Non-noxious treatment method for waste electronic lead-containing glass
A technology of harmless treatment and glass, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as lead pollution of lead-containing glass, and achieve the effects of short smelting cycle, low industrial cost and large processing capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
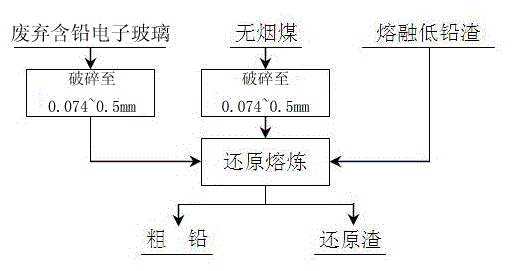
[0031] Break the waste electronic lead-containing glass and anthracite to 0.074~0.5mm respectively, mix them evenly, and add them to the molten low-lead slag melt, wherein the low-lead slag is 200g, the waste electronic lead-containing glass is 20g, and the amount of anthracite is 200g. 1.5 times the molar amount of lead oxide in electronic lead-containing glass; melting the mixed material at 1200°C for 1.0h to obtain crude lead and reducing slag.
[0032] After analysis, the crude lead content is 98.26%, the lead content in the reduction slag is 1.47%, and the recovery rate of lead is 92.71%.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Crush the waste electronic lead-containing glass and anthracite to 0.074~0.5mm respectively, mix them evenly, and add them to the molten low-lead slag melt, wherein the low-lead slag is 200g, the waste electronic lead-containing glass is 40g, and the amount of anthracite is waste 1.2 times the molar amount of lead oxide in electronic lead-containing glass; melting the mixed material at 1250°C for 0.8h to obtain crude lead and reducing slag.
[0035] After analysis, the crude lead content is 98.55%, the lead content in the reduction slag is 1.35%, and the recovery rate of lead is 93.33%.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Break the waste electronic lead-containing glass and anthracite to 0.074~0.5mm respectively, mix them evenly, and add them to the molten low-lead slag melt, wherein the low-lead slag is 200g, the waste electronic lead-containing glass is 20g, and the amount of anthracite is 200g. 1.0 times the molar amount of lead oxide in electronic lead-containing glass; melting the mixed material at 1250°C for 0.5h to obtain crude lead and reducing slag.
[0038] After analysis, the crude lead content is 98.23%, the lead content in the reduction slag is 1.25%, and the recovery rate of lead is 94.01%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com