Multi-axial fatigue calculation method for complex working conditions of frame including welding simulation
A technology of welding simulation and complex working conditions, applied in the field of fatigue calculation, can solve the problems of saving resources, social progress, repeated research and development, disadvantages, etc., and achieve the effects of avoiding repeated research and development, improving accuracy and saving resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
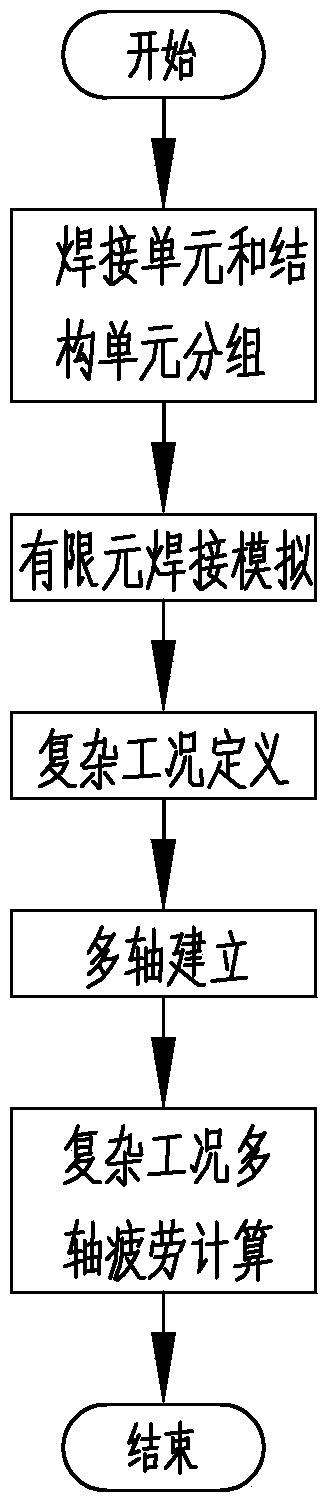
[0036] Embodiment 1, a method for calculating multi-axis fatigue under complex working conditions of frame overturning moment fatigue including welding simulation, comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1, grouping of welding units and structural units: set the spatial coordinate system of X, Y, Z and coordinate origin, and group welding units and structural units;
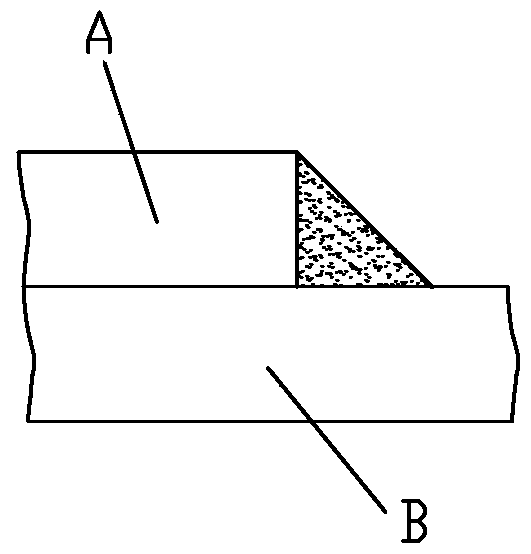
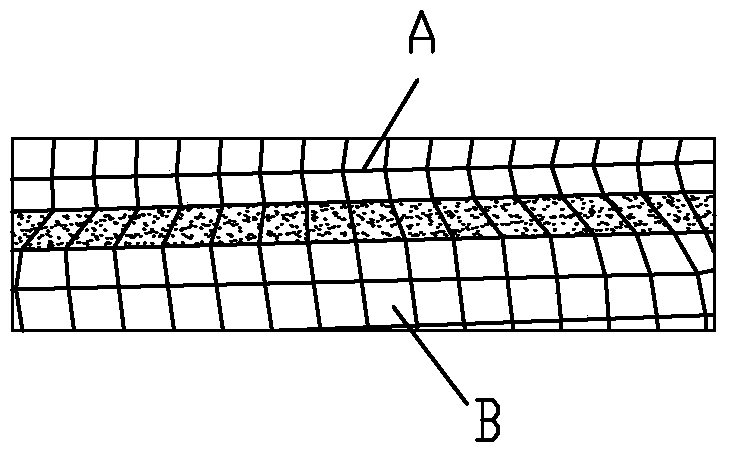
[0038] S2, finite element welding simulation: perform finite element welding simulation on sheet metal welding and surface welding in the form of fillet welds; among them, the welding unit adopts a quadrilateral grid with a side length of 3 to 5mm; the warpage of the grid is less than 5%; there is no triangular mesh in the weld layer, and the proportion of triangular mesh in the grid units of the welded connection layer adjacent to the weld layer is less than 5%; it is best that there is no mesh at the beginning and end of the fillet weld Curved elements and triangular mesh elements, the edges of the weld layer...
Embodiment 2
[0045]Embodiment 2, a multi-axial fatigue calculation method for S-shaped steering tilting fatigue complex working conditions including welding simulation, including S1 welding unit and structural unit grouping; S2 finite element welding simulation; S3 complex working condition definition; S4 multi-axis establishment and S5 multiaxial fatigue calculation steps;
[0046] Among them, the definition of complex working conditions includes defining S-shaped steering overturning fatigue loads and fatigue cycle conditions; the fatigue loads include the size, direction and loading position of the load; the fatigue load size of the S-shaped steering overturning fatigue conditions , direction, loading position and other load parameters can be obtained through the snake test to obtain the attitude parameters of the vehicle, that is, the pitch, lateral bending angle, tipping moment and acceleration parameters; the simulation parameters can also be obtained by multi-body dynamics software; ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3, a multi-axis fatigue calculation method for continuous brake tilting fatigue complex working conditions including welding simulation, including S1 welding unit and structural unit grouping; S2 finite element welding simulation; S3 complex working condition definition; S4 multi-axis establishment and S5 multiaxial fatigue calculation steps;
[0050] Among them, the definition of complex working conditions includes the definition of S-shaped steering overturning fatigue loads and fatigue cycle conditions; the fatigue load includes the magnitude, direction and loading position of the load; wherein, the fatigue load size of the continuous brake overturning fatigue condition , direction, and loading position are, in order to load the mechanical parameters of eight loads including the braking force and torque of the front left, front right, rear right, and rear left wheels on the connection position between the frame and the suspension, and ensure that the force ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com