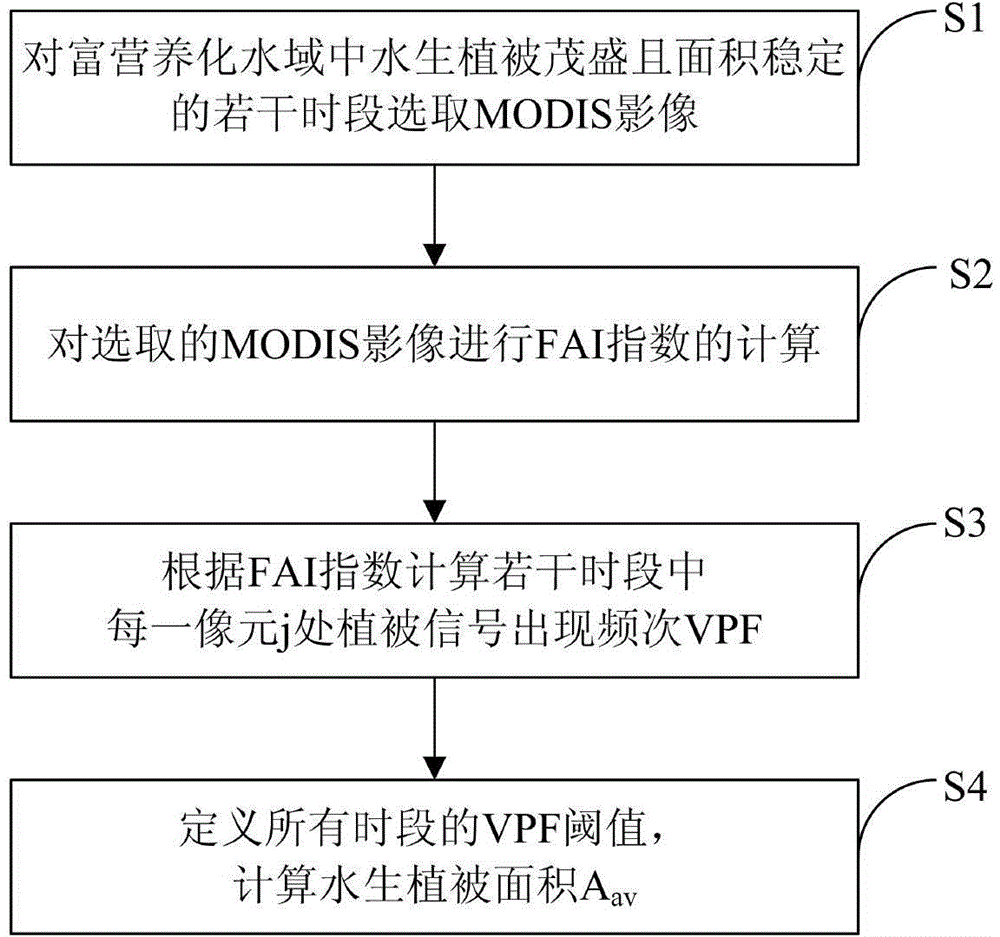
Eutrophic water aquatic vegetation remote sensing extraction method based on alga index frequency method
A technology for aquatic vegetation and algae index, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, optical devices, etc., can solve problems such as errors and inability to truly reflect the evolution process of water ecosystems, and achieve low cost, obvious advantages, innovation, and operation easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
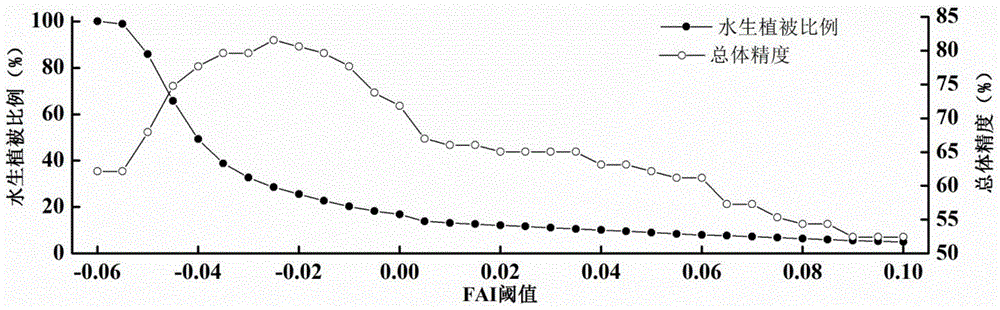
[0099] figure 2 is the optimal threshold T for the identification of aquatic vegetation FAI Select a schematic.
[0100] Since the original threshold T FAI It is used to discriminate the area of planktonic algae in the water body, so the present invention takes Taihu Lake as an example to improve this threshold, making it suitable for discriminating the distribution of aquatic vegetation. From figure 2 It can be seen from the figure that the comparison with the measured values in the same period (104 measured stations evenly distributed on the lake surface) shows that the threshold T FAIWhen the value is -0.025, the discrimination effect on the vegetation signal in the water area is the best, and the overall accuracy consistent with the measured results is 81.55%.
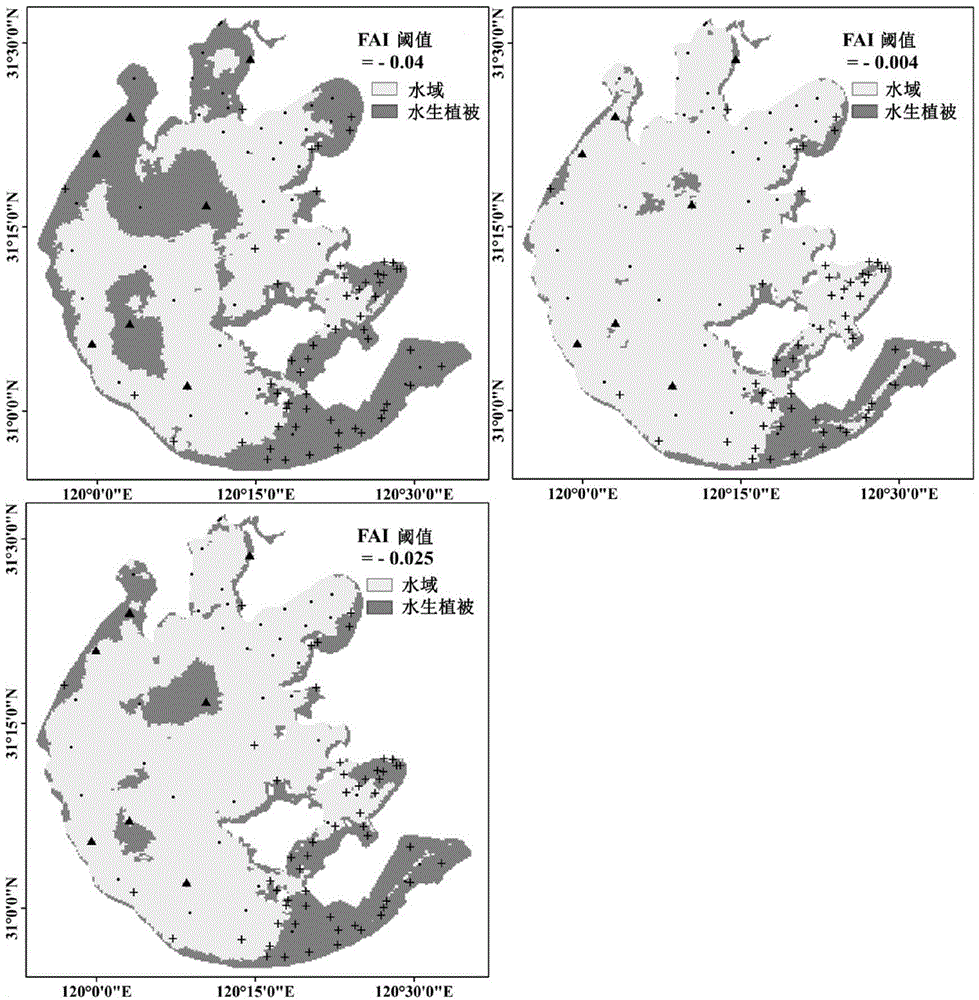
[0101] image 3 for different thresholds T FAI The comparison chart of the discrimination results, in which the black dots indicate that the measured results are water areas, the black crosses indicate ...
Embodiment 2
[0105] In this embodiment, scheme 2 is used to calculate the distribution of aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake in 2008-2012, and the obtained results are verified with the measured data of aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake in 2008-2012 (the measured data are 48 points per year, uniformly distributed, in Figure 5 in 2008 and 2009 are missing one measured point).
[0106] (1) The division of typical growth periods of algae and aquatic vegetation. According to the phenological growth characteristics of algae and aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake, MODIS images that meet the standards throughout the year are divided into the following three groups:
[0107] Period 1 (algae and aquatic vegetation luxuriant period): June-October;
[0108] Period 2 (coexistence period of accumulating algae and overwintering vegetation): February and March;
[0109] Period 3 (overwintering vegetation period): December of the previous year and January of the current year.
[0110] (2) Calculate the FAI ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com