A kind of monolithic ruthenium catalyst for PTA oxidation tail gas purification, preparation method and use thereof
A ruthenium catalyst, a technology for oxidizing tail gas, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc. Halogen poisoning and other problems, to achieve the effect of high activity, low cost and stable catalytic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
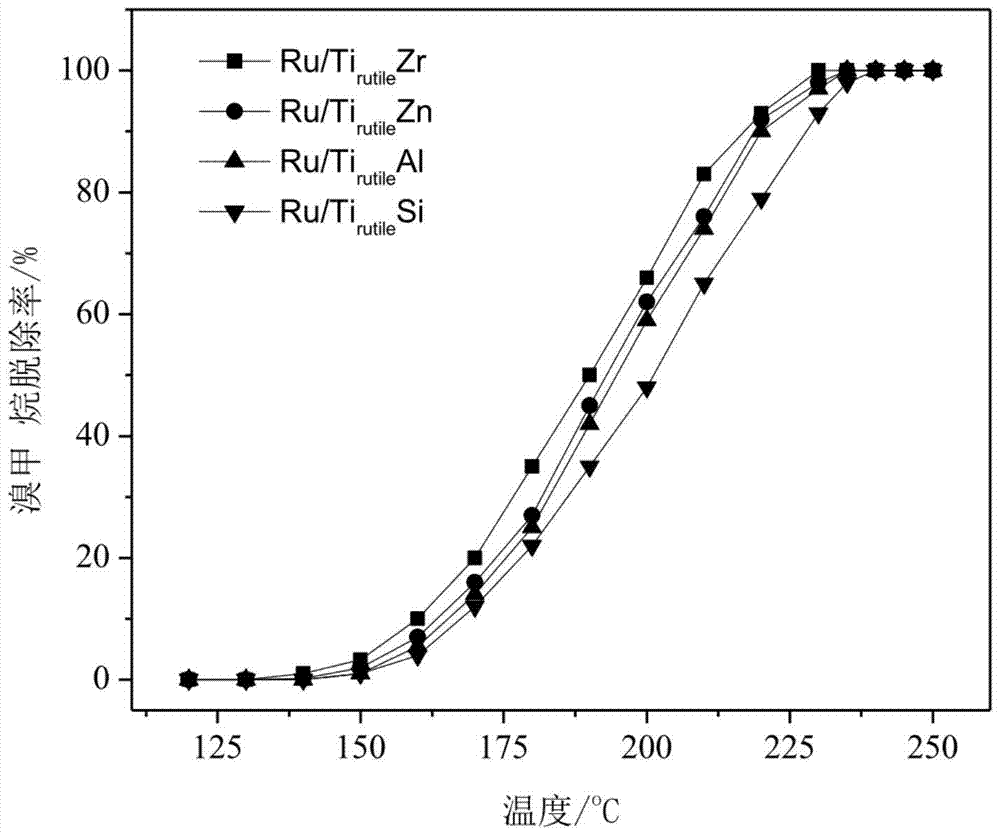
[0045] A catalyst for catalyzing and oxidizing PTA waste gas is mainly divided into two processes: powder catalyst preparation and integral catalyst preparation. Wherein, the powder catalyst includes an active component, a first support and a second support, the active component is ruthenium, and the first support is rutile phase TiO 2 , the second carrier is ZrO 2 , based on 100 wt% of the mass of the powder catalyst, the mass percentage of ruthenium in the active component of the powder catalyst is 1 wt%, and the mass ratio of the first carrier to the second carrier is 5:1. In the monolithic catalyst, the catalyst coating amount was 160 g / L.
[0046] Above-mentioned catalyst preparation comprises the steps:
[0047] (1) The rutile phase TiO 2 Add it into the aqueous solution of zirconium nitrate and stir it at the same time to obtain a mixed slurry, then let it stand for 1 hour, after the impregnation is sufficient, place it in an oven at 110°C to remove water for the fir...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Except that the mass percentage of the active component ruthenium element in the catalyst is 0.2wt.%, the rest is the same as that of Example 1.
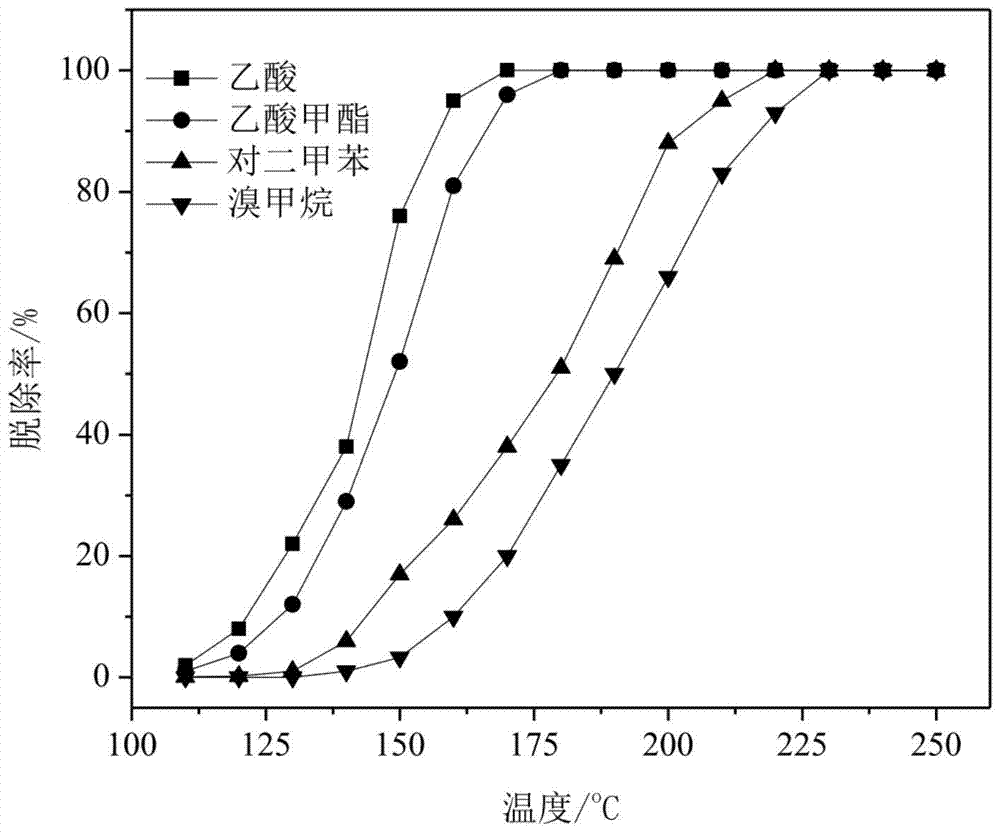
[0053] The complete oxidation temperatures of the catalyst p-bromomethane, acetic acid, methyl acetate, and p-xylene are 320°C, 235°C, 240°C, and 260°C, respectively. 2 Selectivity ≥ 99%.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Except that the mass percentage of the active component ruthenium element in the catalyst is 2wt.%, the rest is the same as that of Example 1.
[0056] The complete oxidation temperatures of the catalyst p-bromomethane, acetic acid, methyl acetate, and p-xylene are 235°C, 170°C, 190°C, and 220°C, respectively. 2 Selectivity ≥ 99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com