A pixel structure and an organic light-emitting display using the pixel structure
A pixel structure and pixel technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electric solid state devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems affecting the PPI increase of the aperture ratio of sub-pixels, the improvement of the working brightness of monochromatic devices, and the shortening of the life of the display screen. , the effect of increasing strength and reducing difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
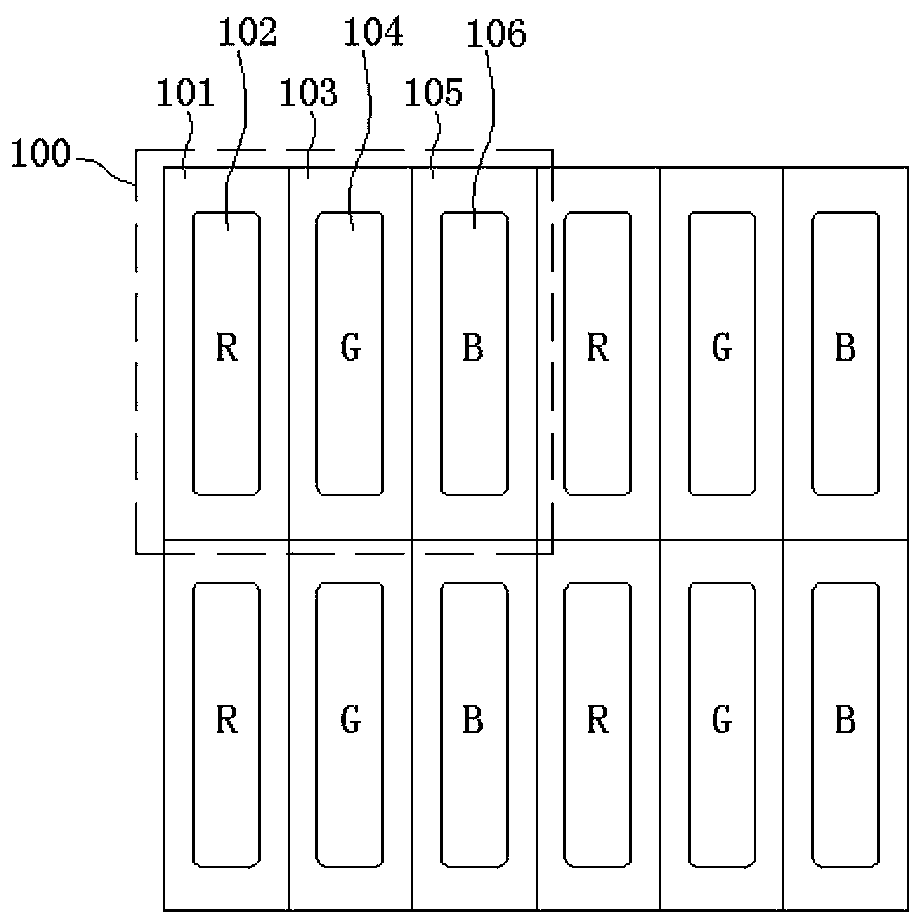
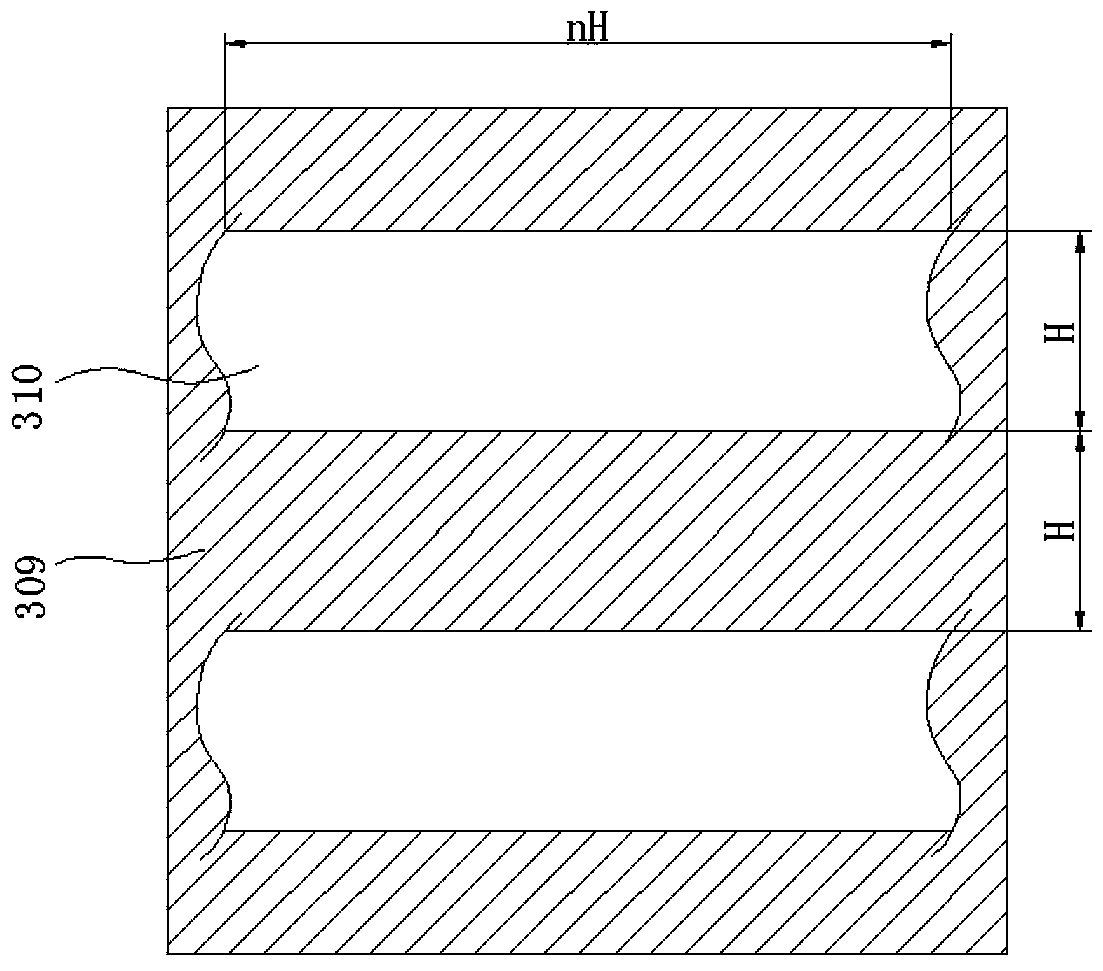
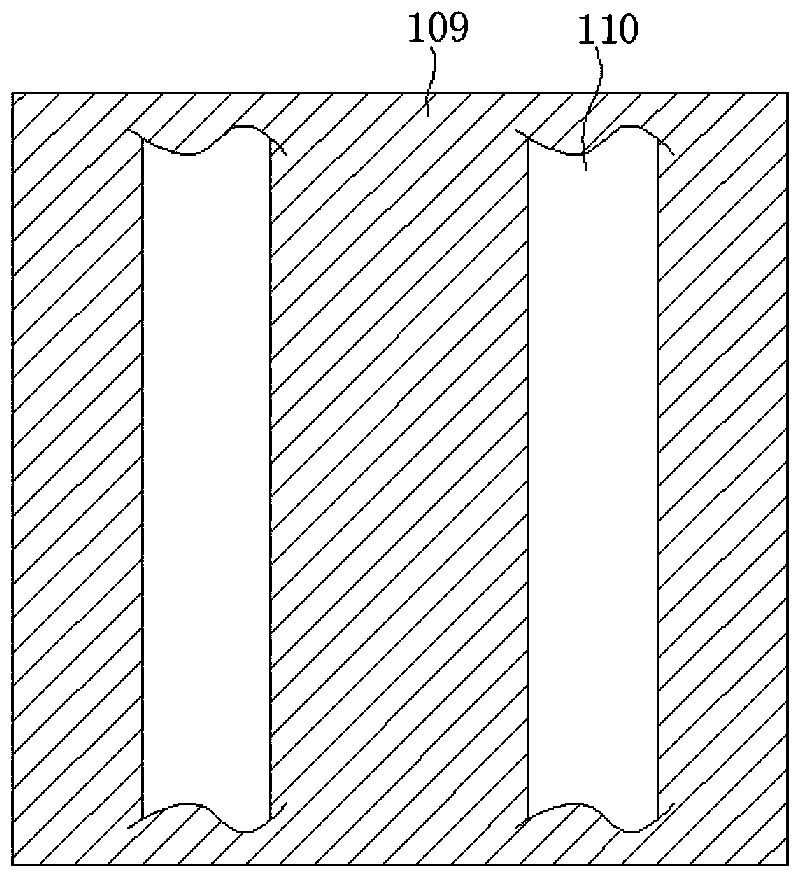
[0067] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the pixel structure of the organic light emitting display of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the display includes a plurality of pixels 300, and each pixel 300 is composed of a plurality of sub-pixels. Each pixel 300 includes an R sub-pixel area 301 , an R light-emitting area 302 , a G sub-pixel area 303 , a G light-emitting area 304 , a B sub-pixel area 305 and a B light-emitting area 306 . The size of each pixel is H×H.
[0068] In this embodiment, the R, G, and B sub-pixels of each pixel are quadrangular, and the sub-pixels are arranged in the shape of a "pin" or an inverted "pin". Wherein, the length and width of the R and G sub-pixels are both 1 / 2H, and the width of the B sub-pixel is H, and the height is 1 / 2H, that is, the area of the B sub-pixel is twice that of the G sub-pixel or the R sub-pixel.
[0069] Wherein, each pixel unit in this embodiment may be composed of an odd num...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Such as Figure 5 A second embodiment of the invention is shown. In this embodiment, the display includes a plurality of pixels 500, and each pixel is composed of a plurality of sub-pixels. The shape of each sub-pixel is a triangle. Preferably, as Figure 5 As shown, each sub-pixel is an isosceles right-angled triangle, and the right angles of every four sub-pixels are arranged opposite to each other to form a pixel. Four sub-pixels constituting one pixel include one R sub-pixel 501 , one G sub-pixel 503 and two B sub-pixels 502 , wherein the two B sub-pixels 502 are arranged opposite to each other. In this way, the area of the B sub-pixel 502 is also twice that of the R sub-pixel 501 or the G sub-pixel 503, thereby ensuring the display effect of the display.
[0081] Such as Figure 5 As shown, this figure only shows a part of the organic light emitting display, and the number of pixels in the actual product is not limited to this. The first row, the second row...
Embodiment 3
[0092] For Example 2, we can replace some of the color sub-pixels with other colors, such as Figure 6 In the third embodiment of the present invention shown, each pixel 600 in this embodiment is composed of an R sub-pixel 601 , a G sub-pixel 603 , a B sub-pixel 602 and a W (white) sub-pixel 604 . This example is compatible with Figure 5 Compared with the illustrated embodiment, one of the B sub-pixels is replaced by a W sub-pixel 604, and the positions of the R sub-pixel and the G sub-pixel are exchanged. The advantage of this embodiment is that since each pixel includes a W sub-pixel, it can display white more purely and achieve higher brightness.
[0093] Specifically, such as Figure 6 As shown, the display includes a plurality of pixels 600, and each pixel is composed of a plurality of sub-pixels. The shape of each sub-pixel is a triangle. Preferably, as Figure 6 As shown, each sub-pixel is an isosceles right-angled triangle, and the right angles of every four sub-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com