Graph theory analysis method for common mode current path of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
A common-mode current and current path technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, AC network circuits, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as relying on inspiration and attempts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
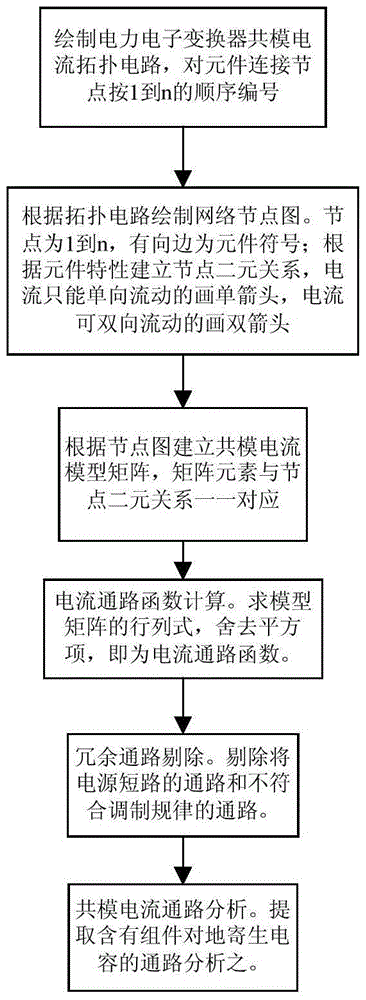
[0040] figure 1 It is an operation flowchart of the graph theory analysis method for the common-mode current path of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter proposed by the present invention. The analytical method is carried out in the following six steps:
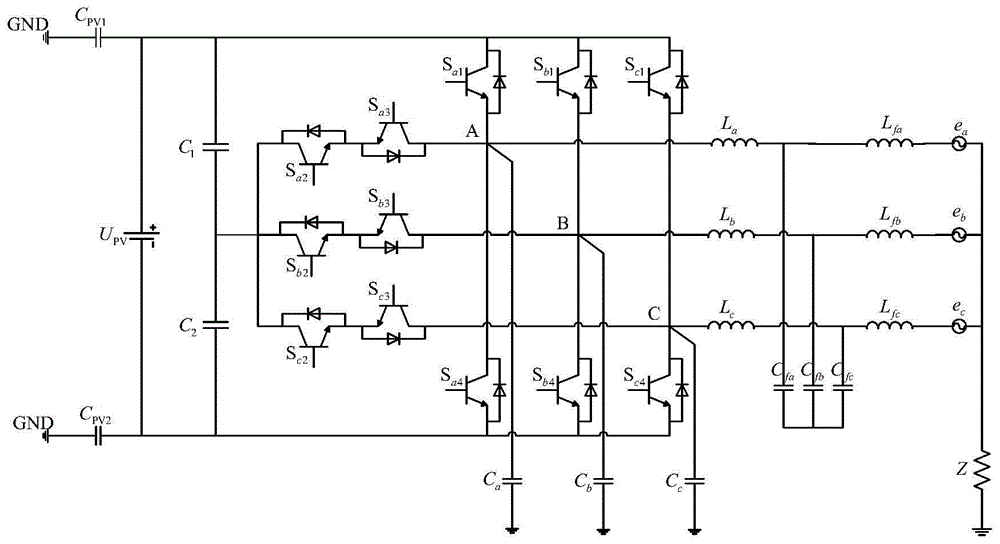
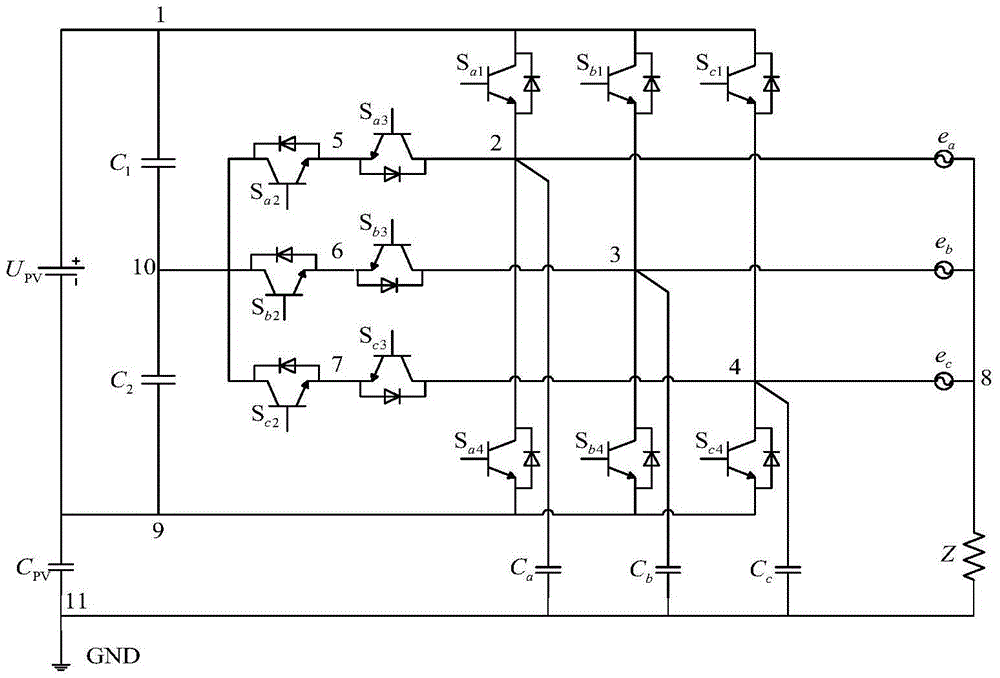
[0041] Step 1. Draw the common-mode current topology circuit of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter, and number the connection points of the components in the order of 1 to n;
[0042] Step 2. Draw the network node diagram of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. The nodes are from 1 to n, and the directed edge is the symbol of the component; the node binary relationship is established according to the characteristics of the component, the edge where the current can only flow in one direction is marked with a one-way arrow according to the flow direction, and the edge where the current can flow in both directions is marked with a two-way arrow;
[0043] Step 3. Establishing an n×n matrix model according to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com