Method for producing tunable non-gradient optical force on surface of liquid crystal material and metal multi-layer core-housing by slanting incidence-light
A non-gradient optical force, liquid crystal material technology, applied in the fields of biology, medicine and nano-manipulation, can solve the problems of complex incident light source, difficult to capture, untunable gradient optical force, etc., to achieve the effect of simple system and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
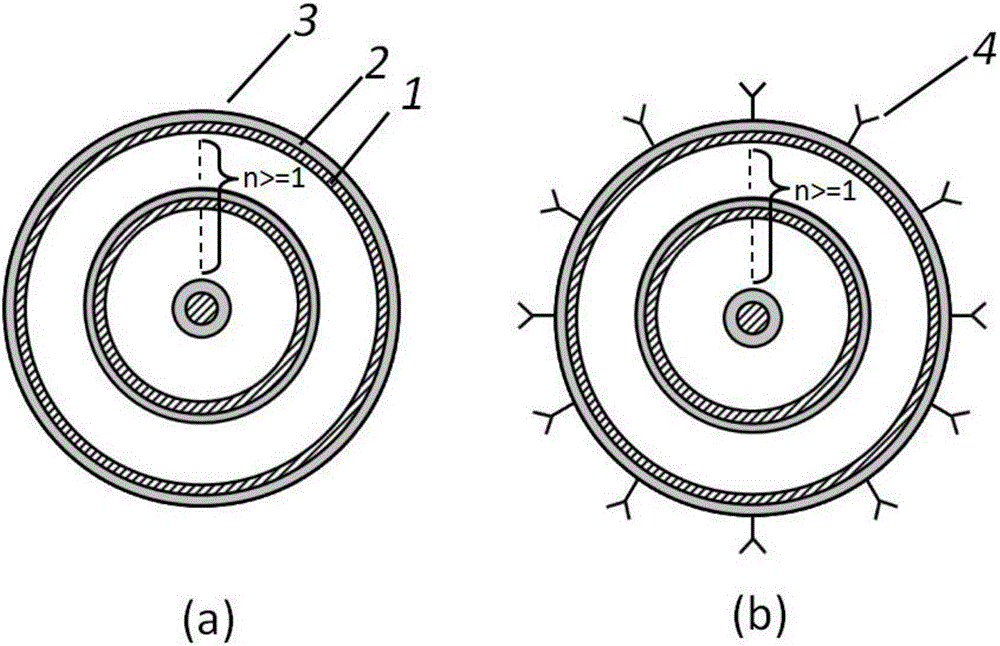
[0021] First of all, n layers (n>1) are produced by material growth process, which is composed of liquid crystal material layer 1, metal layer 2, and liquid crystal material / metal multilayer core-shell 3 alternately, as shown in the attached figure 1 (a) shown. The geometric shape and size of the liquid crystal material / metal multilayer core-shell 3 can be determined by algorithms such as finite time domain difference method and finite element method.
[0022] Secondly, nano-sized molecules 4 are attached to the outer surface of the liquid crystal material / metal multilayer core-shell 3, such as attached figure 1 (b) shown.
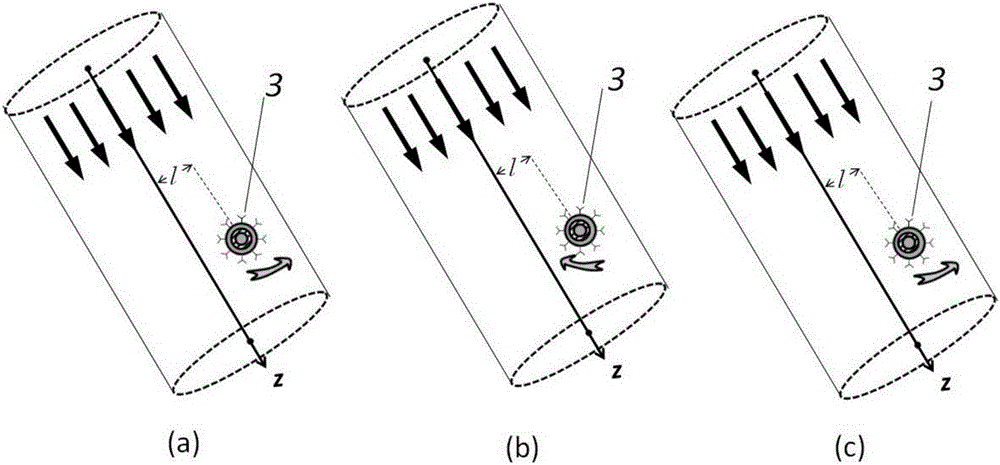
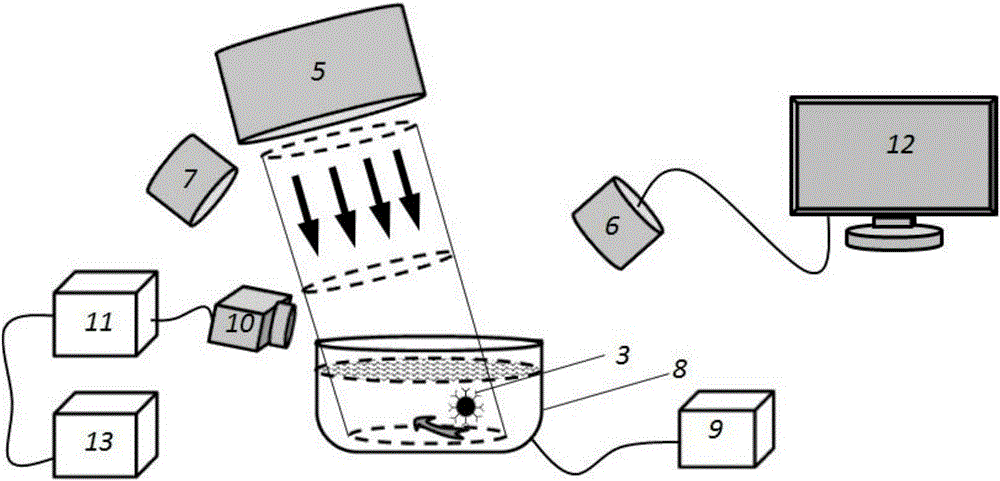
[0023] Then, the liquid crystal material / metal multilayer core-shell 3 with nanometer-sized molecules 4 attached to the surface is placed in the linearly polarized obliquely incident light beam. The Poynting vectors around the liquid crystal material / metal multilayer core-shell 3 in the light are asymmetrically distributed, that is, the total Poynting ve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle of incidence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com