An identification method for electromagnetic excitation load of electric motor
A technology of electromagnetic excitation and identification method, which is applied in the testing of machines/structural components, vibration testing, measuring devices, etc., and can solve problems such as increasing the difficulty of testing and installation, inaccurate measurement, and potential safety hazards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: is a basic embodiment. A method for identifying an electromagnetic excitation load of a motor, the steps of which are:
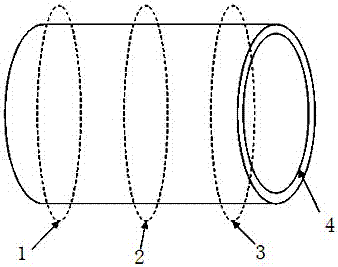
[0025] Step 1, determine the equivalent method of the electromagnetic excitation load: uniformly equivalent to the excitation force of three sections in the axial direction of the stator, and equivalent to eight excitation forces uniformly in the circumferential direction of each section, a total of 24 excitations force; the equivalent 24 excitation forces and the actual excitation force all have the effect of making the structure produce the same vibration response, and this equivalent excitation force can be used to simulate the loading of the excitation; the three sections are: the section near the non-driving end 1, the central section 2 and the section 3 near the driving end;
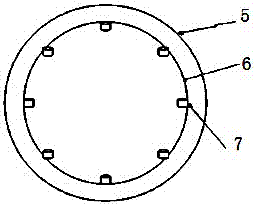
[0026] Step 2, measuring point arrangement: Determine the equivalent excitation point 7 of the electromagnetic excitation source of the motor, that is, arra...
Embodiment 2
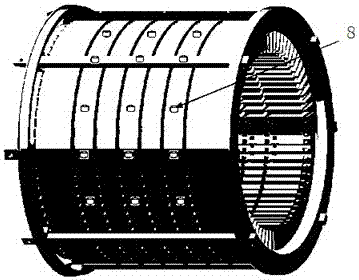
[0030] Embodiment 2: it is a further embodiment: in the described step 3, it is based on the hammering method and utilizes the transfer function testing device to test the transfer function from the excitation point 7 to the reference point 8, and the transfer function testing device includes a force hammer 9, an acceleration Sensors, data acquisition front-end, and PC, the acceleration sensor is arranged at the reference point 8, and the force hammer 9 hits the excitation point 7 to generate a broadband pulse excitation force signal. The force hammer and the acceleration sensor are connected to the PC through the data acquisition front-end, and the data acquisition The data to be collected by the front end are: the excitation force signal generated by the hammer 9 hitting the excitation point 7, the vibration acceleration response signal of the reference point 8, and the data is processed by the PC into a transfer function from the excitation point 7 to the reference point 8. ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: be a preferred embodiment. Taking a large motor as an example, the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
[0034] The main process includes: determining the equivalent excitation point 7 of the electromagnetic excitation source, the arrangement of the reference point 8, the transfer function test when the rotor is removed from the motor, the working condition response test of the reference point 8 under the rated operating condition of the motor, and the electromagnetic excitation Vibration load identification. details as follows:
[0035] 1. Determine the equivalent excitation point of the electromagnetic excitation source: for a large motor, the electromagnetic excitation source is mainly the radial electromagnetic force that the air gap magnetic field acts on the inner surface of the stator core. According to the radial electromagnetic force in time and space (stator axial and circumferential positi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com