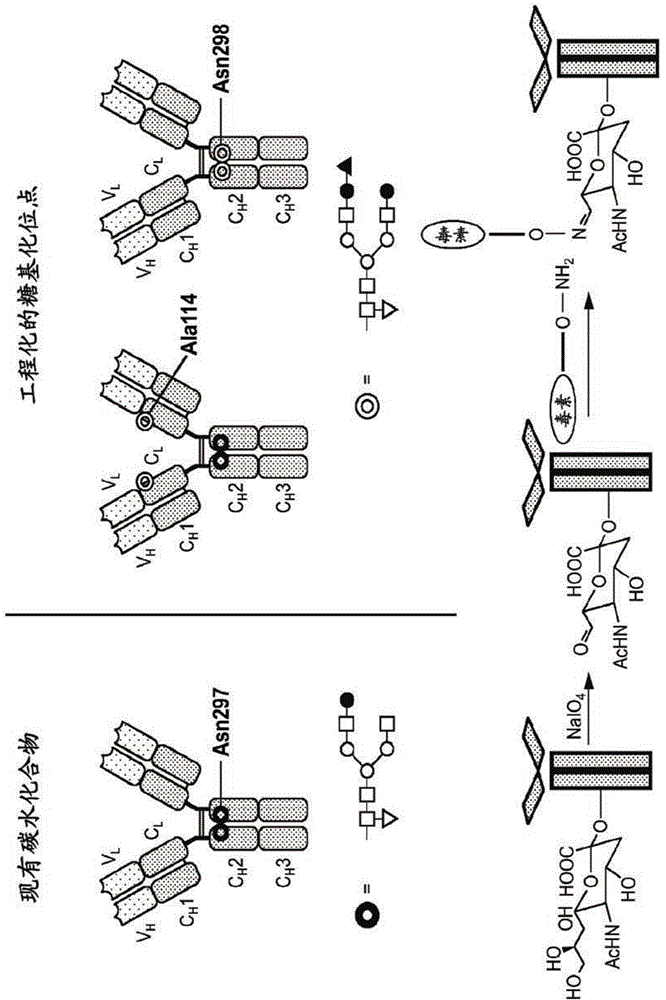
Fc containing polypeptides with altered glycosylation and reduced effector function
A technology of effectors and glycosylation, applied in chemical instruments and methods, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, peptides, etc., can solve problems such as poor biophysical properties of antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0349] Example 1. Design, preparation and characterization of 2C3 anti-CD-52 highly glycosylated antibody mutants
[0350] Multiple hyperglycosylation mutations are designed in the heavy chain of the anti-CD-52 antibody 2C3 for the purpose of adding large groups to the interaction interface (for example, FcRn binding sites to regulate antibody pharmacokinetics), For adjusting the antibody effector function by changing its interaction with FcγRs, or for introducing new cross-linking site subsequence chemical modification for effector part coupling, the effector part includes but not limited to drugs, toxins , Cytotoxic agents and radionuclides. The highly glycosylated 2C3 mutants are described in Table 3.
[0351] Table 3. Highly glycosylated 2C3 anti-CD-52 mutants
[0352]
[0353] 1A. Generation of 2C3 anti-CD-52 antibody highly glycosylated mutant
[0354] The A114N mutation assigned based on the Kabat numbering system was introduced into the CH1 domain by mutagenic PCR. To gene...
Embodiment 2
[0369] Example 2. Preparation of highly glycosylated mutants in various antibody frameworks
[0370] In addition to the 2C3 anti-CD-52 antibody, the A114N mutation was engineered into multiple antibody backbones to demonstrate that unique hyperglycosylation sites can introduce unrelated heavy chain variable region sequences. The highly glycosylated anti-TEM1, anti-FAP and anti-Her2 mutants are described in Table 5.
[0371] Table 5. A114N and / or S298N mutants designed in a variety of unrelated antibody frameworks
[0372]
[0373] 2A. Generation of highly glycosylated mutants of anti-TEM1 and anti-FAP antibodies
[0374] The A114N mutation assigned based on the Kabat numbering system was introduced into the anti-TEM1 and anti-FAP CH1 domains by mutagenic PCR. To generate a full-length antibody, the mutated VH plus residue 114 was inserted into the pENTR-LIC-IgG1 vector encoding antibody CH domains 1-3 by ligation-independent cloning (LIC). The full-length mutant was then cloned int...
Embodiment 3
[0396] Example 3: Generation of S298N / Y300S Fc mutant
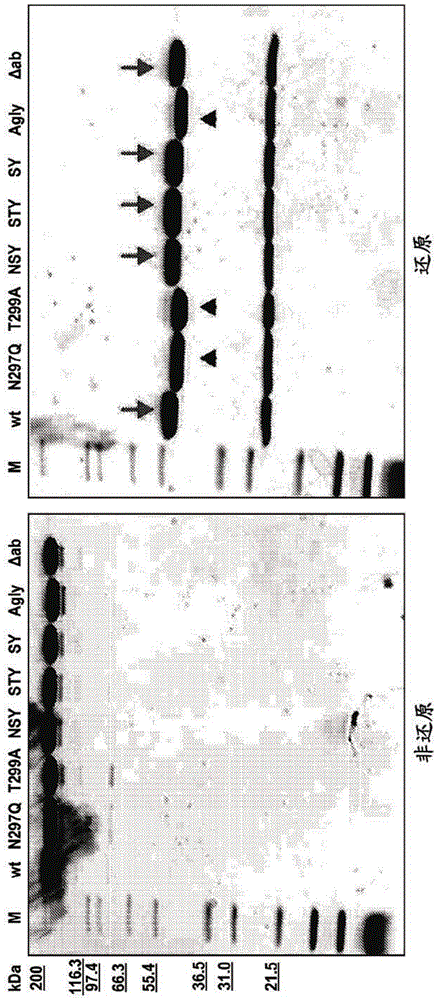
[0397] Design and generate engineered Fc mutants, in which a new glycosylation site is introduced at EU site Ser298, next to the naturally occurring Asn297 site. Glycosylation maintained at Asn297 or eliminated by mutation. The mutations and expected glycosylation results are set out in Table 9.
[0398] Table 9: Glycosylation status of various antibody variants
[0399]
[0400] 3A. Generation of altered glycosylation variants of H66 αβ-TCR antibody
[0401] The mutation was generated on the heavy chain of αβ T-cell receptor antibody clone #66 by using the pENTR_LIC_IgG1 template. The VH domain of HEBE1Δab IgG1#66 was amplified with LIC primers before cloning into mutant or wild-type pENTR_LIC_IgG1 by LIC to generate full-length mutant or wild-type antibodies. The subcloning was verified by DraIII / XhoI double digestion, and an insert fragment with a size of about 1250bp was generated in the successful clone. Those full-leng...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com