Direct-driven elevator system
An elevator system, direct drive technology, applied in propulsion systems, elevators in buildings, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as excessive self-weight, unreasonable force, and difficulty in ensuring the long-distance working air gap of direct drive elevators, etc. Achieve the effects of less quantity, less pressure, lower motor material and processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
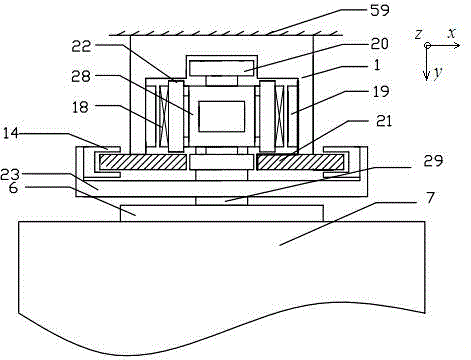
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this description, the normal direction of the linear motor is defined as the X-axis coordinate direction, also known as the left-right direction or the left and right sides; the movement direction is defined as the Z-axis direction, also known as the up-down direction or the upper end and the lower end ; The direction perpendicular to the XZ plane is defined as the Y-axis direction, also known as the front-back direction.
[0032] The direct-drive elevator system of the present invention includes a U-shaped support assembly 1, a linear motor mover 18, a linear motor stator 19, a brake guide rail 21, a brake 14, a safety gear, a mover frame 28, and an air gap guide wheel Group 20, front and rear anti-tilt wheel groups 22, U-shaped frame II 23, car frame 6 and main coupling shaft 29.
[0033] The U-shaped support assembly 1 is installed on the elevator shaft wall 59, and the linear motor stator 19 is relatively arranged on the two parallel s...
Embodiment 2
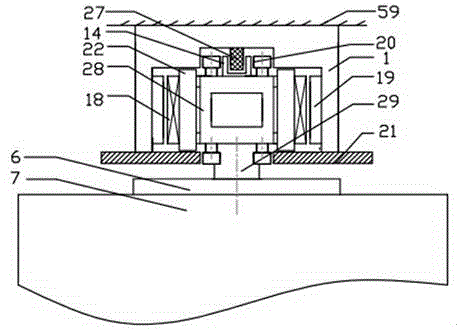
[0043] Such as figure 2 As shown, the air gap guide wheel set 20 is arranged on the front and rear sides of the mover frame 28, and the positioning wheel 1 of the air gap guide wheel set 20 is composed of two parallel small wheels, and these two small wheels are connected with the U-shaped support assembly respectively. The left and right side walls of the bar-shaped groove forming the positive side of 1 are in rolling contact. The positioning wheel II of the air gap guide wheel set 20 is composed of two parallel small wheels, and these two small wheels are respectively in rolling contact with the transverse inner end surfaces of the two rows of brake guide rails 21, and the air gap guide wheel set 20 is used to ensure the straight line. The air gap between the motor stator 19 and the linear motor mover 18.
[0044] A bar-shaped brake rail 27 is set in the center of the bar-shaped groove on the front side of the U-shaped support assembly 1, and the brake rail 27 cooperates w...
Embodiment 3
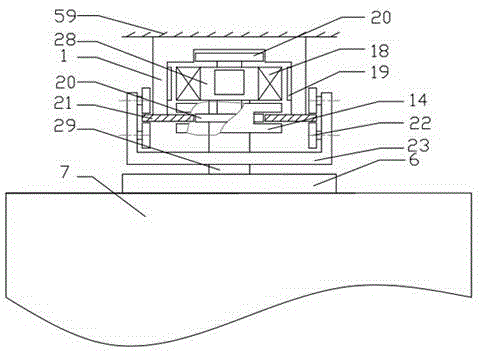
[0047] Such as image 3 As shown, the brake 14 is arranged on the front side of the mover frame 28 and cooperates with the brake guide rail 21 .
[0048] The front and rear anti-tilt wheel sets 22 are symmetrically arranged on the left and right ends of the U-shaped frame II 23, and the left support wheel set of the front and rear anti-tilt wheel sets 22 is composed of two parallel small wheels, and these two small wheels are connected with the left end of the guide rail 21 respectively. The front and rear sides are in rolling contact, and correspondingly, the right support wheel set of the front and rear anti-tilt wheel set 22 is formed by two parallel small wheels, and these two small wheels are respectively in rolling contact with the front and rear sides of the right end of the guide rail 21 for Prevent the car from tipping over in the front and rear directions.
[0049] All the other structures are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com