Somatic mutation site excavation method based on genomic sequencing
A technology of genome sequencing and somatic mutation, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as lack of methods, achieve low price, shorten the time for detecting mutation sites, and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
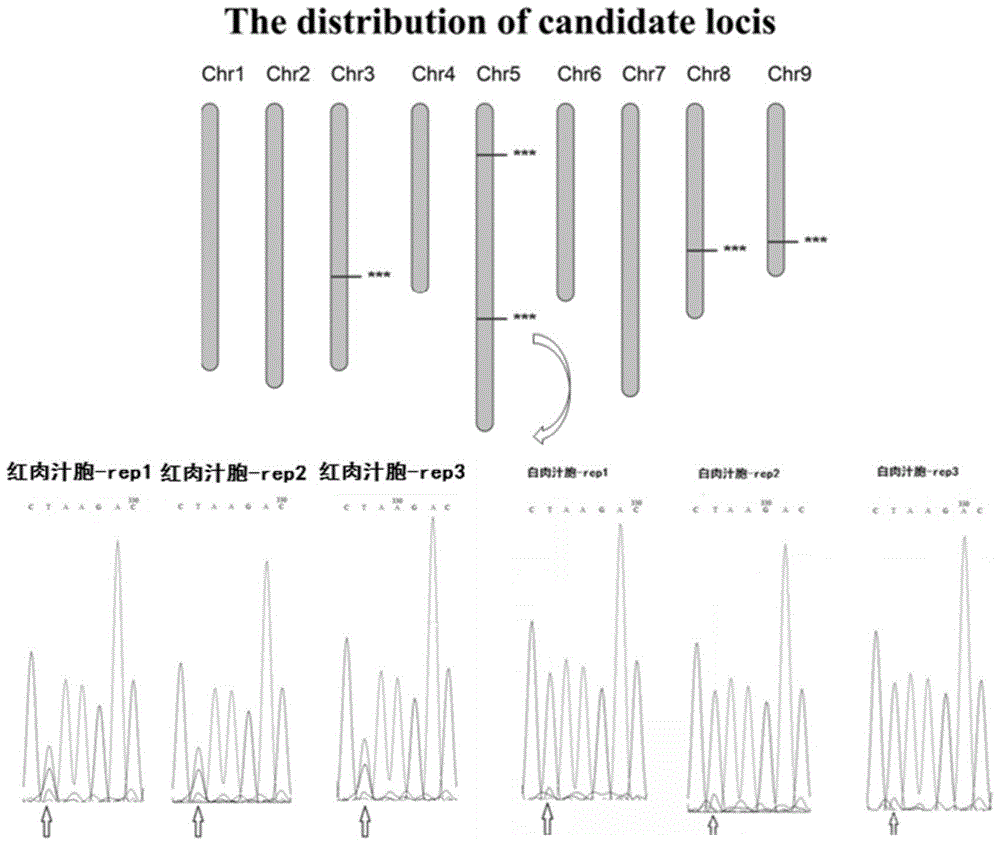
[0036] Example 1 Mining of mutation sites of red meat mutants of Guanxi honey pomelo
[0037] 1. Preparation of the genomic DNA of the red meat mutant of Guanxi honey pomelo
[0038] In this example, the modified CTAB method was used to extract the genomic DNA of four tissues (exocarp, mesocarp, sac coat and juice cell) of the wild-type Guanxi pomelo and its red-fleshed mutant.
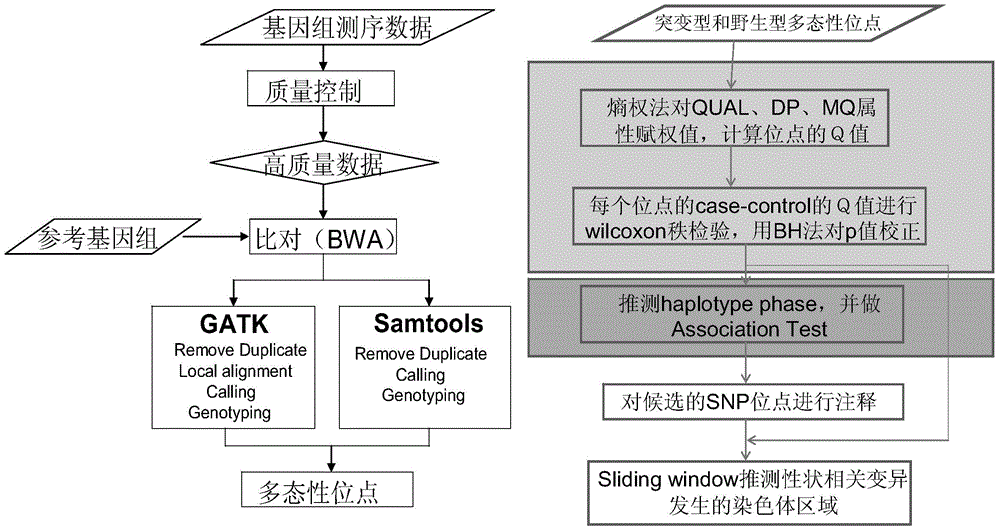
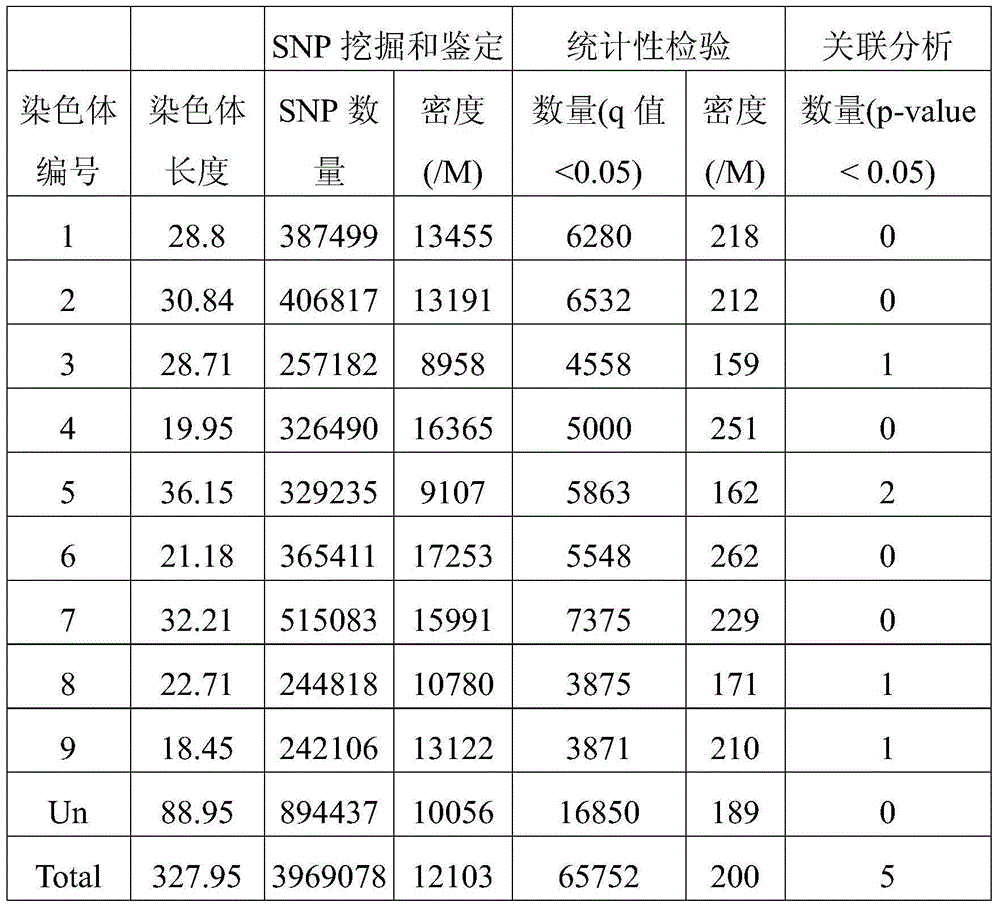
[0039] 2. Genome sequencing
[0040] 2.1 Construction of DNA sequencing library
[0041] Fragmentation of genomic DNA (fragmentation of genomic DNA into the range of 200-1000 bp with an ultrasonic fragmenter); blunt-end (generates blunt-ended 5' phosphorylated fragments); magnetic bead purification; A addition (adds dAMP to double strands) 3' end of DNA library fragment); adding adapter (connecting a double-stranded DNA adapter with a 3'-dTMP end to the library fragment); magnetic bead purification; cutting gel to recover DNA fragments of about 500bp in size; library amplification (PCR amplification...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com