Prophylactic or therapeutic agent for hepatic diseases
一种肝脏疾病、预防剂的技术,应用在疾病诊断、测试药物制剂、微生物的测定/检验等方向,能够解决肝脏疾病发病和进展未知等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0289] Example 1: Fatty liver promotion by feeding AIM knockout mice with a high fat diet (HFD)
[0290] Liver weight, liver weight relative to body weight, weight of neutral fat in the liver, and tissue staining by hematoxylin-eosin were studied by feeding AIM knockout mice and WT mice with a high-fat diet (HFD). Accumulation of liver fat. As a result, feeding WT mice with HFD until week 20 did not result in a significant difference in liver weight / body weight, but feeding AIM knockout mice with HFD resulted in a significant difference in liver weight / body weight from week 6 onwards compared to WT. A significant increase( figure 1 A). Furthermore, the results of neutral fat weight in the liver showed that feeding AIM knockout mice with HFD resulted in the accumulation of fat in the liver from week 6 onwards, and it has been clarified that fatty liver is promoted compared to WT ( figure 1 B).
Embodiment 2
[0291] Example 2: Progression of liver fibrosis (cirrhosis) by feeding AIM knockout mice with a high fat diet (HFD)
[0292] Wild-type mice (male, 10 mice, 12 weeks old) and AIM knockout mice (male, 10 mice, 12 weeks old) were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), 0, 6, 12, After 20, 45, and 55 weeks, the livers were fixed with formalin, the sections were stained with Sirius red, and the stained fibrotic areas were quantified by NIH-J images ( figure 2 A). Three discrete slices were analyzed per mouse and mean values (ratio of fibrosis to whole slice) are shown ( figure 2 B). As a result, the area of fibrosis increased with longer HFD feeding period, but no significant difference was found between wild type mice and AIM knockout mice. In addition, RNA was extracted from parts of liver tissue before fixation, and the mRNA expression levels of αSMA and TGFβ, which are representative genes involved in liver fibrosis, were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR ( figure 2 C). Due to the...
Embodiment 3
[0293] Example 3: Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma by feeding AIM knockout mice with a high fat diet (HFD)
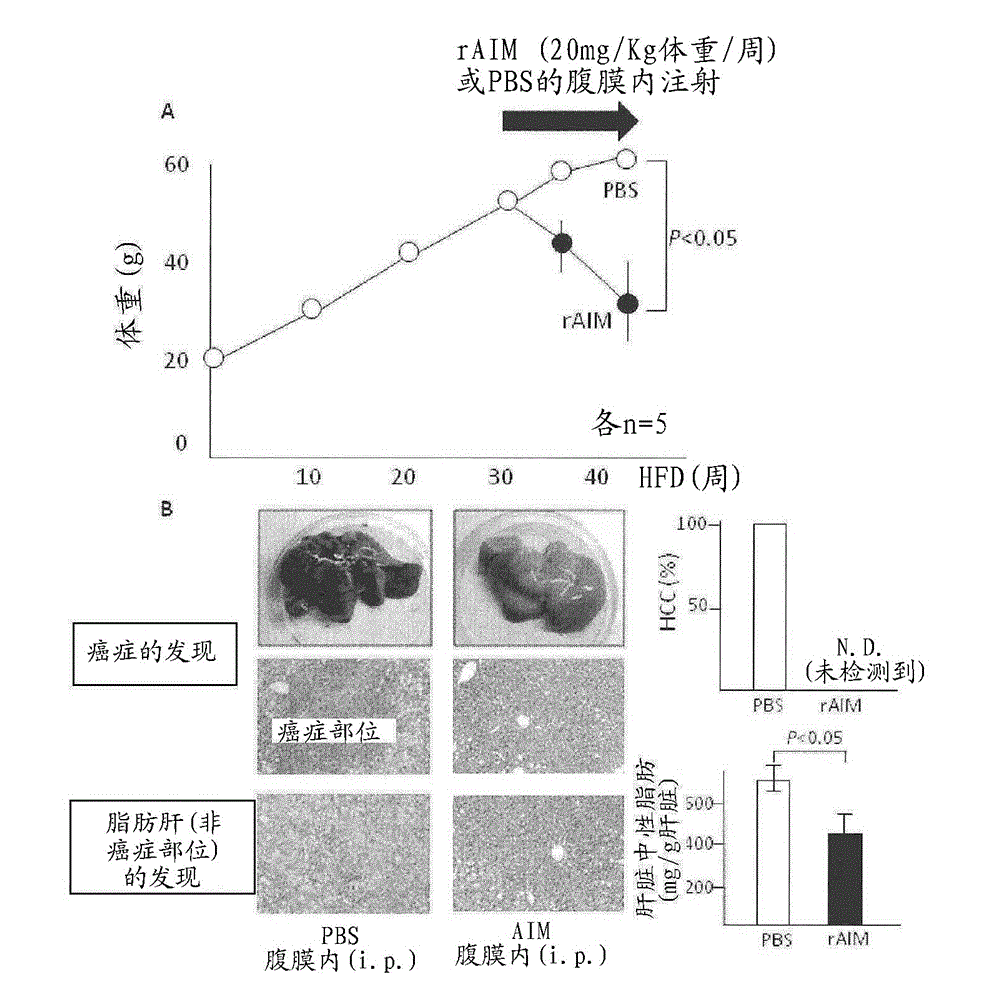
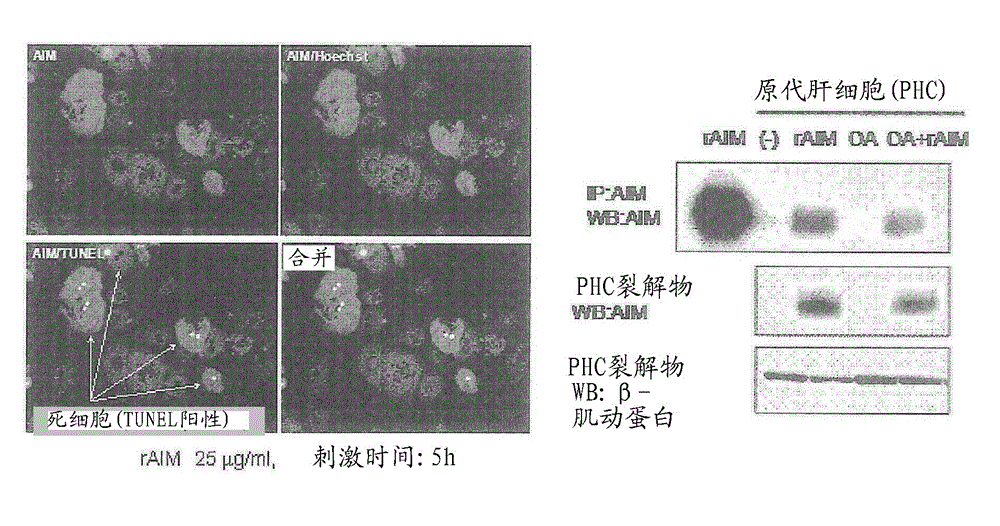
[0294] When WT mice were fed with HFD for 52 weeks, fatty liver was observed, but hepatocellular carcinoma mostly did not develop. However, hepatocellular carcinoma was observed in all AIM knockout mice, and almost all observed tumors were highly differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ( image 3 A, B, C). Hepatocellular carcinoma was confirmed in the liver of AIM knockout mice by Hoechst / AFP staining ( Figure 4 ), and the promoted expression of AFP in the liver was also confirmed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com