Inverter control device
A control device, inverter technology, applied in control systems, motor control, control/regulation systems, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
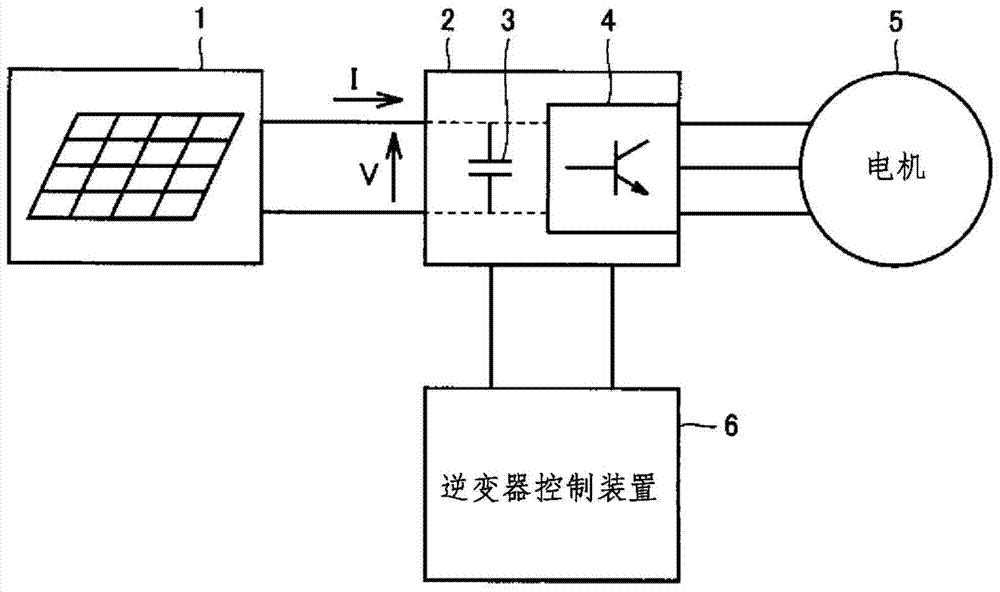
[0032] As an example of the power conversion system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 1 As shown, a solar cell 1 , an inverter 2 , a motor 5 and an inverter control device 6 are provided. The solar cell 1 converts solar energy into direct current as a power generating element. The inverter 2 is controlled by the inverter control device 6, and converts the direct current generated by the solar battery 1 into an alternating current with adjustable frequency and voltage. The inverter 2 includes: a smoothing capacitor 3 that smoothes the output voltage V of the solar cell 1 ; and a switching element 4 that is on / off-controlled by an inverter control device 6 .
[0033] The motor 5 is driven by the alternating current generated at the inverter 2 for driving a compressor and a pump of a refrigerator, for example. The motor 5 may be a synchronous motor that is rotationally driven at a rotational speed corresponding to the frequency of the alternating curren...
Embodiment approach 2
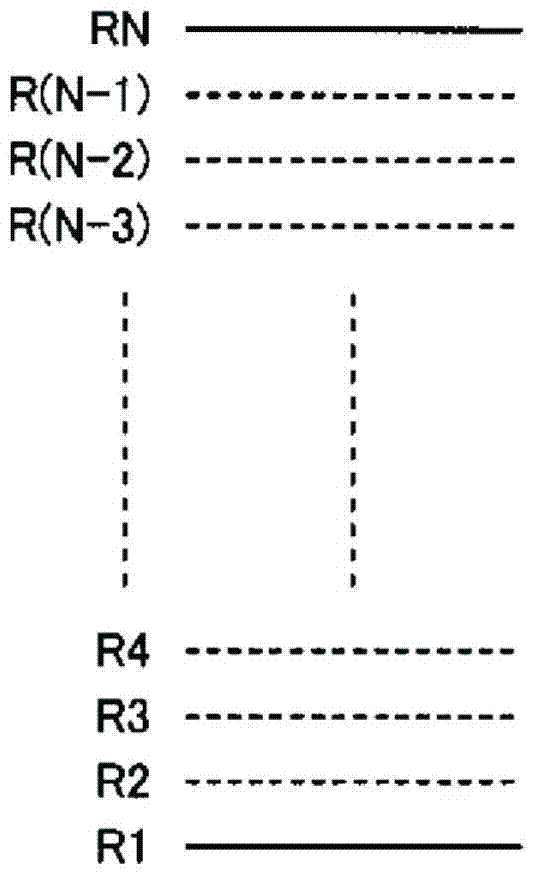
[0062] Figure 9 and Figure 10 is a timing chart showing the operation of the inverter control device included in the power conversion system according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, and is and Figure 4Comparison chart. The previous stable control mode is executed at times t0 to t1, and the motor 5 is rotationally driven at a certain fixed rotational speed Rn. At time t1, the inverter control device detects the output voltage V0 of the solar battery 1, determines the next target rotation speed R(n+1) (for example, 2250 rpm) according to the current rotation speed Rn (for example, 2000 rpm), and switches to the acceleration control mode. In addition, the rotational speed between Rn and R(n+1), for example, [Rn+R(n+1)] / 2 is set as the threshold rotational speed RTH (at this time, 2125 rpm).
[0063] When the inverter control device is in the acceleration control mode, while increasing the rotational speed of the motor 5 from Rn to R(n+1), it detects the output vo...
Embodiment approach 3
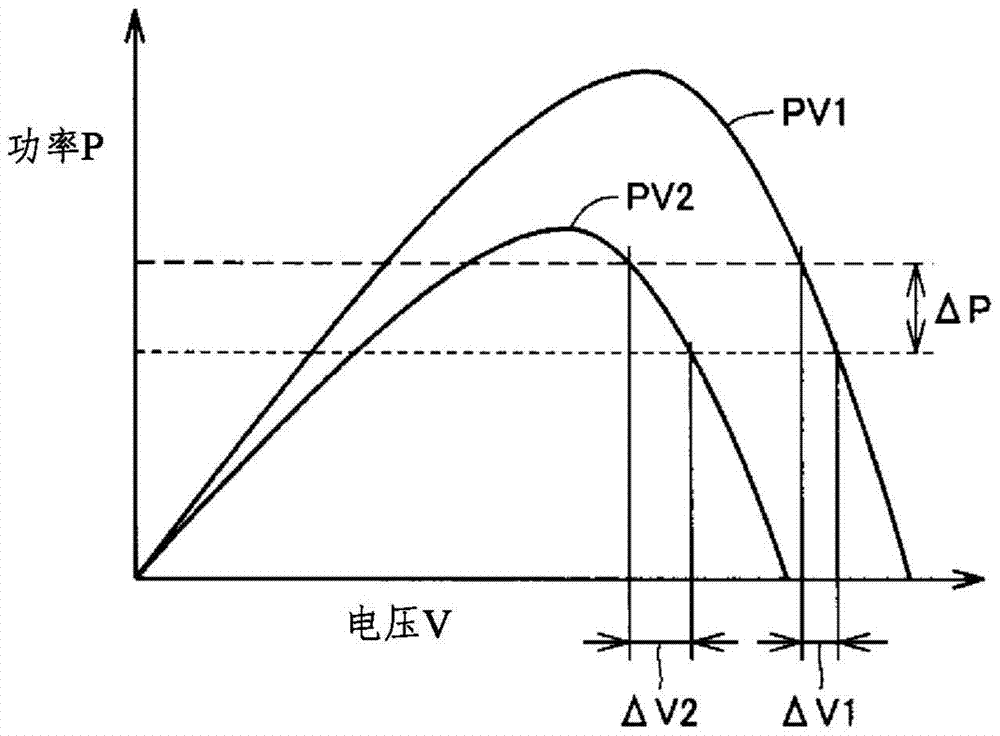
[0081] In Embodiments 1 and 2, in the acceleration control mode, the rotational speed of the motor 5 is increased by a predetermined rotational speed each time, and the output voltage V1 of the solar battery 1 is detected each time, and the voltage variation ΔV=V0-V1 is obtained, and compared ΔV and the magnitude of the threshold voltage VTH. For example, the output voltage V1 of the solar cell 1 is detected every time the rotation speed is increased by a scale amount of 10 rpm, and the voltage change amount ΔV=V0-V1 is obtained. In this way, since the current rotation speed R can be accurately detected, the comparison between the target rotation speed of the current rotation speed R and the threshold rotation speed can be performed more accurately.
[0082]On the other hand, in the deceleration control mode, it is necessary to quickly restore the power supply capability of the solar battery 1 to ample, so it is preferable to end the deceleration as early as possible. However...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com