Multi-robot cooperation odor source localization method based on improved bacterial foraging algorithm
A bacterial foraging algorithm and multi-robot technology, applied in the field of automatic detection and robotics, can solve the problems that it is difficult for robots to quickly find smoke plumes, low search efficiency, and high energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
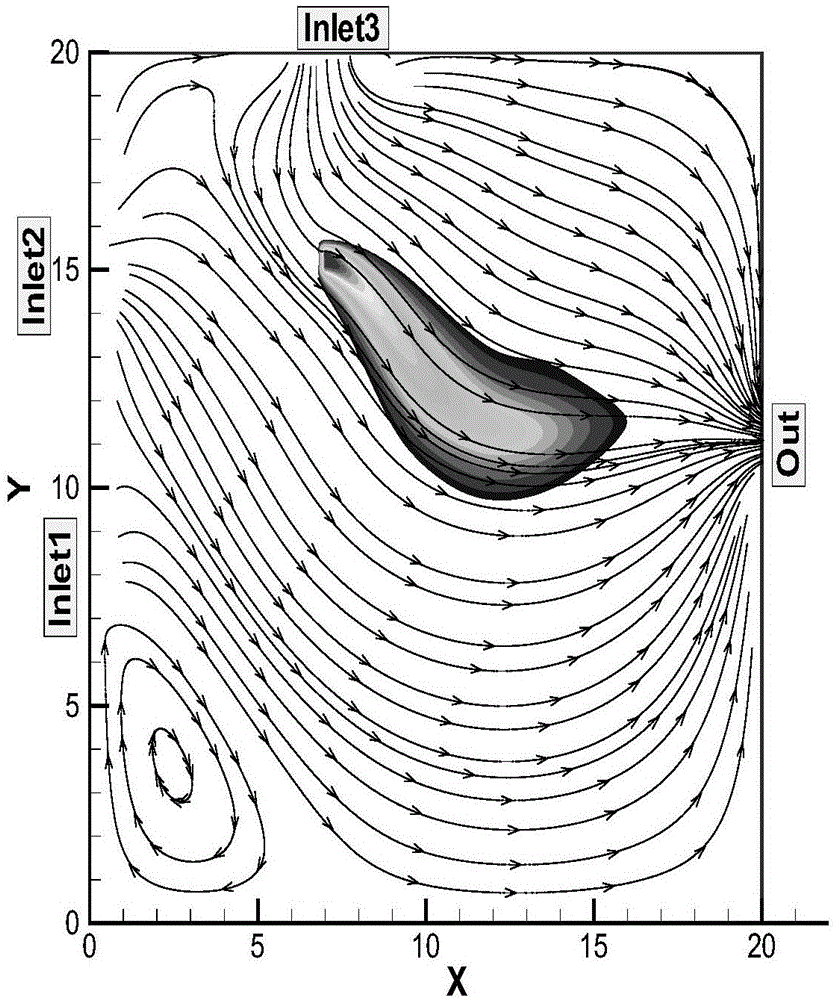
[0047] Such as figure 1 Shown is a visual view of the experimental environment in the embodiment of the present invention. In a two-dimensional space of 20m×20m, using Gambit and Fluent software, a group of ethanol odor experiment environments were generated. The environmental parameters are as follows: Inlet1, Inlet2 and Inlet3 in the figure are three air inlets with a width of 2m, and the position coordinates are (x=0,y=[7,9]), (x=0,y=[14,16] ) and (x=[6,8], y=20), the wind speeds of the three air inlets are (1m / s, 2m / s, 3m / s), and the arrows indicate the wind direction. Out is the air outlet, the location coordinates are (x=20, y=[10,12]), the location of the ethanol odor source is at (7,15), and the darker the gray color, the greater the odor concentration.
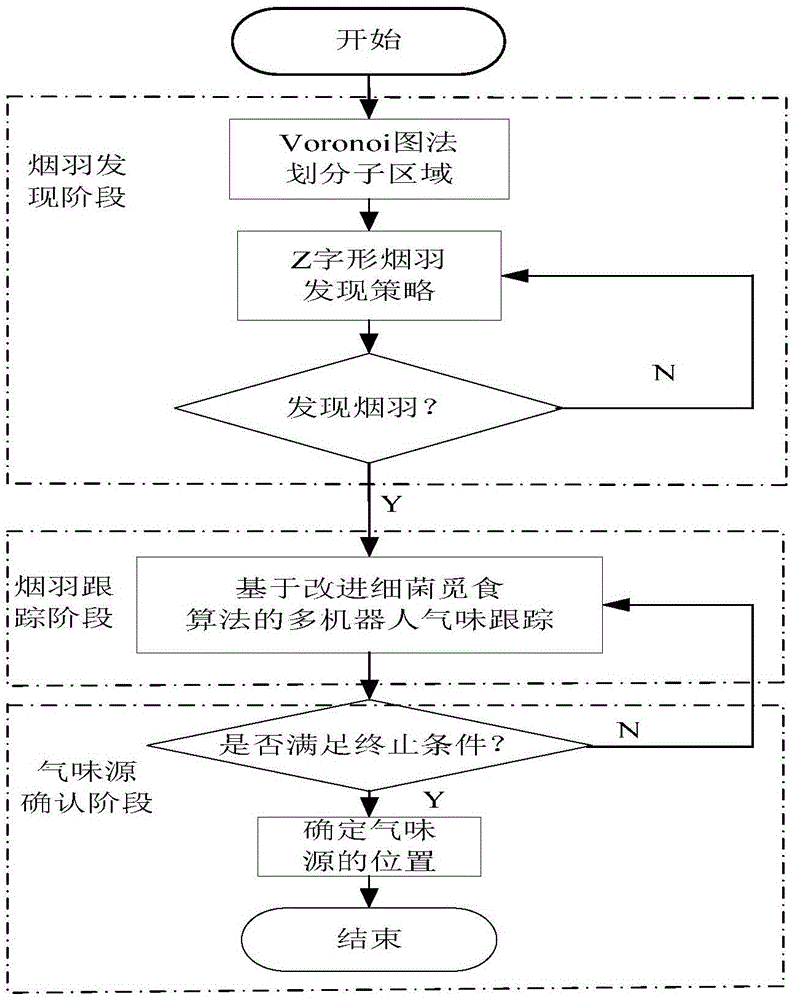
[0048] Such as figure 2 Shown, adopt the multi-robot cooperative odor source...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com