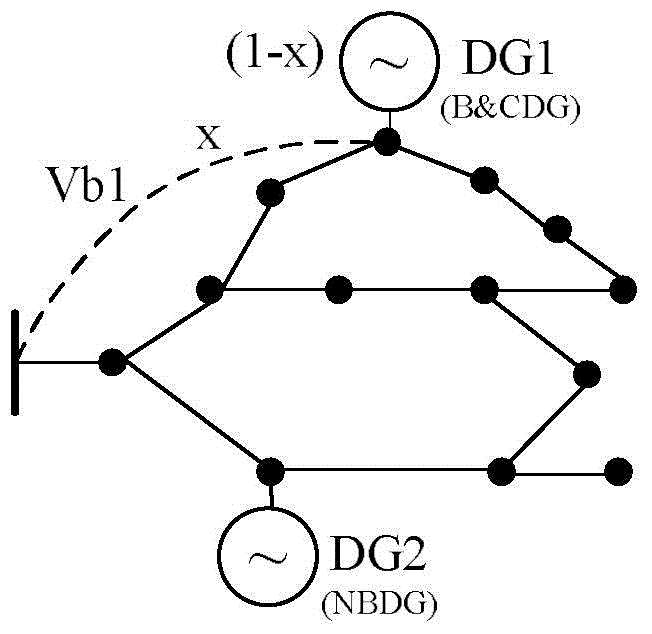
Major network and island synchronization fault restoration algorithm for power distribution network including DGs
A distributed power supply and distribution network failure technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve problems such as coordination of load shedding mode, complex recovery scheme, and inability to achieve global optimization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0094] Examples, case analysis
[0095] The advantages mentioned above will be explained one by one through the comparison of three sets of calculation examples:
[0096] The power distribution system used in the example is as follows: Image 6 . The system contains a total of 118 nodes and 132 branches, all of which are equipped with tie switches or section switches. The power supply voltage is 11kV, and the total load is 22709.7+j17041.1 kVA. See the appendix for basic system data and DG information.
[0097] Reference scheme: Assuming that a serious failure occurs in the system, such as the failure of line 1-63, the algorithm proposed by the present invention is used for optimization. The recovery scheme is shown in Table 1, and the corresponding system single-line diagram is shown in Figure 7 , as can be seen from the figure, the scheme reconfigures the main network, forms isolated islands (2 isolated islands, Is1, Is2), forms de-energized areas (3 de-energized areas...
comparative approach 1
[0101] Comparison scheme 1: the same is the fault of line 1-63; however, the recovery scheme is formulated using the two-stage optimization idea of "creating an island first and then reconfiguring the main network" which is commonly used at present.
[0102] The recovery scheme in this case is shown in Table 2, and the corresponding one-line diagram is shown in Figure 8 , the area inside the dotted line in the figure is the island solution obtained after the first step "island generation". This method mainly has the following two problems: 1) Due to the two-step nature of the algorithm, the island generation algorithm has an absolute priority. Driven by the optimization goal, the island will expand the power supply range as much as possible, and then seize the important load first. Leading to the destruction of important power supply paths in the main network reconstruction. From the optimization results, on the one hand, the island generation process preempts almost all i...
comparative approach 2
[0106] Comparison scheme 2: Assume a mild fault, such as the fault of line 30-31, and use the algorithm proposed by the present invention to optimize.
[0107] The recovery plan for this situation is shown in Table 3, and the corresponding one-line diagram is shown in Figure 9 . Under this scheme, the algorithm realizes fault recovery in the power-off area by complex network reconfiguration. It can be seen from the figure that the non-faulty area passes through 3 groups of contact feeders (40-9—8-24—25-35), feeder (43-54) and feeder (49-62) supported the power-off area, and finally no isolated island was formed. However, in the reference scheme, DG mainly recovered the load in the form of an isolated island. The main reasons are as follows: 1) The recovery ability of the main network the difference. In the reference scheme, before the main network expands the power supply range to the vicinity of the DG island, the recovery ability has reached its limit. At this time, even ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com