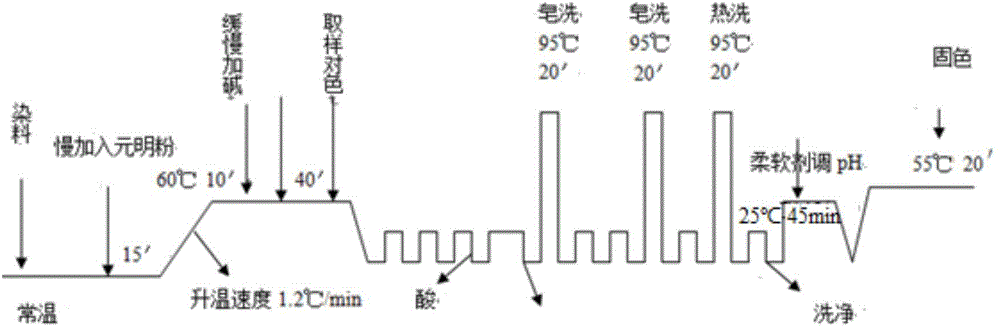
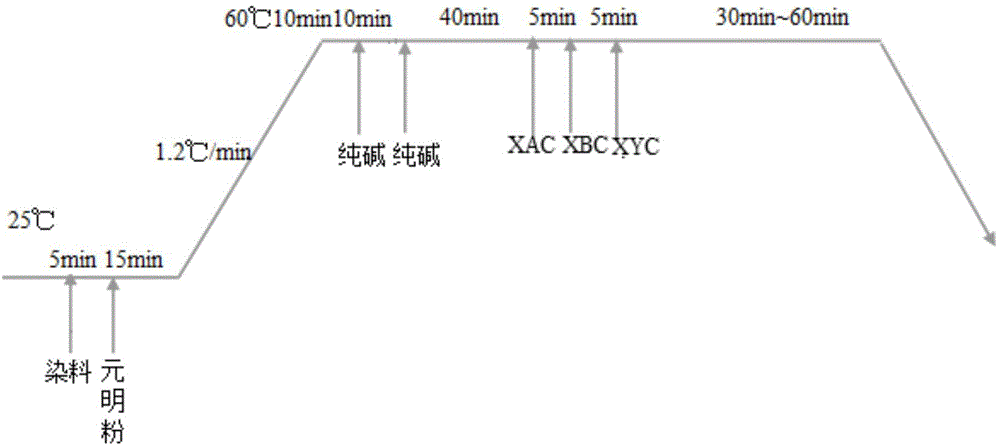
Cellulosic fiber in-situ mineralization deep water-saving and emission reduction dyeing aftertreatment method and additive
A technology of in-situ mineralization of cellulose fibers, applied in dyeing, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of undiscovered new dyeing technology, high pollution, high water consumption in cellulose fiber dyeing and processing, and achieve fluffy and soft hand feeling , Reduce damage, natural and bright color effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0071] The preparation method of cellulose fiber post-dyeing treatment auxiliary agent XAC specifically implements according to the following steps:
[0072] Step 1, take the following raw materials respectively according to the mass percentage:
[0073] Polyacrylamide 0.001% to 5%, polyaluminum sulfate or polyaluminum chloride 0.001% to 2.5%, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride 5.0% to 40%, dioctadecyl-methyl benzyl Ammonium chloride 0.1%~5.0%, Dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride 0.05%~2.0%, Fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether 10%~30%, Purified water 15.5%~84.848%, the above components The sum of the contents is 100%;
[0074] Step 2, heating the purified water weighed in step 1 to 40°C to 50°C;
[0075] Step 3, polyacrylamide, polyaluminum sulfate or polyaluminum chloride, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride, dioctadecyl-methyl benzyl ammonium chloride, Dioctadecyldimethylammonium chloride and fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether are added together to the puri...
Embodiment 1
[0108] Cellulose fiber post-dyeing treatment aid XAC, composed of the following raw materials by mass percentage: polyacrylamide 1%, polyaluminum sulfate 1.5%, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride 6.0%, dioctadecyl - 0.5% of methyl benzyl ammonium chloride, 1.0% of dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, 15% of flat plus O, 75% of purified water, the total content of the above components is 100%;
[0109] The preparation method of XAC, the post-processing auxiliary agent for cellulose fiber dyeing: Weigh the following raw materials according to the mass percentage: polyacrylamide 1%, polyaluminum sulfate 1.5%, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride 6.0%, bis 0.5% octadecyl-methylbenzyl ammonium chloride, 1.0% dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, 15% Ping Pinga O, 75% pure water, the total content of the above components is 100%; Heat the weighed pure water to 40°C; weigh the weighed polyacrylamide, polyaluminum sulfate, dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride, diocta...
Embodiment 2
[0116] The post-treatment auxiliary XAC for cellulose fiber dyeing is composed of the following raw materials by mass percentage: polyacrylamide 1.5%, polyaluminum sulfate 2.0%, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride 5.0%, dioctadecyl - 0.8% of methyl benzyl ammonium chloride, 1.5% of dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, 12% of flat plus O, 77.2% of purified water, the total content of the above components is 100%;
[0117] The preparation method of XAC, the post-treatment auxiliary agent for cellulose fiber dyeing: Weigh the following raw materials according to the mass percentage: polyacrylamide 1.5%, polyaluminum sulfate 2.0%, dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride 5.0%, bis 0.8% of octadecyl-methylbenzyl ammonium chloride, 1.5% of dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride, 12% of Ping Pinga O, 77.2% of pure water, the total content of the above components is 100%; Heat the weighed pure water to 40°C; weigh the weighed polyacrylamide, polyaluminum sulfate, dodecyldime...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com