Moving Bed Methanol to Hydrocarbon Process
A methanol-to-hydrocarbon and moving-bed technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, from oxygen-containing organic compounds to hydrocarbons, and the preparation of liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, etc., can solve problems such as wear, difficulty in maintaining heat balance in reaction regeneration systems, and economic losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
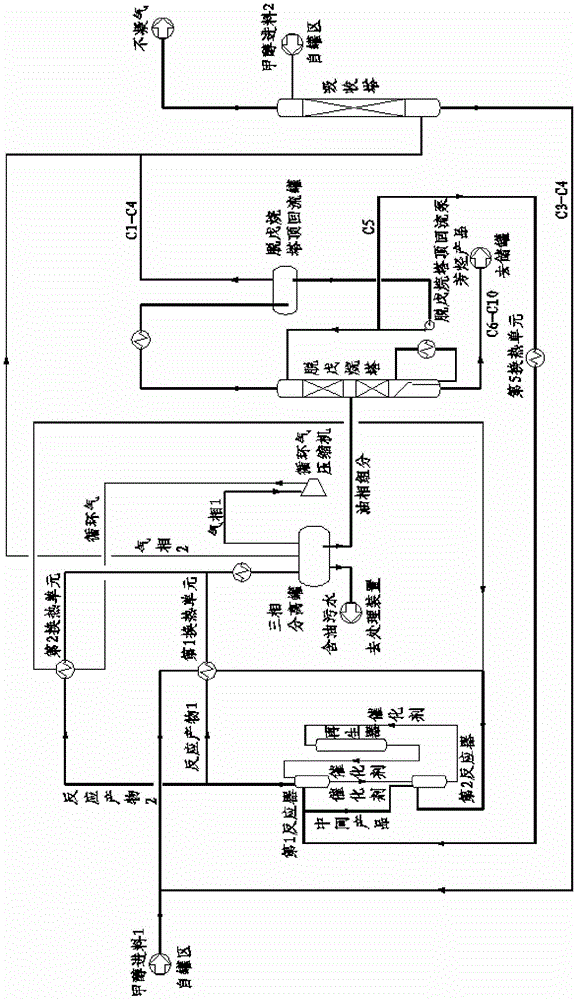
[0044] Embodiment one (see figure 1 ): Contains the first and second two reactors, and the separation step adopts depentanizer fractionation.
[0045] The fresh methanol feed is pumped outside the boundary area, the pressure is increased to 0.5MPaG, and the temperature is 25°C. Fresh methanol feed 1 first enters the second reactor (equivalent to the last reactor) after heat exchange with the reaction product, and passes through the pre-passivated catalyst from the first reactor (equivalent to the initial end reactor). To the moving bed contact reaction, the liquid hourly space velocity is 1.0h -1 , to generate an intermediate product (that is, the reaction product of the second reactor), with a pressure of 0.45MPaG and a temperature of 520°C. After leaving the second reactor, the intermediate product enters the first reactor, and conducts a radial moving bed contact reaction with the high-activity catalyst from the regenerator. The liquid hourly space velocity is 1.0h -1 , ...
Embodiment 2
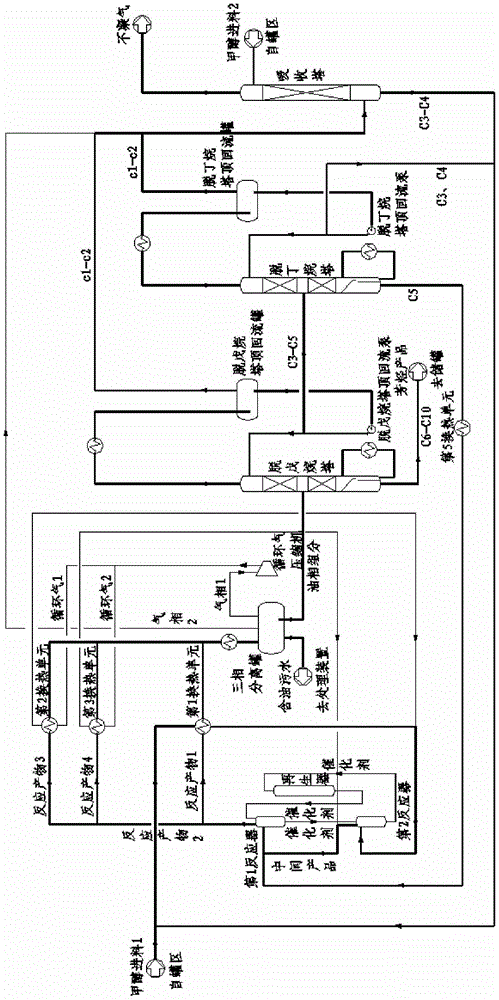
[0050] Embodiment two (see figure 2 ): Contains the first and second two reactors, and the separation step adopts two-stage fractional distillation of a depentanizer and a debutanizer.
[0051] The fresh methanol feed is pumped outside the boundary area, the pressure is increased to 1.76MPaG, and the temperature is 30°C. Fresh methanol feed 1 first enters the second reactor (equivalent to the last reactor) after heat exchange with the reaction product, and passes through the pre-passivated catalyst from the first reactor (equivalent to the initial end reactor). To the moving bed contact reaction, the liquid hourly space velocity is 4.8h -1 , can also be 5.0h -1 , to generate an intermediate product (that is, the reaction product of the second reactor), the pressure is 1.74 MPaG or 1.75 MPaG, and the temperature is 350 ° C or 320 ° C. After leaving the second reactor, the product enters the first reactor, and conducts a radial moving bed contact reaction with the high-activ...
Embodiment 3
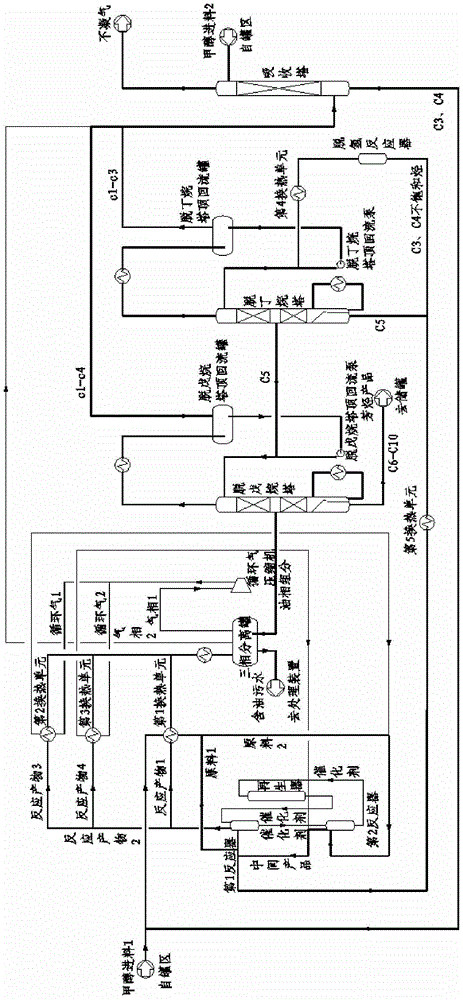
[0057] Embodiment three (see image 3 ): Contains the first and second two reactors, the separation step adopts depentanizer and debutanizer two-stage fractional distillation, and adopts dehydrogenation reactor to C 3 ~C 4 For dehydrogenation, the raw material of methanol is divided into two stocks and enters two reactors respectively.
[0058] The fresh methanol feed is pumped through the boundary area, the pressure is increased to 0.3MPaG, and the temperature is 30°C. The fresh methanol feed 1 is divided into two shares after heat exchange with the reaction product: raw material 1 and raw material 2, which are respectively used as the first reactor (equivalent to the initial reactor) and the second reactor (equivalent to the final reactor). ) feed, the flow ratio is 1:9. Raw material 2 enters the second reactor, and conducts a radial moving bed contact reaction with the pre-passivated catalyst from the first reactor, and the liquid hourly space velocity is 2.5h -1 , to g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com