Distributed finite time tracking control method for multi-robot system in view of interference and model uncertainty
A multi-robot, limited-time technology, applied in the direction of adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., can solve the problems of heavy communication burden and poor robustness of the multi-robot system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0036] Distributed finite-time tracking control method for multi-robot systems considering disturbance and model uncertainty,
[0037] Based on the following assumptions:
[0038] (1) The time-varying control input u of the pilot robot N+1 is unknown to all following robots, and its upper bound information Can be obtained by some following robots;
[0039] (2) Generalized interference is time-varying and unknown, satisfying in is an unknown, bounded, normal constant; define d ‾ = m a x ( d ‾ 1 , ... , d ‾ N ) ;
[0040] (3) The directed graph G has a directed spanning tree;
[0041] A distributed finite-time tracking control method for multi-robot syst...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0054] The specific implementation steps of step 2 of the present embodiment are as follows:
[0055] For a multi-robot system, including N follower robots, To follow the robot assembly, is the set of pilot robots, and the set of multi-robot systems is ν=ν L ∪ν F ;
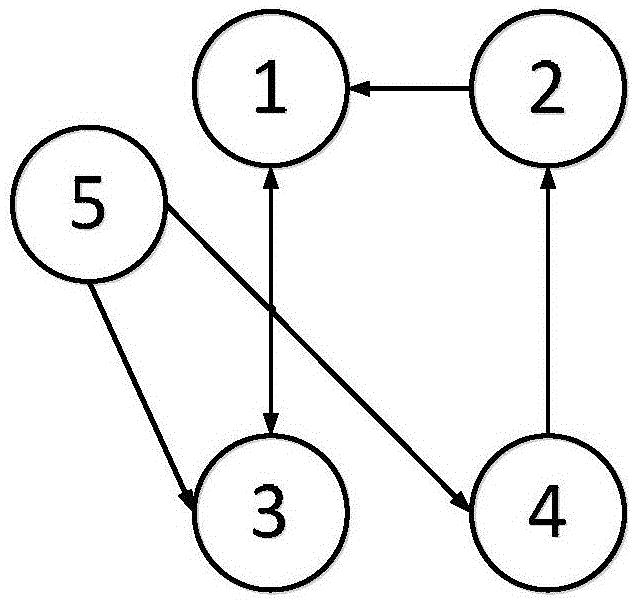
[0056] The communication topology between robots is represented by a directed graph G=(ν,ε), where ν is the set of all nodes, is the set of all edges; for robot i and robot j, edge (ν i ,ν j )∈ε means that robot j can receive information from robot i, but the opposite is not necessarily true; node ν i The neighbors of are defined as satisfying (ν j ,ν i ) ∈ ε relation of all robots j set, denoted as N i ={ν j :(ν j ,ν i )∈ε}; j is a serial number different from robot i;
[0057] The weighted adjacency matrix A of the directed graph = [a ij ] is defined as: if (v j ,v i )∈ε, then a ij = 1, otherwise a ij = 0; it is generally assumed that the node itself does not have connectivity, that is, a i...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0068] The specific implementation steps of step 3 of the present embodiment are as follows:
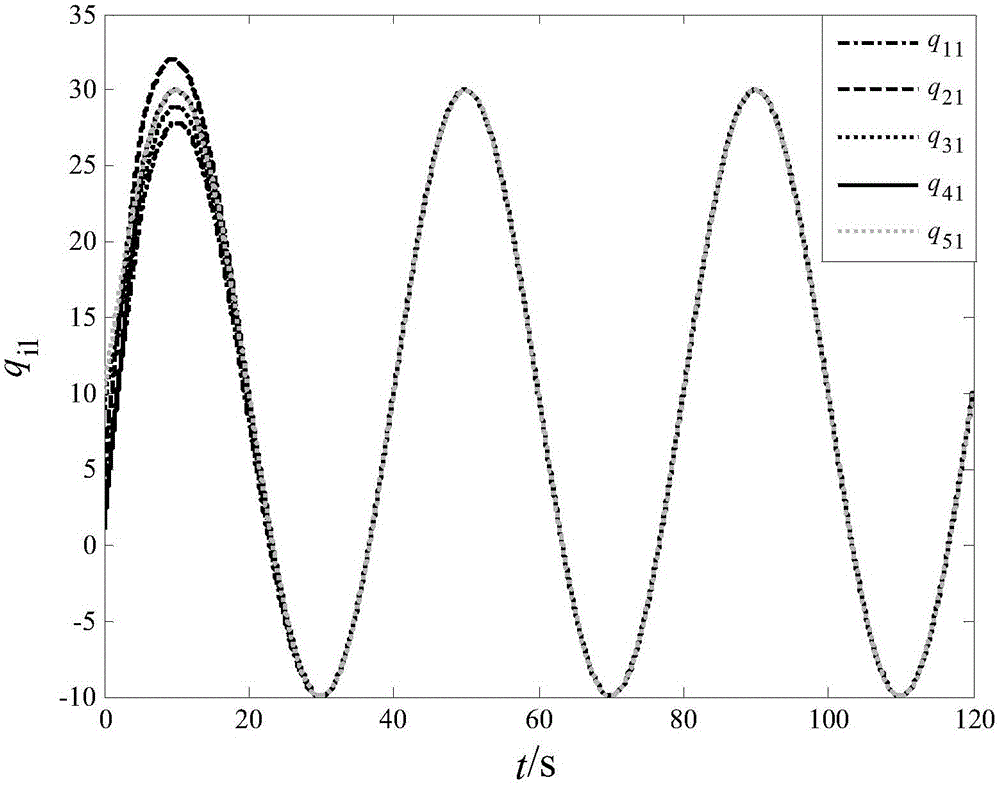
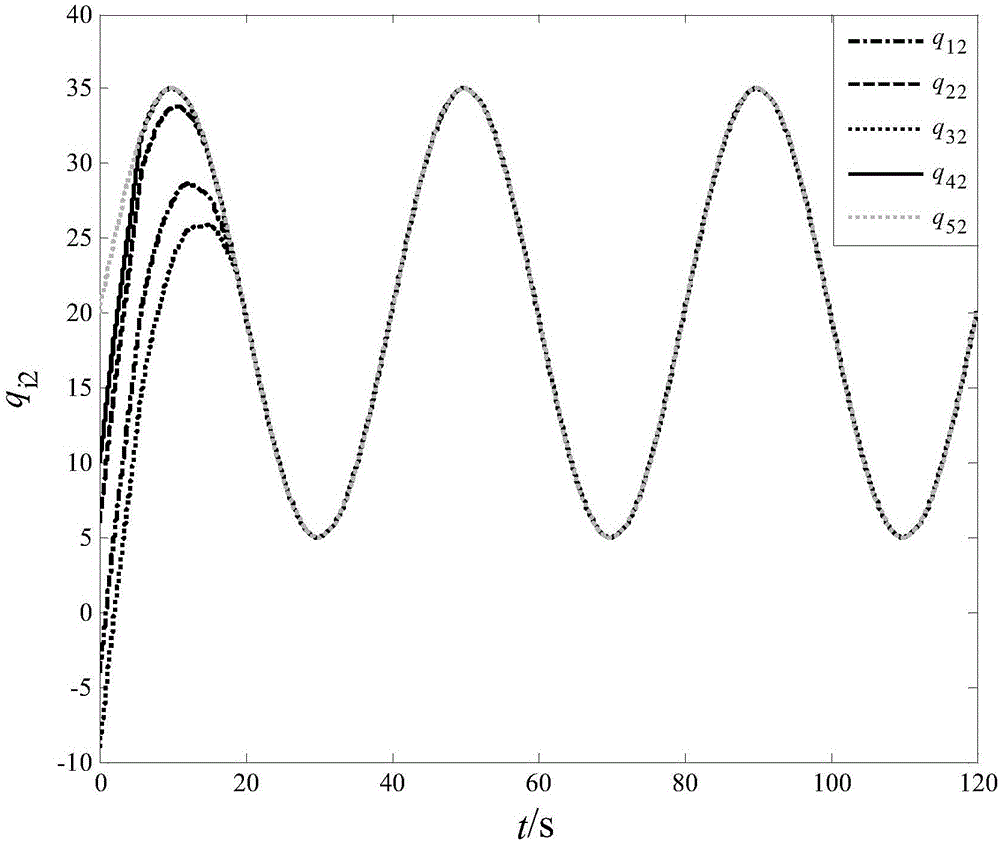
[0069] Define the error function for following the robot and for:
[0070] e i F x ( t ) = Σ j F = 1 N a i F j F ( q i F - q j F ) + b i F ( q i F ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com